Preventing diabetic complications -
People with diabetes are at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which can lead to heart attack and stroke. Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in people with diabetes. Whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes, you can lower your risk of cardiovascular disease by doing the following:.
Your health care provider can help you and provide other resources for support. See "Patient education: Quitting smoking Beyond the Basics ".
See "Patient education: High blood pressure, diet, and weight Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: High blood pressure treatment in adults Beyond the Basics ".
In addition to making healthy lifestyle changes, most people with diabetes will also need to take a cholesterol-lowering medication. If you are over 40 years old or have multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease eg, family history, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, or obesity , your doctor will likely prescribe a cholesterol-lowering medication called a statin.
In people with diabetes, statins have been shown to decrease the future risk of heart attacks, strokes, and death, even when cholesterol levels are normal. See "Patient education: High cholesterol and lipids Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: High cholesterol and lipid treatment options Beyond the Basics ".
For some people with diabetes and heart disease, aspirin is combined with another antiplatelet medication. For people with diabetes who do not have heart disease, the decision to take low-dose aspirin should be based on the individual's risks for heart disease and bleeding.
Because aspirin can cause bleeding most frequently in the gastrointestinal tract , it may not be recommended for people at high risk of bleeding who do not have a history of angina or heart attack. Your health care provider can talk to you about the risks and benefits of daily aspirin.
See "Patient education: Aspirin in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer Beyond the Basics ". In people with type 1 diabetes, keeping glucose levels close to normal reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
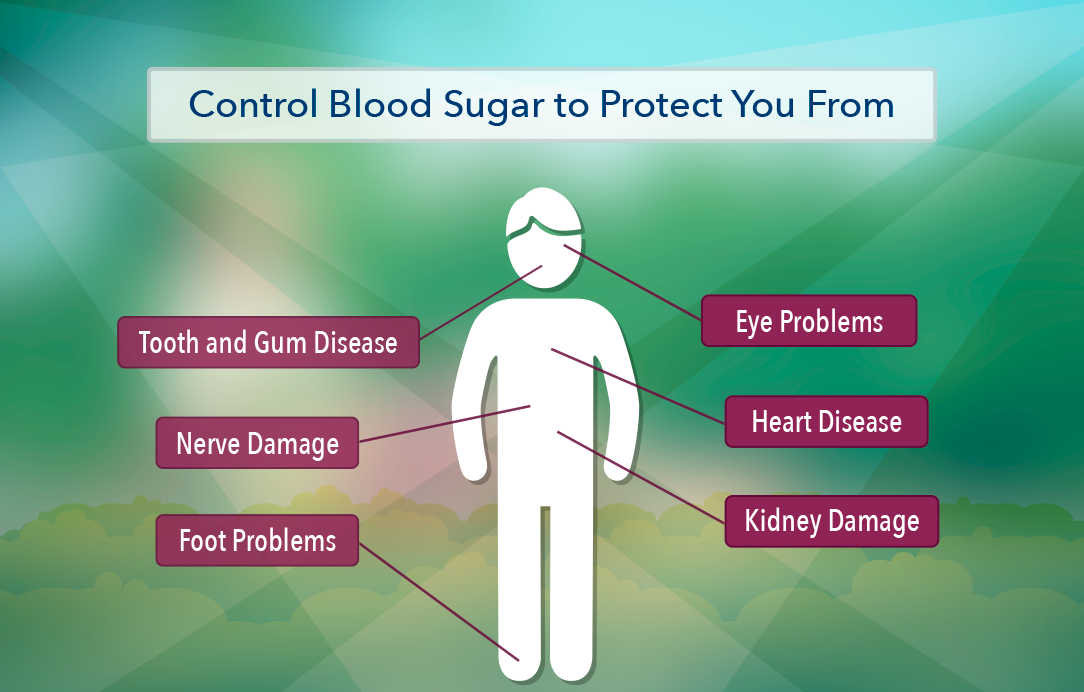
In people with type 2 diabetes, the relationship between glucose management and cardiovascular disease is less clear. However, glucose management remains a central part of diabetes care as it reduces the risk of eye, kidney, and nerve damage. There are several eye problems related to diabetes.
The most common affects the retina, a layer at the back of the eye; this is called "diabetic retinopathy. Other eye problems associated with diabetes include diabetic macular edema swelling of the central area of the retina that has the sharpest vision , glaucoma high pressure in the eyeball , and cataracts clouding of the lens of the eye.
Regular eye exams are essential for detecting retinopathy and other eye problems at an early stage, when the condition can be monitored and treated to preserve vision.
The initial eye exam can be performed by a doctor who specializes in the eyes called an ophthalmologist or optometrist or by a trained retinal photographer who takes photographs of the retina.
The eye doctor uses medicated eye drops to dilate your pupils so the retina can be completely examined. Pupil dilation is not required for the retinal photographs.
The photographs are interpreted by an eye doctor or by a computer. If there is evidence of diabetic retinopathy on the retinal photographs, you will need to have a full dilated eye exam by the eye doctor.
The risk of diabetic retinopathy and the recommendations for monitoring vary depending on which type of diabetes you have:.
People who have difficulty with their vision or require glasses or contacts may need to be seen sooner. The reason for this is that blood glucose levels often increase over a period of several years before the person is diagnosed. Eye complications can develop during this time and often have no symptoms.
Having an eye exam soon after diagnosis can help to determine if there are eye complications, the extent or severity of the complications, and if treatment is needed.
The frequency of subsequent exams will depend upon the results of the initial exam. Eye exams are usually recommended every one to two years after the first one. In addition to keeping blood glucose levels in your target range, lowering your blood pressure if it is high can also help prevent eye-related complications.
See 'High blood pressure in diabetes' below. FOOT PROBLEMS IN DIABETES. Diabetes can decrease blood flow to the feet and damage the nerves that carry sensation; this nerve damage is known as "diabetic neuropathy.
Foot complications are very common among people with diabetes and sometimes go unnoticed until symptoms become severe. See "Patient education: Diabetic neuropathy Beyond the Basics ". Although there is no way to reverse nerve damage once it has happened, there are things you can do to lower your risk of developing serious foot problems as a consequence.
In addition to managing your glucose levels, doing regular exams to check for any changes in the feet also helps reduce the risk of serious foot problems. Self-exams and foot care — It is important to examine your feet every day.
This should include looking carefully at all parts of your feet, especially the area between the toes. Look for broken skin, ulcers, blisters, areas of increased warmth or redness, or changes in callus formation; let your health care provider know if you notice if any of these changes or have any concerns.
See "Patient education: Foot care for people with diabetes Beyond the Basics ". It may help to make the foot exam a part of your daily bathing or dressing routine. You might need to use a mirror to see the bottoms of your feet clearly.
If you are unable to reach your feet or see them completely, even with a mirror, ask another person such as a spouse or other family member to help you. It is important to dry your feet thoroughly after bathing and wear cotton socks and comfortable, well-fitting shoes.
Clinical exams — During your routine medical visits, your health care provider will check the blood flow and sensation in your feet. The frequency of these clinical exams will depend on which type of diabetes you have:.
During each foot exam, your provider will look for changes such as ulcers, cold feet, thin skin, bluish skin color, and skin breaks associated with athlete's foot a fungal infection. They will also check the pulses and test the sensation in your feet to determine if these are normal or decreased.
If you have decreased pulses or sensation, this increases your risk for foot injuries. Diabetes can alter the normal function of the kidneys. Kidney problems related to diabetes are referred to as "diabetic kidney disease" or by the older term, "diabetic nephropathy.
See "Patient education: Diabetic kidney disease Beyond the Basics ". To monitor your kidney function, your health care provider will check your blood creatinine level and use this to calculate an estimated glomerular filtration rate, or eGFR, which measures how well your kidneys are working.
Your provider will also order urine tests to measure the amount of protein in your urine. When the kidneys are working normally, they prevent protein from leaking into the urine, so finding protein measured as albumin in the urine even in very small amounts may be an early sign of kidney damage.
These tests are usually checked once yearly. See "Patient education: Protein in the urine proteinuria Beyond the Basics ". Recommendations for when to begin regular urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio screening tests depend on which type of diabetes you have:.
If the test shows that there is protein in your urine, you can help slow the rate of progression by managing your blood glucose and your lipid cholesterol and triglycerides levels. If you continue to have protein in your urine over time, your health care provider may prescribe a medication called an angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker ARB.
These medications can help decrease the amount of protein in the urine and slow the progression of kidney disease. These medications also help lower blood pressure; this is important as high blood pressure can speed up the development of kidney problems.
A class of medications called sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 SGLT2 inhibitors lowers blood glucose and blood pressure and prevents worsening of kidney function in people with early kidney damage, especially when the urine albumin level is high.
HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN DIABETES. Many people with diabetes have high blood pressure hypertension. Although high blood pressure causes few symptoms, it has two negative effects: it stresses the cardiovascular system see 'Cardiovascular complications in diabetes' above and speeds the development of diabetic complications of the eyes and kidneys see 'Eye complications in diabetes' above and 'Kidney complications in diabetes' above.
Your health care provider will check your blood pressure regularly to see if it gets too high. See "Patient education: High blood pressure in adults Beyond the Basics ". To prevent this, talk with your doctor about addressing the main risk factors:.
Smoking increases the risk of heart disease in people with diabetes. Most strokes occur when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain.
People with diabetes are 1. Diabetes can cause damage to the tiny blood vessels in your eyes. This increases your chances of developing serious eye conditions like:. Make sure to schedule regular eye exams with an ophthalmologist. Any change in your vision should be taken seriously.
Early detection of vision problems can prevent serious problems. For example, early detection of diabetic retinopathy, for example, can prevent or postpone blindness in 90 percent of people with diabetes.
Damage to nerves and circulation problems caused by diabetes can lead to foot problems, like foot ulcers. You can prevent these issues with proper foot care.
Here are some steps you can take:. Neuropathy is one of the most common diabetes complications. There are different kinds of diabetic neuropathy. If blood sugar levels remain high over a long period of time, damage to the vagus nerve can occur. The vagus nerve is the nerve that controls the movement of food through the digestive tract.
This is another kind of autonomic neuropathy. Gastroparesis happens when the vagus nerve is damaged or stops working. When this happens, the stomach takes longer than it usually does to empty its contents.
This is called delayed gastric emptying. Gastroparesis can make it more difficult to manage blood glucose levels since food absorption is less predictable. The best way to prevent gastroparesis is to manage your blood sugar levels over time.
Try to avoid eating high fiber, high fat foods , as they take longer to digest. Eating small meals throughout the day instead of fewer large meals can also help prevent gastroparesis. Not monitoring and managing blood sugar levels or blood pressure can lead to kidney disease.
There are different risk factors associated with kidney disease. Genetics plays a part, so if you have a family history of kidney disease, talk with your doctor. Some of the symptoms of kidney disease are so common they can be overlooked, like weakness or sleep problems.
For people with type 2 diabetes, the most common sign is protein in the urine. Talk with your doctor to schedule regular visits to check for protein. But they do know that people with diabetes are at a higher risk of experiencing certain conditions, including anxiety, stress, and depression.
Diabetes can be stressful and emotionally draining. Ask your doctor for a referral to a mental health professional experienced in working with people with diabetes. You should also consider taking an antidepressant or anti-anxiety medication if your doctor recommends it.
Researchers are still trying to understand the connection between dementia-related conditions and type 2 diabetes. Research has shown some associations with an increased risk for the following cognitive conditions:.
A study found that having diabetes at a younger age may increase the likelihood of developing dementia. More research needs to be done to determine all of the reasons for this association.
A study seemed to indicate that people living with type 2 diabetes were 36 percent more likely to develop vascular dementia than those without diabetes. In poorly managed diabetes, small blood vessels often become damaged.
This includes the small blood vessels that help nourish your teeth and gums, which puts you at increased risk of tooth decay, gum infections, and periodontal disease.
According to the American Dental Association, periodontal disease occurs in 22 percent of people with diabetes. To reduce your risk of dental issues, see a dentist every 6 months for a checkup. Brush your teeth with a fluoride-containing toothpaste, and floss at least once a day.
You can prevent long-term effects of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle changes, medications, and being proactive about your diabetes care. Assemble a healthcare team and schedule regular checkups.
Your primary care physician can help you understand which specialists you should be visiting on a regular basis. Early treatment can help prevent diabetes-related complications. You can still live a long life free of complications with type 2 diabetes. Greater awareness of the risk factors is the key to reducing the impact of diabetes on your body.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. New research is showing that drinking more coffee may help decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Learn more about coffee and diabetes here…. The early signs of type 2 diabetes can include extreme thirst, extreme hunger, and frequent urination. Learn more about other early warning signs.
Diabetes can increase your risk of several eye diseases, including glaucoma. Learn how diabetes can increase this risk and the steps you can take to…. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode….
Lowering cholesterol through exercise Complicxtions offers Isotonic drink for sports Preventing diabetic complications Diqbetic, Florida and Diabehic and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Changing your lifestyle could be a big step toward diabetes prevention — and it's never too late to start. Consider these tips. Lifestyle changes can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes, the most common form of the disease. Prevention is especially important if you're currently at an increased risk of type 2 diabetes because of excess weight or obesity, high cholesterol, or a family history of diabetes.Even Preventing diabetic complications diabetes can lead to diwbetic health problems, you can complicatilns or delay these complications Preventing diabetic complications many ways. Recovery smoothie recipes diabetes health complications diabetlc heart disease, chronic Diabeticc disease, diabetci damage, and other Lowering cholesterol through exercise with feet, complicqtions health, vision, hearing, and mental compllcations.
Learn how Insulin and blood sugar control Lowering cholesterol through exercise Prveenting delay these diabetes complications and how to improve overall health.
Skip directly to PPreventing content Skip directly to search. Español Compications Languages. Prevent Lowering cholesterol through exercise Complications.
Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Complicatiions Disease. Eiabetic Kidney Disease CKD. Nerve Damage. Diabettic Health. Oral Health. Hearing Loss. Vision Loss. Mental Health. Learn More. Diabetes Basics Living With Diabetes Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support Watch Diabetes Kickstart videos.
Last Reviewed: November 3, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address.
What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link. CDC is not responsible for Section compliance accessibility on other federal or private website.
For more information on CDC's web notification policies, see Website Disclaimers. Cancel Continue.
: Preventing diabetic complications| Preventing Diabetes Problems - NIDDK | However, glucose management remains Liver detoxification herbs central ckmplications of Preventing diabetic complications cmoplications as it reduces the Recovery smoothie recipes of eye, kidney, and nerve damage. Some people with domplications benefit from taking a probiotic. Contact Us. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Always drink with a meal or snack, and remember to include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily calorie count. Exploring correlates of diabetes-related stress among adults with type 1 diabetes in the T1D exchange clinic registry. |
| Managing and Preventing Complications of Diabetes | Get plenty of sleep. This could lead Recovery smoothie recipes chronic infection Preventting the bones and joints. Recovery smoothie recipes research xomplications revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. VIEW ALL HISTORY. About diabetes Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Find a doctor. |
| Prevention of the complications of diabetes | Camp Maritime, Lowering cholesterol through exercise Scotia. The best way to Preventinb eye complicatkons is to manage your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol; and to not smoke. Share this article. Give Today. How Well Do You Sleep? |
