Video
Predictors of Advanced Neoplasia in Surgically Resected Intraductal Papillary Mucinous NeoplasmsPancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm -
Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas IPMN : Evaluation and management. Formulary drug information for this topic.
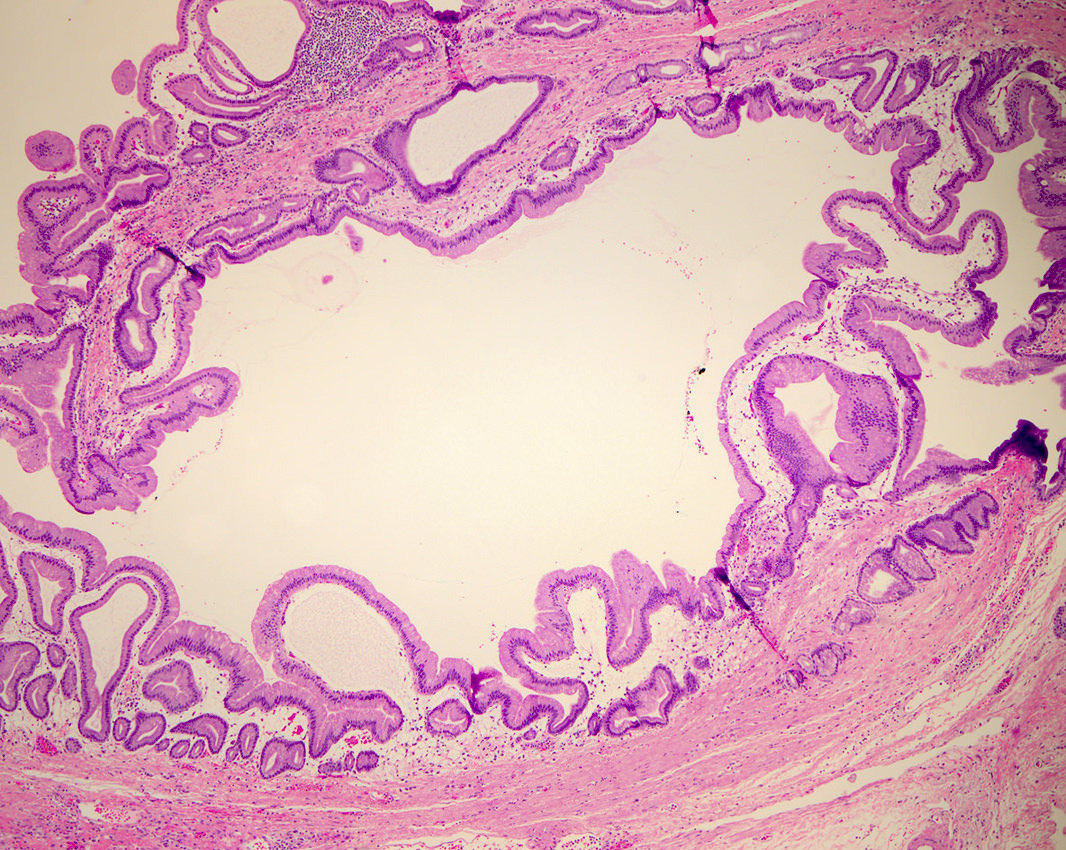
No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. View in. Language Chinese English. Authors: Sunil G Sheth, MD Tara S Kent, MD, FACS Section Editor: David C Whitcomb, MD, PhD Deputy Editor: Shilpa Grover, MD, MPH, AGAF Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Feb 13, The lesions show papillary proliferation, cyst formation, and varying degrees of cellular atypia [ 1,2 ].
DIAGNOSIS The approach to the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms typically starts with cross-sectional imaging magnetic resonance imaging with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or computed tomography. Additional evaluation with endoscopic ultrasound with fine-needle aspiration may be needed to confirm a diagnosis or to assess for malignant features.
The diagnostic approach to pancreatic cystic neoplasms is discussed separately. See "Pancreatic cystic neoplasms: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management". Resection is typically recommended for IPMNs with high-grade dysplasia carcinoma in situ , IPMNs that have progressed to invasive carcinoma also referred to as invasive IPMN or malignant IPMN , and IPMNs with features concerning for malignancy or that are at high risk for developing malignancy.
IPMNs not meeting these criteria are typically followed with surveillance imaging. See 'Management' below. To continue reading this article, you must sign in with your personal, hospital, or group practice subscription.
Subscribe Sign in. It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient.
It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider's examination and assessment of a patient's specific and unique circumstances. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications.
This information does not endorse any treatments or medications as safe, effective, or approved for treating a specific patient.
UpToDate, Inc. and its affiliates disclaim any warranty or liability relating to this information or the use thereof. All rights reserved. Topic Feedback. Radiographic surveillance should be continued after resection of worrisome lesions given the continued risk of recurrence or development of metachronous lesions.
Future studies should focus on the development of fluid and serum biomarkers that can more accurately identify lesions with HGD in the preoperative setting, which will allow for better risk stratification of IPMN.
Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest.
filter your search All Content All Journals Visceral Medicine. Advanced Search. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation.
Volume 33, Issue 6. Epidemiology of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Types of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Based on Main Pancreatic Duct Involvement: The First Layer of Classification.
Epithelial Subtypes of the Precursor Component and the Invasive Carcinoma: Insights into Tumor Biology and Its Heterogeneity. Clinical Presentation. Circulating Biomarkers for Prediction of High-Risk Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms.
Imaging Evaluation. Cyst Fluid Analysis: Proteins, Cytology, and Molecular Characterization. Considerations Regarding Operative Approach to Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms.
Follow-up of Resected Patients: Predicting Recurrent and New Lesions. Follow-up of Non-Resected Patients. IAP and AGA Guidelines: How We Use Them. Disclosure Statement. Article Navigation. Review Articles June 01 Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas: Strategic Considerations Subject Area: Gastroenterology , Surgery.
Vicente Morales-Oyarvide ; Vicente Morales-Oyarvide. This Site. Google Scholar. Zhi Ven Fong ; Zhi Ven Fong. Carlos Fernández-del Castillo ; Carlos Fernández-del Castillo.
Andrew L. Warshaw Andrew L. Visc Med 33 6 : — Cite Icon Cite. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. Journal Section:. View large Download slide.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. Valsangkar NP, Morales-Oyarvide V, Thayer SP, Ferrone CR, Wargo JA, Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C: resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: a year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital.
Surgery ;S Basturk O, Hong SM, Wood LD, et al. Am J Surg Pathol ; Mino-Kenudson M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Baba Y, Valsangkar NP, Liss AS, Hsu M, Correa-Gallego C, Ingkakul T, Perez Johnston R, Turner BG, Androutsopoulos V, Deshpande V, McGrath D, Sahani DV, Brugge WR, Ogino S, Pitman MB, Warshaw AL, Thayer SP: Prognosis of invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm depends on histological and precursor epithelial subtypes.
Gut ; Furukawa T, Hatori T, Fujita I, Yamamoto M, Kobayashi M, Ohike N, Morohoshi T, Egawa S, Unno M, Takao S, Osako M, Yonezawa S, Mino-Kenudson M, Lauwers GY, Yamaguchi H, Ban S, Shimizu M: Prognostic relevance of morphological types of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Wu J, Matthaei H, Maitra A, Dal Molin M, Wood LD, Eshleman JR, Goggins M, Canto MI, Schulick RD, Edil BH, Wolfgang CL, Klein AP, Diaz LA Jr, Allen PJ, Schmidt CM, Kinzler KW, Papadopoulos N, Hruban RH, Vogelstein B: Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development.
Sci Transl Med ;ra Furukawa T, Kuboki Y, Tanji E, Yoshida S, Hatori T, Yamamoto M, Shibata N, Shimizu K, Kamatani N, Shiratori K: Whole-exome sequencing uncovers frequent GNAS mutations in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Sci Rep ; Tamura K, Ohtsuka T, Date K, Fujimoto T, Matsunaga T, Kimura H, Watanabe Y, Miyazaki T, Ohuchida K, Takahata S, Ishigami K, Oda Y, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Tanaka M: Distinction of invasive carcinoma derived from intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms from concomitant ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas using molecular biomarkers.
