
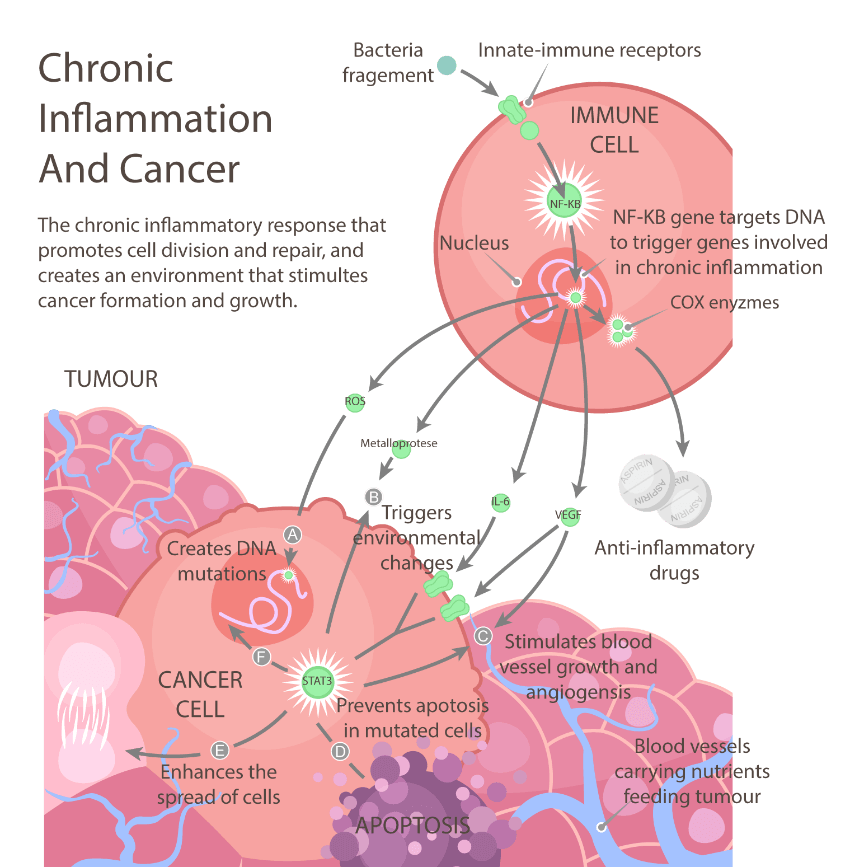
Inflammation and cancer risk -
Our skin constitutes the first line of defence against microscopic invaders. But whenever this barrier is breached, the wrath of the immune system is unleashed — and things get ugly. This highly trained militia gets to work immediately, showering intruders with toxic chemicals, punching holes in their surface or swallowing them whole.
As the enemy is eaten and beaten into surrender, signals urge victorious immune cells to return to base camp. Repair and recovery teams move in to direct the process of healing. Blood vessels sprout. A scab forms. Skin grows. While we might not be able to live without it, too much inflammation can cause serious damage.
Chronic, persistent inflammation is behind a host of health problems such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
And after finding immune cells in tumour samples, Rudolf Virchow was the first to ask whether inflammation might also contribute to cancer. And cancers caused by infectious agents like stomach cancer caused by infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori, or liver cancer caused by infection with the hepatitis B or C virus are characterised by one thing: chronic inflammation.
In the case against inflammation, the evidence is damning. Rudolf Virchow was the first to link inflammation and cancer. When a tiny tumour starts growing from a few rogue cells, it can scavenge enough oxygen and nutrients from its surroundings.
But as it grows bigger, demand starts to outstrip supply, and things start getting desperate. As they struggle to survive, and as they accumulate more and more genetic faults, the cancer cells release chemical signals that lure immune cells called macrophages and granulocytes to infiltrate the tumour.
Meanwhile, other inflammatory cells spritz the tumour with molecules free radicals that further damage their DNA. Inflammation might also fire the starting gun for metastasis by producing chemicals that help tumour cells nibble through the molecules tethering them to their surroundings.
Thanan R, Pairojkul C, Pinlaor S, Khuntikeo N, Wongkham C, Sripa B, et al. Free Radic Biol Med. Thanan R, Techasen A, Hou B, Jamnongkan W, Armartmuntree N, Yongvanit P, et al.
