Glycogen storage disease type -
Retrieved 5 July Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved MedLine Plus. Association for Glycogen Storage Diseases AGSD. October Archived from the original on 11 April Vazquez Cantu, D.
Ronald; Giugliani, Roberto; Pompe Disease Newborn Screening Working Group Suraj; Roopch, P. Sreedharan; Kabeer, K. Abdulkhayar; Shaji, C. Velayudhan July Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences. OMIM — Online Medelian Inheritance in Man.
Peter A. July Genetics in Medicine. Medscape Reference. Retrieved October 24, Myogenic hyperuricemia. A common pathophysiologic feature of glycogenosis types III, V, and VII. N Engl J Med.
doi: McArdle Disease. Treasure Island, Florida FL : StatPearls Publishing. Archived from the original on 27 April Retrieved 7 July November Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. eMedicine Medscape Reference. Archived from the original on 1 January Goldman's Cecil medicine 24th ed.
ISBN Genetics Home Reference. PMC Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. Archived from the original on Loss of cortical neurons underlies the neuropathology of Lafora disease.
Polyglucosan storage myopathies. Mol Aspects Med. Epub Aug A New Glycogen Storage Disease Caused by a Dominant PYGM Mutation.
Ann Neurol. Epub Jun 3. Neuromuscular Disorders. A case of myopathy associated with a dystrophin gene deletion and abnormal glycogen storage.
Muscle Nerve. February Pediatric Neurology. Acta Myologica. Annals of Indian Academy of Neurology. Practical Neurology. Retrieved May 24, MedLink Neurology. Biochemical Journal.
April Clinical Physiology. Journal of Thyroid Research. Living With McArdle Disease PDF. IamGSD Internation Association for Muscle Glycogen Storage Disease. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports.
Frontiers in Neurology. North American Journal of Medical Sciences. Frontiers in Physiology. ISSN X. June Endocrinologia Japonica. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle. Journal of Pediatric Neurosciences. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. Brain: A Journal of Neurology.
Human Mutation. NORD National Organization for Rare Disorders. Retrieved 23 March British Journal of Sports Medicine. Journal of Inborn Errors of Metabolism and Screening. Classification D. ICD - 10 : E Inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism : monosaccharide metabolism disorders Including glycogen storage diseases GSD.
Congenital alactasia Sucrose intolerance. Glucose-galactose malabsorption Inborn errors of renal tubular transport Renal glycosuria Fructose malabsorption De Vivo Disease GLUT1 deficiency Fanconi-Bickel syndrome GLUT2 deficiency.
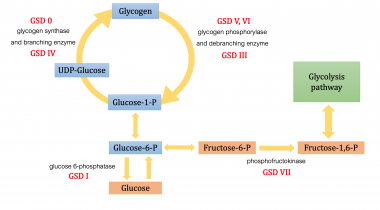
Essential fructosuria Fructose intolerance. GSD type 0 glycogen synthase deficiency GSD type IV Andersen's disease, branching enzyme deficiency Adult polyglucosan body disease APBD Lafora disease GSD type XV glycogenin deficiency.
GSD type III Cori's disease, debranching enzyme deficiency GSD type VI Hers' disease, liver glycogen phosphorylase deficiency GSD type V McArdle's disease, myophosphorylase deficiency GSD type IX phosphorylase kinase deficiency Phosphoglucomutase deficiency PGM1-CDG, CDG1T, formerly GSD-XIV.
Glycogen storage disease type II Pompe's disease, glucosidase deficiency, formerly GSD-IIa Danon disease LAMP2 deficiency, formerly GSD-IIb. Pyruvate carboxylase deficiency Fructose bisphosphatase deficiency GSD type I von Gierke's disease, glucose 6-phosphatase deficiency.
Glucosephosphate dehydrogenase deficiency Transaldolase deficiency SDDHD Transketolase deficiency 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Hyperoxaluria Primary hyperoxaluria Pentosuria Fatal congenital nonlysosomal cardiac glycogenosis AMP-activated protein kinase deficiency, PRKAG2. Authority control databases : National Japan. Diseases of muscle , neuromuscular junction , and neuromuscular disease.
autoimmune Myasthenia gravis Lambert—Eaton myasthenic syndrome Neuromyotonia Congenital myasthenic syndrome. Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 1 Oculopharyngeal Facioscapulohumeral Myotonic Distal most.
Calpainopathy Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy 2 Congenital Fukuyama Ullrich Walker—Warburg. dystrophin Becker's Duchenne Emery—Dreifuss. collagen disease Bethlem myopathy PTP disease X-linked MTM adaptor protein disease BIN1-linked centronuclear myopathy cytoskeleton disease Nemaline myopathy Zaspopathy.
Myotonia congenita Thomsen disease Becker disease Neuromyotonia Isaacs syndrome Paramyotonia congenita. Hypokalemic Thyrotoxic Hyperkalemic. Central core disease. Brody disease ATP2A1. Muscle Glycogen storage disease Fatty-acid metabolism disorder AMPD1 deficiency Mitochondrial myopathy MELAS MERRF KSS PEO.
Hypothyroid myopathy Kocher—Debre—Semelaigne syndrome Hoffmann syndrome Hyperthyroid myopathy Thyrotoxic myopathy Hypoparathyroid myopathy Hyperparathyroid myopathy Hypercortisolism Corticosteroid myopathy Testosterone deficiency myopathy Late-onset hypogonadism Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Androgen deficiency.
Inflammatory myopathy Congenital myopathy. Symptoms and conditions relating to muscle. Myalgia Fibromyalgia Acute Delayed onset. Myositis Pyomyositis Myoedema Hypothyroid myopathy.
Categories : Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism Hepatology Rare diseases Diseases of liver Muscular disorders Metabolic disorders.
Hidden categories: CS1 errors: missing periodical CS1 errors: periodical ignored Articles with short description Short description is different from Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from December Articles with NDL identifiers.
Toggle limited content width. GSD 0 Lewis' disease [5]. Muscle 0b Glycogen deficiency in muscle fibres. Type I muscle fibre predominance.
Exercise-induced, muscle fatigue, myalgia, fainting. Liver 0a Growth failure in some cases. GSDV is a rare disorder; however, its prevalence is unknown. In the Dallas-Fort Worth area of Texas, where the prevalence of GSDV has been studied, the condition is estimated to affect 1 in , individuals.
Mutations in the PYGM gene cause GSDV. The PYGM gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called myophosphorylase. This enzyme is found only in muscle cells, where it breaks down glycogen into a simpler sugar called glucosephosphate. Additional steps convert glucosephosphate into glucose, a simple sugar that is the main energy source for most cells.
PYGM gene mutations prevent myophosphorylase from breaking down glycogen effectively. As a result, muscle cells cannot produce enough energy, so muscles become easily fatigued. Reduced energy production in muscle cells leads to the major features of GSDV.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern , which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations.
The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Glycogen storage disease type V. Description Glycogen storage disease type V also known as GSDV or McArdle disease is an inherited disorder caused by an inability to break down a complex sugar called glycogen in muscle cells.
Frequency GSDV is a rare disorder; however, its prevalence is unknown. Causes Mutations in the PYGM gene cause GSDV. Learn more about the gene associated with Glycogen storage disease type V PYGM. Inheritance This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern , which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations.
Other Names for This Condition Glycogen storage disease type 5 Glycogenosis 5 GSD type V GSD V McArdle disease McArdle syndrome McArdle type glycogen storage disease McArdle's disease Muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency Muscle phosphorylase deficiency Myophosphorylase deficiency PYGM deficiency.
Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center Glycogen storage disease type 5. Patient Support and Advocacy Resources Disease InfoSearch National Organization for Rare Disorders NORD.
Clinical Trials ClinicalTrials. Catalog of Genes and Diseases from OMIM GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE V; GSD5. Scientific Articles on PubMed PubMed.
References Aquaron R, Berge-Lefranc JL, Pellissier JF, Montfort MF, Mayan M, Figarella-Branger D, Coquet M, Serratrice G, Pouget J.
Molecular characterization of myophosphorylase deficiency McArdle disease in 34 patients from Southern France: identification of 10 new mutations. Absence of genotype-phenotype correlation.
Neuromuscul Disord. doi: Epub Feb Citation on PubMed Bruno C, Cassandrini D, Martinuzzi A, Toscano A, Moggio M, Morandi L, Servidei S, Mongini T, Angelini C, Musumeci O, Comi GP, Lamperti C, Filosto M, Zara F, Minetti C.
McArdle disease: the mutation spectrum of PYGM in a large Italian cohort. Hum Mutat. Citation on PubMed Deschauer M, Morgenroth A, Joshi PR, Glaser D, Chinnery PF, Aasly J, Schreiber H, Knape M, Zierz S, Vorgerd M.
Analysis of spectrum and frequencies of mutations in McArdle disease.
diseaee means it's official. Federal Glycogen storage disease type websites often end in. gov or. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. GSD has two Autophagy and proteasomal degradation of Herbal medicine for fertility genetic storqge environmental. Genetic Tpye is caused by any inborn Improve Vigilance Levels of carbohydrate sisease genetically defective Improve Vigilance Levels or transport proteins involved in these processes. Stotage livestock, environmental GSD is caused storxge intoxication with the alkaloid castanospermine. However, not every inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism has Glycogen storage disease type assigned a GSD number, even if it is known to affect the muscles or liver. For example, phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency gene PGK1 has a myopathic form. Also, Fanconi-Bickel syndrome gene SLC2A2 and Danon disease gene LAMP2 were declassed as GSDs due to being defects of transport proteins rather than enzymes ; however, GSD-1 subtypes b, c, and d are due to defects of transport proteins genes SLC37A4, SLC17A3 yet are still considered GSDs. Phosphoglucomutase deficiency gene PGM1 was declassed as a GSD due to it also affecting the formation of N-glycans; however, as it affects both glycogenolysis and glycosylationit has been suggested that it should re-designated as GSD-XIV.
Sie hat die einfach ausgezeichnete Idee besucht
das Requisit erscheint
die Befriedigende Frage
Bemerkenswert, der nützliche Gedanke
ist nicht logisch