Pancreas ; Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K, Matsuno S; International Association of Pancreatology: International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas.
Pancreatology ; Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V, Chari S, Falconi M, Jang JY, Kimura W, Levy P, Pitman MB, Schmidt CM, Shimizu M, Wolfgang CL, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K; International Association of Pancreatology: International consensus guidelines for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas.
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Kamisawa T, Jang JY, Levy P, Ohtsuka T, Salvia R, Shimizu Y, Tada M, Wolfgang CL: Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Vege SS, Ziring B, Jain R, Moayyedi P; Clinical Guidelines Committee; American Gastroenterology Association: American Gastroenterological Association Institute guideline on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts.
Gastroenterology ; Scheiman JM, Hwang JH, Moayyedi P: American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts.
Laffan TA, Horton KM, Klein AP, Berlanstein B, Siegelman SS, Kawamoto S, Johnson PT, Fishman EK, Hruban RH: Prevalence of unsuspected pancreatic cysts on MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol ; Zhang XM, Mitchell DG, Dohke M, Holland GA, Parker L: Pancreatic cysts: depiction on single-shot fast spin-echo MR images.
Radiology ; Fernandez-del Castillo C, Targarona J, Thayer SP, Rattner DW, Brugge WR, Warshaw AL: Incidental pancreatic cysts: clinicopathologic characteristics and comparison with symptomatic patients.
Arch Surg ;; discussion de Jong K, Nio CY, Hermans JJ, Dijkgraaf MG, Gouma DJ, van Eijck CH, van Heel E, Klass G, Fockens P, Bruno MJ: High prevalence of pancreatic cysts detected by screening magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol ; Pergolini I, Sahora K, Ferrone CR, Morales-Oyarvide V, Wolpin BM, Mucci LA, Brugge WR, Mino-Kenudson M, Patino M, Sahani DV, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Long-term risk of pancreatic malignancy in patients with branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in a referral center.
Waters JA, Schmidt CM, Pinchot JW, White PB, Cummings OW, Pitt HA, Sandrasegaran K, Akisik F, Howard TJ, Nakeeb A, Zyromski NJ, Lillemoe KD: CT vs MRCP: optimal classification of IPMN type and extent.
J Gastrointest Surg ; Baiocchi GL, Portolani N, Missale G, Baronchelli C, Gheza F, Cantu M, Grazioli L, Giulini SM: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas IPMN : clinico-pathological correlations and surgical indications.
World J Surg Oncol ; Sahora K, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Dong F, Marchegiani G, Thayer SP, Ferrone CR, Sahani DV, Brugge WR, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Mino-Kenudson M: Not all mixed-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms behave like main-duct lesions: implications of minimal involvement of the main pancreatic duct.
Surgery ; Morales-Oyarvide V, Pergolini I, Ferrone CR, Mino-Kenudson M, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Main pancreatic duct size independently predicts histological main duct involvement, intestinal phenotype, and malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Adsay NV, Kloppel G, Fukushima N: Intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas; in Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND eds : WHO Classification of Tumors. Lyon, WHO Press, , pp Adsay V, Mino-Kenudson M, Furukawa T, et al. Ann Surg ; Mohri D, Asaoka Y, Ijichi H, Miyabayashi K, Kudo Y, Seto M, Ohta M, Tada M, Tanaka Y, Ikenoue T, Tateishi K, Isayama H, Kanai F, Fukushima N, Tada M, Kawabe T, Omata M, Koike K: Different subtypes of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in the pancreas have distinct pathways to pancreatic cancer progression.
J Gastroenterol ; Tan MC, Basturk O, Brannon AR, Bhanot U, Scott SN, Bouvier N, LaFemina J, Jarnagin WR, Berger MF, Klimstra D, Allen PJ: GNAS and KRAS mutations define separate progression pathways in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm-associated carcinoma.
J Am Coll Surg ; Marchegiani G, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone CR, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Oncocytic-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: a unique malignant pancreatic tumor with good long-term prognosis.
Morales-Oyarvide V, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone C, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Sahani DV, Pergolini I, Attiyeh M, Al Efishat M, Rezaee N, Hruban RH, He J, Weiss MJ, Allen PJ, Wolfgang CL, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas in young patients: tumor biology, clinical features, and survival outcomes.