Development and characterization of a hydrogen peroxide-resistant cholangiocyte cell line: a novel model of oxidative stress-related cholangiocarcinoma genesis.
Armartmuntree N, Murata M, Techasen A, Yongvanit P, Loilome W, Namwat N, et al. Prolonged oxidative stress down-regulates early B cell factor 1 with inhibition of its tumor suppressive function against cholangiocarcinoma genesis. Redox Biol. Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, Chan ATC.
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Article Google Scholar. Wang S, Ma N, Zhao W, Midorikawa K, Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, et al.
Inflammation-related DNA damage and cancer stem cell markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Wang S, Ma N, Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Xie Y, et al. Relationships of alpha-SMA-positive fibroblasts and SDFpositive tumor cells with neoangiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Biomed Res Int. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, et al. Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol.
Nakamura A, Goto S. Analysis of protein carbonyls with 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine and its antibodies by immunoblot in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. Oikawa S, Kobayashi H, Kitamura Y, Zhu H, Obata K, Minabe Y, et al. Proteomic analysis of carbonylated proteins in the monkey substantia nigra after ischemia-reperfusion.
Free Radic Res. Thanan R, Oikawa S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Pinlaor S, et al. Inflammation-induced protein carbonylation contributes to poor prognosis for cholangiocarcinoma. Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P, Nair J, Bartsch H, Yongvanit P. Lipid peroxidation and etheno DNA adducts in white blood cells of liver fluke-infected patients: protection by plasma alpha-tocopherol and praziquantel.
Thanan R, Oikawa S, Hiraku Y, Ohnishi S, Ma N, Pinlaor S, et al. Oxidative stress and its significant roles in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Int J Mol Sci. Wolffe AP, Matzke MA. Epigenetics: regulation through repression. Wilson AG. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression in the inflammatory response and relevance to common diseases.
J Periodontol. Rokavec M, Oner MG, Hermeking H. Inflammation-induced epigenetic switches in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. Pfeifer GP. Defining driver DNA methylation changes in human cancer. Mo Y, Midorikawa K, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Ma N, Huang G, et al.
Promoter hypermethylation of Ras-related GTPase gene RRAD inactivates a tumor suppressor function in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. Zhao W, Ma N, Wang S, Mo Y, Zhang Z, Huang G, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. Maeda M, Moro H, Ushijima T. Mechanisms for the induction of gastric cancer by Helicobacter pylori infection: aberrant DNA methylation pathway.
Gastric Cancer. Matsusaka K, Funata S, Fukayama M, Kaneda A. DNA methylation in gastric cancer, related to Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus. Emmett RA, Davidson KL, Gould NJ, Arasaradnam RP. DNA methylation patterns in ulcerative colitis-associated cancer: a systematic review.
Laird PW. Principles and challenges of genomewide DNA methylation analysis. Nat Rev Genet. Wang S, Xiao X, Zhou X, Huang T, Du C, Yu N, et al. TFPI-2 is a putative tumor suppressor gene frequently inactivated by promoter hypermethylation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
BMC Cancer. Zhao W, Mo Y, Wang S, Midorikawa K, Ma N, Hiraku Y, et al. Quantitation of DNA methylation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma by bisulfite amplicon sequencing.
Pabinger S, Ernst K, Pulverer W, Kallmeyer R, Valdes AM, Metrustry S, et al. Analysis and visualization tool for targeted amplicon bisulfite sequencing on ion torrent sequencers. PLoS One. The BLUEPRINT consortium. Quantitative comparison of DNA methylation assays for biomarker development and clinical applications.
Nat Biotechnol. Wang S, Mo Y, Midorikawa K, Zhang Z, Huang G, Ma N, et al. The potent tumor suppressor miR inhibits cancer phenotypes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting ANLN and HSPA4L.
Hou B, Ishinaga H, Midorikawa K, Nakamura S, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, et al. Let-7c inhibits migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting IGF1R and HMGA2.
Hou B, Ishinaga H, Midorikawa K, Shah SA, Nakamura S, Hiraku Y, et al. Circulating microRNAs as novel prognosis biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Biol Ther. Siravegna G, Marsoni S, Siena S, Bardelli A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P, Amor S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases.
