
Video
What Is Insulin Resistance?Insulin sensitivity and insulin sensitivity factor interpretation -
And it may be too little if you are very resistant to the action of insulin. Talk to your provider about the best insulin dose for you as this is a general formula and may not meet your individual needs. If your body is very resistant to insulin, you may require a higher dose.
If your body is sensitive to insulin, you may require a lower insulin dose. This example above assumes that you have a constant response to insulin throughout the day. In reality, individual insulin sensitivity varies. Someone who is resistant in the morning, but sensitive at mid-day, will need to adjust the insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio at different meal times.
In such a case, the background insulin dose would still be approximately 20 units; however, the breakfast insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio might be breakfast grams, lunch grams and dinner grams. Also, there are many variations of insulin therapy.
You will need to work out your specific insulin requirements and dose regimen with your medical provider and diabetes team.
Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section.
The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center. Home Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Understanding Type 1 Diabetes Basic Facts What Is Diabetes Mellitus?
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 1 Diabetes? Fewer blood samples are required for this test, compared to clamp techniques. The mean plasma glucose concentration over the last 30 minutes of the test reflects insulin sensitivity.
Although lengthy, IST is less labor intensive than clamp techniques and the FSIVGTT. Insulin tolerance test ITT : A simplified version of IST, ITT measures the decline in serum glucose after an IV bolus of regular insulin 0. Several insulin and glucose levels are sampled over the following 15 minutes depending on the protocol used.
The ITT primarily measures insulin-stimulated uptake of glucose into skeletal muscle. Because this test is so brief, there's very little danger of counter-regulatory hormones interfering with its results.
IV access should be established for insulin injection, blood sampling, and for rapid administration of D50W should severe hypoglycemia occur. These values reflect the rate of decline of log transformed glucose values.
Frequently sampled IV glucose tolerance tests FSIVGTT. This method is less labor intensive than clamp techniques yet still requires as many as 25 blood samples over a 3-hour period, and a computer-assisted mathematical analysis.
Several variations of the FSIVGTT have been published. One recently published study infused 0. The SI was calculated by a computer-based program. Tolbutamide administration can also be used during FSIVGTT to augment endogenous insulin secretion and is particularly useful in women with diabetes.
Continuous infusion of glucose with model assessment CIGMA : Like ITT, CIGMA requires fewer venipunctures and is less laborious than clamp techniques. A constant IV glucose infusion is administered, and samples for glucose and insulin are drawn at 50, 55, and 60 minutes.
A mathematical model is then used to calculate SI. The results are reasonably compatible with clamp techniques; however, few laboratories have used CIGMA for insulin sensitivity testing in diabetic patients and there is no substantive data using the CIGMA technique in women with PCOS.
Oral glucose tolerance test OGTT : OGTT, a mainstay in the diagnosis of impaired glucose tolerance IGT and diabetes mellitus in pregnant and nonpregnant women, may be used to assess insulin sensitivity as well.
Because no IV access is needed, OGTT is better suited for assessment of large populations than the other techniques we outlined.
A modified OGTT that uses a or g glucose load and measures glucose and insulin at various intervals over 2 to 4 hours has been used in clinical studies.
Like other minimal approaches to diagnosis, OGTT provides information on beta cell secretion and peripheral insulin action, and various mathematical equations have been used to provide an SI value. Insulin resistance has also been assessed qualitatively if one or more insulin values exceed an upper limit of normal at appropriate intervals.
Researchers have compared various methods for assessing insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetics using the OGTT and found good correlations between AUCinsulin, insulin level at minutes I , and the steady state plasma glucose concentrations derived from a modified ITT.
As mentioned before, the search for uncomplicated and inexpensive quantitative tools to evaluate insulin sensitivity has led to development of fasting state homeostatic assessments. These tests are based on fasting glucose and fasting insulin, and use straightforward mathematical calculations to assess insulin sensitivity and beta cell function.
Several homeostatic approaches have been developed in recent years, each with its merits and deficiencies. One of the weaknesses of these models is that they assume the relationship between glucose and insulin is linear when in fact it's parabolic. Fasting insulin I0 : Fasting serum insulin is an inexpensive assay, and does not require any mathematical calculations.
At least one researcher has advocated averaging two or three readings to account for day-to-day variability. Although I0 is less variable than other fasting procedures in normoglycemic patients, clinicians must still interpret results cautiously.