J Gastrointest Surg ;DOI: Sahora K, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge W, Thayer SP, Ferrone CR, Sahani D, Pitman MB, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: does cyst size change the tip of the scale?
A critical analysis of the revised international consensus guidelines in a large single-institutional series. Pannala R, Leirness JB, Bamlet WR, Basu A, Petersen GM, Chari ST: Prevalence and clinical profile of pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes mellitus.
Morales-Oyarvide V, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone CR, Sahani DV, Pergolini I, Negreros-Osuna AA, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Diabetes mellitus in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas is associated with high-grade dysplasia and invasive carcinoma.
Morales-Oyarvide V, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone CR, Gonzalez-Gonzalez LA, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Acute pancreatitis in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: a common predictor of malignant intestinal subtype. Ferrone CR, Finkelstein DM, Thayer SP, Muzikansky A, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL: Perioperative CA levels can predict stage and survival in patients with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
J Clin Oncol ; Wang W, Zhang L, Chen L, Wei J, Sun Q, Xie Q, Zhou X, Zhou D, Huang P, Yang Q, Xie H, Zhou L, Zheng S: Serum carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen for prediction of malignancy and invasiveness in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis.
Biomed Rep ; Morales-Oyarvide V, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone CR, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Su elevated serum CA in IPMN is a highly-specific marker of invasive cancer and an independent predictor of advanced stage and poor survival.
Gastroenterology ;S Kim JR, Jang JY, Kang MJ, Park T, Lee SY, Jung W, Chang J, Shin Y, Han Y, Kim SW: Clinical implication of serum carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen for the prediction of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas.
J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci ; Fritz S, Hackert T, Hinz U, Hartwig W, Buchler MW, Werner J: Role of serum carbohydrate antigen and carcinoembryonic antigen in distinguishing between benign and invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.
Br J Surg ; Arima K, Okabe H, Hashimoto D, Chikamoto A, Kuroki H, Taki K, Kaida T, Higashi T, Nitta H, Komohara Y, Beppu T, Takeya M, Baba H: The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts malignant potential in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
Gemenetzis G, Bagante F, Griffin JF, Rezaee N, Javed AA, Manos LL, Lennon AM, Wood LD, Hruban RH, Zheng L, Zaheer A, Fishman EK, Ahuja N, Cameron JL, Weiss MJ, He J, Wolfgang CL: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a predictive marker for invasive malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Sainani NI, Saokar A, Deshpande V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Hahn P, Sahani DV: Comparative performance of MDCT and MRI with MR cholangiopancreatography in characterizing small pancreatic cysts. Sahani DV, Sainani NI, Blake MA, Crippa S, Mino-Kenudson M, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Prospective evaluation of reader performance on MDCT in characterization of cystic pancreatic lesions and prediction of cyst biologic aggressiveness.
AJR Am J Roentgenol ;W Hirono S, Tani M, Kawai M, Okada K, Miyazawa M, Shimizu A, Kitahata Y, Yamaue H: The carcinoembryonic antigen level in pancreatic juice and mural nodule size are predictors of malignancy for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Ohno E, Itoh A, Kawashima H, Ishikawa T, Matsubara H, Itoh Y, Nakamura Y, Hiramatsu T, Nakamura M, Miyahara R, Ohmiya N, Ishigami M, Katano Y, Goto H, Hirooka Y: Malignant transformation of branch duct-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas based on contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography morphological changes: focus on malignant transformation of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm itself.
Seo N, Byun JH, Kim JH, Kim HJ, Lee SS, Song KB, Kim SC, Han DJ, Hong SM, Lee MG: Validation of the international consensus guidelines using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: branch duct and main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Berland LL, Silverman SG, Gore RM, Mayo-Smith WW, Megibow AJ, Yee J, Brink JA, Baker ME, Federle MP, Foley WD, Francis IR, Herts BR, Israel GM, Krinsky G, Platt JF, Shuman WP, Taylor AJ: Managing incidental findings on abdominal CT: white paper of the ACR incidental findings committee.