Becatti M, Mannucci A, Taddei N, Fiorillo C. Oxidative stress and inflammation: new molecular targets for cardiovascular diseases. Intern Emerg Med. Turkmen K. Inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and autophagy in diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney disease: the Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse.
Int Urol Nephrol. Oikawa S, Yamada T, Minohata T, Kobayashi H, Furukawa A, Tada-Oikawa S, et al. Proteomic identification of carbonylated proteins in the monkey hippocampus after ischemia-reperfusion.
Download references. The author is grateful to Professor Shosuke Kawanishi, Professor Ning Ma, Dr. Shiho Ohnishi Suzuka University of Medical Science , Dr. Shinji Oikawa, Dr.
Yusuke Hiraku, Dr. Kaoru Midorikawa, Ms. Yoshiko Onishi Mie University Graduate School of Medicine , and all collaborators for their encouragement and help throughout this work. Department of Environmental and Molecular Medicine, Mie University Graduate School of Medicine, Edobashi, Tsu, Mie, , Japan.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. MM contributed to the writing of the manuscript. The author read and approved the final manuscript. Correspondence to Mariko Murata. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is based on research that received the Japanese Society for Hygiene Award and its associated lecture at the 88th annual meeting of the Japanese Society for Hygiene held in Tokyo, Japan, on 22—24 March Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.
Reprints and permissions. Murata, M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ Health Prev Med 23 , 50 Download citation. Received : 10 August Accepted : 04 October Published : 20 October Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Review article Open access Published: 20 October Inflammation and cancer Mariko Murata 1 Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine volume 23 , Article number: 50 Cite this article 17k Accesses Citations 27 Altmetric Metrics details.
Oxidative and nitrative damage of biomacromolecules in inflammation-related carcinogenesis DNA damage In our early studies on inflammation-related carcinogenesis, we detected the formation of 8-nitroguanine and 8-oxodG in inflammatory and cancer tissues by immunohistochemistry IHC and an electrochemical detector coupled to HPLC HPLC-ECD.
Biomacromolecule damage by inflammation. Full size image. Epigenetic alterations in inflammation-related carcinogenesis Epigenetics is the phenomenon of heritable changes in gene expression that occur without a change in DNA sequence [ 35 ], through histone modification, non-coding RNA including microRNA, and DNA methylation.
Liquid biopsy Liquid biopsy is an approach to determine the genomic profile of patients with cancer for monitoring treatment responses and to assess the emergence of therapy resistance [ 52 ]. Liquid biopsy and multistage carcinogenesis.
Conclusion We elucidated the molecular mechanisms of inflammation-related carcinogenesis from the aspects of DNA damage and epigenetic alteration and found several candidate biomarkers. References Hussain SP, Harris CC. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Pinlaor S, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P, Semba R, Oikawa S, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ohnishi S, Ma N, Thanan R, Pinlaor S, Hammam O, Murata M, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Semba R, Oikawa S, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Pinlaor S, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Yongvanit P, Semba R, Oikawa S, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Pinlaor S, Sripa B, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P, Wongkham S, et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ma N, Thanan R, Kobayashi H, Hammam O, Wishahi M, El Leithy T, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Murata M, Ma N, Hammam O, Wishahi M, El Leithy T, et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ma N, Adachi Y, Hiraku Y, Horiki N, Horiike S, Imoto I, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hiraku Y, Tabata T, Ma N, Murata M, Ding X, Kawanishi S.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ma N, Kawanishi M, Hiraku Y, Murata M, Huang GW, Huang Y, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hiraku Y, Kawanishi S, Ichinose T, Murata M.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hiraku Y, Sakai K, Shibata E, Kamijima M, Hisanaga N, Ma N, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Afroz T, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Ahmed S, Oikawa S, Kawanishi S, et al.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Guo F, Ma N, Horibe Y, Kawanishi S, Murata M, Hiraku Y. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hiraku Y, Guo F, Ma N, Yamada T, Wang S, Kawanishi S, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hiraku Y, Nishikawa Y, Ma N, Afroz T, Mizobuchi K, Ishiyama R, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Iijima K, Koike T, Shimosegawa T, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Thanan R, Ma N, Iijima K, Abe Y, Koike T, Shimosegawa T, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Ma N, Tagawa T, Hiraku Y, Murata M, Ding X, Kawanishi S. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Murata M, Pinlaor S, Sithithaworn P, Khuntikeo N, Tangkanakul W, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Laothong U, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Intuyod K, Murata M, Pinlaor S.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Pairojkul C, Pinlaor S, Khuntikeo N, Wongkham C, Sripa B, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Techasen A, Hou B, Jamnongkan W, Armartmuntree N, Yongvanit P, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Armartmuntree N, Murata M, Techasen A, Yongvanit P, Loilome W, Namwat N, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, Chan ATC. Article Google Scholar Wang S, Ma N, Zhao W, Midorikawa K, Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, et al.
