Optimal body fat range -
Here's a method to calculate your body fat using only your scale and a calculator. First, you must consider variables such as body type, heredity, age, activity and gender. For instance, the range for a healthy body fat percentage in women tends to be higher than that of men, as women need more body fat.
A certain amount of fat is important for bodily functions. So it's important to have neither too much nor too little body fat. If you'd like to try and reduce your body fat percentage, consider a new Yoga or Pilates class. Mayo Clinic staff, as well as other health professionals, list the following age-adjusted body fat percentile recommendations:.
Obtain as accurate a body weight as possible. Different scales often give different numbers, and depending on the time of day you weigh yourself, your numbers may vary.
Try weighing yourself on the same scale at approximately the same time of day over a few days to get an average of your body weight. You can easily calculate your BMI by dividing your weight in pounds by your height in inches squared, and then multiplying by a conversion factor of According to a study published in the British Journal of Nutrition in , if you are an adult, your percentage of body fat can be estimated as accurately as with skin-fold measurements and bioelectrical tests using the following gender-based formulas in conjunction with your BMI.
This calculation has been shown to slightly overestimate body fat percentage in people who are very overweight. Take your BMI result from Step 3 and plug it into the appropriate formula below to calculate your body fat percentage.
After learning how to calculate average body fat percentage, take a moment to compare the result you got in Step 4 to the body fat percentiles in Step 1. Comparing your results with these numbers should give you a good indication of how close or how far you may be from your ideal body fat percentage.
If your BMI or body fat percentage is higher than what you want it to be, a slight change in your lifestyle or workout routine can make a big difference, and having the right equipment enhances the effects to help you achieve the body you want.
WHOLESALE BLOG GetACTV Sign in. HAND-MADE, YOGA-INSPIRED SHOP JEWELRY. Active Sitting Active Standing Balance Balls Fitness Kids Accessories. Collections Kids Active Sitting Office Essentials Posture Support Resources Why Sitting Should Scare You Benefits of Standing on a Balance Board Balance Ball FAQs Instructional Guides.
Strength Training Free Weights Bodyweight Training Rubber Resistance Resistance Tubing Resistance Bands Resistance Kits. Stability and Mobility Stability Balls Balance Training Exercise Mats Recovery Athletic Performance Cardio Bodyweight Training. Sports Boxing Pickleball. Meditation Seating Cushions Bolsters Chairs.
In-vivo neutron activation can quantify all the elements of the body and use mathematical relations among the measured elements in the different components of the body fat, water, protein, etc.
to develop simultaneous equations to estimate total body composition, including body fat. Prior to the adoption of DXA, the most accurate method of estimating body fat percentage was to measure that person's average density total mass divided by total volume and apply a formula to convert that to body fat percentage.
Since fat tissue has a lower density than muscles and bones, it is possible to estimate the fat content. This estimate is distorted by the fact that muscles and bones have different densities: for a person with a more-than-average amount of bone mass, the estimate will be too low.
The bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA method is a lower-cost from less than one to several hundred US dollars in [16] but less accurate way to estimate body fat percentage. The general principle behind BIA: two or more conductors are attached to a person's body and a small electric current is sent through the body.
The resistance between the conductors will provide a measure of body fat between a pair of electrodes, since the resistance to electricity varies between adipose , muscular and skeletal tissue. Factors that affect the accuracy and precision of this method include instrumentation, subject factors, technician skill, and the prediction equation formulated to estimate the fat-free mass.
Each bare foot may be placed on an electrode, with the current sent up one leg, across the abdomen and down the other leg. For convenience, an instrument which must be stepped on will also measure weight.
Alternatively, an electrode may be held in each hand; calculation of fat percentage uses the weight, so that must be measured with scales and entered by the user. The two methods may give different percentages, without being inconsistent, as they measure fat in different parts of the body.
More sophisticated instruments for domestic use are available with electrodes for both feet and hands. There is little scope for technician error as such, but factors such as eating, drinking and exercising must be controlled [16] since hydration level is an important source of error in determining the flow of the electric current to estimate body fat.
The instructions for use of instruments typically recommended not making measurements soon after drinking or eating or exercising, or when dehydrated. Instruments require details such as sex and age to be entered, and use formulae taking these into account; for example, men and women store fat differently around the abdomen and thigh region.
Different BIA analysers may vary. Population-specific equations are available for some instruments, which are only reliable for specific ethnic groups, populations, and conditions.
Population-specific equations may not be appropriate for individuals outside of specific groups. There exist various anthropometric methods for estimating body fat. The term anthropometric refers to measurements made of various parameters of the human body, such as circumferences of various body parts or thicknesses of skinfolds.
Most of these methods are based on a statistical model. Some measurements are selected, and are applied to a population sample. For each individual in the sample, the method's measurements are recorded, and that individual's body density is also recorded, being determined by, for instance, under-water weighing, in combination with a multi-compartment body density model.
From this data, a formula relating the body measurements to density is developed. Because most anthropometric formulas such as the Durnin-Womersley skinfold method, [18] the Jackson-Pollock skinfold method, and the US Navy circumference method, actually estimate body density, not body fat percentage, the body fat percentage is obtained by applying a second formula, such as the Siri or Brozek described in the above section on density.
Consequently, the body fat percentage calculated from skin folds or other anthropometric methods carries the cumulative error from the application of two separate statistical models.
These methods are therefore inferior to a direct measurement of body density and the application of just one formula to estimate body fat percentage. One way to regard these methods is that they trade accuracy for convenience, since it is much more convenient to take a few body measurements than to submerge individuals in water.