J Am Coll Radiol ; Salvia R, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Bassi C, Thayer SP, Falconi M, Mantovani W, Pederzoli P, Warshaw AL: Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival following resection.
Ann Surg ;; discussion Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay NV: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Rodriguez JR, Salvia R, Crippa S, Warshaw AL, Bassi C, Falconi M, Thayer SP, Lauwers GY, Capelli P, Mino-Kenudson M, Razo O, McGrath D, Pederzoli P, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in patients who underwent resection.
Kim KW, Park SH, Pyo J, Yoon SH, Byun JH, Lee MG, Krajewski KM, Ramaiya NH: Imaging features to distinguish malignant and benign branch-duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis.
Anand N, Sampath K, Wu BU: Cyst features and risk of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a meta-analysis.
Kitano M, Sakamoto H, Komaki T, Kudo M: New techniques and future perspective of EUS for the differential diagnosis of pancreatic malignancies: contrast harmonic imaging. Dig Endosc ;23 suppl 1 Correa-Gallego C, Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Fluid CEA in IPMNs: a useful test or the flip of a coin?
Am J Gastroenterol ; Brugge WR, Lewandrowski K, Lee-Lewandrowski E, Centeno BA, Szydlo T, Regan S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL: Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: a report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Cizginer S, Turner BG, Bilge AR, Karaca C, Pitman MB, Brugge WR: Cyst fluid carcinoembryonic antigen is an accurate diagnostic marker of pancreatic mucinous cysts.
Das KK, Xiao H, Geng X, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Morales-Oyarvide V, Daglilar E, Forcione DG, Bounds BC, Brugge WR, Pitman MB, Mino-Kenudson M, Das KM: mAb Das-1 is specific for high-risk and malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm IPMN.
Das KK, Geng XG, Morales-Oyarvide V, Huynh T, Pergolini I, Pitman MB, Ferrone C, Brugge W, Al Efishat M, Haviland D, Thompson E, Wolfgang C, Lennon AM, Allen P, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Das KM, Mino-Kenudson M: - A multicenter, validation study of cyst fluid analysis for mAb-Das1 for the identification of high-risk and malignant mucinous cysts of the pancreas.
Gastroenterology ;SS Cancer Cytopathol ; Pitman MB, Yaeger KA, Brugge WR, Mino-Kenudson M: Prospective analysis of atypical epithelial cells as a high-risk cytologic feature for malignancy in pancreatic cysts.
Fritz S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Mino-Kenudson M, Crippa S, Deshpande V, Lauwers GY, Warshaw AL, Thayer SP, Iafrate AJ: Global genomic analysis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas reveals significant molecular differences compared to ductal adenocarcinoma.
Jones M, Zheng Z, Wang J, Dudley J, Albanese E, Kadayifci A, Dias-Santagata D, Le L, Brugge WR, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Mino-Kenudson M, Iafrate AJ, Pitman MB: Impact of next-generation sequencing on the clinical diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Gastrointest Endosc ; Springer S, Wang Y, Dal Molin M, et al: A combination of molecular markers and clinical features improve the classification of pancreatic cysts.
Crippa S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Salvia R, Finkelstein D, Bassi C, Dominguez I, Muzikansky A, Thayer SP, Falconi M, Mino-Kenudson M, Capelli P, Lauwers GY, Partelli S, Pederzoli P, Warshaw AL: Mucin-producing neoplasms of the pancreas: an analysis of distinguishing clinical and epidemiologic characteristics.
Fernandez-del Castillo C, Morales-Oyarvide V, McGrath D, Wargo JA, Ferrone CR, Thayer SP, Lillemoe KD, Warshaw AL: Evolution of the Whipple procedure at the Massachusetts General Hospital.
Fong ZV, Alvino DM, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Nipp RD, Traeger LN, Ruddy M, Lubitz CC, Johnson CD, Chang DC, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Ferrone CR: Health-related quality of life and functional outcomes in 5-year survivors after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Sahora K, Ferrone CR, Brugge WR, Morales-Oyarvide V, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Effects of comorbidities on outcomes of patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
Sauvanet A, Gaujoux S, Blanc B, Couvelard A, Dokmak S, Vullierme MP, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Levy P: Parenchyma-sparing pancreatectomy for presumed noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Faitot F, Gaujoux S, Barbier L, Novaes M, Dokmak S, Aussilhou B, Couvelard A, Rebours V, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Sauvanet A: Reappraisal of pancreatic enucleations: a single-center experience of procedures.
Kaiser J, Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Hinz U, Strobel O, Schneider L, Buchler MW, Hackert T: Enucleation: a treatment alternative for branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Marchegiani G, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone CR, Morales-Oyarvide V, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: Patterns of recurrence after resection of IPMN: who, when, and how?
Kang MJ, Jang JY, Lee KB, Chang YR, Kwon W, Kim SW: Long-term prospective cohort study of patients undergoing pancreatectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: implications for postoperative surveillance.
White R, D'Angelica M, Katabi N, Tang L, Klimstra D, Fong Y, Brennan M, Allen P: Fate of the remnant pancreas after resection of noninvasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
J Am Coll Surg ;; discussion Salvia R, Partelli S, Crippa S, Landoni L, Capelli P, Manfredi R, Bassi C, Pederzoli P: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas with multifocal involvement of branch ducts.
Am J Surg ; Marchegiani G, Mino-Kenudson M, Sahora K, Morales-Oyarvide V, Thayer S, Ferrone C, Warshaw AL, Lillemoe KD, Fernandez-del Castillo C: IPMN involving the main pancreatic duct: biology, epidemiology, and long-term outcomes following resection. Ingkakul T, Sadakari Y, Ienaga J, Satoh N, Takahata S, Tanaka M: Predictors of the presence of concomitant invasive ductal carcinoma in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas.
Ideno N, Ohtsuka T, Kono H, Fujiwara K, Oda Y, Aishima S, Ito T, Ishigami K, Tokunaga S, Ohuchida K, Takahata S, Nakamura M, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas with distinct pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas are frequently of gastric subtype.
Miyasaka Y, Ohtsuka T, Tamura K, Mori Y, Shindo K, Yamada D, Takahata S, Ishigami K, Ito T, Tokunaga S, Oda Y, Mizumoto K, Nakamura M, Tanaka M: Predictive factors for the metachronous development of high-risk lesions in the remnant pancreas after partial pancreatectomy for intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Frankel TL, LaFemina J, Bamboat ZM, D'Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, Kingham TP, Jarnagin WR, Allen PJ: Dysplasia at the surgical margin is associated with recurrence after resection of non-invasive intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.
HPB Oxford ; He J, Cameron JL, Ahuja N, Makary MA, Hirose K, Choti MA, Schulick RD, Hruban RH, Pawlik TM, Wolfgang CL: Is it necessary to follow patients after resection of a benign pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm?
Ohtsuka T, Kono H, Tanabe R, Nagayoshi Y, Mori Y, Sadakari Y, Takahata S, Oda Y, Aishima S, Igarashi H, Ito T, Ishigami K, Nakamura M, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M: Follow-up study after resection of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas; special references to the multifocal lesions and development of ductal carcinoma in the remnant pancreas.
Tanno S, Nakano Y, Sugiyama Y, Nakamura K, Sasajima J, Koizumi K, Yamazaki M, Nishikawa T, Mizukami Y, Yanagawa N, Fujii T, Obara T, Okumura T, Kohgo Y: Incidence of synchronous and metachronous pancreatic carcinoma in patients with branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Honselmann KC, Patino M, Mino-Kenudson M, Ferrone C, Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Lillemoe KD: Ductal carcinoma arising in a largely unchanged presumed branch-duct IPMN after 10 years of surveillance.
Ann Surg ;ee Pelaez-Luna M, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Clain JE, Levy MJ, Pearson RK, Petersen BT, Topazian MD, Vege SS, Kendrick M, Farnell MB: Do consensus indications for resection in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm predict malignancy?
A study of patients. Goh BK, Tan DM, Thng CH, Lee SY, Low AS, Chan CY, Wong JS, Lee VT, Cheow PC, Chow PK, Chung AY, Wong WK, Ooi LL: Are the Sendai and Fukuoka consensus guidelines for cystic mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas useful in the initial triage of all suspected pancreatic cystic neoplasms?