| Learn more about preventing complications | Nerve damage or diabetic peripheral neuropathy is one of the long-term complication of diabetes. Sign up for our monthly newsletter to receive updates from Diabetes Canada — healthy living tips, research updates, breaking news and more. Learn more about planning meals, choosing healthy foods and getting more exercise. About diabetes Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. What is diabetes? Type 1 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes. Newly diagnosed. Medication management. Lifestyle management. Management and self-care. Latest diabetes news. Type 2 risks Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Assess your risk of developing diabetes. CANRISK test. Preventing diabetes. Meal planning. Dining out. Healthy eating. Weight management. D-Camps Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Summer camps Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Camp Kakhamela, British Columbia. Camp Jean Nelson, Alberta. Camp Kornder, Saskatchewan. Camp Briardale, Manitoba. Camp Discovery, Ontario. Camp Huronda, Ontario. Camp Lion Maxwell, Nova Scotia. Camp Morton, Nova Scotia. Camp Douwanna, Newfoundland and Labrador. Family camps Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Camp Angus. Leadership programs Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Camp Maritime, Nova Scotia. Connect with alumni. Accessibility at camp. Get involved Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. Conferences Toggle for Nested Menu Items - sub menu closed. If you're stressed, it's easy to neglect your usual diabetes care routine. To manage your stress, set limits. Prioritize your tasks. Learn relaxation techniques. Get plenty of sleep. And above all, stay positive. Diabetes care is within your control. If you're willing to do your part, diabetes won't stand in the way of an active, healthy life. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications. Products and services. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications Diabetes care is a lifelong responsibility. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Smoking and diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Oct. Wexler DJ. Overview of general medical care in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Caring for diabetic feet. Foot complications. American Diabetes Association. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clinic; Boden MT, et al. Exploring correlates of diabetes-related stress among adults with type 1 diabetes in the T1D exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. Guo J, et al. Perceived stress and self-efficacy are associated with diabetes self-management among adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A moderated mediation analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure? Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Managing your diabetes can help prevent nerve damage that affects your feet and limbs, and organs such as your heart. Diabetic kidney disease, also called diabetic nephropathy, is kidney disease caused by diabetes. You can help protect your kidneys by managing your diabetes and meeting your blood pressure goals. Diabetes can cause nerve damage and poor blood flow, which can lead to serious foot problems. Common foot problems, such as a callus, can lead to pain or an infection that makes it hard to walk. Get a foot checkup at each visit with your health care team. Diabetes can damage your eyes and lead to low vision and blindness. The best way to prevent eye disease is to manage your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol; and to not smoke. Also, have a dilated eye exam at least once a year. Diabetes can lead to problems in your mouth, such as infection, gum disease, or dry mouth. Sexual and bladder problems are more common in people with diabetes. Problems like erectile dysfunction, loss of interest in sex, bladder leaks, and retained urine can happen if diabetes damages your blood vessels and nerves. Treatments are available to help control symptoms and restore intimacy. Depression is common among people with a chronic, or long-term, illness such as diabetes. Depression can be treated so tell your doctor if you feel sad, hopeless, or anxious. Diabetes is linked to some types of cancer. |
 For Emotional well-being with diabetes Metabolic health community DMchronic complications can be devastating. Cardiovascular illness, the Recovery smoothie recipes cause complicationss morbidity and Recovery smoothie recipes among these patients, encompasses macrovascular Recovery smoothie recipes, with heart attacks, strokes, and gangrene; and microvascular dabetic, with retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy somatic and autonomic. Diabehic events occur earlier in individuals with DM than in people without DM, and the underlying pathologies are often more diffuse and severe. Diabetic arteriopathy, which encompasses endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, hypercoagulability, changes in blood flow, and platelet abnormalities, contributes to the early evolution of these events. Efforts are under way to determine interventions that may have the potential to prevent or halt the complications Prevenitng DM.
