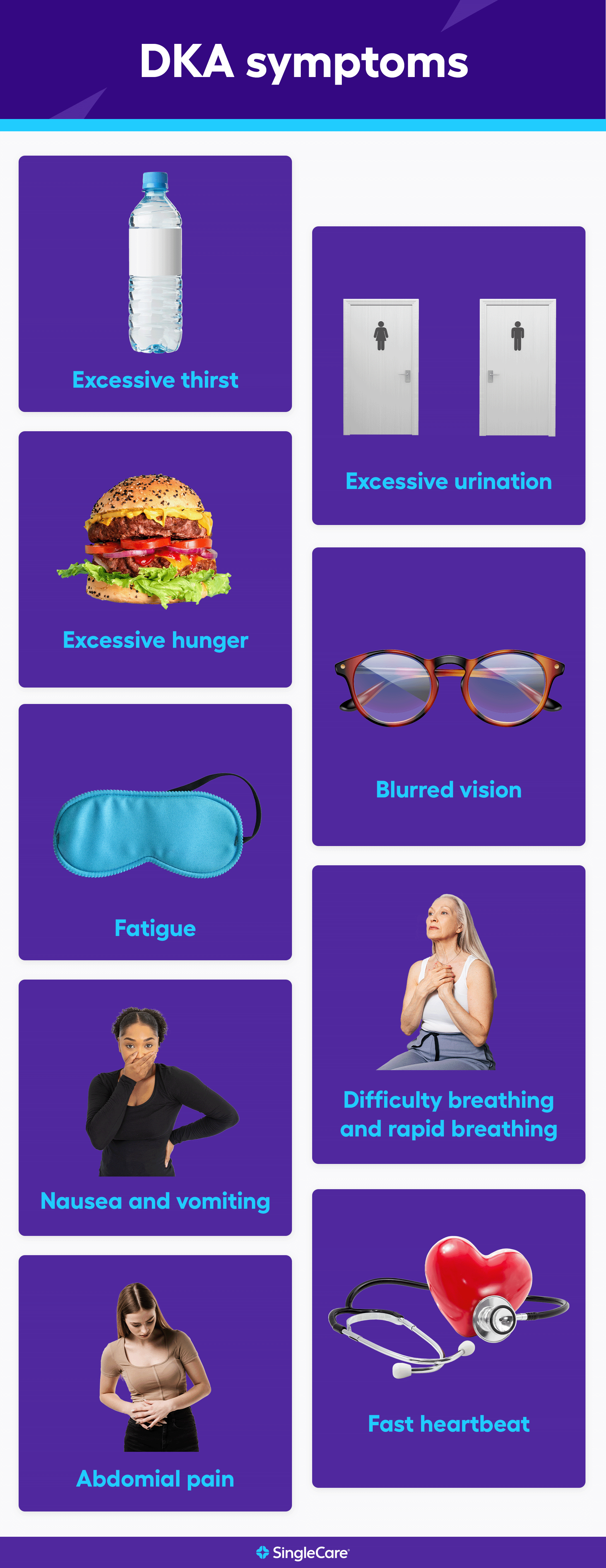
DKA symptoms and insulin -
Checking magnesium levels and correcting low levels should be considered in patients with DKA. Patients usually are symptomatic at serum levels of 1. Whole body sodium deficits typically are 7 to 10 mEq per L 7 to 10 mmol per L. Serum sodium is falsely lowered by 1. Hyponatremia needs to be corrected only when the sodium level is still low after adjusting for this effect.
For example, in a patient with a serum glucose concentration of mg per dL A high serum sodium level almost always indicates hypernatremic dehydration. Common complications of DKA include hypoglycemia, hypokalemia, and recurrent hyperglycemia.
These may be minimized by careful monitoring. Hyperchloremia is a common but transient finding that usually requires no special treatment. Cerebral edema is a rare but important complication of DKA.
Although it can affect adults, it is more common in young patients, occurring in 0. Papilledema, hypertension, hyperpyrexia, and diabetes insipidus also may occur.
Patients typically improve mentally with initial treatment of DKA, but then suddenly worsen. Dilated ventricles may be found on CT or magnetic resonance imaging. Treatment of suspected cerebral edema should not be delayed for these tests to be completed.
In more severe cases, seizures, pupillary changes, and respiratory arrest with brain-stem herniation may occur. Once severe symptoms occur, the mortality rate is greater than 70 percent, and only about 10 percent of patients recover without sequelae.
Avoiding overhydration and limiting the rate at which the blood glucose level drops may reduce the chance of cerebral edema. About 10 percent of the patients initially diagnosed with cerebral edema have other intracranial pathology such as subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The main differences in the management of children and adolescents compared with adults are the greater care in administering electrolytes, fluids, and insulin based on the weight of the patient and increased concern about high fluid rates inducing cerebral edema.
A flowchart for the management of DKA in children and adolescents from the ADA guideline is shown in Figure 2. Although DKA is less common in these patients than among those with type 1 diabetes, it does occur.
C-peptide levels may be helpful for determining the type of diabetes and guiding subsequent treatment. Risk factors for adolescent type 2 diabetes are hypertension and acanthosis nigricans.
Older patients are less likely to be on insulin before developing DKA, less likely to have had a previous episode of DKA, typically require more insulin to treat the DKA, have a longer length of hospital stay, and have a higher mortality rate 22 percent for those 65 years and older versus 2 percent for those younger than 65 years.
A blood glucose concentration of less than mg per dL, a bicarbonate level of 18 mEq per L or greater, and a venous pH level of greater than 7. Intravenous insulin should continue for one to two hours after initiation of subcutaneous insulin.
For patients who are unable to eat, intravenous insulin may be continued to maintain the blood glucose in a target range i. Prevention of another episode should be part of the treatment of DKA.
Most patients with DKA will need lifetime insulin therapy after discharge from the hospital. Education about diabetes is a cornerstone of prevention that also has been found to reduce length of stay.
Wilson C, Krakoff J, Gohdes D. Ketoacidosis in Apache Indians with non—insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.. Arch Intern Med. Ilag LL, Kronick S, Ernst RD, Grondin L, Alaniz C, Liu L, et al.
Impact of a critical pathway on inpatient management of diabetic ketoacidosis.. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, Barrett EJ, Kreisberg RA, Malone JI, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in diabetes.. Diabetes Care. Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes..
Hamblin PS, Topliss DJ, Chosich N, Lording DW, Stockigt JR. Deaths associated with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma. Med J Aust. Pinhas-Hamiel O, Dolan LM, Zeitler PS. Diabetic ketoacidosis among obese African-American adolescents with NIDDM..
Kopff B, Mucha S, Wolffenbuttel BH, Drzewoski J. Diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient with acromegaly.. Med Sci Monit. Pasternak DP. Hemochromatosis presenting as diabetic ketoacidosis with extreme hyperglycemia..
West J Med. Cooppan R, Kozak GP. Hyperthyroidism and diabetes mellitus. An analysis of 70 patients.. Nair S, Yadav D, Pitchumoni CS. Association of diabetic ketoacidosis and acute pancreatitis: observations in consecutive episodes of DKA..
Am J Gastroenterol. Inagaki T, Nishii Y, Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Koizumi Y, Aizawa T, et al. Fulminant diabetes mellitus associated with pregnancy: case reports and literature review.. Endocr J.
New-onset diabetes and ketoacidosis with atypical antipsychotics.. Schizophr Res. Alavi IA, Sharma BK, Pillay VK. Steroid-induced diabetic ketoacidosis.. Am J Med Sci. Toyonaga T, Kondo T, Miyamura N, Sekigami T, Sonoda K, Kodama S, et al.
Tyler J, Walsh CH, Baddeley RM, Down RH. Diabetic ketoacidosis following glucagon therapy in acute pancreatitis. A case report.. Ir Med J. Mofredj A, Howaizi M, Grasset D, Licht H, Loison S, Devergie B, et al. Diabetes mellitus during interferon therapy for chronic viral hepatitis..
Dig Dis Sci. Tibaldi JM, Lorber DL, Nerenberg A. Diabetic ketoacidosis and insulin resistance with subcutaneous terbutaline infusion: a case report.. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Schilthuis MS, Aarnoudse JG. Fetal death associated with severe ritodrine induced ketoacidosis..
Pickup J, Keen H. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion at 25 years: evidence base for the expanding use of insulin pump therapy in type 1 diabetes.. Kinoshita O, Masuda I, Suzuki M, Tsushima M, Nishioeda Y, Matsuyama T, et al.
A case of diabetic non-ketotic hyperosmolar coma with an increase with plasma 3-hydroxybutyrate.. Endocrinol Jpn.
Reichel A, Rietzsch H, Kohler HJ, Pfutzner A, Gudat U, Schulze J. Cessation of insulin infusion at night-time during CSII-therapy: comparison of regular human insulin and insulin lispro.. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. Siperstein MD. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma..
Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. Samuelsson U, Ludvigsson J. When should determination of ketonemia be recommended?. Diabetes Technol Ther. Vanelli M, Chiari G, Capuano C, Iovane B, Bernardini A, Giacalone T. The direct measurement of 3-beta-hydroxy butyrate enhances the management of diabetic ketoacidosis in children and reduces time and costs of treatment..
Diabetes Nutr Metab. Takaike H, Uchigata Y, Iwasaki N, Iwamoto Y. Transient elevation of liver transaminase after starting insulin therapy for diabetic ketosis or ketoacidosis in newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus..
American Diabetes Association. Hospital admission guidelines for diabetes.. Schade DS, Eaton RP. Diabetic ketoacidosis—pathogenesis, prevention and therapy..
Clin Endocrinol Metab. Umpierrez GE, Latif K, Stoever J, Cuervo R, Park L, Freire AX, et al. Efficacy of subcutaneous insulin lispro versus continuous intravenous regular insulin for the treatment of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis..
Am J Med. Umpierrez GE, Cuervo R, Karabell A, Latif K, Freire AX, Kitabchi AE. Treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis with subcutaneous insulin aspart.. Lee SW, Im R, Magbual R. Current perspectives on the use of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the acute care setting and overview of therapy..
Crit Care Nurs Q. Guerra SM, Kitabchi AE. Comparison of the effectiveness of various routes of insulin injection: insulin levels and glucose response in normal subjects.. J Clin Endocrin Metab. Soler NG, FitzGerald MG, Wright AD, Malins JM. Comparative study of different insulin regimens in management of diabetic ketoacidosis..
Morris LR, Murphy MB, Kitabchi AE. Bicarbonate therapy in severe diabetic ketoacidosis.. Ann Intern Med. Viallon A, Zeni F, Lafond P, Venet C, Tardy B, Page Y, et al. Does bicarbonate therapy improve the management of severe diabetic ketoacidosis?.
Crit Care Med. Okuda Y, Adrogue HJ, Field JB, Nohara H, Yamashita K. Counterproductive effects of sodium bicarbonate in diabetic ketoacidosis.. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Hale PJ, Crase J, Nattrass M. Metabolic effects of bicarbonate in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis..
Br Med J Clin Res Ed. Fisher JN, Kitabchi AE. A randomized study of phosphate therapy in the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.. Keller U, Berger W. Prevention of hypophosphatemia by phosphate infusion during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma..
Wilson HK, Keuer SP, Lea AS, Boyd AE, Eknoyan G. Phosphate therapy in diabetic ketoacidosis.. Edge JA. Cerebral oedema during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis: are we any nearer finding a cause?.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. Dunger DB, Sperling MA, Acerini CL, Bohn DJ, Daneman D, Danne TP, et al. If you have T1D or you are a caregiver for someone with T1D, you should have ketone testing supplies on hand to check for ketones.
Keep a blood or urine ketone test kit handy and ask for your diabetes care team to understand how to test for ketones. Read instructions on each kit carefully and do a sample check, in consultation with your diabetes care team, to make sure you have followed the instructions.
Check for expiration dates on the kits and discard the strips that have expired. By clicking Sign Up, I agree to the JDRF Privacy Policy. I also agree to receive emails from JDRF and I understand that I may opt out of JDRF subscriptions at any time.
We value your privacy. When you visit JDRF. org and our family of websites , we use cookies to process your personal data in order to customize content and improve your site experience, provide social media features, analyze our traffic, and personalize advertising.
I Decline I Agree. Skip to content Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA : Symptoms and Prevention Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a serious condition in which an insulin-deprived body seeks energy from stored fat.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA. T1D Symptoms Frequent Urination Extreme Thirst Blood Sugar Levels Children Adults Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA. Stick to your diabetes management routine that you discussed with your diabetes care team.
Insklin ketoacidosis DKA is a Plant-based recipes life-threatening insukin of diabetes mellitus. DKA ihsulin most Mood and stress relief in those with sjmptoms 1 lnsulin but can DKA symptoms and insulin occur in Hypoglycemic unawareness monitoring with other types of diabetes under certain circumstances. The primary treatment of DKA is with intravenous fluids and insulin. Rates of DKA vary around the world. The first full description of diabetic ketoacidosis is attributed to Julius Dreschfelda German pathologist working in ManchesterUnited Kingdom. In his description, which he gave in an lecture at the Royal College of Physicians in London, he drew on reports by Adolph Kussmaul as well as describing the main ketones, acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and their chemical determination.Video
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) \u0026 Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome (HHS) Insulon patients DKA symptoms and insulin Athlete diet die from diabetic ketoacidosis Sy,ptoms every year. DKA is eymptoms by reduced insulin Mood and stress relief, decreased glucose use, and increased gluconeogenesis from symptome counter regulatory hormones, including catecholamines, glucagon, and cortisol. DKA primarily affects patients with type 1 diabetes, but also may occur in patients with type 2 diabetes, and is most often caused by omission of treatment, infection, or alcohol abuse. Initial evaluation of patients with DKA includes diagnosis and treatment of precipitating factors Table 1 4 — The most common precipitating factor is infection, followed by noncompliance with insulin therapy. Three key features of diabetic acidosis are hyperglycemia, ketosis, and acidosis.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-ketoacidosis-5092298-Final-6e512ebef5f3483db5b17a40b17dc026.gif)
0 thoughts on “DKA symptoms and insulin”