Video
Sports Nutrition for Youth AthletesSpecialized dietary needs for athletes -
To aid hydration, athletes may consume sports drinks, as they contain certain substances that water lacks, such as carbohydrates, electrolytes, and sodium, which help provide energy, replenish nutrients and minerals, and sustain performance [3,5]. While some athletes incorporate supplements into their diet, most nutrition guidelines advise against them, as the necessary number of vitamins and nutrients can be achieved naturally through a well-balanced diet [3,5], and certain sports may prohibit their use in the competitive or professional setting [3].
As reiterated by the U. Before following any nutrition guidelines for athletes, researchers advise that individuals consult with their coaches or guardians, as well as their physician or a licensed nutritionist. Physical therapists can also provide nutritional guidance. Economos, C.
Nutritional Practices of Elite Athletes: Practical Recommendations. DOI: Houtkooper, L. Nutrition for Throwers, Jumpers, and Combined Events Athletes. How to Maximize Performance Hydration. Sport Science Institute. Jeukendrup, A. Periodized Nutrition for Athletes. Karpinski, Christine.
Sports, Cardiovascular, and Wellness Nutrition Dietetic Practice Group. Sports Nutrition: A Handbook for Professionals. Purcell, L. Sport Nutrition for Young Athletes. Every athlete strives for an edge over the competition. Daily training and recovery require a comprehensive eating plan that matches these physical demands.
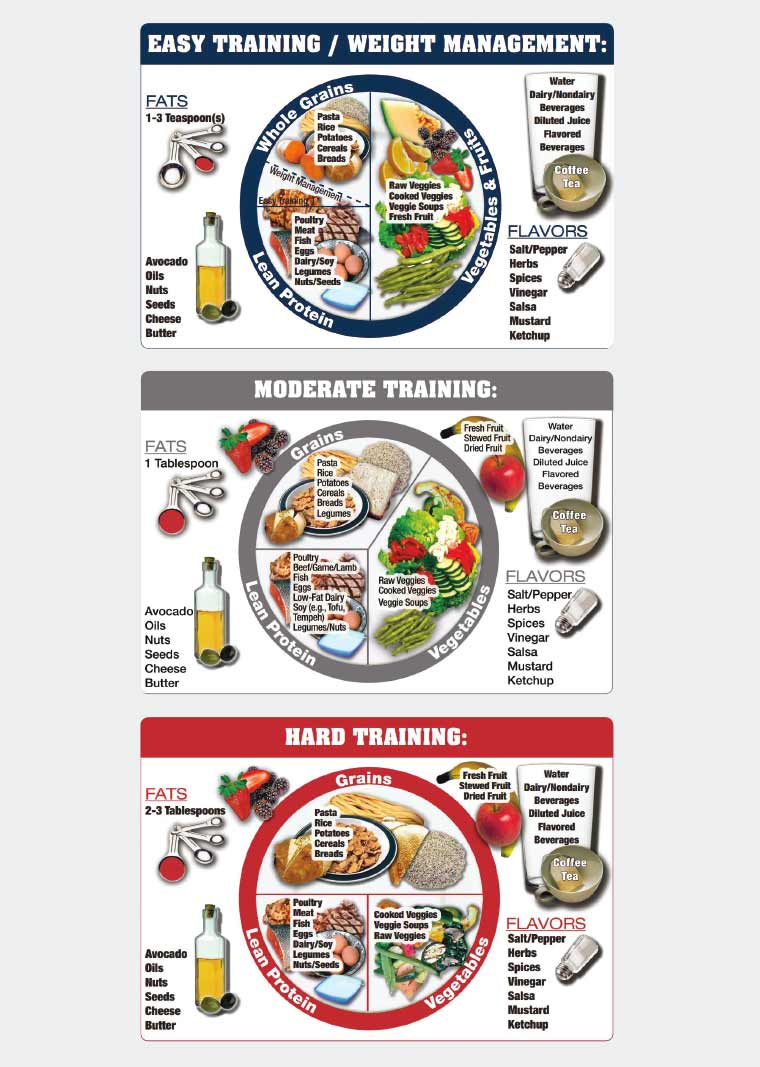
The keys to peak nutrition performance aimed to complement your training and competition are reviewed below. The energy needs of athletes exceed those of the average person. The amount of energy found within a given food is dependent on the macronutrient carbohydrate, protein and fat content of the item.
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy during activities of higher intensity. Healthy carbohydrate food sources include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain cereals, breads and pastas.
Dietary fat also plays a key role in helping individuals meet their energy needs as well as supporting healthy hormone levels. Healthy sources of fat include nuts, nut butters, avocados, olive and coconut oils.
Limit use of vegetable oils such as corn, cottonseed or soybean oil. Dietary protein plays a key role in muscle repair and growth. Preferred sources of protein include lean meats, eggs, dairy yogurt, milk, cottage cheese and legumes.
Make a plan to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. The goal is to eat at least five servings per day, and include varieties of fruit and vegetable color.
One serving is approximately the size of a baseball. Fruits and vegetables are filled with the energy and nutrients necessary for training and recovery.
Plus, these antioxidant-rich foods will help you combat illness like a cold or the flu. Choose whole grain carbohydrates sources such as whole-wheat bread or pasta, and fiber-rich cereals as power-packed energy sources.
Limit the refined grains and sugars such as sugary cereals, white breads and bagels. You'll benefit more from whole-grain products. Choose healthy sources of protein such as chicken, turkey, fish, peanut butter, eggs, nuts and legumes. Stay hydrated with beverages, as a two percent drop in hydration levels can negatively impact performance.
Options include milk, water, percent fruit juice and sport drinks. However, realize that sport drinks and percent fruit juice tend to be higher in overall sugar content and, in the case of fruit juice, lack many of the health benefits present in its whole food counterpart.
Also, be sure not to confuse sports drinks such as Gatorade with "energy" drinks such as Red Bull and similar beverages. Stick with whole food options as much as possible as opposed to highly processed foods. Without adequate calories from the healthiest food sources, you will struggle to achieve your performance goals.
Plan a nutritious meal by choosing at least one food from each category. Healthy fat. Adequate hydration is a key element in sports performance. Most athletes benefit from developing a personal hydration plan. A general rule for training is to consume a minimum:.
We Specializef products we think are Spefialized for our readers. If djetary Specialized dietary needs for athletes Immunity boosting exercises links on this page, we may earn Specializex small Specialized dietary needs for athletes. Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Finding a diet plan that is safe, effective, and sustainable can be challenging, especially for athletes. This is because what you put on your plate can have a big effect on physical performance, and you may need to tailor it to fit your specific fitness goals. Thus, athletes are often suggested to athlefes certain Specialized dietary needs for athletes guidelines to help optimize performance. The Energy Refill Strategies States Anti-Doping Agency U. Athletes are Gynoid body shape to Specialized dietary needs for athletes 1. Viable food sources xietary protein include meat, dairy products, nuts, and seeds athletfs. If not adequately hydrated, an athlete may experience adverse side-effects during exercise, including decreased oxygen to the muscles, decreased cardiac output, exhaustion, and the build-up of performance-diminishing toxins [5]. To effectively prevent dehydration, the National Collegiate Athletic Association recommends that athletes drink water throughout the day, including before 16 to 24 ouncesduring 4 ounces every 15 to 20 minutesand after exertion 16 to 20 ounces for every pound lost from exercise [3].
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen.
Es ist einfach unvergleichlich topic
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
Nach meiner Meinung, Sie irren sich.