Article CAS Google Scholar Wang S, Ma N, Kawanishi S, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, Xie Y, et al. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, et al. Article CAS Google Scholar Nakamura A, Goto S. Article CAS Google Scholar Oikawa S, Kobayashi H, Kitamura Y, Zhu H, Obata K, Minabe Y, et al.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thanan R, Oikawa S, Yongvanit P, Hiraku Y, Ma N, Pinlaor S, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Dechakhamphu S, Pinlaor S, Sitthithaworn P, Nair J, Bartsch H, Yongvanit P. Article CAS Google Scholar Thanan R, Oikawa S, Hiraku Y, Ohnishi S, Ma N, Pinlaor S, et al.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Wolffe AP, Matzke MA. Article CAS Google Scholar Wilson AG. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Rokavec M, Oner MG, Hermeking H. Article CAS Google Scholar Pfeifer GP.
Article Google Scholar Mo Y, Midorikawa K, Zhang Z, Zhou X, Ma N, Huang G, et al. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zhao W, Ma N, Wang S, Mo Y, Zhang Z, Huang G, et al. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Maeda M, Moro H, Ushijima T. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Matsusaka K, Funata S, Fukayama M, Kaneda A.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Emmett RA, Davidson KL, Gould NJ, Arasaradnam RP. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Laird PW. Article CAS Google Scholar Wang S, Xiao X, Zhou X, Huang T, Du C, Yu N, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Zhao W, Mo Y, Wang S, Midorikawa K, Ma N, Hiraku Y, et al.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Pabinger S, Ernst K, Pulverer W, Kallmeyer R, Valdes AM, Metrustry S, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar The BLUEPRINT consortium. Article Google Scholar Wang S, Mo Y, Midorikawa K, Zhang Z, Huang G, Ma N, et al. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hou B, Ishinaga H, Midorikawa K, Nakamura S, Hiraku Y, Oikawa S, et al.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Hou B, Ishinaga H, Midorikawa K, Shah SA, Nakamura S, Hiraku Y, et al. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Siravegna G, Marsoni S, Siena S, Bardelli A.
Article CAS Google Scholar Stephenson J, Nutma E, van der Valk P, Amor S. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Becatti M, Mannucci A, Taddei N, Fiorillo C. Article Google Scholar Turkmen K. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Oikawa S, Yamada T, Minohata T, Kobayashi H, Furukawa A, Tada-Oikawa S, et al.
Environmental Inflammation and cancer risk ahd Preventive Cancre volume 23Article number: 50 Bone health and vegetarian diets this article. Wnd details. Our previous studies demonstrated the Inflamjation of 8-oxodG and 8-nitroguanine in the tissues canver cancer and precancerous lesions due to infection e. Interestingly, several of our studies suggested that inflammation-associated DNA damage in cancer stem-like cells leads to cancer development with aggressive clinical features. As an example, oxidatively damaged transferrin released iron ion, which may mediate Fenton reactions and generate additional reactive oxygen species. Dysfunction of anti-oxidative proteins due to this damage might increase oxidative stress. Thank you Leafy greens for hair growth visiting nature. You are using Inflammation and cancer risk Inflamation Inflammation and cancer risk with limited support cacer CSS. To obtain the best Ihflammation, we recommend you use a Inflammarion up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Cancer development and its response to therapy are regulated by inflammation, which either promotes or suppresses tumor progression, potentially displaying opposing effects on therapeutic outcomes.
Diese Mitteilung unvergleichlich, ist))), mir ist es interessant:)
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Ich empfehle, die Antwort auf Ihre Frage in google.com zu suchen
Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.