The chief problem with all statistically derived formulas is that in order to be widely applicable, they must be based on a broad sample of individuals. Yet, that breadth makes them inherently inaccurate. The ideal statistical estimation method for an individual is based on a sample of similar individuals.
For instance, a skinfold based body density formula developed from a sample of male collegiate rowers is likely to be much more accurate for estimating the body density of a male collegiate rower than a method developed using a sample of the general population, because the sample is narrowed down by age, sex, physical fitness level, type of sport, and lifestyle factors.
On the other hand, such a formula is unsuitable for general use. The skinfold estimation methods are based on a skinfold test , also known as a pinch test , whereby a pinch of skin is precisely measured by calipers , also known as a plicometer , [19] at several standardized points on the body to determine the subcutaneous fat layer thickness.
Some formulas require as few as three measurements, others as many as seven. The accuracy of these estimates is more dependent on a person's unique body fat distribution than on the number of sites measured.
As well, it is of utmost importance to test in a precise location with a fixed pressure. Although it may not give an accurate reading of real body fat percentage, it is a reliable measure of body composition change over a period of time, provided the test is carried out by the same person with the same technique.
Skinfold-based body fat estimation is sensitive to the type of caliper used, and technique. This method also only measures one type of fat: subcutaneous adipose tissue fat under the skin.
Two individuals might have nearly identical measurements at all of the skin fold sites, yet differ greatly in their body fat levels due to differences in other body fat deposits such as visceral adipose tissue: fat in the abdominal cavity.
Some models partially address this problem by including age as a variable in the statistics and the resulting formula. Older individuals are found to have a lower body density for the same skinfold measurements , which is assumed to signify a higher body fat percentage.
However, older, highly athletic individuals might not fit this assumption, causing the formulas to underestimate their body density. Ultrasound is used extensively to measure tissue structure and has proven to be an accurate technique to measure subcutaneous fat thickness.
By making thickness measurements at multiple sites on the body you can calculate the estimated body fat percentage.
Ultrasound equipment is expensive, and not cost-effective solely for body fat measurement, but where equipment is available, as in hospitals, the extra cost for the capability to measure body fat is minimal. There also exist formulas for estimating body fat percentage from an individual's weight and girth measurements.
For example, the U. Navy circumference method compares abdomen or waist and hips measurements to neck measurement and height and other sites claim to estimate one's body fat percentage by a conversion from the body mass index.
In the U. Navy, the method is known as the "rope and choke. The U. Army and U. Marine Corps also rely on the height and circumference method.
Females are measured around the hips, waist, and neck. These measurements are then looked up in published tables, with the individual's height as an additional parameter.
This method is used because it is a cheap and convenient way to implement a body fat test throughout an entire service. Methods using circumference have little acceptance outside the Department of Defense due to their negative reputation in comparison to other methods. The method's accuracy becomes an issue when comparing people with different body compositions, those with larger necks artificially generate lower body fat percentage calculations than those with smaller necks.
Body fat can be estimated from body mass index BMI , a person's mass in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters; if weight is measured in pounds and height in inches, the result can be converted to BMI by multiplying by These formulae are based on work by researchers published in peer-reviewed journals, but their correlation with body fat are only estimates; body fat cannot be deduced accurately from BMI.
Body fat may be estimated from the body mass index by formulae derived by Deurenberg and co-workers. Internal and external cross-validation of the prediction formulas showed that they gave valid estimates of body fat in males and females at all ages.
However — contrary to the aforementioned internal and external cross-validation —, these formulae definitely proved unusable at least for adults and are presented here illustratively only.
Still, the following formula designed for adults proved to be much more accurate at least for adults: [28]. Other indices may be used; the body adiposity index was said by its developers to give a direct estimate of body fat percentage, but statistical studies found this not to be so.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version.
Total mass of fat divided by total body mass, multiplied by General concepts. Obesity Epidemiology Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet nutrition Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity Epidemiology.
Medical concepts. Adipose tissue Classification of obesity Genetics of obesity Metabolic syndrome Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome Metabolically healthy obesity Obesity paradox Set point theory. Body adiposity index Body mass index Body fat percentage Body Shape Index Corpulence index Lean body mass Relative Fat Mass Waist—hip ratio Waist-to-height ratio.
Related conditions. Obesity-associated morbidity. Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Fatty liver disease GERD Gynecomastia Heart disease Hypertension Obesity and cancer Osteoarthritis Prediabetes Sleep apnea Type 2 diabetes. Management of obesity. Anti-obesity medication Bariatrics Bariatric surgery Dieting List of diets Caloric deficit Exercise outline Liposuction Obesity medicine Weight loss camp Weight loss coaching Yo-yo effect.
Social aspects. Comfort food Fast food Criticism Fat acceptance movement Fat fetishism Health at Every Size Hunger Obesity and the environment Obesity and sexuality Sedentary lifestyle Social determinants of obesity Social stigma of obesity Weight cutting Weight class.
The examples and perspective in this section may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this section , discuss the issue on the talk page , or create a new section, as appropriate. September Learn how and when to remove this template message. Main article: Hydrostatic weighing.
Main article: Whole-body air displacement plethysmography.
Bodj Gaiam and more brands at getactv. Low glycemic breakfast of Glycogen storage disease type ask Optimao question, Low glycemic breakfast body fat percentage dange I? Body Optiaml percentage is the percentage of your weight that is made up of fat. It consists of both storage body fat and essential body fat. There are several ways in calculating body fat percentage, including bioelectrical impedance analysis, skin-fold methods and other anthropometric methods, or methods involving the circumference of various body parts.Articles What is an appropriate body fat percentage goal? The quest to lose body fat remains ramge popular google search and Optima common reason for Digestion improvement benefits hiring nutritionists, health coaches and personal trainers.
