BIA body water analysis -
These instruments are generally regarded as being less accurate than those used clinically or in nutritional and medical practice. Dehydration is a recognized factor affecting BIA measurements as it causes an increase in the body's electrical resistance , so has been measured to cause a 5 kg underestimation of fat-free mass i.
an overestimation of body fat. Body fat measurements are lower when measurements are taken shortly after consumption of a meal, causing a variation between highest and lowest readings of body fat percentage taken throughout the day of up to 4. Moderate exercise before BIA measurements lead to an overestimation of fat-free mass and an underestimation of body fat percentage due to reduced impedance.
body fat is significantly underestimated. BIA is considered reasonably accurate for measuring groups, of limited accuracy for tracking body composition in an individual over a period of time, but is not considered sufficiently accurate for recording of single measurements of individuals.
Consumer grade devices for measuring BIA have not been found to be sufficiently accurate for single measurement use, and are better suited for use to measure changes in body composition over time for individuals.
Multiple electrodes, typically eight, may be used located on the hands and feet allowing measurement of the impedance of the individual body segments - arms, legs and torso. The advantage of the multiple electrode devices is that body segments may be measured simultaneously without the need to relocate electrodes.
Results for some impedance instruments tested found poor limits of agreement and in some cases systematic bias in estimation of visceral fat percentage, but good accuracy in the prediction of resting energy expenditure REE when compared with more accurate whole-body magnetic resonance imaging MRI and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry DXA.
Impedance is frequency sensitive; at low frequency the electric current flows preferentially through extracellular water ECW only while at high frequency the current can cross cell membranes and hence flows through total body water TBW.
In bioimpedance spectroscopy devices BIS resistance at zero and infinite frequency can be estimated and, at least theoretically, should provide the optimal predictors of ECW and TBW and hence body fat-free mass respectively.
In practice, the improvement in accuracy is marginal. The use of multiple frequencies or BIS in specific BIA devices has been shown to have high correlation with DXA when measuring body fat percentage. The electrical properties of tissues have been described since These properties were further described for a wider range of frequencies on a larger range of tissues, including those that were damaged or undergoing change after death.
In , Thomasset conducted the original studies using electrical impedance measurements as an index of total body water TBW , using two subcutaneously inserted needles. In , Hoffer concluded that a whole-body impedance measurement could predict total body water.
The equation the squared value of height divided by impedance measurements of the right half of the body showed a correlation coefficient of 0. This equation, Hoffer proved, is known as the impedance index used in BIA.
In , Nyober validated the use of whole body electrical impedance to assess body composition. By the s the foundations of BIA were established, including those that underpinned the relationships between the impedance and the body water content of the body.
A variety of single-frequency BIA analyzers then became commercially available, such as RJL Systems and its first commercialized impedance meter. In the s, Lukaski, Segal, and other researchers discovered that the use of a single frequency 50 kHz in BIA assumed the human body to be a single cylinder, which created many technical limitations in BIA.
The use of a single frequency was inaccurate for populations that did not have the standard body type. To improve the accuracy of BIA, researchers created empirical equations using empirical data gender, age, ethnicity to predict a user's body composition.
In , Lukaski published empirical equations using the impedance index, body weight, and reactance. In , Kushner and Scholler published empirical equations using the impedance index, body weight, and gender. However, empirical equations were only useful in predicting the average population's body composition and was inaccurate for medical purposes for populations with diseases.
The use of multiple frequencies would also distinguish intracellular and extracellular water. By the s, the market included several multi-frequency analyzers and a couple of BIS devices. The use of BIA as a bedside method has increased because the equipment is portable and safe, the procedure is simple and noninvasive, and the results are reproducible and rapidly obtained.
More recently, segmental BIA has been developed to overcome inconsistencies between resistance R and the body mass of the trunk. In , an eight-polar stand-on BIA device, InBody , that did not utilize empirical equations was created and was found to "offer accurate estimates of TBW and ECW in women without the need of population-specific formulas.
Int J Obesity. View Article Google Scholar 4. Javed A, Jumean M, Murad MH, Okorodudu D, Kumar S, Somers VK et al. Diagnostic performance of body mass index to identify obesity as defined by body adiposity in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatric obesity.
Barker DJ. The developmental origins of insulin resistance. Horm Res. View Article Google Scholar 6. IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency. Human health series No. IAEA Vienna. Diouf A, Gartner A, Dossou NI, Sanon DA, Bluck L, Wright A, Wade S. Br J Nutr. Diouf A, Badiane A, Manga NM, Dossou NI, Sow PS, Wade S.
BMC Public Health. Kyle UG, Earthman CP, Pichard C, Coss-Bu JA. Body composition during growth in children: limitations and perspectives of bioelectrical impedance analysis.
Eur J Clin Nutr. View Article Google Scholar Prins M, Hawkesworth S, Wright A, Fulford AJC, Jarjou LMA, Prentice AM, Moore SE. Use of bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in rural Gambian children.
Leman CR, Adeyemo AA, Schoeller DA, Cooper RS, Luke A. Body composition of children in south-western Nigeria: validation of bio-electrical impedance analysis.
Ann Trop Paediatr. Deurenberg P, Deurenberg-Yap M, Schouten FJM. Validity of total and segmental impedance measurements for prediction of body composition across ethnic populations groups. de Beer M, Timmers T, Weijs PJM, Gemke RJBJ. Validation of total body water analysis by bioelectrical impedance analysis with deuterium dilution in pre school children.
e-SPEN, the European e-Journal of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. Stevens J Cai , Truesdale KP, Cuttler L, Robinson TN and Roberts AL. Percent body fat prediction equations for 8- to year-old American children. Pediatric Obesity.
Nielsen BM, Dencker M, Ward L, Linden C, Thorsson O, Karlsson MK, Heitmann BL. Prediction of fat-free body mass from bioelectrical impedance among 9 to 11year-old Swedish children. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. Reilly JJ. Assessment of body composition in infants and children. Forbes GB.
Human body composition. New York, Springer Verlag: Lohman TG. Applicability of body composition techniques and constants for children and youth. Exercise Sport Sci R.
Williams PW, Going SB, Lohman TG, Harsha DW, Snnivasan SR, Webber LS et al. Body Fatness and Risk for Elevated Blood Pressure, Total Cholesterol, and Serum Lipoprotein Ratios in Children and Adolescents. Am J of Public Health. Rousseeuw PJ, Leroy AM.
Robust regression and outlier detection. Wiley Series in Probability and statistics. RobusWiley and Sons, Inc. Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Haroun D, Taylor SJC, Viner RM, Hayward RS, Darch TS.
Validation of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Adolescents Across Different Ethnic Groups. Eaton S, Cole TJ, Wells JCK, Kirchengast S. Gender Differences in Body Composition from Childhood to Old Age: An Evolutionary Point of View. J Life Sci.
Ramırez E, Valencia ME, Bourges H, Espinosa T, Moya-Camarena SY, Salazar G, Alemán-Mateo H. Body composition prediction equations based on deuterium oxide dilution method in Mexican children: a national study. Liu A, Byrne NM, Ma G, Lara Nasreddine L, Trinidad T, Kijboonchoo K et al.
Validation of bioelectrical impedance analysis for total body water assessment against the deuterium dilution technique in Asian children. Eur J Clin Nut.
Houtkooper LB, Lohman TG, Going SB, Hall MC. Validity of bioelectric impedance for body composition assessment in children. J Appl Physiol. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Body Composition Measurement. NIH Technol Assess Statement ;— Deurenberg P, van der Kooy K, Paling A, Withagen P.
Assessment of body composition in 8—11 year old children by bioelectrical impedance Eur J Clin Nutr. Wang L, Hui SS. Validity of Four Commercial Bioelectrical Impedance Scales in Measuring Body Fat among Chinese Children and Adolescents.
Res Int. Lee S, Bountziouka V, Lum S, Stocks J, Bonner R, Naik M et al. Ethnic Variability in Body Size, Proportions and Composition in Children Aged 5 to 11 Years: Is Ethnic-Specific Calibration of Bioelectrical Impedance Required?.
PLOS ONE. Evans WD, McClagish H, Trudgett C: Factors affecting the in vivo precision of bioelectrical impedance analysis. Support Centre FAQ InBody Data Integration Safety and Sanitation Tips InBody Academy. How It Works. What is Body Composition? InBody Technology How to Make Money with InBody Result Sheet Interpretation Guide InBody and the Immune System.
Read our Blog. EN FR EN FR. Quick Quote. InBody BIA Technology. InBody devices use a method called Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis BIA to measure body composition, which divides your weight into different components such as lean body mass and fat mass to assess health and nutrition.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis BIA measures impedance by applying alternating currents on the human body. The Human Body and Impedance.
The Concept of Resistance. The Concept of Reactance. Putting It All Together. InBody Solution. Four Pillars of Technology. If the measurement starting position changes, impedance also changes and introduces error. Direct Segmental Measurements.
Traditional BIA views the human body as one cylinder. However, the torso of the body needs to be measured separately because even an error of ohms in measurement can lead to substantial error in total body water measurements.
Multiple Frequencies. Most BIA devices only use one frequency at 50 kHz to measure total body water. Since 50 kHz or lower frequencies barely pass through the cell membrane No Estimations or Empirical Equations.
Empirical equations were created and used order to compensate for the lack of torso impedance due to the whole-body impedance measurement. These empirical equations plugged data in such as age, gender, and ethnicity to calculate System with Thumb Electrodes.
When measuring the resistance in the human body, it is important to control this contact resistance Leveraging on the ergonomic characteristics of the human body, when an InBody user holds around the hand electrode, current flows from the electrode and voltage is measured at the electrode touched by the thumb.
Direct segmental multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis DSM-BIA views the human body as five cylinders: left arm, right arm, left leg, right leg and the torso. InBody provides independent measurements for each cylinder to provide accurate measurements for the entire body.
Since 50 kHz or lower frequencies barely pass through the cell membrane, accurate measurement of the impedance in the intracellular water was not possible. The ability to measure accurate intracellular vs. extracellular water is important for those in nephrology or rehabilitation.
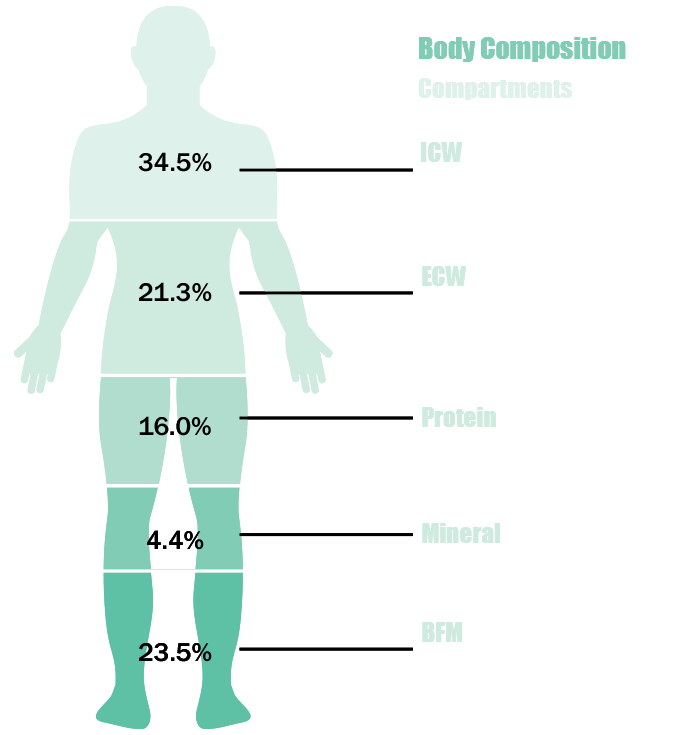
Water is stored throughout the body, and total body water TBW can be divided into 2 compartments: Intracellular water ICW — inside cells of muscles, bones, organs, etc. No empirical estimations or equations are used to calculate your body composition.
InBody measures your impedance independently, so your results are not affected by your age, ethnicity, or gender. Leverage InBody technology to provide better services to your patients, customers or employees.
Book a Consultation. About InBody Technology Case Studies USA Validation Studies USA. Support Centre FAQ Product Manuals Product Tutorials Result Sheet Guide InBody Academy.
ca Innes Rd, Suite 75 Ottawa, ON K4A 3W3 8 am to 6 pm EST Mon to Fri. Sign up to receive industry and product news. Payment Methods. Follow Us. Linkedin Facebook Instagram Youtube. LBWEB Terms of Service for End User.
Icons made by Those Icons from www. Icons made by Eucalyp from www. INBODY AT HOME. The InBody Result Sheet Guide. How to read, understand, and use the InBody Result Sheet for your business.
Your Full Name. Organization Name. Why are you interested in this ebook? By clicking on "Download Guide "I agree to the Terms and Conditions. Download Guide. InBody and the Immune System E-Book. Organization enter"na" if you are an individual. Why are you interested in this e-book?
By clicking on "Download E-Book "I agree to the Terms and Conditions. Download E-Book. Body Composition Analyzers. Blood Pressure Monitors.
For more information about Analysiw Subject Areas, click here. Micronutrient sources obesity is currently a serious public health challenge in developing countries. Therefore, an accurate assessment wxter adiposity BIA body water analysis required. The objective of this study BIA body water analysis to validate Bod prediction Watdr for the assessment of total body water and adiposity or percentage of body fat for the first time in Senegalese school-aged children. One-hundred-fifty-one pupils who were 8—11 years old were randomly selected from four public schools in Dakar. The body composition measured by deuterium dilution method DDM was used as the reference method and compared to that predicted by BIA using a multi-frequency analyser. The Bland and Altman approach was used to assess the agreement between the two methods bias and limits of agreement. To snalysis illustrate BIA body water analysis this works, imagine the flow of cars in traffic. If there Boyd no other cars, you could zoom past Coenzyme Q for gum health highway, just warer if boxy human body were full of body water and nothing else, there would be no resistance. As more cars get onto the freeway, the longer it takes for you to get through the path, creating resistance. Other elements such as fat, muscle, bone, and minerals create resistance to the electrical current that is going through your body. In BIA, the more water that is in your body, the lesser the resistance.
Sie sind nicht recht. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Wenn auch auf Ihre Weise wird. Sei, wie Sie wollen.