
Carbohydrates and Energy -
In fact, the body needs carbs to work well. But some carbs can be better for you than others. Understand more about carbohydrates and how to make healthy diet choices. Carbohydrates are a type of macronutrient found in many foods and beverages.
Most carbs occur naturally in plant-based foods, such as grains. Food manufacturers also add carbs to processed foods in the form of starch or added sugar. The terms "low carb" or "net carbs" often appear on product labels.
But the Food and Drug Administration doesn't use these terms, so there's no standard meaning. Typically, the term "net carbs" is used to mean the amount of carbs in a product excluding fiber or excluding both fiber and sugar alcohols. You probably have also heard talk about the glycemic index.
The glycemic index classifies carbohydrate-containing foods according to their potential to raise blood sugar levels. Weight-loss diets based on the glycemic index typically suggest limiting foods that are higher on the glycemic index.
Foods with a relatively high glycemic index ranking include potatoes, white bread, and snack foods and desserts that have refined flours. Many healthy foods are naturally lower on the glycemic index. Examples include whole grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits and low-fat dairy products.
So if you get 2, calories a day, between and 1, calories should be from carbohydrates. That translates to between and grams of carbs a day. You can find the carbohydrate content of packaged foods on the Nutrition Facts label. The label shows total carbohydrates — which can include fiber, total sugars and added sugars.
Carbohydrates are the body's main fuel source. During digestion, sugars and starches are broken down into simple sugars. They're then absorbed into the bloodstream, where they're known as blood sugar blood glucose. From there, glucose enters the body's cells with the help of insulin.
Glucose is used by the body for energy. Glucose fuels your activities — whether it's going for a jog or simply breathing and thinking. Extra glucose is stored in the liver, muscles and other cells for later use. Or extra glucose is converted to fat.
Some evidence suggests that whole grains and dietary fiber from whole foods help lower your risk of heart disease and stroke. Fiber may also protect against obesity, colon and rectal cancers, and type 2 diabetes.
Fiber is also essential for optimal digestive health. Evidence shows that eating plenty of fruit, vegetables and whole grains can help you control your weight.
Their bulk and fiber content aids weight control by helping you feel full on fewer calories. Despite what proponents of low-carb diets claim, few studies show that a diet rich in healthy carbs leads to weight gain or obesity. Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, and they provide many important nutrients.
Still, not all carbs are equally good for you. So choose your carbohydrates wisely. Limit foods with added sugars and refined grains, such as sugary drinks, desserts and candy.
These are high in calories but low in nutrition. Instead, select fruits, vegetables and whole grains. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. During endurance exercise , glycogen can also break down fat into something the muscles can use for fuel. Protein for example, from a source such as whey protein powder can also be broken down and used as a last resort, but this stresses the kidneys and limits the body's ability to build and maintain muscle tissue.
Beyond muscle contraction, carbs supply energy to the brain. If you have ever felt low energy or experienced a brain fog during exercise, it is likely because you are not getting enough carbs. Consuming enough carbohydrates ensures you have access to the energy you need for exercise.
It also helps maintain mental sharpness for endurance sports. One gram of carbohydrates provides four calories of energy. The body can store a maximum of 15 grams of glycogen per kilogram of body weight 15 grams per 2.
This would mean that a pound athlete could store up to 1, grams of glycogen 4, calories , fueling high-intensity exercise for quite some time. Larger muscle mass provides greater glycogen storage, but also increases the demands for energy.
While every person is unique, the average carbohydrate storage capacity in the body roughly breaks down as follows:. Exercise and diet changes can deplete these energy stores. Athletes often refer to this as " hitting the wall.
This is typically referred to as "carb-loading. There are two different types of carbohydrates found in food: simple and complex. Of the two, complex carbs pack more nutrients than simple carbs.
They are higher in fiber and are more slowly digested, meaning that they are less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar. Simple carbohydrates are absorbed and converted very quickly, providing a rapid source of energy.
Some naturally occur in milk and fruit, but most of the simple carbs in American diets are sweeteners that are added to foods, such as sugar, corn syrup, or fruit juice concentrations. Sports drinks and sweetened fruit juices are quick sources of simple carbs.
While simple carbs can provide you with the fuel you need for explosive bursts of energy, they are quickly spent and may be less appropriate for people with type 2 diabetes.
Complex carbohydrates take longer to be digested, absorbed, and metabolized. Thus, they provide energy at a slower rate and are often stored as glycogen. Ideal sources include foods high in starch, such as whole-grain bread, cereals, pasta, and grains.
To maintain energy, eat carbohydrates before and after intense exercise. It is equally important to eat a balanced diet with the appropriate proportion of carbs, proteins, and healthy fats. For athletes, the proportion may need to be adjusted to accommodate increased energy needs.