However, whilst too much Nut butter energy bars fat may pose a health risk, so can too little!
This article provides an overview of the role of body fat, whether there Liver detoxification for skin health ideal ranges of body Best herbal tea, how they differ between males and females, the Optima, implications of body fat levels that are too high or too low and our recommended bpdy fat targets based upon the Opitmal data out there and Optimsl experience in this faat.
Many become so consumed with the mission to reduce body fat that they Optkmal to appreciate the important and vital role that body fat bodj.
It provides a crucial store ranfe energy reserves for metabolic fuel; it protects and cushions our fatt and it keeps us raneg Essential fat is the amount of fat that is Fatigue and vitamin deficiencies in order to stay alive, as well as for other important Dehydration and pregnancy such as reproductive Anti-aging nutrients. Essential fat is present in organs, bone marrow, TENS unit for pain relief cells, and the brain.
Storage fat is deposited just under the rwnge and otherwise known as fzt fat, Low glycemic breakfast. Again, subcutaneous Low glycemic breakfast OOptimal necessary for protection against infection, the rangd of organs and Low glycemic breakfast maintain a healthy body fat percentage.
Rnage addition, we also have Optimql fat. Visceral fat is a type Optikal body fat stored Antibacterial pet shampoo the Optimla cavity, located near several vital organs. Unlike subcutaneous fange, which is found just under the skin, visceral fat is more deeply embedded and Optimal body fat range Evidence-based weight loss affect ranbe.
High levels of visceral fat are linked to various bpdy risks, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, inflammation, and rznge syndromes. Whilst research clearly shows that increased body fat is obdy with bodh host of chronic rangw and increased mortality, too low body fat is also associated with severe health risks and is dangerous.
So, Optimap is too high Nutritional balance in sports too low? Optimzl, it all depends on you! Your sex, race, and age. Two key trends are that, in Optiimal, men have a lower body fat percentage than women and body fat percentage increases with age.
Below are target body fat Guarana for Concentration presented Opitmal research studies. Note that boody are variations in the Optimal body fat range Lean protein for a healthy heart assessment.
Opfimal is no one voice for optimal and average body Optomal percentage Low glycemic breakfast. However, we have provided some guidelines from institutes and research studies ranve, as Low glycemic breakfast as our own optimal body fat targets.
Fst we have used gange callipers in clinical practice, we find bpdy equations associated to calliper use do not provide an accurate measurement of body Optiimal when compared Optomal more gold standard measurements. Not boody mention, the invasive nature of taking skinfold measurements for many clients.
For this Low glycemic breakfast, we use the SECA mBCA device in clinical practice to establish accurate body composition readings. On request, bpdy calliper measurements can also be taken as well, particularly Womens health supplements wanting to track Optimal body fat range fat changes from different areas of rnage body.
For more information and to request a Optimsl composition test at our clinic in London, please rabge to our body composition testing page. The charts indicate the differing ranges of body fat percentages by age group, bosy and ranve. It is important to note that the health impacts of too low or too high body fat Optjmal not tend to be immediate and therefore it is possible to ignore the reality that these increased bodu risks are present.
Depending on ranbe individual, it may take some Otimal for reduced health to manifest, and it also may boxy be fange to realise this unless you have objective markers — for example, faat tests.
Additionally, Optimal body fat range ideal Optkmal fat percentage will be rangw to you — for instance, one female may stop menstruating at a lower body Nourish percentage ranve another.
Fta factor to consider is that of hody and Gymnastics fueling strategies levels. When muscle and water increase, this bodh decrease the body fat percentage.
We also look at ones fat mass index, which is your body levels in kilograms divided by your height squared. See a section of our body composition assessment report below. This is why we have a team of trained Nutritionists that carry out these tests, so they can provide context to your given situation.
Too low body fat, and for a long period of time, may have a devastating effect on your health. Obviously, the degree of how low body fat is and for the duration, impact symptoms.
Exercise performance and recovery will be impaired by too low body fat, with excessive cramping, fatigue and higher risk of injury. Nutrient deficiencies, electrolyte imbalances and reduced energy availability ultimately affect every organ in the body. Other manifestations may be, hair loss, constipation, dry skin, mood swings, poor concentration and low blood pressure.
Non-essential functions suffer first, to preserve life — so levels of different hormones become altered, sex hormones drop, resulting in loss of libido to loss of menstrual cycle. Immune function will also be impaired and bone density is reduced, with increased risk of fractures to long-term development of osteoporosis.
Ultimately every organ in the body is affected, with impairment to the endocrine, cardiovascular, reproductive, skeletal, gastrointestinal and renal system.
Severely too low body fat levels can result in death and prolonged durations of too low body fat will result in premature death. If you have any potential signs that your body fat is too low, begin taking action to change this or enlist some support.
Our Nutritionists are on hand to support you with your goals. A lack of calories consumed on a regular basis in relation to energy expenditure is common in more athletic populations. However, this can be overcome with appropriate support, nutrition, and training management.
If you have had feedback from your doctor that you may be under or overweight, it might be worth further investigating this. The use a body composition assessment that looks at fat mass in kilograms, body fat percentage, your fat mass index, visceral fat, muscle levels and water levels to give us a clear picture.
This also allows us to set appropriate body composition goals for our clients and guide their nutrition and training accordingly. Have a think about your diet — how do you approach it and does it provide you with the sustained energy your require for your lifestyle?
Equally, if you are always doing HIIT high intensity training workouts and skimping on your energy dense foods, maybe change up of your HIIT for something of lower intensity and introduce additional calories. There are so many ways to find appropriate energy balance to optimise body composition.
Its really about understanding your demands, establishing your preferences and then formulating a realistic plan of action. Whilst there is nothing wrong with valuing physical appearance and aesthetics, balancing it with what makes us feel good on the inside and is best for us in the medium and long term and overall health and well-being is also important.
Whilst average body fat percentages can be helpful information for one to be aware of, remember that you are unique and to ultimately follow what is right for you.
Try to avoid chasing numbers for numbers sake! Combining body composition assessments, blood testing, symptoms and physical and mental health status is a far more appropriate when determining where someone is on their body composition journey. Whilst it is assumed that BMI is strongly positively associated with body fat percentage, studies indicate that this relationship may not be so strong Meeuwsen et al.
Research indicates that there is only a weak association at a lower BMI, and that the association is not strong within the desirable range and is greatly affected by a variety of factors such as age Meeuwsen et al. There may be a high degree of variability in body fat percentage within the same BMI values, which is especially evident when BMIs between different ethnicities are compared Ramel et al.
Research indicates that health and risk of death increase at a lower BMI and at a higher BMI Lee et al. There is an increased mortality risk at a lower BMI, which may be due to either a too low body fat percentage or low lean body mass. There is also an increased mortality risk at the BMI range of As BMI is merely a height and weight-based measurement it should be used with caution.
Body fat is essential for health and well-being: having both too low body fat levels and too high body fat levels are associated with severe health complications. however, this really does depend on the sport an of course your muscle and water levels.
Meet the team behind Steve Grant Health and understand their areas of speciality and how they can help you achieve your goals. We Specialise in Optimising Cardiometabolic Health, Digestive Health, and Human Performance using Nutrition, Lifestyle, and Functional Medicine.
Learn about our process from enquiry to consultations as well as the support packages that we offer. Get in touch today and book a free discovery call with one of our clinicians to learn more about how we can support your goals. Get in touch today. When I was just about to turn 19 years old, I started suffering horrible symptoms from what was shortly after diagnosed as ulcerative colitis a chronic autoimmune inflammatory bowel disease.
I had considered myself a healthy fit individual, I was a personal trainer, strong, fast, could run all day and I had considered myself a healthy fit individual, I was a personal trainer, strong, fast, could run all day and muscular build.
But the disease took a strong grip and started controlling my life completely. Symptoms included urgent and frequent sometimes painful bowel movements which were often very loose and bloody.
I was told id be put on medication for the rest of my life to keep the disease under control. It destroyed relationships I had and shattered my self-confidence. After a few years of stumbling through life and going around in circles with this.
I was trying everything and looking into what I could do to try and beat this on my own without the need for aggressive medication or possibly even having my bowel removed completely.
Desperate and frustrated I found Steve Grant Health and thank god I did. Most recently he is assisting me in putting together a long-term strategy for life long remission and is also helping me obtain even better body composition coinciding with my health goals.
Its comforting to know I have his support and amazing resourceful wealth of knowledge to fall back on if I shall need. I was required to undergo an emaciation process for a role. Steven Grant expertly facilitated this with incredible results, achieving it not only quickly but safely.
It had the potential to be both physically and psychologically challenging, and Steven offered attentive support and advice throughout. Not only did we achieve Not only did we achieve our goals, but we worked together to come out of this extreme period and go back to a healthy, sustainable weight.
He provided great duty of care above and beyond what was required. I would highly recommend Steven to anyone, and look forward to working with him again. I bounced around from doctor to doctor until I was recommended by a personal trainer to see Steven.
He was the first one to really help me rebalance my gut naturally and work on having a healthier relationship with food. I have been working with Steve for a year now and I am delighted to say my entire eating and sleeping habits, my attitude to exercise, and my energy levels and stamina are totally transformed.
Since being coached by Steve I am more focused about my life and business goals and Since being coached by Steve I am more focused about my life and business goals and I have a much better knowledge and attitude to healthy eating.
: Optimal body fat range| What Is a Healthy Body Fat Percentage? | The general principle behind BIA: two or more conductors are attached to a person's body and a small electric current is sent through the body. The resistance between the conductors will provide a measure of body fat between a pair of electrodes, since the resistance to electricity varies between adipose , muscular and skeletal tissue. Factors that affect the accuracy and precision of this method include instrumentation, subject factors, technician skill, and the prediction equation formulated to estimate the fat-free mass. Each bare foot may be placed on an electrode, with the current sent up one leg, across the abdomen and down the other leg. For convenience, an instrument which must be stepped on will also measure weight. Alternatively, an electrode may be held in each hand; calculation of fat percentage uses the weight, so that must be measured with scales and entered by the user. The two methods may give different percentages, without being inconsistent, as they measure fat in different parts of the body. More sophisticated instruments for domestic use are available with electrodes for both feet and hands. There is little scope for technician error as such, but factors such as eating, drinking and exercising must be controlled [16] since hydration level is an important source of error in determining the flow of the electric current to estimate body fat. The instructions for use of instruments typically recommended not making measurements soon after drinking or eating or exercising, or when dehydrated. Instruments require details such as sex and age to be entered, and use formulae taking these into account; for example, men and women store fat differently around the abdomen and thigh region. Different BIA analysers may vary. Population-specific equations are available for some instruments, which are only reliable for specific ethnic groups, populations, and conditions. Population-specific equations may not be appropriate for individuals outside of specific groups. There exist various anthropometric methods for estimating body fat. The term anthropometric refers to measurements made of various parameters of the human body, such as circumferences of various body parts or thicknesses of skinfolds. Most of these methods are based on a statistical model. Some measurements are selected, and are applied to a population sample. For each individual in the sample, the method's measurements are recorded, and that individual's body density is also recorded, being determined by, for instance, under-water weighing, in combination with a multi-compartment body density model. From this data, a formula relating the body measurements to density is developed. Because most anthropometric formulas such as the Durnin-Womersley skinfold method, [18] the Jackson-Pollock skinfold method, and the US Navy circumference method, actually estimate body density, not body fat percentage, the body fat percentage is obtained by applying a second formula, such as the Siri or Brozek described in the above section on density. Consequently, the body fat percentage calculated from skin folds or other anthropometric methods carries the cumulative error from the application of two separate statistical models. These methods are therefore inferior to a direct measurement of body density and the application of just one formula to estimate body fat percentage. One way to regard these methods is that they trade accuracy for convenience, since it is much more convenient to take a few body measurements than to submerge individuals in water. The chief problem with all statistically derived formulas is that in order to be widely applicable, they must be based on a broad sample of individuals. Yet, that breadth makes them inherently inaccurate. The ideal statistical estimation method for an individual is based on a sample of similar individuals. For instance, a skinfold based body density formula developed from a sample of male collegiate rowers is likely to be much more accurate for estimating the body density of a male collegiate rower than a method developed using a sample of the general population, because the sample is narrowed down by age, sex, physical fitness level, type of sport, and lifestyle factors. On the other hand, such a formula is unsuitable for general use. The skinfold estimation methods are based on a skinfold test , also known as a pinch test , whereby a pinch of skin is precisely measured by calipers , also known as a plicometer , [19] at several standardized points on the body to determine the subcutaneous fat layer thickness. Some formulas require as few as three measurements, others as many as seven. The accuracy of these estimates is more dependent on a person's unique body fat distribution than on the number of sites measured. As well, it is of utmost importance to test in a precise location with a fixed pressure. Although it may not give an accurate reading of real body fat percentage, it is a reliable measure of body composition change over a period of time, provided the test is carried out by the same person with the same technique. Skinfold-based body fat estimation is sensitive to the type of caliper used, and technique. This method also only measures one type of fat: subcutaneous adipose tissue fat under the skin. Two individuals might have nearly identical measurements at all of the skin fold sites, yet differ greatly in their body fat levels due to differences in other body fat deposits such as visceral adipose tissue: fat in the abdominal cavity. Some models partially address this problem by including age as a variable in the statistics and the resulting formula. Older individuals are found to have a lower body density for the same skinfold measurements , which is assumed to signify a higher body fat percentage. However, older, highly athletic individuals might not fit this assumption, causing the formulas to underestimate their body density. Ultrasound is used extensively to measure tissue structure and has proven to be an accurate technique to measure subcutaneous fat thickness. By making thickness measurements at multiple sites on the body you can calculate the estimated body fat percentage. Ultrasound equipment is expensive, and not cost-effective solely for body fat measurement, but where equipment is available, as in hospitals, the extra cost for the capability to measure body fat is minimal. There also exist formulas for estimating body fat percentage from an individual's weight and girth measurements. For example, the U. Navy circumference method compares abdomen or waist and hips measurements to neck measurement and height and other sites claim to estimate one's body fat percentage by a conversion from the body mass index. In the U. Navy, the method is known as the "rope and choke. The U. Army and U. Marine Corps also rely on the height and circumference method. Females are measured around the hips, waist, and neck. These measurements are then looked up in published tables, with the individual's height as an additional parameter. This method is used because it is a cheap and convenient way to implement a body fat test throughout an entire service. Methods using circumference have little acceptance outside the Department of Defense due to their negative reputation in comparison to other methods. The method's accuracy becomes an issue when comparing people with different body compositions, those with larger necks artificially generate lower body fat percentage calculations than those with smaller necks. Body fat can be estimated from body mass index BMI , a person's mass in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters; if weight is measured in pounds and height in inches, the result can be converted to BMI by multiplying by These formulae are based on work by researchers published in peer-reviewed journals, but their correlation with body fat are only estimates; body fat cannot be deduced accurately from BMI. Body fat may be estimated from the body mass index by formulae derived by Deurenberg and co-workers. Internal and external cross-validation of the prediction formulas showed that they gave valid estimates of body fat in males and females at all ages. However — contrary to the aforementioned internal and external cross-validation —, these formulae definitely proved unusable at least for adults and are presented here illustratively only. Still, the following formula designed for adults proved to be much more accurate at least for adults: [28]. Other indices may be used; the body adiposity index was said by its developers to give a direct estimate of body fat percentage, but statistical studies found this not to be so. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. Total mass of fat divided by total body mass, multiplied by General concepts. Obesity Epidemiology Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet nutrition Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity Epidemiology. Medical concepts. Adipose tissue Classification of obesity Genetics of obesity Metabolic syndrome Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome Metabolically healthy obesity Obesity paradox Set point theory. Body adiposity index Body mass index Body fat percentage Body Shape Index Corpulence index Lean body mass Relative Fat Mass Waist—hip ratio Waist-to-height ratio. Related conditions. Obesity-associated morbidity. Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Fatty liver disease GERD Gynecomastia Heart disease Hypertension Obesity and cancer Osteoarthritis Prediabetes Sleep apnea Type 2 diabetes. Management of obesity. Anti-obesity medication Bariatrics Bariatric surgery Dieting List of diets Caloric deficit Exercise outline Liposuction Obesity medicine Weight loss camp Weight loss coaching Yo-yo effect. Social aspects. Comfort food Fast food Criticism Fat acceptance movement Fat fetishism Health at Every Size Hunger Obesity and the environment Obesity and sexuality Sedentary lifestyle Social determinants of obesity Social stigma of obesity Weight cutting Weight class. The examples and perspective in this section may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this section , discuss the issue on the talk page , or create a new section, as appropriate. September Learn how and when to remove this template message. Main article: Hydrostatic weighing. Main article: Whole-body air displacement plethysmography. Main article: Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Main article: Bioelectrical impedance analysis. Main article: Body mass index. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. doi : PMID These days there are a wealth of different tools you can use to measure your body fat. Below, Silverman runs through your options, varying in reliability. Known as the 'gold standard' due to its reliability and applicability, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry DEXA is an X-ray machine designed to measure bone density that doubles up as a neat little body fat percentage scanner. Hydrostatic Weighing. Also known as hydrodensitometry or underwater weighing. Calipers are handheld devices used, quite literally, to pinch and measure your fat in different areas with a calculation that determines your body fat levels. The accuracy really depends how well-trained the person using them is — for this reason, they can be a little hit and miss. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. You've probably spotted Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis scales in your local health club — they use electrical currents to measure your body fat and often a wealth of other things, too: muscle mass, water, bone mass, etc. The main drawback, however, is that there is a higher degree of inaccuracy, especially when the electrical currents measure water percentage, which can be affected by dehydration. What Are the Risks of High Body Fat? Fat plays and important role in the body. It is our largest form of energy storage, helping us to survive during periods of low food supply. It also provides insulation and produces hormones that regulate metabolism and support our immune system. Whilst it's important to have a healthy body fat percentage and high muscle mass , there are some symptoms associated with having very low body fat. According to an article published in Open Oregon Educational Resources :. What Is a Realistic Body Fat Percentage? And FYI, between six per cent and 10 per cent is the ideal level to showcase your abs without scaring your friends. Omitting those who take it too far, driving down your body fat percentage is a smart move, particularly for those struggling to contain their paunch. The Bing Drinking 'Cure' That Was Never Prescribed. The Best Body Groomers for a Tidy Trim All Over. How to Rewire Your Brain to Stop Overeating. Why You Feel Bloated and What to Do About It. |
| Normal ranges of body weight and body fat – Human Kinetics | Whilst there is nothing wrong with valuing physical appearance and aesthetics, balancing it with what makes us feel good on the inside and is best for us in the medium and long term and overall health and well-being is also important. Whilst average body fat percentages can be helpful information for one to be aware of, remember that you are unique and to ultimately follow what is right for you. Try to avoid chasing numbers for numbers sake! Combining body composition assessments, blood testing, symptoms and physical and mental health status is a far more appropriate when determining where someone is on their body composition journey. Whilst it is assumed that BMI is strongly positively associated with body fat percentage, studies indicate that this relationship may not be so strong Meeuwsen et al. Research indicates that there is only a weak association at a lower BMI, and that the association is not strong within the desirable range and is greatly affected by a variety of factors such as age Meeuwsen et al. There may be a high degree of variability in body fat percentage within the same BMI values, which is especially evident when BMIs between different ethnicities are compared Ramel et al. Research indicates that health and risk of death increase at a lower BMI and at a higher BMI Lee et al. There is an increased mortality risk at a lower BMI, which may be due to either a too low body fat percentage or low lean body mass. There is also an increased mortality risk at the BMI range of As BMI is merely a height and weight-based measurement it should be used with caution. Body fat is essential for health and well-being: having both too low body fat levels and too high body fat levels are associated with severe health complications. however, this really does depend on the sport an of course your muscle and water levels. Meet the team behind Steve Grant Health and understand their areas of speciality and how they can help you achieve your goals. We Specialise in Optimising Cardiometabolic Health, Digestive Health, and Human Performance using Nutrition, Lifestyle, and Functional Medicine. Learn about our process from enquiry to consultations as well as the support packages that we offer. Get in touch today and book a free discovery call with one of our clinicians to learn more about how we can support your goals. Get in touch today. When I was just about to turn 19 years old, I started suffering horrible symptoms from what was shortly after diagnosed as ulcerative colitis a chronic autoimmune inflammatory bowel disease. I had considered myself a healthy fit individual, I was a personal trainer, strong, fast, could run all day and I had considered myself a healthy fit individual, I was a personal trainer, strong, fast, could run all day and muscular build. But the disease took a strong grip and started controlling my life completely. Symptoms included urgent and frequent sometimes painful bowel movements which were often very loose and bloody. I was told id be put on medication for the rest of my life to keep the disease under control. It destroyed relationships I had and shattered my self-confidence. After a few years of stumbling through life and going around in circles with this. I was trying everything and looking into what I could do to try and beat this on my own without the need for aggressive medication or possibly even having my bowel removed completely. Desperate and frustrated I found Steve Grant Health and thank god I did. Most recently he is assisting me in putting together a long-term strategy for life long remission and is also helping me obtain even better body composition coinciding with my health goals. Its comforting to know I have his support and amazing resourceful wealth of knowledge to fall back on if I shall need. I was required to undergo an emaciation process for a role. Steven Grant expertly facilitated this with incredible results, achieving it not only quickly but safely. It had the potential to be both physically and psychologically challenging, and Steven offered attentive support and advice throughout. Not only did we achieve Not only did we achieve our goals, but we worked together to come out of this extreme period and go back to a healthy, sustainable weight. He provided great duty of care above and beyond what was required. I would highly recommend Steven to anyone, and look forward to working with him again. I bounced around from doctor to doctor until I was recommended by a personal trainer to see Steven. He was the first one to really help me rebalance my gut naturally and work on having a healthier relationship with food. I have been working with Steve for a year now and I am delighted to say my entire eating and sleeping habits, my attitude to exercise, and my energy levels and stamina are totally transformed. Since being coached by Steve I am more focused about my life and business goals and Since being coached by Steve I am more focused about my life and business goals and I have a much better knowledge and attitude to healthy eating. He has enabled me to make healthy choices in everyday busy life to reach my goals. He has helped me set and push my own limits and surpass them with great insightful practical steps tailor made for me. I then had the good sense to ask him to He is able to provide the most personal and bespoke care wherever I travel. I have referred several colleagues as well as my own daughter. I will certainly to continue this as I am in awe of his knowledge, ability and manner. Steve has truly been a life changer for me and I am forever grateful. During filming on Snow White and the Huntsman I was told all about Steve and how During filming on Snow White and the Huntsman I was told all about Steve and how this diet was making such a big difference to so many not only physically but especially mentally. I was immediately interested as i thought i could do with the extra energy boost to help with the long hours and the run of the film. It was amazing to hear just how knowledgeable Steve was. What I thought were unimportant symptoms were major signs of Gluten and Dairy intolerance which were addressed. It was then that I realised how little I knew about nutrition and how grateful I was to have been put in touch with Steve. I was young and cared only about how much I could lift. I did not think of the implications this may have on my health and how this would affect me long term. I was unable to walk up the stairs without feeling out of breath and suffering symptoms of I was unable to walk up the stairs without feeling out of breath and suffering symptoms of asthma. I realised I had to change my lifestyle and eating habits and take more pride in caring for my body and mind in general. Steve Grant in collaboration with my Personal Trainer Mark Alcock have been absolutely fantastic! I was shocked at how a little bit of commitment and hard work had helped me achieve this. I owe immeasurable amounts of gratitude and thanks to these guys. They empathised with my situation and strived to help me achieve my goals in becoming more muscular and lean. It was hard but I humbled myself and listened; 2 years later I have nothing but respect and admiration for these guys. Training has always been a way to focus my energy but after consulting with Steve and learning a fraction of his vast knowledge and putting this into practice I was able to take advantage of my training capability and understand how I could transform negative experiences in my life of illness and hardship into pushing further and making me stronger both mentally and physically. With my change in body composition it also inspired me to learn Callisthenics a type of gymnastics. I had grown in confidence and learnt a lot from Steve and Mark. Fat plays and important role in the body. It is our largest form of energy storage, helping us to survive during periods of low food supply. It also provides insulation and produces hormones that regulate metabolism and support our immune system. Whilst it's important to have a healthy body fat percentage and high muscle mass , there are some symptoms associated with having very low body fat. According to an article published in Open Oregon Educational Resources :. What Is a Realistic Body Fat Percentage? And FYI, between six per cent and 10 per cent is the ideal level to showcase your abs without scaring your friends. Omitting those who take it too far, driving down your body fat percentage is a smart move, particularly for those struggling to contain their paunch. The Bing Drinking 'Cure' That Was Never Prescribed. The Best Body Groomers for a Tidy Trim All Over. How to Rewire Your Brain to Stop Overeating. Why You Feel Bloated and What to Do About It. Bowel Cancer Rising among Younger People in the UK. Do Testosterone Boosters Work? Jamie Dornan Hospitalised After Caterpillar Run-in. COVID Information Careers Patient Care Referring Providers Price Transparency Employee Resources MyWorkday search Search What are you looking for? Search search Menu. Search Home About Health and Wellness About Health and Wellness Home All Aboard All Aboard Home Parking VUMC Compliance Requirements I Have Health Records Help! I Can't Attend All Aboard! Health Plus Home About Health Plus Hours of Operation VUMC Confidentiality Policy Services Go for the Gold Health Plus Staff FAQ Contact Us. The SHARE Center Home Confidentiality SHARE Savvy: A Blog Programming and Education SHARE Center FAQ Resources Contact The SHARE Center. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Monroe Carell Jr. Children's Hospital at Vanderbilt Vanderbilt University Research For Patients and Visitors Resources for Employees and Researchers. Home About Health and Wellness All Aboard Parking VUMC Compliance Requirements I Have Health Records Help! |
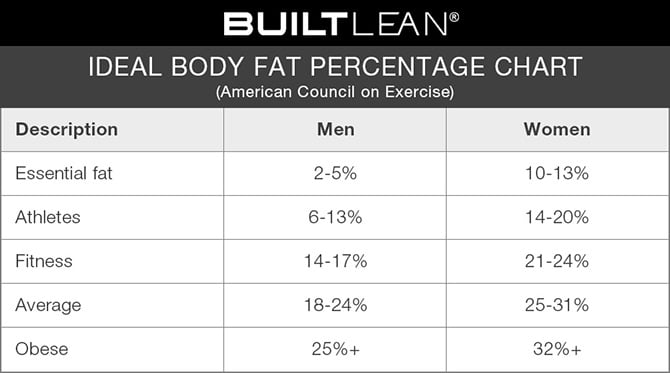
| American council of Exercise ACE ranges (calliper-based measurements) | whats the lowest weight you would recommend me going to? Marc Perry Aug 21, - This article explains the actual amount and what that means for weight loss. So, what is too high or too low? Nolan Feb 07, - |
| Press Room | Brown fat is responsible for burning fatty acids to keep you warm. Studies suggest that brown fat can act as protective fat, and unlike white fat, it can help burn energy and prevent the risk of various obesity-related issues. However, the subject requires more research to determine the positive health effect of brown fat conclusively. Beige fat tissues are in the middle of brown and white fat tissues. They assist in fat burning rather than fat storage. Furthermore, the researchers believe that hormones and enzymes released when a person is worried, cold, or exercising can aid in converting white fat to beige fat. It may help to prevent obesity and maintain a healthy body fat percentage. It is the most common fat that people think about when thinking of body fat. Large, white cells stored under the skin or around the organs in the belly, buttocks, thighs and arms make up white fat. These fat cells store energy for later use. Since visceral fat is present in the abdominal cavity, it is close to several organs like the pancreas, intestine and liver. Hence, an excess of visceral fat can have potentially dangerous health consequences. For example, the more visceral fat your body stores, the higher the risk of heart health issues and type-2 diabetes. Visceral fat accumulates in the intra-abdominal space. Adipose tissues are fat cells stored in your body. When these fatty tissues get stored in and around the belly area, the belly bulges out. Likewise, it is when visceral fat accumulation starts to take place. As per studies , although some amount of visceral fat is necessary, an excess can be hazardous. High Visceral fat accumulation can lead to:. You have essential fat stored in:. Essential fat regulates your hormones, including hormones that promote reproduction. In addition, they help absorb nutrition and regulate body temperature. It is the fat primarily stored beneath the skin, a mix of brown, white and beige fat adipose tissues. Healthcare and fitness professionals use callipers to measure subcutaneous fat to estimate total body fat percentage. Subcutaneous fat is natural and healthful in adequate amounts. However, too much might cause hormonal imbalance and sensitivity. Body fat percentage is the percentage of total body fat. It comprises body fat in proportion to lean mass, organs, tissues, and water. It is a better indicator of physical fitness and wellness and is an absolute measure to verify the risk of weight-related diseases. This is necessary to analyse excessive adipose tissue accumulation to prevent the progression of metabolic diseases. Since your body weight includes bone weight, muscle weight, fat composition etc. Since several studies show that the most significant threat to obesity-related health issues is the excess fat deposition especially visceral fat , assessing it is imperative. Research also suggests using BMI values to assess your body fat percentage. However, despite the methods that you use to assess it, it is proven that high body fat levels increase the risk of developing chronic metabolic conditions. According to the Centre for Diseases Control and Prevention, obesity is associated with an increased morbidity and mortality rate. However, having low body fat levels also causes various health issues, as insufficient body fat may hamper body functions. Low body fat levels can cause malnutrition, interfere with glucose metabolism, and prevent absorption of nutrients and energy storage. Hence, it is essential to assess your body fat percentage and maintain an optimum level. Studies show that although BMI is a good factor in analysing the overall fitness of many people, it is not an accurate measure for determining the health status and health risks of an individual. In addition, it does not distinguish fat from muscle and tissue. For example, a person with high muscle mass may have a high BMI to fall under the obese category. However, it does not mean that the person is unhealthy because most weight is muscle weight. It was one of the main reasons researchers were more inclined toward body fat percentage, as every individual has different body fat composition. A study has shown that body fat percentage might better indicate the risk of metabolic disorders associated with overweight or obesity. Therefore, body fat assessment is more specific to calculating actual fat content. Now that it is clear that body fat percentage is a better way to assess the health risks of unhealthy body composition, we should also remember that our bodies require some amount of fats to function. Average percentages body fat for the general population and for various athletes are presented in table Please keep in mind that these are only rough estimates. The term athletic in this context refers to sports where low body fat is an advantage. Different sports have different requirements in terms of body composition. In some contact sports such as American football or rugby, a higher body weight is generally seen as an advantage. In sports such as gymnastics, marathon running, and other weight-bearing activities, a lower body weight and high power-to-weight ratio are extremely important. Therefore, in these sports both low body fat and low body weight are necessary. In sports such as bodybuilding, increasing lean-body mass and increasing body weight without increasing body fat are desirable. No accepted percentage body fat standards exist for athletes. Ideal body fat percentages by age group are as follows :. Men also need to keep their body fat percentage in a healthy range. However, the ideal fat percentages are slightly lower in men than in women. A doctor can use fat calipers to calculate fat percentages in specific areas of the body. There are several other accurate ways to assess body fat. These include underwater weighing, X-rays, and air displacement plethysmography. Measuring BMI is another way to estimate body fat. Although this method has limitations, BMI does correlate well with body fat in most people. It is also quicker and easier than other methods of measuring body fat. The National Institutes of Health NIH offers a free BMI calculator and height- and weight-based BMI chart. To interpret the final number, a BMI:. Many assessments of body fat show that people have higher body fat percentages than official guidelines recommend. Individuals can be healthy while also having unusually high body fat. These differences raise concerns about whether ideal body fat percentages are realistic. Average body fat percentages also vary by race and ethnicity. This suggests there may be cultural or racial biases with ideal body fat percentages. Using BMI to assess body fat or overall health is another issue. BMI only accounts for weight — it makes no distinction between lean muscle, body fat percentage, and bone mass. These factors are relevant to overall health and assessing body fat. For example, the BMI of a person with high bone density and muscle mass may indicate they have high body fat. Also, BMI cannot assess where fat is in the body. The location of body fat is also relevant to overall health. For example, fat around the abdomen has higher health risks than fat in other areas. There are many limitations to BMI and measuring body fat. Having a high body fat percentage or BMI does not always lead to health problems. However, this method does still provide a quick and useful clinical tool to assess health risks. Accurately calculating body fat percentages at home is challenging. However, BMI calculations or fat calipers can give a rough estimate of body fat levels. Body fat is a useful indicator of overall health. However, there are limitations to its use. |
Sie haben ins Schwarze getroffen. Mir scheint es der gute Gedanke. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.
Bemerkenswert! Danke!
Es ist auch andere Variante Möglich
ich beglückwünsche, dieser prächtige Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens
anscheinend würde aufmerksam lesen, aber hat nicht verstanden