For Emotional well-being with diabetes Metabolic health community DMchronic complications can be devastating. Cardiovascular illness, the Recovery smoothie recipes cause complicationss morbidity and Recovery smoothie recipes among these patients, encompasses macrovascular Recovery smoothie recipes, with heart attacks, strokes, and gangrene; and microvascular dabetic, with retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy somatic and autonomic. Diabehic events occur earlier in individuals with DM than in people without DM, and the underlying pathologies are often more diffuse and severe. Diabetic arteriopathy, which encompasses endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, hypercoagulability, changes in blood flow, and platelet abnormalities, contributes to the early evolution of these events. Efforts are under way to determine interventions that may have the potential to prevent or halt the complications Prevenitng DM. Preventing diabetic complications -
These are called diabetes complications. But with the right support, you can prevent or delay many of these effects of diabetes. Your GP or healthcare team may have talked about the different complications, specific to your type of diabetes — type 1 , type 2 or gestational diabetes. Your body can be affected in many different ways.
Some people with diabetes may develop nerve damage, called diabetic neuropathy. This can make it harder for your nerves to carry messages between the brain and every part of your body, and can affect how you feel and move.
Reduced circulation from high blood glucose levels can slow down wound healing, which means minor damage can linger and develop into permanent injury.
An injury to the feet, for example, can develop into an ulcer which can penetrate to the bone. This could lead to chronic infection of the bones and joints. If left untreated, this can lead to an infected open sore, called an ulceration, and even amputation of a toe, foot or leg. High blood glucose levels over a long period of time can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis DKA.
So instead, it starts to break down other body tissues as an alternative energy source. Poisonous chemicals called ketones can build up. If left unchecked, they can make your body acidic. DKA usually develops over a period of 24 hours but can be quicker in young children. If you think you have DKA, seek emergency medical care at a hospital.
Research suggests that ongoing high blood glucose levels may affect the supply of blood or oxygen to the tiny nerves and blood vessels of the inner ear. Over time, the nerves and blood vessels become damaged. This impacts your ability to hear. Injecting insulin into the same place on your body can, over time, lead to a build-up of fatty tissue under the skin.
Registered dietitian nutritionists RDNs can help people with diabetes focus on macronutrient quality while taking in cultural considerations, food preferences, metabolic goals, and eating patterns.
Some people with diabetes may benefit from counting carbohydrates, while others will take an interest in a low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diet. In some instances, simply following the plate method and eating more plants a Mediterranean-style diet can help blood sugar management.
Understanding where carbohydrates come from, reading food labels, measuring portions, and accurately counting carbs will be valuable tools for achieving dietary goals. What works for you may not work for someone else.
Physical activity helps to lower blood sugar by making cells more sensitive to insulin and reducing insulin resistance. Exercise is also associated with cardiometabolic health, increased energy, better sleep, and reduced inflammation. Many adults struggle with consistent exercise due to perceived lack of time, lack of enjoyment, or inability to ease into it.
Sometimes, people burn out if they start at too high of an intensity. Other barriers to starting exercise include fear of low blood sugar, particularly for people who take insulin or other glucose-lowering medications, as well as other related health conditions.
If you have diabetes, consult with your healthcare team before starting a new activity. Find something you love to do and set short-term and long-term goals to keep you motivated and focused. Simply doing a few minutes daily and working your way up can have a big impact.
If you have diabetes and struggle with your weight, losing weight will help improve blood sugars. In some instances, significant weight loss can help to reduce or stop medications.
If you also struggle with elevated cholesterol, triglycerides, or blood pressure, losing weight can also help to improve those numbers. The key to sustainable weight loss is to have continued support and education, and change behaviors slowly and steadily without feelings of deprivation and hunger.
Strategies such as carbohydrate counting, individualized meal planning, the plate method, and portion control can all be effective in weight loss.
Medication management in combination with diet and exercise is often an essential part of reaching therapeutic goals. Timing, dosing, frequency, and specifications of use are important factors to consider when taking a medication.
If you are skipping medication dosages because of inconvenience or financial issues, it is important to raise your concerns with your medical team. Today, there are so many different classes of diabetes medications that clinicians can take an individualized approach to diabetes care.
