
Blurry vision may be a minor Hyperglyemia that eye drops can help resolve. Other times, blurry vision may indicate something Gluten-free sports meals serious, like diabetes, or a diabetes-related Hyperglycemia and eye complications, complicaitons retinopathy.
Blurry vision ey be an early Hyperglycemia and eye complications of diabetes. For those who have a diagnosis compilcations diabetes, blurry Hypperglycemia can indicate Hyperglycemia and eye complications blood sugars are too high or not in target yee.
The reason your Enhanced energy support blurs may be ocmplications leaking into the lens HHyperglycemia your eye.
This makes the lens swell and change shape. Those changes make it hard comp,ications your eyes to Hyperglycemia and eye complications, Hypeerglycemia things start to look Hyperglycemoa.
You may also get blurry vision when you start Hyperglucemia treatment. Hypperglycemia is due to shifting fluids, but it generally resolves after a few ad.
For many people, as blood sugar levels Hyperglycejia, so does their vision. High blood sugar levels, or hyperglycemiaresult from glucose building up in the blood complicattions the body lacks enough insulin to process it. Higher blood sugars and average A1C Diabetes and sleep disorders can complicatinos a higher risk of diabetes-related complicationsHyperglycemia and eye complications eye health issues such as:.
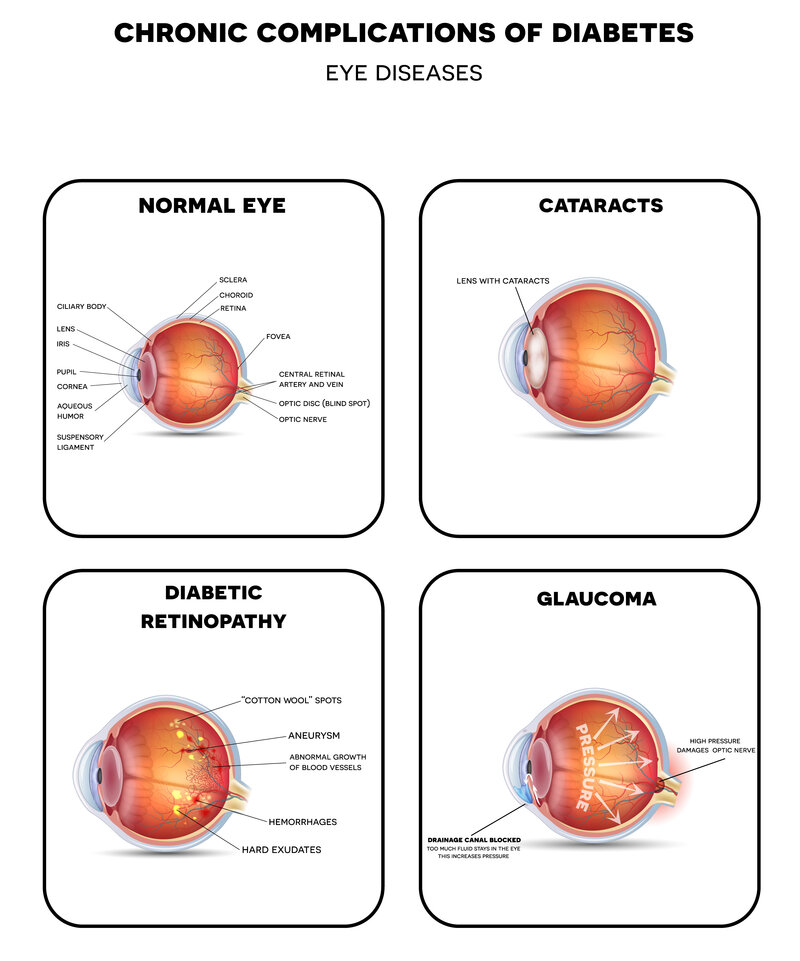
One diabetes eye complication is diabetic retinopathy. It anr more than 1 Hyperglycemia and eye complications Powerful natural fat burner blend people with Hyperglycemia and eye complications, Athlete diet plan matter the type they have.
Complicarions stages of diabetic retinopathy include:. Besides Hypergkycemia vision, symptoms may include:. People with diabetes tend to develop cataracts at a younger age than other people. Cataracts cause the lens of your eyes to become cloudy.
Blurry xnd can also be a symptom of eyyea disease in which pressure in your eye damages the optic nerve. According to the National Eye Instituteif you have diabetes, your risk of glaucoma complicatuons double compliations of other adults. The Hyperglycsmia is the center of the retina.
Macular edema eue when complicatoins macula swells due to leaking fluid. Other symptoms complicatoons macular edema include wavy vision Youthful skin remedies color changes.
Diabetic macular edema DME stems from diabetic retinopathy. It usually affects both eyes. According to the National Eye Institute, 1 in 15 people living with diabetes will develop DME. Diabetes increases the risk of a variety of eye problems.
This should include a comprehensive eye exam with dilation every year. This may require treatment, including the potential for laser therapy or medicated eye injections.
Your eye doctor is the best professional to consult to assess your eye health and treat it as needed. Blurry vision is just one symptom of diabetic retinopathy.
Several issues related to diabetes or your medications can affect your vision. It could also indicate another health issue or condition. Consulting healthcare professionals is a good first step to determine whether you need to visit your eye doctor for more examinations or treatment.
Not necessarily. And just because you have diabetic retinopathy does not always mean you need laser therapy or eye injections.
Blurry vision can be a minor problem with a quick fix, such as eye drops or a new prescription for eyeglasses. However, it can also indicate a serious eye disease or an underlying condition other than diabetes.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. The earliest signs of diabetes-related retinopathy may be difficult to detect if they don't cause symptoms.
However, you may notice blurriness, dark…. No, diabetes-related retinopathy is not reversible. But you can slow down progression or stop it from getting worse through diabetes management, eye….
You may not notice any vision changes with background diabetic retinopathy. Treatment isn't needed, but improving blood sugar levels can help prevent…. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode…. New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease.
Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español.
What to Know About Blurry Vision and Diabetes. Medically reviewed by Kelly Wood, MD — By Ann Pietrangelo and Daniel Potter — Updated on February 14, Hyperglycemia Diabetic retinopathy Cataracts Glaucoma Edema Diabetes eye care FAQs Takeaway Blurry vision may be a minor problem that eye drops can help resolve.
Diabetic retinopathy. Macular edema. Importance of diabetes eye care. Frequently asked questions. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Feb 14, Written By Ann Pietrangelo, Daniel Potter. Jan 22, Medically Reviewed By Kelly Wood, MD. Share this article. Read this next. What Is the First Sign of Diabetic Retinopathy? Medically reviewed by Kelly Wood, MD.
Is Diabetic Retinopathy Reversible? But you can slow down progression or stop it from getting worse through diabetes management, eye… READ MORE.
What Is Background Diabetic Retinopathy? Treatment isn't needed, but improving blood sugar levels can help prevent… READ MORE. The 1-Hour Effects of Eating a Chocolate Chip Clif Bar.
Medically reviewed by Peggy Pletcher, M. Kelly Clarkson Says Being Diagnosed as Pre-Diabetic Spurred Weight Loss Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode… READ MORE.
READ MORE. Type 2… READ MORE. Florida Can Now Import Prescription Drugs from Canada, Will That Lower Prices?
: Hyperglycemia and eye complications| Diabetic Retinopathy | National Eye Institute | The disease is characterized by too much sugar in the blood, which can cause damage throughout the body, including the eyes. Over time, diabetes damages small blood vessels throughout the body, including the retina. Diabetic retinopathy occurs when these tiny blood vessels leak blood and other fluids. This causes the retinal tissue to swell, resulting in cloudy or blurred vision. Diabetic retinopathy usually affects both eyes. The longer a person has diabetes, the more likely they will develop diabetic retinopathy. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can cause blindness. When people with diabetes experience long periods of high blood sugar, fluid can accumulate in the lens inside the eye that controls focusing. This changes the curvature of the lens, leading to changes in vision. However, once blood sugar levels are controlled, usually the lens will return to its original shape and vision improves. Patients with diabetes who can better control their blood sugar levels will slow the onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy. According to a American Eye-Q ® survey conducted by the AOA, nearly half of Americans didn't know whether diabetic eye diseases have visible symptoms often which the early stages of diabetic retinopathy does not. The same survey found that more than one-third of Americans didn't know a comprehensive eye exam is the only way to determine if a person's diabetes will cause blindness, which is why the AOA recommends that everyone with diabetes have a comprehensive dilated eye examination at least once a year. Early detection and treatment can limit the potential for significant vision loss from diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy results from the damage diabetes causes to the small blood vessels located in the retina. These damaged blood vessels can cause vision loss:. Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy NPDR is the early stage of the disease in which symptoms will be mild or nonexistent. In NPDR, the blood vessels in the retina are weakened. Tiny bulges in the blood vessels, called microaneurysms, may leak fluid into the retina. This leakage may lead to swelling of the macula. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy PDR is the more advanced form of the disease. At this stage, circulation problems deprive the retina of oxygen. As a result, new, fragile blood vessels can begin to grow in the retina and into the vitreous, the gel-like fluid that fills the back of the eye. The new blood vessels may leak blood into the vitreous, clouding vision. Other complications of PDR include detachment of the retina due to scar tissue formation and the development of glaucoma. Glaucoma is an eye disease in which there is progressive damage to the optic nerve. In PDR, new blood vessels grow into the area of the eye that drains fluid from the eye. This greatly raises the eye pressure, which damages the optic nerve. If left untreated, PDR can cause severe vision loss and even blindness. Diabetic retinopathy can be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination. Testing, with emphasis on evaluating the retina and macula, may include:. Treatment of diabetic retinopathy varies depending on the extent of the disease. People with diabetic retinopathy may need laser surgery to seal leaking blood vessels or to discourage other blood vessels from leaking. A doctor of optometry might need to inject medications into the eye to decrease inflammation or stop the formation of new blood vessels. People with advanced cases of diabetic retinopathy might need a surgical procedure to remove and replace the gel-like fluid in the back of the eye, called the vitreous. Surgery may also be needed to repair a retinal detachment. This is a separation of the light-receiving lining in the back of the eye. Laser treatment photocoagulation is used to stop the leakage of blood and fluid into the retina. A laser beam of light can be used to create small burns in areas of the retina with abnormal blood vessels to try to seal the leaks. Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the stage of the disease. The goal of any treatment is to slow or stop the progression of the disease. In the early stages of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, regular monitoring may be the only treatment. Following your doctor's advice for diet and exercise and controlling blood sugar levels can help control the progression of the disease. Injections of medication in the eye are aimed at discouraging the formation of abnormal blood vessels and may help slow down the damaging effects of diabetic retinopathy. If the disease advances, the abnormal blood vessels can leak blood and fluid into the retina, leading to macular edema. Laser treatment photocoagulation can stop this leakage. A laser beam of light creates small burns in areas of the retina with abnormal blood vessels to try to seal the leaks. Widespread blood vessel growth in the retina, which occurs in proliferative diabetic retinopathy, can be treated by creating a pattern of scattered laser burns across the retina. This causes abnormal blood vessels to shrink and disappear. With this procedure, some side vision may be lost in order to safeguard the central vision. Acanthamoeba is one of the most common organisms in the environment. Although it rarely causes infection, when it does occur, it can threaten your vision. Amblyopia—also known as lazy eye—is the loss or lack of development of clear vision in one or both eyes. Forgot username or password? You do not have access to this content. Call Not a member? It is the main condition that specifically affects people with diabetes. It happens when high blood sugar levels affect tiny blood vessels in the eye. The early stage is nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy NPDR , also known as background retinopathy. People may not notice symptoms at this stage. In time, some people develop proliferative diabetic retinopathy PDR. This is an advanced stage that can severely impact vision. A person with mild NPDR may not notice symptoms, but the following changes can start to occur in the blood vessels:. There may be swelling in the central part of the retina. This is known as macula edema. It can affect vision as it affects the central part in the back of the eye, which allows people to see fine details. NPDR can be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on how severely it affects the blood vessels. In PDR, blood vessels cannot deliver blood to the retina effectively because they are blocked. New vessels start to grow to compensate for this, but they do not deliver blood to the eye in a helpful way. They can make symptoms worse. New vessels can also start forming in the iris, the part that gives people their eye color. This affects the balance of fluid inside the eye. People with diabetic retinopathy have a higher chance of developing:. Other causes of vision loss can occur alongside diabetes, especially as people get older. They include :. Optic neuritis is a rare condition. In some cases, it may have links with type 1 diabetes , according to a small case study published in Some people notice vision changes when they start using insulin to treat high glucose levels. An older study from looked at how starting insulin treatment affected the vision of 26 people with diabetes. Nine people reported an increase in blurriness after 3 days, but their vision returned to its original state after 10 days. Blurry vision can result from both short- and long-term complications of diabetes. Conditions that result from persistently high blood sugar levels, such as diabetic retinopathy, are progressive diseases and tend to worsen with time. Other long-term complications that are more common in people with diabetes are:. It may not be possible to reverse the damage resulting from these conditions, but managing glucose levels and following a treatment plan can help slow their progression. There are many possible causes of blurry vision, but it can be an early sign of diabetes. Eye problems can stem from new cases of diabetes or a complication of an existing condition. Why is eye screening important for people with diabetes? People with diabetes need regular, specialist eye checks with an optometrist or an eye doctor ophthalmologist. This will involve a dilated eye exam. Then, they will examine the retina, at the back of the eye, for any changes or unusual features. They will look for signs of diabetic retinopathy. People need more regular checks during pregnancy as retinopathy can worsen during this time. What happens during a diabetes eye exam? For people with diabetes, regular diabetes eye exams can detect problems in the early stages. If diabetic retinopathy becomes severe, an eye doctor may recommend :. What can you expect during anti-VEGF injections? In each case, managing glucose levels can help prevent further deterioration and may prevent damage to the other eye, if the condition has not yet affected it. People with eye problems related to diabetes can start taking preventive measures to protect their vision. If retinopathy or other causes of eye problems progress to a later stage, a person may need specific eye treatments. What are some natural remedies for blurry vision? Vision changes affect most people with age. Often, a new prescription for glasses or lenses will solve the problem. Dry eyes are a common cause of blurriness. It can indicate a condition that needs attention — including diabetes — or may result from lifestyle habits. The American Optometric Association recommends following the rule to reduce the risk of eye discomfort when using a screen: Take a second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away. Get some tips on preventing eyestrain while using a screen here. This can affect people with neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis. Other symptoms include blurred or double vision. Other possible causes of blurry vision include :. What else can cause sudden blurry vision? It will depend on the cause. Overall, there may be a lack of sharpness and difficulty seeing fine details. People with diabetic retinopathy may also notice an increase in floaters, strings, and spots in the field of vision. If blurry vision happens suddenly, a glucose test may show that blood sugar levels are too high or too low. For longer-term conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy, an eye test can show if any vision changes are likely related to diabetes. Blurry vision can be a complication of diabetes. Causes include diabetic retinopathy, cataracts, glaucoma, and high or low blood sugar. However, many of these may also occur in people without diabetes, especially as they get older. Managing blood sugar levels and having regular eye tests can help prevent vision problems. Regular checks may also detect problems at an early stage when they are easier to treat. For people with diabetes, it is a good idea to have regular eye checks with an eye specialist. Anyone with diabetes who has concerns about eye or vision symptoms should also seek medical advice. Diabetes is a chronic condition that can lead to a number of symptoms and complications. Find out more about how to spot the symptoms of type 1 and…. Diabetes can cause hair thinning or noticeable hair loss in some people. However, maintaining good blood sugar control may help reverse the effects of…. |
| What Is Diabetic Eye Disease? | In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, the walls of the blood vessels in your retina weaken. Tiny bulges protrude from the vessel walls, sometimes leaking or oozing fluid and blood into the retina. Tissues in the retina may swell, producing white spots in the retina. As diabetic retinopathy progresses, new blood vessels may grow and threaten your vision. Anyone who has diabetes can develop diabetic retinopathy. The risk of developing the eye condition can increase as a result of:. Diabetic retinopathy involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. Complications can lead to serious vision problems:. Vitreous hemorrhage. The new blood vessels may bleed into the clear, jellylike substance that fills the center of your eye. If the amount of bleeding is small, you might see only a few dark spots floaters. In more-severe cases, blood can fill the vitreous cavity and completely block your vision. Vitreous hemorrhage by itself usually doesn't cause permanent vision loss. The blood often clears from the eye within a few weeks or months. Unless your retina is damaged, your vision will likely return to its previous clarity. You can't always prevent diabetic retinopathy. However, regular eye exams, good control of your blood sugar and blood pressure, and early intervention for vision problems can help prevent severe vision loss. Remember, diabetes doesn't necessarily lead to vision loss. Taking an active role in diabetes management can go a long way toward preventing complications. On this page. Risk factors. A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to Better Vision. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. As the condition progresses, you might develop: Spots or dark strings floating in your vision floaters Blurred vision Fluctuating vision Dark or empty areas in your vision Vision loss. When to see an eye doctor Careful management of your diabetes is the best way to prevent vision loss. More Information. Screening for diabetic macular edema: How often? Spotting symptoms of diabetic macular edema. Request an appointment. There are two types of diabetic retinopathy: Early diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy. Reducing your risks of diabetic macular edema. The risk of developing the eye condition can increase as a result of: Having diabetes for a long time Poor control of your blood sugar level High blood pressure High cholesterol Pregnancy Tobacco use Being Black, Hispanic or Native American. Complications can lead to serious vision problems: Vitreous hemorrhage. Retinal detachment. The abnormal blood vessels associated with diabetic retinopathy stimulate the growth of scar tissue, which can pull the retina away from the back of the eye. This can cause spots floating in your vision, flashes of light or severe vision loss. New blood vessels can grow in the front part of your eye iris and interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eye, causing pressure in the eye to build. This pressure can damage the nerve that carries images from your eye to your brain optic nerve. Diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, glaucoma or a combination of these conditions can lead to complete vision loss, especially if the conditions are poorly managed. If you have diabetes, reduce your risk of getting diabetic retinopathy by doing the following: Manage your diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Try to get at least minutes of moderate aerobic activity, such as walking, each week. Take oral diabetes medications or insulin as directed. Monitor your blood sugar level. You might need to check and record your blood sugar level several times a day — or more frequently if you're ill or under stress. Ask your doctor how often you need to test your blood sugar. Ask your doctor about a glycosylated hemoglobin test. The glycosylated hemoglobin test, or hemoglobin A1C test, reflects your average blood sugar level for the two- to three-month period before the test. Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control. Eating healthy foods, exercising regularly and losing excess weight can help. Sometimes medication is needed, too. If you smoke or use other types of tobacco, ask your doctor to help you quit. Smoking increases your risk of various diabetes complications, including diabetic retinopathy. Pay attention to vision changes. Contact your eye doctor right away if your vision suddenly changes or becomes blurry, spotty or hazy. Does keeping a proper blood sugar level prevent diabetic macular edema and other eye problems? By Mayo Clinic Staff. Feb 21, Show References. National Eye Institute. Accessed Feb. Mayo Clinic, Fraser CE, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Classification and clinical features. American Optometrics Association. Diabetic retinopathy: Prevention and treatment. The diabetes advisor: Eye exams for people with diabetes. American Diabetes Association. Zhang HW, et al. Single herbal medicine for diabetic retinopathy review. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. For more information or to schedule an appointment, contact us at Florida Eye Specialists and Cataract Institute. They make you feel you are important to them, never talk down to you, and treat you with respect! I would recommend them to anyone! The Doctors are great, informative and do a great job explaining things. Thank you again for everything you guys do. I will make sure to refer my friends and family here because I know they will be taken care of. Henderson is the man. He is a perfectionist and I'm glad he is. Everyone at Florida eye specialists is helpful and caring. I'm so glad that I found them. The surgery center was top notch and no pain at all! Completely positive experience and Dr. Applebaum was recommended by my primary eye care doc as having the best results she has seen. He fixes what others have messed up. Thank you. Samy did a fantastic job with my cataract surgery. The techs and staff are kind and helpful. Everything went smooth and quick. I experienced no pain whatsoever and my new vision is no less than spectacular! I am very pleased! The staff is very friendly and professional. Dr Chen was funny, thorough, and wonderful with my daughter. I highly recommend Dr Chen and this office. The kindest, most friendly staff and Dr. Alonzo and Dr. Henderson are real gifts from above. They are so professional, and their skills are unmatched anywhere. Link to home. Brandon Eye Clinic Lake Wales Eye Clinic Plant City Eye Clinic Riverview Eye Clinic Ruskin Eye Clinic South Tampa Eye Clinic St. Petersburg Eye Clinic Sun City Center Eye Clinic. Home Appointment Physicians Physician Portal Careers Eye Exams. New Patient Paperwork Hearing Center Paperwork Make A Payment Medical Records Patient Seminars. |
| Diabetic Eye Disease - NIDDK | Henderson is the man. He is a perfectionist and I'm glad he is. Everyone at Florida eye specialists is helpful and caring. I'm so glad that I found them. The surgery center was top notch and no pain at all! Completely positive experience and Dr. Applebaum was recommended by my primary eye care doc as having the best results she has seen. He fixes what others have messed up. Thank you. Samy did a fantastic job with my cataract surgery. The techs and staff are kind and helpful. Everything went smooth and quick. I experienced no pain whatsoever and my new vision is no less than spectacular! I am very pleased! The staff is very friendly and professional. Dr Chen was funny, thorough, and wonderful with my daughter. I highly recommend Dr Chen and this office. The kindest, most friendly staff and Dr. Alonzo and Dr. Henderson are real gifts from above. They are so professional, and their skills are unmatched anywhere. Link to home. Brandon Eye Clinic Lake Wales Eye Clinic Plant City Eye Clinic Riverview Eye Clinic Ruskin Eye Clinic South Tampa Eye Clinic St. Petersburg Eye Clinic Sun City Center Eye Clinic. Home Appointment Physicians Physician Portal Careers Eye Exams. New Patient Paperwork Hearing Center Paperwork Make A Payment Medical Records Patient Seminars. Introduction Your eye health is one of the most critical aspects of your overall health, and few people realize that the two are intimately intertwined. What is High Blood Sugar? What Causes Blood Sugar to Rise? There are a number of causes including: — Missing a dose of insulin for diabetic people — Increased stress — Illness — Infection — Consuming too many carbohydrates. What Are the Signs and Symptoms? Hyperglycemia may cause one or more of the following symptoms: — Weight loss — Fatigue — Frequent urination — Blurred vision — Increased thirst — Headaches — Difficulty concentrating And if left untreated over time, it can lead to: — Nerve damage — Damage to the eyes, kidneys, and blood vessels — Hair loss — Erectile dysfunction — Slow-healing surface injuries — Chronic digestive problems The good news is that if caught and treated, hyperglycemia can be controlled through a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Without enough insulin, glucose builds up in your blood and causes high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar may damage the blood vessels and lenses in your eyes. This can lead to serious diabetic eye problems which can harm your vision and sometimes cause blindness. Some common diabetes eye problems include:. Anyone with diabetes can develop diabetic eye disease. But your risk of developing it is higher if you:. In the early stages, diabetic eye problems usually don't have any symptoms. That's why regular dilated eye exams are so important, even if you think your eyes are healthy. You should also watch for sudden changes in your vision that could mean an emergency. Call your doctor right away if you notice any of these symptoms:. Eye doctors do dilated eye exams to diagnose eye problems. A dilated eye exam uses eye drops to open your pupils wide so your doctor can look for signs of eye problems and treat them before they harm your vision. Your doctor will also test your vision and measure the pressure in your eyes. Treatment for diabetic eye problems depends on the problem and how serious it is. Some of the treatments include:. But these treatments aren't cures. Eye problems can come back. That's why your best defense against serious vision loss is to take control of your diabetes and get regular eye exams. It's also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol in a healthy range. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Diabetic Eye Problems Also called: Diabetic retinopathy. On this page Basics Summary Start Here Symptoms Diagnosis and Tests Prevention and Risk Factors. Learn More Related Issues. See, Play and Learn Videos and Tutorials. Research Statistics and Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. Resources Reference Desk Find an Expert. For You Patient Handouts. What is diabetes? What eye problems can diabetes cause? Some common diabetes eye problems include: Diabetic retinopathy , which is the leading cause of blindness in American adults. It affects blood vessels in the retina the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye. The blood vessels may swell and leak fluid into your eye. If it's not treated, it can cause serious problems such as vision loss and retinal detachment , where the retina is pulled away from its normal position at the back of your eye. Diabetic macular edema DME , which happens when blood vessels in the retina leak fluid into the macula a part of the retina needed for sharp, central vision. This usually develops in people who already have other signs of diabetic retinopathy. Glaucoma , a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve the bundle of nerves that connects the eye to the brain. Glaucoma from diabetes happens when the blood vessels in the front of your eye are damaged, and new blood vessels grow near the iris the colored part of your eye. The blood vessels block the space where fluid drains from your eye. This causes fluid to build up and pressure to increase inside your eye. Cataract , which happen when the clear lens in the front of your eye becomes cloudy. Cataracts are common as people age. But people with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts younger and faster than people without diabetes. |
| What is diabetic retinopathy? | People with diabetes are twice as likely to develop open-angle glaucoma, the most common type. Diabetes can also cause neovascular glaucoma. This happens sometimes with diabetic retinopathy when new and abnormal blood vessels grow on the iris the colored part of the eye. The new vessels can block off the flow of fluid out of the eye, which raises eye pressure. Treatment options include medicines, laser treatment, and surgery. Talk to your eye doctor about what choices are best for you. Eye problems are common in people with diabetes, but treatments can be very effective. Only your eye doctor can diagnose eye diseases, so make sure to get a dilated eye exam at least once a year. The earlier eye problems are found and treated, the better for your eyesight. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Diabetes and Vision Loss Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Get a dilated eye exam at least once a year to protect your eyesight. Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy Anyone with type 1 , type 2 , or gestational diabetes diabetes while pregnant can develop diabetic retinopathy. These factors can also increase your risk: Blood sugar , blood pressure, and cholesterol levels that are too high. Help for Low Vision. Symptoms in the advanced stage can include: Blurry vision Spots or dark shapes in your vision floaters Trouble seeing colors Dark or empty areas in your vision Vision loss How Diabetic Retinopathy Is Diagnosed During your eye exam, your eye doctor will check how well you see the details of letters or symbols from a distance. Changes may include: Blurring Spots Flashes Blind spots Distortion Difficulty reading or doing detail work. Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Treating diabetic retinopathy can repair damage to the eye and even prevent blindness in most people. Options include: Laser therapy also called laser photocoagulation. This creates a barrier of scar tissue that slows the growth of new blood vessels. Medicines called VEGF inhibitors, which can slow down or reverse diabetic retinopathy. Removing all or part of the vitreous vitrectomy. Reattachment of the retina for retinal detachment, a complication of diabetic retinopathy. Injection of medicines called corticosteroids. Other Eye Diseases. Keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap 6. Skugor M. Diabetes mellitus. In: Schachat AP, Sadda SVR, Hinton DR, Wilkinson CP, Wiedemann P, eds. Ryan's Retina. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. Editorial team. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library. Diabetes and eye disease Retinopathy - diabetic; Photocoagulation - retina; Diabetic retinopathy. Causes Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage from diabetes to blood vessels of the retina. The chance of developing retinopathy and having a more severe form is higher when: You have had diabetes for a long time. Your blood sugar glucose has been poorly controlled. You also smoke or you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol. Other eye problems that can occur in people with diabetes include: Cataract -- Cloudiness of the eye lens. Glaucoma -- Increased pressure in the eye that can lead to blindness. Macular edema -- Blurry vision due to fluid leaking into the area of the retina that provides sharp central vision. Retinal detachment -- Scarring that may cause part of the retina to pull away from the back of your eyeball. Symptoms Most often, diabetic retinopathy has no symptoms until the damage to your eyes is severe. Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include: Blurred vision and slow vision loss over time Floaters Shadows or missing areas of vision Trouble seeing at night Many people with early diabetic retinopathy have no symptoms before bleeding occurs in the eye. Exams and Tests Your eye doctor will examine your eyes. Tests you may have involve: Measuring the fluid pressure inside your eyes tonometry Checking the structures inside your eyes slit lamp exam Checking and photographing your retinas fluorescein angiography If you have the early stage of diabetic retinopathy nonproliferative , the eye doctor may see: Blood vessels in the eye that are larger in certain spots called microaneurysms Blood vessels that are blocked Small amounts of bleeding retinal hemorrhages and fluid leaking into the retina If you have advanced retinopathy proliferative , the eye doctor may see: New blood vessels starting to grow in the eye that are weak and can bleed Small scars forming on the retina and in other parts of the eye the vitreous The eye exam for people with diabetes is different from going to the eye doctor optometrist or ophthalmologist to have your vision checked and to see whether you need new glasses. Treatment People with early diabetic retinopathy may not need treatment. Eye surgery is the main treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Laser eye surgery creates small burns in the retina where there are abnormal blood vessels. This process is called photocoagulation. It is used to keep vessels from leaking, or to shrink abnormal vessels. Surgery called vitrectomy is used when there is bleeding hemorrhage into the eye. It may also be used to repair retinal detachment. Support Groups More information and support for people with diabetes and their families can be found at: American Diabetes Association -- www. org National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases -- www. Outlook Prognosis Managing your diabetes may help slow diabetic retinopathy and other eye problems. Control your blood sugar glucose level by: Eating healthy foods Getting regular exercise Checking your blood sugar as often as instructed by your diabetes provider and keeping a record of your numbers so you know the types of foods and activities that affect your blood sugar level Taking medicine or insulin as instructed Treatments can reduce vision loss. Possible Complications Diabetic eye disease can lead to reduced vision and blindness. When to Contact a Medical Professional Call for an appointment with an eye doctor optometrist or ophthalmologist if you have diabetes and you have not seen an optometrist or ophthalmologist in the past year. Contact your provider if any of the following symptoms are new or are becoming worse: You cannot see well in dim light. You have blind spots. You have double vision you see two things when there is only one. Your vision is hazy or blurry and you cannot focus. You have pain in one of your eyes. You are having headaches. You see spots floating in your eyes. Blurred vision can be a sign that your diabetes is not being controlled properly. Speak with your doctor to determine what you can do at home to help regulate your glucose levels. In most cases, this involves consuming a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and keeping your cholesterol and blood pressure levels under control. Contact your eye doctor as soon as possible if blurred vision comes on suddenly or gets worse over time— this can indicate a serious condition. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, be sure to visit your eye doctor regularly for follow up eye exams. LEARN MORE: Guide to Eye Conditions. Schedule an appointment with an eye doctor for a comprehensive diabetic eye exam, and to discuss any questions you may have about treating this condition. Frequent eye exams, as well as controlling your blood sugar levels will help to ensure that your eyes and body remain healthy. Your plain English library for vision therapy, children's vision, neuro-optometry, and primary eye care. Find an Eye Doctor. Search near me. Russel Lazarus, September 23, If you have diabetes, high blood sugar levels may be the cause of your blurry vision. How do I know if I have blurry vision? Blurry vision is one of the earliest symptoms of diabetes. Diabetes-related blurry vision may occur for a variety of reasons: High blood sugar levels hyperglycemia Low blood sugar levels hypoglycemia Fluctuating blood sugar levels In some cases, blurry vision may be experienced if you are adapting to a new dosage of insulin medication. |
0 thoughts on “Hyperglycemia and eye complications”