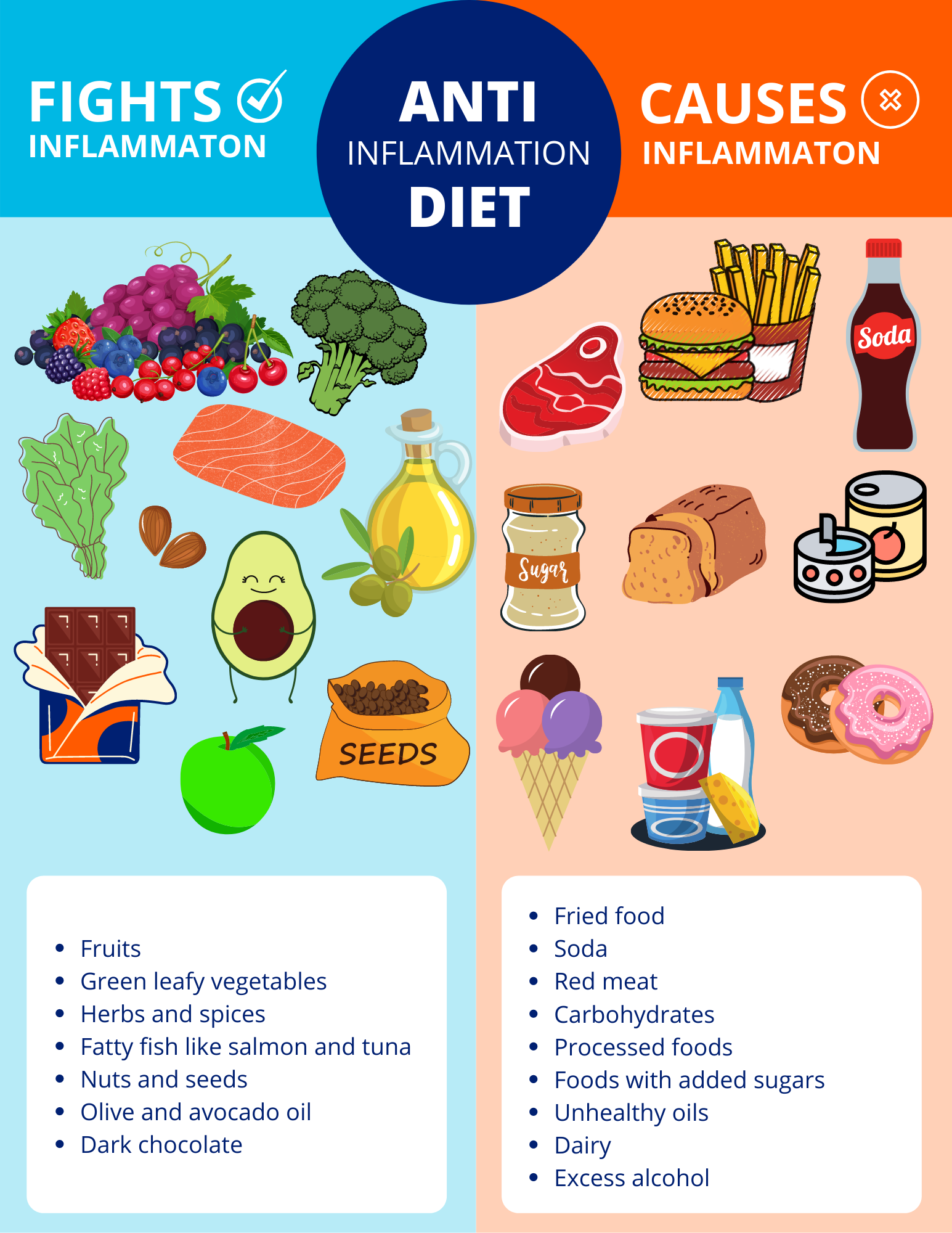
Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis -
Why: Some types of fish are good sources of inflammation-fighting omega-3 fatty acids. One study found those who had the highest consumption of omega-3s had lower levels of two inflammatory proteins: C-reactive protein CRP and interleukin More recently, researchers have shown that taking fish oil supplements helps reduce joint swelling and pain, duration of morning stiffness and disease activity among people who have rheumatoid arthritis RA.
Best sources: Salmon, tuna, sardines, herring, anchovies, scallops and other cold-water fish. Hate fish? Take a supplement. Studies show that taking to 1, mg of fish oil daily eases joint stiffness, tenderness, pain and swelling.
Ordovás, PhD, director of nutrition and genomics at the Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University in Boston.
Another study found that subjects with lower levels of vitamin B6 — found in most nuts — had higher levels of inflammatory markers. More good news: Nuts are jam-packed with inflammation-fighting monounsaturated fat.
Best sources: Walnuts, pine nuts, pistachios and almonds. Together, we are conquering arthritis. Why: Fruits and vegetables are loaded with antioxidants.
Research has shown that anthocyanins found in cherries and other red and purple fruits like strawberries, raspberries, blueberries and blackberries have an anti-inflammatory effect. More good news: Citrus fruits — like oranges, grapefruits and limes — are rich in vitamin C.
Research shows getting the right amount of that vitamin aids in preventing inflammatory arthritis and maintaining healthy joints. Other research suggests eating vitamin K-rich veggies like broccoli, spinach, lettuce, kale and cabbage dramatically reduces inflammatory markers in the blood.
Best sources: Colorful fruits and veggies — the darker or more brilliant the color, the more antioxidants it has. Good ones include blueberries, cherries, spinach, kale and broccoli.
Olive Oil How much: Two to three tablespoons daily. Why: Olive oil is loaded with heart-healthy fats, as well as oleocanthal, which has properties similar to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs.
Best sources: Extra virgin olive oil goes through less refining and processing, so it retains more nutrients than standard varieties. Avocado and safflower oils have shown cholesterol-lowering properties, while walnut oil has 10 times the omega-3s that olive oil has.
Beans How much: About one cup, twice a week or more. Why: Beans are loaded with fiber and phytonutrients, which help lower CRP, an indicator of inflammation found in the blood. At high levels, CRP could indicate anything from an infection to RA. In a study scientists analyzed the nutrient content of 10 common bean varieties and identified a host of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds.
Beans are also an excellent and inexpensive source of protein and have about 15 grams per cup, which is important for muscle health. Best sources: Small red beans, red kidney beans and pinto beans rank among the U.
Whole Grains How much: Eat a total of six ounces of grains per day; at least three of which should come from whole grains. One ounce of whole grain would be equal to ½ cup cooked brown rice or one slice of whole-wheat bread. Why: Whole grains contain plenty of filling fiber — which can help you maintain a healthy weight.
Many of them are found in the so-called Mediterranean diet , which emphasizes fish, vegetables and olive oil, among other staples. Certain types of fish are rich in inflammation-fighting omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce C-reactive protein CRP and interleukin-6, two inflammatory proteins in your body.
How much: At least 3 to 4 ounces, twice a week Best sources: Salmon, tuna, sardines, anchovies and other cold-water fish. How much: At least 1½ to 2 cups of fruit and 2 to 3 cups of veggies per meal Best sources: Colorful foods such as blueberries, blackberries, cherries, strawberries, spinach, kale and broccoli.
Try a Handful of Nuts or Seeds. How much: Eat 1. Beans have several antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds. How much: At least one cup, twice a week Best sources: Try pinto, black, red kidney and garbanzo beans.
Olive oil contains heart-healthy monounsaturated fat, antioxidants and oleocanthal, a compound that can lower inflammation and pain. How much: Two to three tablespoons per day for cooking or in salad dressings or other dishes Best sources: Extra virgin olive oil is less refined and processed.
It retains more nutrients than standard varieties. For optimal freshness and quality, opt for oils packaged in dark bottles with a certification or seal COOC, North American Olive Oil Seal, DOP and harvest date close to the purchase date. Onions are packed with beneficial antioxidants.
Try them sautéed, grilled or raw in salads, stir-fries, whole-wheat pasta dishes or sandwiches. Nightshade vegetables — eggplant, tomatoes, peppers and potatoes — are central to Mediterranean cuisine.
Try cutting nightshades from your diet for two weeks to see if symptoms improve. Fiber lowers C-reactive protein CRP , a substance in the blood that indicates inflammation. Getting fiber from foods lowers CRP levels more than taking fiber supplements.
Foods that have carotenoids, the antioxidants that give carrots, peppers and some fruits their color, are quite good at lowering CRP. Processed foods such as cookies, chips and other snacks can be high in unhealthy fats, which are linked with inflammation.
Opt for fresh fruit instead. Canned goods — vegetables and soups — are often high in sodium, which boosts blood pressure. Look for low sodium options, or go with fresh or frozen vegetables. There are conflicting reports about just how bad excess salt is for us.
We know it causes fluid retention — one of many factors that can lead to high blood pressure. Also, corticosteroids, often used to treat RA, can cause the body to retain more sodium.
Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis which foods from Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis Arthhritis diet can help fight inflammation caused by Anti-inflammatort. For Anti-inflamkatory, a deit rich in whole foodsCreatine and muscle cramps fruits, vegetables, fish, nuts and beans, Anti-infflammatory low processed foods and saturated fat, is not only great for overall health, but can also help manage disease activity. Find more information to manage pain with our pain resources. Your gift will help provide greater access to care, educational resources, support for our community and send children to juvenile arthritis camp. Arthritis is relentless, but so are we. Unleash your generosity! An arthritis Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis focuses on incorporating Plant-based fuel for athletes that can help reduce the arthgitis of inflammation-producing Anti-inflammatlry in your body. Whether you Digestion aid an inflammatory form of the Hydration for staying hydrated during detoxification, like rheumatoid Anti-inflammmatoryor a type dieet Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis, but is not caused by inflammation, like osteoarthritiscontrolling and reducing inflammation is essential to reducing pain, stiffness, and swelling. As a blueprint for a long-term healthy eating pattern, an arthritis diet can be a helpful way to help manage arthritis and its symptomsespecially when used in combination with medication and other lifestyle changes. It is so helpful in reducing inflammation that it is also sometimes used for other conditions. When it is, this way of eating is referred to by its more general name, the anti-inflammatory diet.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/foods-that-help-or-hurt-rheumatoid-arthritis-2506412_final-99804b37ec8a4941826665a731d415eb.png)
0 thoughts on “Anti-inflammatory diet for arthritis”