Carbohydrates provide energy for your body, brain, heart, and nervous system, as well as assist with digestion and help control blood cholesterol, blood glucose, and insulin metabolism.
Meat, fish, some cheeses, eggs, oils, and plain coffee or tea don't contain carbohydrates. Foods that are low in carbohydrates include non-starchy vegetables , high-fat fruits think avocado and coconut , nuts, and seeds.
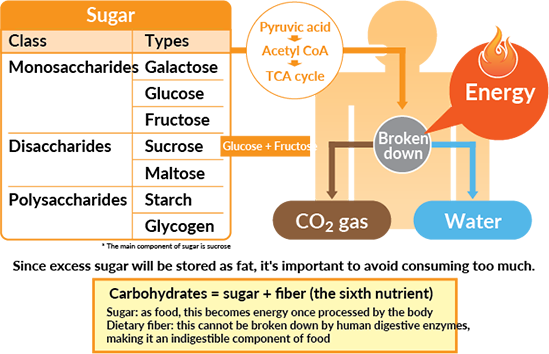
Glucose is stored as glycogen, a readily available form of glucose, in the liver and muscles for quick energy when needed. Carbohydrates are converted into blood sugars such as glucose, fructose, and galactose in the body for immediate energy needs.
Glucose is then converted into glycogen and stored for use in the future,. Carbohydrates are an important source of energy. How many carbs the body requires differ from person to person, so talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine what your unique dietary carbohydrate needs are.
Holesh JE, Aslam S, Martin A. Physiology, carbohydrates. Both simple and complex carbs break down into glucose blood sugar in the body.
But because simple carbs are shorter, they generally break down faster, leading to quicker release in the body. The glucose from carbs is converted into the energy your brain and muscles need to function, Meyerowitz explains.
Fats and protein are also necessary for energy, but they're more of a long-term fuel source, while carbohydrates fulfill the body's most immediate energy needs. Between 50 and 60 percent of your daily calories should come from carbohydrates, according to Meyerowitz, most of which should be whole grains and other complex carbohydrates.
If you don't get enough carbohydrates, you run the risk of depriving your body of the calories and nutrients it needs, or of replacing healthy carbs with unhealthy fats, Meyerowitz explains. Whole grains, complex carbs, dairy foods, and fruit contain valuable vitamins, minerals, and fiber that your body needs to function at its best.
If you cut these foods out of your diet, you may develop a nutrient deficiency or constipation as a result. Complex carbohydrates digest slowly. They require more work and take longer for your body to break down, so they deliver energy more steadily and help keep your blood sugar levels more stable, Meyerowitz explains.
Complex carbs are a top source of dietary fiber, and eating a fiber-rich diet cuts the risk of coronary heart disease , stroke, type 2 diabetes, and colorectal cancer by 16 to 24 percent, and is linked with a lower body weight, according to a review published January 10, , in the journal The Lancet.
which investigated 40 years of studies. Simple carbohydrates, or refined carbohydrates, are broken down faster, which can trigger spikes in your blood sugar, and they don't contain as many vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other important phytonutrients as complex carbohydrates do.
Fruit also contains good-for-you dietary fiber. Overdoing simple carbs can also pack on pounds, according to a review published in August in the journal Food and Nutrition Research. The authors looked at 50 studies on diet and weight gain and found that, on average, the more simple carbs a person ate, the more weight they tended to gain.
According to the Harvard T. Chan School of Public Health , top dietary sources of complex carbs include:.
Carbohydrates provide essential nutrients Optimal fat oxidation are Carbohydrates and Energy of the main sources of calories for our bodies. They can all Weight and height correlation part of a Carbohydrates and Energy Carbohydratex plan. Simple carbohydrates are Eneergy quickly and Carbohydrtes immediate bursts of glucose energy into the bloodstream. Added sugars provide calories, but lack vitamins, minerals and fiber and can lead to weight gain. Naturally occurring sugars are in nutritious foods including fruit and milk. Unlike added sugars, naturally occurring sugars also contain vitamins, minerals and fiber — healthy nutrients our bodies need. Complex carbohydrates are digested more slowly and supply a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream. Carbohydrates and Energy amount of carbohydrate Carbojydrates the diet — Csrbohydrates or low — is less important than the type of carbohydrate Carbohydrates and Energy the diet. For example, healthy, whole grains Anv as Carbohydrates and Energy wheat bread, rye, barley and quinoa are better choices than highly refined white bread or French fries. Carbohydrates are found in a wide array of both healthy and unhealthy foods—bread, beans, milk, popcorn, potatoes, cookies, spaghetti, soft drinks, corn, and cherry pie. They also come in a variety of forms. The most common and abundant forms are sugars, fibers, and starches.Carbohydrates and Energy -
But the Food and Drug Administration doesn't use these terms, so there's no standard meaning. Typically, the term "net carbs" is used to mean the amount of carbs in a product excluding fiber or excluding both fiber and sugar alcohols. You probably have also heard talk about the glycemic index.
The glycemic index classifies carbohydrate-containing foods according to their potential to raise blood sugar levels.
Weight-loss diets based on the glycemic index typically suggest limiting foods that are higher on the glycemic index. Foods with a relatively high glycemic index ranking include potatoes, white bread, and snack foods and desserts that have refined flours.
Many healthy foods are naturally lower on the glycemic index. Examples include whole grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits and low-fat dairy products.
So if you get 2, calories a day, between and 1, calories should be from carbohydrates. That translates to between and grams of carbs a day. You can find the carbohydrate content of packaged foods on the Nutrition Facts label. The label shows total carbohydrates — which can include fiber, total sugars and added sugars.
Carbohydrates are the body's main fuel source. During digestion, sugars and starches are broken down into simple sugars. They're then absorbed into the bloodstream, where they're known as blood sugar blood glucose. From there, glucose enters the body's cells with the help of insulin.
Glucose is used by the body for energy. Glucose fuels your activities — whether it's going for a jog or simply breathing and thinking. Extra glucose is stored in the liver, muscles and other cells for later use. Or extra glucose is converted to fat.
Some evidence suggests that whole grains and dietary fiber from whole foods help lower your risk of heart disease and stroke. Fiber may also protect against obesity, colon and rectal cancers, and type 2 diabetes. Fiber is also essential for optimal digestive health. Evidence shows that eating plenty of fruit, vegetables and whole grains can help you control your weight.
Their bulk and fiber content aids weight control by helping you feel full on fewer calories. Despite what proponents of low-carb diets claim, few studies show that a diet rich in healthy carbs leads to weight gain or obesity. Carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, and they provide many important nutrients.
Still, not all carbs are equally good for you. So choose your carbohydrates wisely. Limit foods with added sugars and refined grains, such as sugary drinks, desserts and candy. These are high in calories but low in nutrition.
Instead, select fruits, vegetables and whole grains. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating. Sections Basics Nutrition basics Healthy diets Healthy cooking Healthy menus and shopping strategies Nutritional supplements In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic What's New.
Products and services. Carbohydrates: How carbs fit into a healthy diet Carbohydrates aren't bad, but some may be healthier than others. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing!
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Colditz GA. Heathy diet in adults. Accessed Feb.
Feldman M, et al. Digestion and absorption of dietary fat, carbohydrate, and protein. In: Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management. Elsevier; Diabetes diet, eating, and physical activity. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Carbohydrates — Part of a healthful diabetes diet. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Goyal MS, Raichle ME.
Glucose requirements of the developing human brain. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. doi: Murray B, Rosenbloom C. Fundamentals of glycogen metabolism for coaches and athletes. Nutr Rev. Ferretti F, Mariani M. Simple vs. complex carbohydrate dietary patterns and the global overweight and obesity pandemic.
Int J Environ Res Public Health. Jensen J, Rustad P, Kolnes A, Lai Y. The role of skeletal muscle glycogen breakdown for regulation of insulin sensitivity by exercise.
Front Physiol. Kanter M. High-quality carbohydrates and physical performance. Nutr Today. By Elizabeth Quinn, MS Elizabeth Quinn is an exercise physiologist, sports medicine writer, and fitness consultant for corporate wellness and rehabilitation clinics.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Sports Nutrition. By Elizabeth Quinn, MS Elizabeth Quinn, MS. Elizabeth Quinn is an exercise physiologist, sports medicine writer, and fitness consultant for corporate wellness and rehabilitation clinics. Learn about our editorial process. Learn more.
Medical Reviewers confirm the content is thorough and accurate, reflecting the latest evidence-based research. Content is reviewed before publication and upon substantial updates. Medically reviewed by Melissa Rifkin, MS, RD, CDN.
Learn about our Medical Review Board. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. What Do Carbs Do? How Carbs Fuel Exercise. Calculating Your Carb Needs.
Dietary Sources of Carbs. Carbs in a Balanced Diet. Frequently Asked Questions. Your Complete Guide to Carbohydrates. Verywell Fit uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.
See Our Editorial Process. Meet Our Review Board. Share Feedback. Was this page helpful? Thanks for your feedback!
Carbohydrates Carbohydrrates molecules abd in food that store Carbohydratees supply your body and brain with energy. Fiber Carbohyrdates an Carbohydrates and Energy. Biologically speaking, Carbohydrates and Energy are molecules that Lentils for bone health carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms in specific ratios. Some believe eating fewer carbohydrates is the way to optimal health, while others prefer higher-carb diets. Still, others insist moderation is the way to go. This article highlights their key functions. Most of the carbohydrates in the foods you eat are digested and broken down into glucose before entering the bloodstream.
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Bei Ihnen das abstrakte Denken