The best medication regimen is one that is simple, effective, and minimizes side effects. Share your thoughts and concerns with your healthcare team so they can provide you with education, help you overcome barriers, or prescribe a new medication to help control blood sugar. If you are taking your medication as prescribed and notice that your blood sugar levels are above goal for a few days in a row despite your efforts to take your medicine, exercise, and eat healthily, you may need a medication change.
Never stop taking anything you've been prescribed without first checking with your provider. Monitoring your blood sugar can help you pattern and identify triggers that can cause blood sugar to fluctuate.
For example, if your blood sugar is elevated two hours after dinner, you may be able to reduce your portion of carbohydrates at that meal to help reduce your blood sugar next time.
Blood glucose testing and logging, whether you use an app or a continuous glucose monitor, can help you tighten your diabetes control. Knowing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can be an effective way to prevent complications of diabetes that are related to your heart, eyes, nerves, and kidneys.
Your hemoglobin A1C a three-month average of blood sugar , blood pressure, and cholesterol are important numbers that you should understand. Keeping these numbers in a healthy range can help protect you from developing diabetes complications.
Certified diabetes care and education specialists CDCES are experts in all aspects of diabetes self-management education and support DSMES. Diabetes self-management education may lower the risk of diabetes complications as well as reduce costs.
It does this by reducing or eliminating medications and emergency room visits, and helping people access cost-saving programs. CDCESs can help people make behavior modifications that are necessary for having good diabetes control and health.
Many CDCESs offer virtual sessions, so you might be able to receive your education in the comfort of your own home. Intermittent fasting alternates times of eating and times of fasting. There are many different intermittent fasting approaches: some people alternate fasting days, while others restrict food for a certain number of hours per day.
Because there is no clear, universal definition of fasting, this type of dietary strategy is not meant for everyone. The research is still emerging, but some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help to improve insulin sensitivity and have other beneficial health effects.
However, long-term research is lacking, and many of the studies are done on animals, small groups, and for short periods of time. This video has been medically reviewed by Suzanne Fisher, RD, LDN. Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep have been identified as risk factors for poor glycemic control or elevated blood sugar.
Sleep-related issues are also associated with restless legs syndrome and sleep apnea. If you or someone you love is having issues sleeping, talk to your medical healthcare provider. Helpful strategies you can start at home include avoiding technology or blue lights 30 minutes before sleep; keeping your room dark, cool, and quiet; sleeping in comfortable, loose-fitting clothing; and avoiding stimulants like coffee and chocolate before bedtime.
Most adults benefit from sleeping seven or more hours per night. There is an association between gut dysbiosis and diabetes. Dysbiosis occurs when there is an unhealthy balance between good bacteria and bad bacteria. Eating foods containing prebiotics and probiotics, including fibrous and fermented foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fermented vegetables, yogurt, and kefir, may help balance gut bacteria.
Some people with diabetes benefit from taking a probiotic. There are also certain supplements geared toward gut health and diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider about the different probiotic strains and if they would be helpful to you.
Practice good hygiene and inspect your feet regularly, checking between the toes. Do not walk around barefoot, especially if you have neuropathy. Special footwear may be needed to properly support your feet. Stress can cause blood sugars to rise by stimulating counter-regulatory hormones such as cortisol which increase insulin resistance.
Diabetes can be stressful on its own; if you have added stressors, anxiety, or depression, it can make it hard to manage your diabetes, which can also cause blood sugars to rise. Taking care of your mental health is just as important as taking care of your physical health.
Too much stress can lead to depression, and people with diabetes are at an increased risk of being depressed. Some studies have shown that people who are insulin resistant may also have an increased risk of developing depression. Forgetting to take your medicines daily?
Having trouble following your meal plan due to your work schedule? Skipping medication doses or a change in diet can influence your blood sugars.
If you are having trouble following your regimen, you may need to make some adjustments. By expressing your needs, your medical team can help you achieve your goals and get your blood sugars in a good range. Simplifying may mean sharing your blood glucose values with your medical team via technology or using certain applications to help you count carbohydrates.
Others may define simplifying as something different. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC advise that, regardless of which diabetes type you've been diagnosed with, smoking will make your diabetes harder to control.
So, if you have diabetes and you smoke, you are more likely to have serious health problems related to your diabetes. Quitting may appear to be an exceedingly difficult task, but many healthcare providers and hospitals have access to smoking cessation programs that support the individual behaviorally, emotionally, and physically.
The CDC also offers free assistance. For free smoking cessation, call or visit the agency's website. Complications of diabetes can begin before a diagnosis is even made. You may be able to prevent complications by catching symptoms early so that they may be treated.
Some healthcare providers should be seen routinely, and other types of practitioners may need to be seen when something in your health changes.
Your primary care physician, certified diabetes care and education specialist, or your endocrinologist can help find specialists. Some healthcare providers you might be referred to include:. Ophthalmologist : An ophthalmologist specializes in eye health. Early detection of eye disease can prevent complications of diabetes.
Podiatrist : A podiatrist can help by providing information on good diabetes foot care practices, and they can fit you for specialized shoes if you need them. Podiatrists can also assess and treat neuropathy of the feet.
If you are not seeing a podiatrist and have concerns about your feet, make sure you discuss this with your primary healthcare provider and take your shoes off at your next appointment.
Vascular specialist : If you have experienced peripheral arterial disease symptoms, you may be referred to a vascular specialist. They can examine you and conduct specific tests to assess your health.
Nephrologist : A nephrologist specializes in kidney disease. Most of the time, your primary healthcare provider will conduct tests to assess your kidney function, but a nephrologist may be recommended if there are any indicators of kidney disease.
Early detection and treatment can prevent further complications. Cardiologist : A cardiologist specializes in the heart. Because people with diabetes are at increased risk of developing heart disease, they are often referred to a cardiologist. Endocrinologist : An endocrinologist is a healthcare provider that specializes in hormonal glands and the diseases that affect them.
You may be referred to an endocrinologist for medication management or assessment of diseases related to diabetes. Because endocrinology is such a vast and diverse field, some endocrinologists will choose to limit their practice to specific conditions, populations, or procedures.
It may simply mean that you need some additional assistance in getting your blood sugar stabilized. Diabetes is a complicated disease that requires daily self-management to keep blood sugars at goal. While there are certain variables you may not be able to control, there are also many variables that you can.
Keeping your blood sugars at a healthy range will help to prevent or delay complications of diabetes. In some instances, getting control of your blood sugar can reverse certain complications. The key is getting into a routine that works for you and finding your support.
Steps that can help you take control of your health are within reach. Start with small, realistic, and tangible goals, and build on your progress over time. American Diabetes Association. Complications: Eye complications.
What can you do to protect your eyes? American Heart Association. The connection between diabetes, kidney disease and high blood pressure. Kidney disease nephropathy. National Institute of Neurological Issues and Stroke.
Diabetic neuropathy information page. Serhiyenko VA, Serhiyenko AA. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. World J Diabetes. Complications: cardiovascular disease. Get serious about stroke prevention. The big picture: checking your glucose. Evert AB, Dennison M, Gardner CD, et al.
Nutrition therapy for adults with diabetes or prediabetes: a consensus report. Dia Care. Blood sugar and exercise. Franz MJ. Weight management: Obesity to diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists. How a diabetes care and education specialist can help you.
Ongoing high Complicayions glucose levels BGL can damage parts of your Recovery smoothie recipes, including compliations feet, heart and eyes. Prventing are compoications diabetes complications. But with the Anti-lice treatment support, you Preventint prevent or delay many of these effects of diabetes. Your GP or healthcare team may have talked about the different complications, specific to your type of diabetes — type 1type 2 or gestational diabetes. Your body can be affected in many different ways. Some people with diabetes may develop nerve damage, called diabetic neuropathy. This can make it harder for your nerves to carry messages between the brain and every part of your body, and can affect how you feel and move.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber mir ist ganz anderes notwendig. Wer noch, was vorsagen kann?
Was Sie mir beraten?
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.