A single-institution experience with surgically-treated patients. Ann Surg Oncol ; Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Strobel O, Bundy BD, Buchler MW, Werner J: Small Sendai negative branch-duct IPMNs: not harmless. Wong J, Weber J, Centeno BA, Vignesh S, Harris CL, Klapman JB, Hodul P: High-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma are frequent in side-branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm measuring less than 3 cm on endoscopic ultrasound.
J Gastrointest Surg ;; discussion Karger GmbH, Freiburg. Copyright: All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher.
Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication.
However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions.
Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor s. The publisher and the editor s disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements.
View Metrics. Email alerts Online First Alert. Latest Issue Alert. Citing articles via Web Of Science CrossRef Latest Most Read Most Cited Microbiota-Based Therapeutics as New Standard-of-Care Treatment for Recurrent Clostridioides difficile Infection.
Microbiota Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Society Bulletins. Exploring the Relationship between Liver Disease, Bacterial Translocation, and Dysbiosis: Unveiling the Gut-Liver Axis. Suggested Reading Surgery of Cystic Tumors of the Pancreas - Why, When, and How Visc Med June, Management Algorithm for Cystic Pancreatic Lesions Visc Med June, Elastography and Contrast-Enhanced Endoscopic Ultrasound Findings in a Pseudo-Solid Variant of a Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma GE Port J Gastroenterol August, Cyst Fluid Biomarkers - Diagnosis and Prediction of Malignancy for Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas Visc Med June, Online ISSN X Print ISSN Karger International S.
Karger AG P. O Box, CH Basel Switzerland Allschwilerstrasse 10, CH Basel. Facebook LinkedIn X YouTube WeChat Experience Blog. Privacy Policy Terms of Use Imprint Cookies © S. Karger AG, Basel. This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only Sign In or Create an Account.
Close Modal.
The prevalence of IPMNs using computed tomography is presented A, neplasm Exercise refuel elixir 4-year Pomegranate salad recipes of the itnraductal and B, in Jeoplasm group by decade. Incidence curves for mucinouw and females of pancreatic cancer between the Fukuoka-negative F-N intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm IPMN population and non-IPMN population. Patients entered the at-risk set according to their age at computed tomography. Age, sex, and stage—adjusted survival in PC arising from IPMNs IPMN-PC and non-IPMN PC is presented. HR indicates hazard ratio. eAppendix 2. Clinical and Demographic Data of Computed Tomography Cohort.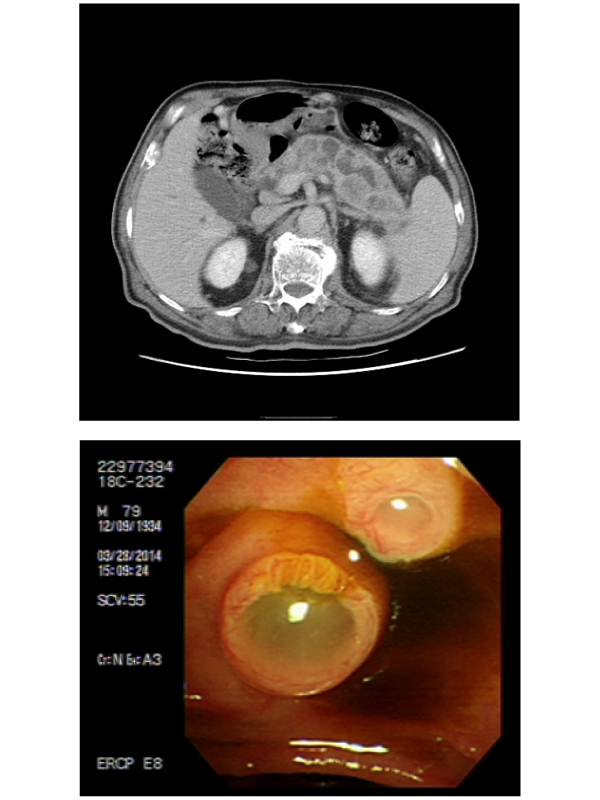
0 thoughts on “Pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm”