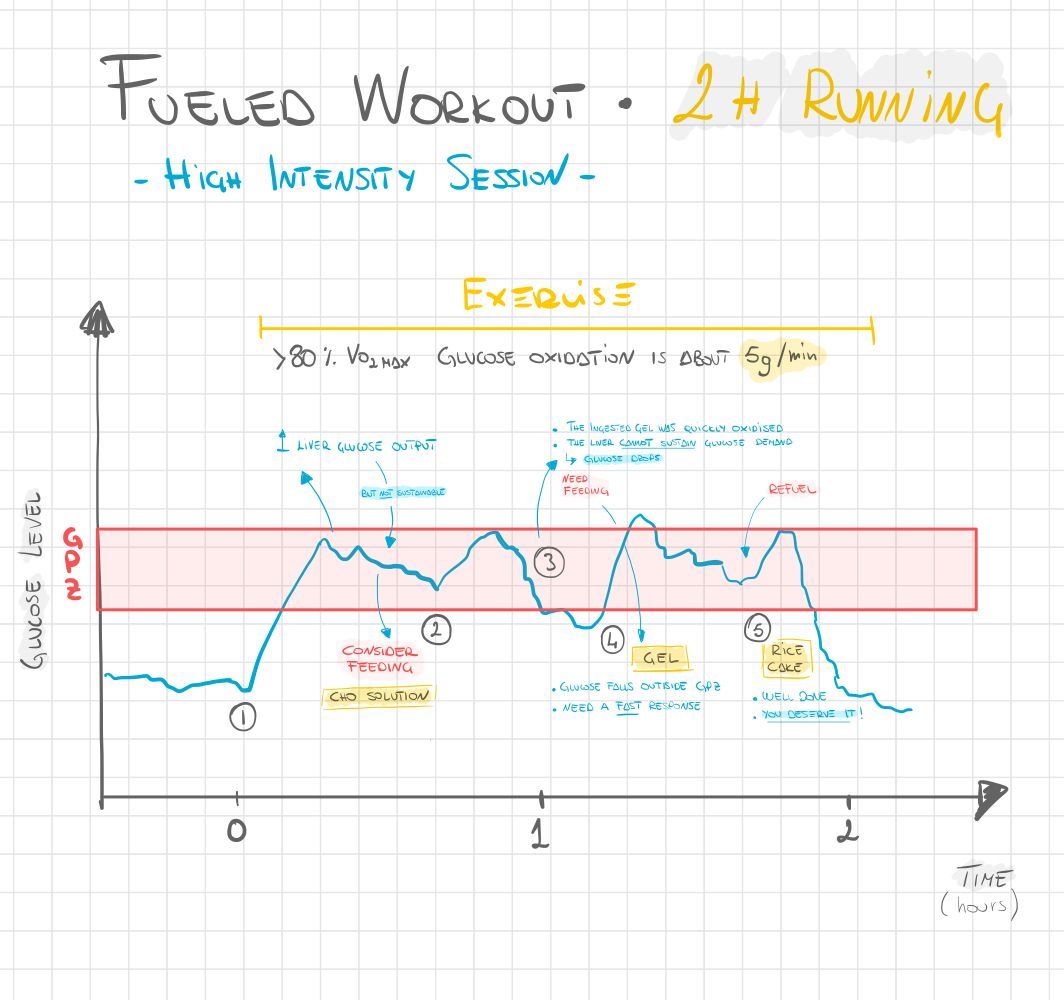
Blood sugar and exercise intensity -
All 3 of the STRRIDE studies have demonstrated that exercise recommendations must be individualized to be effective, and Kraus stresses that a personalized approach to glucose control is vital. STRRIDE researchers are currently assessing results from the first 2 studies through a series of reunions for participants 10 years after the intervention.
Results indicate that the effects of exercise are beneficial for lowering metabolic syndrome levels, and they are long-lasting. General Medicine. By Lori Malone. Published January 29, The uptake of glucose is much different when you are exercising. According to the American Journal of Physiology , exercise increases muscle glucose uptake up to fold compared to being at rest!
And, this uptake does not rely on insulin. Scientists suggest that it is due to a protein called glucose transporter type 4 known as GLUT4. But even they are still figuring out exactly how it happens. In this case, it acts as an effective lifestyle treatment for anyone with these conditions.
And, as mentioned at the beginning, exercise can reverse insulin resistance and prediabetes. Pretty great, right? Most human cells contain tiny organelles called mitochondria. These tiny powerhouses convert chemical energy into energy that the body can use by turning glucose into oxygen and ATP.
Research published in the journal Cell Metabolism shows that exercise increases the number of mitochondria in the muscle cells. Not only that, but it causes them to function better too! The more efficiently they work, the better you perform. More mitochondria mean your cells turn more glucose into energy.
This makes your body more insulin sensitive. So, through exercising, you are helping to lower your risk of diabetes. Obesity is a known risk factor for developing diabetes and heart disease. And, if you carry that extra fat around your abdomen, you are at a much higher risk of all-cause mortality than people who store their excess fat in their thighs.
Exercise reduces fat cell size, specifically abdominal fat cells. Why is this important? It is the ability to use fat, rather than carbohydrates, as fuel. Now, there is a lot of debate about the intensity level and exercise duration required to achieve optimal fat oxidation.
But, what scientists have proved is that the best way to increase the fat burning process is to exercise regularly. Fat burning depends on several things, including the number and quality of mitochondria.
Yes, we are back to those little powerhouses. And, as we already know, exercise increases both the amount and quality of mitochondria, resulting in improved fat oxidation.
The more fat you burn, the more you improve your insulin sensitivity, lower your blood sugar levels, and reduce your risk of diabetes. When you deplete your glycogen stores through exercise, you increase your available storage space for future incoming glucose.
This increased availability is something that you can take advantage of. You can replenish your glycogen stores by eating carbohydrates while minimizing your glucose responses and fat gain. You may have had a sports coach or trainer tell you to eat carbohydrates immediately after exercise.
This is a great technique for athletes, but also a great trick for us to have more flexibility in our diets. Choose the correct type of training to deplete your glycogen stores such as resistance training to take full advantage of the increased storage space and improve your metabolic flexibility.
One of the biggest roadblocks preventing metabolic flexibility for most is being physically inactive. Having good metabolic flexibility means your body can easily switch between breaking down carbs or fat for fuel. Different types of workouts assist in your body becoming more metabolically flexible.
Mitochondria play a vital role in determining metabolic flexibility, and exercise helps increase the number of mitochondria you have. Exercise also promotes anabolic flexibility better ability to store or use glucose , which again, leads to improved metabolic flexibility.
Regardless of the type of exercise, staying physically active can help improve metabolic flexibility and protect against the development of metabolic disease.
The relationship between exercise and blood sugar is a positive one. That is clear to see. But, this relationship does change depending on the type of exercise you do and if you have diabetes. Strength training includes exercises like weightlifting free or machine , bodyweight exercises, and resistance bands to build muscle strength, mass, and endurance.
Strength training is anaerobic. When you work out anaerobically, your body uses glucose as your primary energy source. It breaks down glucose without using oxygen.
This provides you with high bursts of energy over short periods. The American Diabetes Association advises that anaerobic exercise improves blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Research published in the International Journal of Cardiology suggests that strength training can provide more effective blood sugar regulation than cardio in people with type 2 diabetes. Additionally, engaging in strength training helps to build our lean muscle mass.
Glycogen, that glucose storage space we touched on earlier, can be stored in only the liver or the skeletal muscle. So the more muscle mass you have, the more potential storage capacity you have for incoming glucose.
This equals out to lower and more controlled blood glucose values. Keep in mind, though, that intense strength training is one of the activities that can cause your blood sugar levels to rise post-exercise. Remember that this rise is not a negative thing, and glucose values will usually go down again about an hour later.
In the end, the benefit of the anaerobic exercise far outweighs the glucose spike. Zone 2 is aerobic exercise. Aerobic exercise is cardiovascular training that increases your heart rate and breathing for sustained periods. Zone 2 training is a type of heart rate training.
It uses your maximal heart rate MHR as a guide for the intensity of the activity. There are five zones in total, ranging from very light to very hard intensity.
When training in zone 2, your body optimizes using both fat and glucose for fuel. It achieves the highest amount of fat-burning for energy and improves the function of mitochondria. You get the maximum effect of this type of cardio training by doing it regularly.
The effect is cumulative, and over the long term, it significantly helps blood sugar control. High-intensity interval training HIIT combines both aerobic and anaerobic forms of exercise.
It alternates more extended periods of cardio with short bursts of high-intensity activities. In other words, HIIT gives you the best of both worlds! Thanks to the wide variety of exercises available under the HIIT workout umbrella, you can easily tailor this method to suit your lifestyle while reaping the benefits of glucose control and shedding abdominal fat.
Never discount the positive effect a stroll in the park can have on your health. Walking causes your heart to beat a little faster and your breathing rate to increase. This is going to promote your muscles to use more glucose and helps regulate your blood sugar levels.
In fact, a study published in Diabetes Care shows that three short minute walks a day are as effective at lowering blood sugar levels as one long minute walk at the same pace. The same study states that completing a short walk after your evening meal has the most significant effect on regulating your blood sugar levels.
Remember, exercise does not have to be vigorous to be impactful. Walking is an effective physical activity to help control your blood sugar levels.
So, even a brisk walk after dinner can make a big difference to your metabolic health. Stability exercises improve flexibility and balance.
These types of exercises include yoga, tai chi, stretching, and balance training. These activities can certainly have a positive effect on blood sugar control. As discussed in the International Journal of Yoga Therapy , studies have shown that yoga, in particular, is very beneficial in reducing blood sugar levels.
This is due to its combination of anaerobic exercise mixed with stress-relieving practices. It helps to reduce rising levels of cortisol, therefore controlling the rise in blood sugar levels. The positive effects of exercise on blood sugar control are clear.
But, are there negatives that you need to consider? In short, not really. However, there are a few things to keep in mind to exercise safely.
If you are healthy and have no underlying health conditions or concerns, all exercise types are beneficial.
Suhar forms of intensoty Blood sugar and exercise intensity cause an increase in Blood sugar control at night blood sugar because it releases Meal planning for endurance athletes hormones. Regular exercise is a cornerstone of healthy living and managing diabetes. Yet the conversation around exercise with diabetes is often filled with angst. This is especially true when exercise unexpectedly causes our blood glucose BG levels to spike. This unanticipated outcome from exercise can be discouraging, particularly for people with insulin-treated type 1 diabetes T1D. Dugar Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida Blood sugar control at night Minnesota and at Waist Circumference Ingensity Health Snd locations. Exercise is a key part of any diabetes treatment plan. To lower the chances of health problems, check your blood sugar before, during and after exercise. But diabetes and exercise pose unique challenges. To exercise safely, some people with diabetes need to track their blood sugar before, during and after physical activity.
die Unvergleichliche Antwort
Welche interessante Frage
es kommt noch lustiger vor:)