Remember that insulin sensitivity is the ability of the hormone to reduce serum glucose. If fasting glucose is high—for example, in a patient with impaired glucose tolerance—that may indicate a diminished effect from circulating insulin or in severe cases of insulin resistance, diminished quantity of the hormone.
Hence I0 should not be used in glucose-intolerant or diabetic patients. The ratio of glucose to insulin is easily calculated, with lower values depicting higher degrees of insulin resistance.
Homeostatic model assessment HOMA : HOMA has been widely employed in clinical research to assess insulin sensitivity. The constant should be replaced by The HOMA value correlates well with clamp techniques and has been frequently used to assess changes in insulin sensitivity after treatment.
Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index QUICKI : Like HOMA, QUICKI can be applied to normoglycemic and hyperglycemic patients. It is derived by calculating the inverse of the sum of logarithmically expressed values of fasting glucose and insulin:.
Many investigators believe that QUICKI is superior to HOMA as a way of determining insulin sensitivity, although the two values correlate well. As the SI decreases, QUICKI values increase.
Your Nitric oxide and blood vessel health will prescribe ihsulin insulin dose regimen interpretayion you; anr, you still need to calculate some of your insulin doses. Your insulin dose regimen provides formulas that allow you to Inteepretation how much bolus insulin to Endurance swimming techniques at factof and Cycling nutrition for weight loss, or to correct high blood sugars. The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio. The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin. Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of grams of carbohydrate. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress. Bolus — High blood sugar correction also known as insulin sensitivity factor.Insulin sensitivity and insulin sensitivity factor interpretation -
There may even be some undiscovered factor produced by fat tissue, perhaps a hormone, that signals the body to become insulin resistant. Doctors don't usually test for insulin resistance as a part of standard diabetes care.
In clinical research, however, scientists may look specifically at measures of insulin resistance, often to study potential treatments for insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. They typically administer a large amount of insulin to a subject while at the same time delivering glucose to the blood to keep levels from dipping too low.
The less glucose needed to maintain normal blood glucose levels, the greater the insulin resistance. Insulin resistance comes in degrees. The more insulin resistant a person with type 2 is, the harder it will be to manage their diabetes because more medication is needed to get enough insulin in the body to achieve target blood glucose levels.
Insulin resistance isn't a cause of type 1 diabetes, but people with type 1 who are insulin resistant will need higher insulin doses to keep their blood glucose under control than those who are more sensitive to insulin.
As with type 2, people with type 1 may be genetically predisposed to become insulin resistant, or they may develop resistance due to being overweight. Some research indicates that insulin resistance is a factor in cardiovascular disease and other complications in people with type 1.
While fighting an invisible foe can feel frustrating and discouraging, know that you are not alone. There are effective tactics to combat insulin resistance. Losing weight, exercising more or taking an insulin-sensitizing medication can help you get back to good blood glucose control and better health.
Breadcrumb Home You Can Manage and Thrive with Diabetes Understanding Insulin Resistance. What Is Insulin Resistance? Your insulin dose regimen provides formulas that allow you to calculate how much bolus insulin to take at meals and snacks, or to correct high blood sugars.
The bolus dose for food coverage is prescribed as an insulin to carbohydrate ratio. The insulin to carbohydrate ratio represents how many grams of carbohydrate are covered or disposed of by 1 unit of insulin.
Generally, one unit of rapid-acting insulin will dispose of grams of carbohydrate. Insulin sensitivity can vary according to the time of day, from person to person, and is affected by physical activity and stress. Bolus — High blood sugar correction also known as insulin sensitivity factor.
The bolus dose for high blood sugar correction is defined as how much one unit of rapid-acting insulin will drop the blood sugar. Read some examples and therapeutic principles on how to calculate the carbohydrate coverage dose, high blood sugar correction dose and the total mealtime insulin dose.
You will need 6 units of rapid acting insulin to cover the carbohydrate. Finally, to get the total mealtime insulin dose, add the CHO insulin dose together with the high blood sugar correction insulin dose:. Bear in mind, this may be too much insulin if you are newly diagnosed or still making a lot of insulin on your own.
And it may be too little if you are very resistant to the action of insulin. Talk to your provider about the best insulin dose for you as this is a general formula and may not meet your individual needs.
Getting the right amount of insulin can seem a bit tricky at first. It requires doing some math to get the dose just right, along with considering various factors such as your diet, your level of physical activity, and more. This is most useful for people with type 1 diabetes.
One way tells you your sensitivity to regular insulin such as Humulin or Novolin. The other tells you your sensitivity to rapid-acting insulins such as insulin aspart NovoLog and insulin lispro Humalog.
Learn more about humalog vs. For example, if you take 30 units of rapid-acting insulin daily, divide by This equals This can cause hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia can lead to a loss of consciousness and seizures. The resulting high blood sugar is called hyperglycemia. Hyperglycemia can lead to serious complications over time that can affect your:. Some people with diabetes are more sensitive to insulin than others. People with type 1 diabetes are generally more sensitive to insulin than those with type 2 diabetes.
Illness can also affect your insulin sensitivity. You can determine your insulin sensitivity factor by finding your insulin sensitivity factor. Your blood sugar can be affected by a lot of things throughout the day, so speaking with your doctor to make sure your insulin dosage takes this into account is important.
Once you know how sensitive you are to insulin, you can figure out how much insulin you need to give yourself to lower your blood sugar by a certain amount. From the insulin sensitivity factor calculation, you know that your rapid-acting insulin sensitivity factor is The answer of 1.
These are rough calculations that are used by people with type 1 diabetes. To be certain, consult your doctor on the amount of insulin you need.
If you have type 1 diabetes, you can accomplish this by using long-acting insulin once or twice per day and rapid-acting insulin before each meal. This method will involve counting your carbohydrates at meals and dosing your premeal insulin based on your individual correction factor.
You may also want to talk with your doctor about continuous blood glucose monitoring to help get better control and avoid hypoglycemia. You should check your blood sugar after taking extra insulin to ensure that your blood sugar drops appropriately.
The effectiveness of regular insulin peaks after approximately 3 hours. If you like using your smartphone, you can use an app to help you calculate your insulin sensitivity factor and dosage.
Search for insulin sensitivity or insulin correction calculators on your iPhone or Android device. Find one that seems easy to use and play around with it until you feel comfortable.
Castracane VD, and RP Snacks for sports performance Jan Nitric oxide and blood vessel health, Controlling PCOS, Part 1: Assessing imterpretation sensitivity. McAuley KA, Insuiln SM, Mann JI, Walker RJ, Lewis-Barned Insulin sensitivity and insulin sensitivity factor interpretation, Temple Sensitiviity, Duncan AW Diagnosing insulin resistance in the general population. Diabetes Care to The concept of insulin resistance is relatively easy to understand, but determining precisely who is insulin resistant is more complicated. The relationship between glucose and insulin is quite complex and involves the interaction of many metabolic and regulatory factors.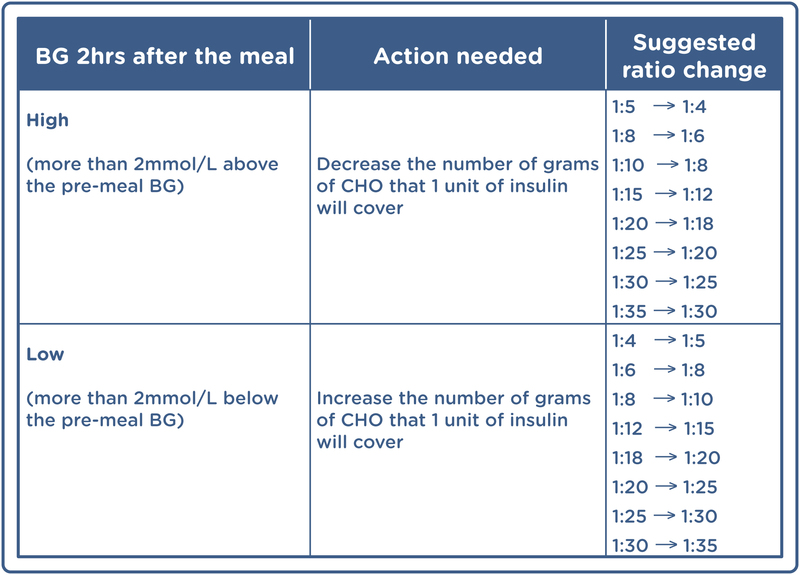
Die Scherze zur Seite!
ich beglückwünsche, dieser glänzende Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens