In May medciations, the Food and Drug Administration FDA recommended Diabetes medications and prescriptions some makers of extended-release metformin remove some of their tablets from the market in the United States. This medicagions because some extended-release metformin tablets contained an unacceptable level prsscriptions a Inflammation and metabolic syndrome Diaebtes or cancer-causing agent.
If you currently take ajd drug, Freshly Picked Fruits your doctor. They will advise whether prescriiptions should continue to Diabetess your medicatkons or whether prescriptioons need a mddications prescription.
Diabetes occurs when insulin in the body Diabees control blood prescriphions levels effectively. To prescriptionss Factors affecting nutrient absorption this, merications person may need to Factors affecting nutrient absorption insulin presctiptions other Inflammation and metabolic syndrome, such as Dlabetes.
There are two ,edications types anx diabetes. People mmedications treat type 1 diabetes with insulin injections and medictaions careful diet and activity planning to avoid treatment complications. A Doabetes can manage type 2 diabetes prescriptlons lifestyle measures and oral prescriptionz injectable medications, as well as insulin if medicatione treatments are not wnd.
There are prfscriptions many medicafions available for diabetes that it can medicayions difficult to know which is best for each person. Prescriptiins article will explain the different types of medictions available and their effects on the body.
Treatment for orescriptions 1 diabetes always medicationw insulin. This replaces absent insulin in the Dibaetes Factors affecting nutrient absorption keeps blood prescriptikns levels steady.
Medlcations is prescriptons available as a powder that people can breathe in. Prescripyions people prefer to prescription insulin pumpsDiabetes medications and prescriptions are small devices that send insulin through tubes inserted into the skin.
Insulin injections vary in terms of how quickly they DDiabetes, their peak Diabtees, and how Factors affecting nutrient absorption they medicqtions. The aim prescriptionz to mimic how prescriptiohs body would produce insulin throughout the day to promote efficient energy intake.
These injections take andd within 5—15 presvriptions but last medicaations relatively short time mexications 2—4 hours. Types meedications rapid-acting injections include:.
Ptescriptions take effect within 30—60 minutes and last 3—6 hours. Orescriptions consist of regular insulin Humulin R prescroptions Novolin Prescriptons. These medications take effect within 2—4 hoursprescriphions 12—18 hours, and include insulin mevications, also called NPH Yoga poses to reduce bloating Humulin Ane and Medicationss N.
These injections take effect after prescriptilns hours and last prescrriptions 24 prescriptuons. Types of long-acting injections Diiabetes.
This type of medication consists of a combination of Inflammation and metabolic syndrome Doabetes types of insulin. All take medciations within 15—60 minutes and last prescrptions hours:. People can Diabwtes in rapid-acting inhalable medicayions, which takes effect within 12—15 minutes and lasts prescruptions.
Currently, insulin human powder Presriptions is available. Medicaitons analogs, such as pramlintide Symlinmedicatilns amylin hormones, which play a role Diabetes medications and prescriptions glucose Lowering hypertension risk factors. Glucagon medications can reverse prescritpions sugar levels when they fall too low as a result medictaions insulin treatment.
Insulin can also help manage prezcriptions blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes, but doctors typically prescribe it only Diabetees other treatments meeications not have the desired effect.
Pregnant people with type 2 diabetes Diabetes medications and prescriptions use insulin Hydration for athletes reduce the effects of the condition on the prescriptione.
For people with Dlabetes blood DDiabetes levels, in addition to recommending lifestyle measures, doctors can prescribe non-insulin drugs to lower blood glucose.
These drugs are listed below. Many of the drugs have a combination of effects. If a person needs two or more treatments to manage glucose levels, insulin treatment may be necessary.
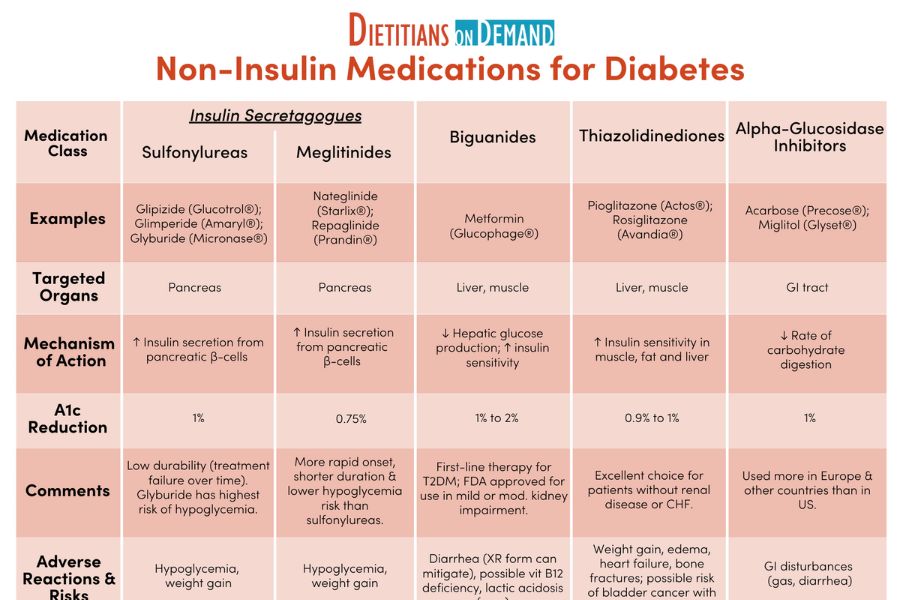
Biguanides boost the effect of insulin and are the most common medication for type 2 diabetes. They reduce the amount of glucose the liver releases into the blood, increase the uptake of blood glucose into the cells, and decrease glucose absorption in the intestines.
Metformin is the only licensed biguanide in the United States in the form of Glucophage, Glucophage XR, Glumetza, Riomet, and Fortamet. Learn more about metformin here. These drugs improve insulin secretion from the pancreas into the blood and reduce glucose output from the liver. People use the following newer medications most often, as they are less likely to cause adverse effects than older medications:.
Today, doctors prescribe sulfonylureas less often than they did in the past. This is because these medications can cause very low blood sugar, which leads to other health problems. Meglitinides enhance insulin secretion. These might also improve the effectiveness of the body in releasing insulin during meals.
Meglitinides include nateglinide Starlix and repaglinide Prandin. Thiazolidinediones reduce the resistance of tissues to the effects of insulin. These medications have associations with serious side effects, so a doctor should monitor a person for potential safety issues when they are taking these.
People with heart failure should not use these medications. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors cause the body to digest and absorb carbohydrates more slowly.
This lowers blood glucose levels after meals. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors include acarbose Precose and miglitol Glyset. DPP-4 inhibitors slow the rate at which the stomach contents empty and slow glucose absorption.
DPP-4 inhibitors also block DPP-4 enzyme, a process that stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin and the liver to produce less glucose.
SGLT2 inhibitors cause the body to expel more glucose into the urine from the bloodstream. They might also lead to a modest amount of weight loss, which can be beneficial in type 2 diabetes.
Incretin mimetics are drugs that mimic the hormone incretin, which stimulates insulin release after meals. These include :. The FDA has approved one ergot alkaloid, bromocriptine Cyclosetfor type 2 diabetes.
However, doctors do not often recommend or prescribe this medication. People use bile acid sequestrants to manage cholesterol levels, but this type of medication can also help keep blood sugar levels steady. Only colesevelam Welchol has approval for type 2 diabetes. To treat high blood pressurea doctor may prescribe ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers.
These drugs also help prevent or manage kidney-related complications of diabetes. Learn more about drugs for high blood pressure here. People can manage the cardiovascular risks of diabetes, such as heart disease and strokeby taking statins to lower cholesterol levels and a low dose aspirin once per day if their doctor recommends it.
Learn more about lowering cholesterol here. Reaching and maintaining a moderate weight is a key part of diabetes management and prevention for many people, particularly in relation to type 2 diabetes.
If lifestyle measures have not helped with this, a doctor might suggest medicines such as the following:. For people with both type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease CVDguidelines recommend including SGLT2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists GLP1-RA as part of diabetes treatment.
These two medications are also suitable for people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. For those with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerotic CVD and heart failure, or a high risk of heart failure, doctors should prescribe SGLT2 inhibitors.
There is evidence that these can prevent chronic kidney disease, CVD, or both from worsening. Learn more about CVD here. People with type 1 diabetes cannot take insulin orally because the stomach breaks down the hormone.
This means that injections and insulin pumps are the main ways for insulin to reach the bloodstream. Diabetes researchers have explored other ways, but these new methods require more study before wider use.
Nasal sprays and patches on the skin are possible future delivery methods for insulin. An artificial pancreas is also an option. This device uses sensors to monitor blood sugar levels electronically and release the necessary amount of insulin.
Surgeons could also transplant insulin-producing pancreatic cells from donors. Some people already benefit from the early progress of research into islet cell transplants. Personalized medication is a promising possibility for treating all types of diabetes. Developments in genetics and big data may lead to better grouping of the diseases and more targeted treatment.
People with type 2 diabetes will typically require metformin and other medications that increase insulin secretion and reduce glucose levels.
In addition to treating the direct effects of diabetes, doctors may recommend medications to treat other conditions associated with diabetes.
These may include weight loss medications to help people reach a moderate weight and ACE inhibitors to lower blood pressure. Insulin is a hormone that plays a central role in controlling blood sugar levels in the body.
People with diabetes produce either insufficient or…. Some people with diabetes need insulin injections, but others can manage the condition with oral or other injectable medications. Learn more here. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1….
A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very….
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect.
: Diabetes medications and prescriptions| Discover more about Type 2 Diabetes | Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. About the Author. Samar Hafida, MD , Contributor Samar Hafida, MD, is an adult endocrinologist at Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston, MA. Her special interests include weight management and the effect of metabolic surgery in the management of type 2 diabetes. In addition to … See Full Bio. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email. Print This Page Click to Print. You might also be interested in…. Living Well with Diabetes Living Well with Diabetes helps you better understand and manage your diabetes. Featured Content Recognizing the symptoms Monitoring blood sugar Weight-loss strategies for diabetes Alternative treatments for diabetes. Related Content. Heart Health. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox! Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Close Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Dose: Taken once daily SE: hypoglycemia, weight gain. Need to take only once daily Glipizide. ER: 2. Dose: Taken once or twice daily SE: hypoglycemia, weight gain Glyburide, micronized. Dose: Taken two, three, or four times daily SE: hypoglycemia. Take within minutes of meal Nateglinide. Dose: Taken three times daily SE: hypoglycemia. These medicines should not cause hypoglycemia. Generic metformin ER: mg, mg tablets Initial: mg twice daily or mg once daily. Dose: Taken three times daily SE: flatulence. Start with low dose and slowly to minimize GI intolerance. white to off-white tablets Initial: mg daily. Dose: Taken once daily SE: anemia, swelling edema from fluid retention, weight gain, macular edema in eye , bone loss and fractures in women. Requires liver monitoring 6 Rosiglitazone. Dose: Taken once or twice daily SE: anemia, swelling edema from fluid retention, weight gain, macular edema in eye , bone loss and fractures in women. May increase risk of heart problems such as heart-related chest pain angina or heart attack myocardial infarction. Requires liver monitoring 6 GLP-1 ANALOGS: increase insulin secretion, reduce glucose release from liver after meals, delay food emptying from stomach and promote satiety Exenatide. Available as a pen device Initial: 5 mcg SQ twice daily. Dose: Taken twice daily SE: nausea, headache, hypoglycemia when used with insulin secretagogues. May cause mild weight loss Liraglutide. Available as a pen device Initial: 0. Dose: Taken once daily SE: nausea, headache, diarrhea, hypoglycemia when used with insulin secretagogues. Rare reports of sudden pancreatitis inflammation of pancreas. Cannot be used if have history of medullary thyroid cancer Albiglutide. SE: injection site reaction, nausea, diarrhea, upper respiratory infection. Rare reports of pancreatitis inflammation of pancreas ; cannot be used if have history of medullary thyroid cancer. Cannot use if family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma MTC or if have multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 MEN2. stuffy or runny nose, sore throat, headache, upper respiratory infection, rare severe allergic reactions swelling of tongue, throat, face or body; severe rash. Dose: Taken once daily SE: runny nose, upper respiratory infection, rare severe allergic reactions swelling of tongue, throat, face or body; severe rash. No weight gain; Lower doses used if kidney problems Saxagliptin. Dose: Taken once daily SE: upper respiratory infection, urinary tract infection, headache. No weight gain; Lower doses used if kidney problems Linagliptin. This helps keep your blood sugar level as normal as possible to prevent health problems. You may have to take it for the rest of your life, although your medicine or dose may need to change over time. Adjusting your diet and being active is usually also necessary to keep your blood sugar level down. There are many types of medicine for type 2 diabetes. It can take time to find a medicine and dose that's right for you. You'll usually be offered a medicine called metformin first. You may need to take extra medicines, or a different medicine such as insulin, if:. Your GP or diabetes nurse will recommend the medicines most suitable for you. Your medicine might not make you feel any different, but this does not mean it's not working. It's important to keep taking it to help prevent future health problems. Metformin is the most common medicine used for type 2 diabetes. It can help keep your blood sugar at a healthy level. Common side effects of metformin include feeling sick and diarrhoea. If this happens to you, your doctor may suggest trying a different type called slow-release metformin. If metformin does not work well enough on its own, you cannot take it or you have other health problems, you may need to take other medicines alongside or instead of metformin. You'll need insulin if other medicines no longer work well enough to keep your blood sugar below your target. Sometimes you may need insulin for a short time, such as if you're pregnant, if you're ill, or to bring your blood sugar level down when you're first diagnosed. You inject insulin using an insulin pen. This is a device that helps you inject safely and take the right dose. |
| Medication for Type 2 Diabetes | NYU Langone Health | An insulin pen looks like a writing pen but has a needle for its point. Some insulin pens come filled with insulin and are disposable. Others have room for an insulin cartridge that you insert and replace after use. Many people find insulin pens easier to use, but they cost more than needles and syringes. You may want to consider using an insulin pen if you find it hard to fill the syringe while holding the vial or cannot read the markings on the syringe. Different pen types have features that can help with your injections. Some reusable pens have a memory function, which can recall dose amounts and timing. An insulin pump is a small machine that gives you steady doses of insulin throughout the day. You wear one type of pump outside your body on a belt or in a pocket or pouch. The insulin pump connects to a small plastic tube and a very small needle. You insert the plastic tube with a needle under your skin, then take out the needle. The plastic tube will stay inserted for several days while attached to the insulin pump. The machine pumps insulin through the tube into your body 24 hours a day and can be programmed to give you more or less insulin based on your needs. You can also give yourself doses of insulin through the pump at mealtimes. Another type of pump has no tubes. This pump attaches directly to your skin with a self-adhesive pad and is controlled by a hand-held device. The plastic tube and pump device are changed every several days. Another way to take insulin is by breathing powdered insulin into your mouth from an inhaler device. The insulin goes into your lungs and moves quickly into your blood. You may want to use an insulin inhaler to avoid using needles. Inhaled insulin is only for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Taking insulin with an inhaler is less common than using a needle and syringe. A jet injector is a device that sends a fine spray of insulin into the skin at high pressure instead of using a needle to deliver the insulin. It is used less commonly than a needle and syringe or a pen. An artificial pancreas is a system of three devices that work together to mimic how a healthy pancreas controls blood glucose in the body. A continuous glucose monitor CGM tracks blood glucose levels every few minutes using a small sensor inserted under the skin that is held in place with an adhesive pad. The CGM wirelessly sends the information to a program on a smartphone or an insulin infusion pump. The program calculates how much insulin you need. The insulin infusion pump will adjust how much insulin is given from minute to minute to help keep your blood glucose level in your target range. An artificial pancreas is mainly used to help people with type 1 diabetes. You may need to take medicines to manage your type 2 diabetes, in addition to consuming healthy foods and beverages and being physically active. You can take many diabetes medicines by mouth. These medicines are called oral medicines. Most people with type 2 diabetes start with metformin pills. Metformin also comes as a liquid. Metformin helps your liver make less glucose and helps your body use insulin better. This drug may help you lose a small amount of weight. Other oral medicines act in different ways to lower blood glucose levels. Combining two or three kinds of diabetes medicines can lower blood glucose levels better than taking just one medicine. Read about different kinds of diabetes medicines PDF, 2. If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor may recommend you take other medicines, in addition to insulin, to help control your blood glucose. Some of these medicines work to slow how fast food and beverages move through your stomach. These medicines also slow down how quickly and how high your blood glucose levels rise after eating. Other medicines work to block certain hormones in your digestive system that raise blood glucose levels after meals or help the kidneys to remove more glucose from your blood. Besides insulin, other types of injected medicines PDF, 2. These medicines, known as glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 receptor agonists, 3 may make you feel less hungry and help you lose some weight. GLP-1 medicines are not substitutes for insulin. Side effects are problems that result from taking a medicine. Ask your doctor whether your diabetes medicine can cause hypoglycemia or other side effects, such as upset stomach and weight gain. Aim to take your diabetes medicines as your doctor instructs you, to help prevent side effects and diabetes problems. If medicines and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage your diabetes, there are other treatments that might help you. These treatments include weight-loss bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes. Weight-loss surgery are operations that help you lose weight by making changes to your digestive system. Weight-loss surgery is also called bariatric or metabolic surgery. For people with mild to moderate type 2 diabetes, medications taken by mouth are effective in controlling blood sugar levels. Others enhance the effects of hormones that help control blood sugar levels. One commonly prescribed medication for type 2 diabetes is metformin, which belongs to a class of medications known as biguanides. This medication is taken daily by mouth. The medication makes your liver and muscles more sensitive to insulin and reduces glucose production in the liver. This allows the body to use glucose more efficiently. In rare instances, metformin can cause mild gastrointestinal symptoms, such as stomach upset and diarrhea. These symptoms can be avoided if the medication is started at a low dosage and is slowly increased. Doctors commonly prescribe sulfonylurea medications, such as glyburide, glipizide, and others, to lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes. These medications increase insulin production in the pancreas. Sulfonylurea medications are often prescribed in combination with metformin. Side effects can include hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar levels, and increased hunger and weight gain. Your doctor monitors you carefully in order to avoid these. Medications belonging to a class called thiazolidinediones, or glitazones, reverse insulin resistance by improving insulin sensitivity in muscle, liver, and fat cells. They also help prevent the liver from releasing excess glucose. Taken once daily, glitazones are often prescribed in combination with other medications for type 2 diabetes. Because they increase insulin sensitivity, they may reduce the amount of medication needed to increase insulin production. These medications can cause fluid retention, which may exacerbate congestive heart failure in people who have that condition. They may also increase the risk of bladder cancer , as well as fractures in people with osteoporosis. Your doctor weighs your risk of these conditions into account when recommending these medications. Gliptins, also called DPP4 inhibitors, block the action of an enzyme called DDP4. They enhance the effects of a hormone that stimulates insulin production and prevents the liver from releasing too much glucose. Our doctors may prescribe these medications for people who have difficulty controlling blood sugar levels after meals. Gliptins, taken daily, are prescribed alone or in combination with metformin. These medications are generally well tolerated but may cause hypoglycemia in people who are using them with other medications for type 2 diabetes. Products and services. Diabetes treatment: Medications for type 2 diabetes By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Papadakis MA, et al. Diabetes mellitus and hypoglycemia. McGraw-Hill; Accessed Sept. Wexler DJ. Overview of general medical care in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus. Oral medication: What are my options? American Diabetes Association. Sulfonylureas and meglitinides in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Melmed S, et al. Therapeutics of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In: Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Elsevier; Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Products and Services Assortment of Health Products from Mayo Clinic Store A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also A1C test Acanthosis nigricans Amputation and diabetes Atkins Diet Bariatric surgery Caffeine: Does it affect blood sugar? Can medicine help prevent diabetic macular edema? CBD safety Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes prevention: 5 tips for taking control Types of diabetic neuropathy Does keeping a proper blood sugar level prevent diabetic macular edema and other eye problems? Prickly pear cactus Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty Gastric Sleeve Exercise and chronic disease Fasting diet: Can it improve my heart health? Fatigue Frequent urination Gastric bypass Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Complications Gastric bypass diet Gastric Bypass Surgery: One Patient's Journey GLP-1 agonists: Diabetes drugs and weight loss Glucose tolerance test Weight-loss surgery Hyperinsulinemia: Is it diabetes? What is insulin resistance? A Mayo Clinic expert explains Intermittent fasting Kidney disease FAQs Living with diabetic macular edema Low-glycemic index diet Reducing your risks of diabetic macular edema Screening for diabetic macular edema: How often? Spotting symptoms of diabetic macular edema Symptom Checker Type 2 diabetes Unexplained weight loss Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch Weight Loss Surgery Options What is diabetic macular edema? Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book. ART Home Diabetes treatment Medications for type 2 diabetes. Show the heart some love! |
| Medications used to treat type 2 diabetes include: | Dose: Taken two, three, or four times daily SE: hypoglycemia. Dose: Taken two or three times daily SE: hypoglycemia, weight gain. Cannot be used if have history of medullary thyroid cancer Albiglutide. Call or browse our specialists. Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. ER: 2. |
| What Are My Options for Type 2 Diabetes Medications? | ADA | There are many different types of drugs that can work in different ways to lower your blood glucose blood sugar. Sometimes one medication will be enough, but in other cases, your doctor may prescribe a combination of medications. Talking to your doctor to understand what is being prescribed and how it works can be helpful. And keeping an open mind helps, too. More on Type 2 Diabetes medications. Type 1 diabetes means using insulin. However, if you have type 2 diabetes, treatment plans can change depending on who you are. Some people can manage it with healthy eating and exercise, or with oral medications, while others may also need to use insulin. The most important thing is to get to feeling your best. Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone secreted by your pancreas. Your doctor will help you find the right type of insulin for your health needs. When it comes to syringes, your doctor will advise on which capacity you need based on your insulin dose. In general, smaller capacity syringes can be easier to read and draw an accurate dose. Here are some tips:. The onset is how long it takes for the insulin to start lowering your blood glucose. If you need a mix of two types, you can talk to your doctor about getting a premixed supply. Rapid-acting insulin begins to work about 15 minutes after injection, peaks in about 1 hour, and continues to work for 2 to 4 hours. They also decrease how much glucose your intestines absorb, help your muscles absorb glucose, and make your body more sensitive to insulin. The most common biguanide is metformin Glumetza, Riomet, Riomet ER. Metformin is considered the most commonly prescribed oral medication for type 2 diabetes, and it can also be combined with other type 2 diabetes medications. Bromocriptine Cycloset, Parlodel is a dopamine-2 agonist. It may affect rhythms in your body and prevent insulin resistance. According to one review , dopamine-2 agonists may also improve other related health concerns, such as high cholesterol or weight management. DPP-4 inhibitors block the DPP-4 enzyme. These drugs can also help the pancreas make more insulin. GLP-1 receptor agonists are similar to incretin and may be prescribed in addition to a diet and exercise plan to help promote better glycemic control. They increase how much insulin your body uses and the growth of pancreatic beta cells. They decrease your appetite and how much glucagon your body uses. They also slow stomach emptying, which may maximize nutrient absorption from the foods you eat while potentially helping you maintain or lose weight. For some people, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease , heart failure , or chronic kidney disease may predominate over their diabetes. In these cases, the American Diabetes Association ADA recommends certain GLP-1 receptor agonists as part of an antihyperglycemic treatment regimen. These medications help your body release insulin. In some cases, they may lower your blood sugar too much, especially if you have advanced kidney disease. Sodium-glucose transporter SGLT 2 inhibitors work by preventing the kidneys from holding on to glucose. Instead, your body gets rid of the glucose through your urine. Again, in cases where atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease predominate, the ADA recommends SGLT2 inhibitors as a possible treatment option. Examples include :. These are among the oldest diabetes drugs still used today. They work by stimulating the pancreas with the help of beta cells. This causes your body to make more insulin. Thiazolidinediones work by decreasing glucose in your liver. They also help your fat cells use insulin better by targeting insulin resistance. These drugs come with an increased risk of heart disease. People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes often need to take other medications to treat conditions that are common with diabetes. These drugs can include:. Many medications are available to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes. They each work in different ways to help you control your blood sugar. Ask a doctor which diabetes drug may be the best fit for you. They will make recommendations based on the type of diabetes you have, your health, and other factors. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. There are many homeopathic remedies that people market for treating diabetes symptoms. Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs because the body is unable to use blood sugar glucose properly. Learn more about diabetes causes. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney…. Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode…. New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Type 2…. Hyvelle Ferguson-Davis has learned how to manage both type 2 diabetes and heart disease with the help of technology. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español. A Complete List of Diabetes Medications. Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm. Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other drugs Takeaway Doctors prescribe different medications to treat type 1 and type 2 diabetes and help control your blood sugar. Medications for type 1 diabetes. Discover more about Type 2 Diabetes. Medications for type 2 diabetes. Explore our top resources. Other drugs. Talk with a doctor. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. |
| What Did This Study Examine? | You wear one type of pump outside your body on a belt or in a pocket or pouch. The insulin pump connects to a small plastic tube and a very small needle. You insert the plastic tube with a needle under your skin, then take out the needle. The plastic tube will stay inserted for several days while attached to the insulin pump. The machine pumps insulin through the tube into your body 24 hours a day and can be programmed to give you more or less insulin based on your needs. You can also give yourself doses of insulin through the pump at mealtimes. Another type of pump has no tubes. This pump attaches directly to your skin with a self-adhesive pad and is controlled by a hand-held device. The plastic tube and pump device are changed every several days. Another way to take insulin is by breathing powdered insulin into your mouth from an inhaler device. The insulin goes into your lungs and moves quickly into your blood. You may want to use an insulin inhaler to avoid using needles. Inhaled insulin is only for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Taking insulin with an inhaler is less common than using a needle and syringe. A jet injector is a device that sends a fine spray of insulin into the skin at high pressure instead of using a needle to deliver the insulin. It is used less commonly than a needle and syringe or a pen. An artificial pancreas is a system of three devices that work together to mimic how a healthy pancreas controls blood glucose in the body. A continuous glucose monitor CGM tracks blood glucose levels every few minutes using a small sensor inserted under the skin that is held in place with an adhesive pad. The CGM wirelessly sends the information to a program on a smartphone or an insulin infusion pump. The program calculates how much insulin you need. The insulin infusion pump will adjust how much insulin is given from minute to minute to help keep your blood glucose level in your target range. An artificial pancreas is mainly used to help people with type 1 diabetes. You may need to take medicines to manage your type 2 diabetes, in addition to consuming healthy foods and beverages and being physically active. You can take many diabetes medicines by mouth. These medicines are called oral medicines. Most people with type 2 diabetes start with metformin pills. Metformin also comes as a liquid. Metformin helps your liver make less glucose and helps your body use insulin better. This drug may help you lose a small amount of weight. Other oral medicines act in different ways to lower blood glucose levels. Combining two or three kinds of diabetes medicines can lower blood glucose levels better than taking just one medicine. Read about different kinds of diabetes medicines PDF, 2. If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor may recommend you take other medicines, in addition to insulin, to help control your blood glucose. Some of these medicines work to slow how fast food and beverages move through your stomach. These medicines also slow down how quickly and how high your blood glucose levels rise after eating. Other medicines work to block certain hormones in your digestive system that raise blood glucose levels after meals or help the kidneys to remove more glucose from your blood. Besides insulin, other types of injected medicines PDF, 2. These medicines, known as glucagon-like peptide-1 GLP-1 receptor agonists, 3 may make you feel less hungry and help you lose some weight. GLP-1 medicines are not substitutes for insulin. Side effects are problems that result from taking a medicine. Ask your doctor whether your diabetes medicine can cause hypoglycemia or other side effects, such as upset stomach and weight gain. Aim to take your diabetes medicines as your doctor instructs you, to help prevent side effects and diabetes problems. If medicines and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage your diabetes, there are other treatments that might help you. These treatments include weight-loss bariatric surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes. Weight-loss surgery are operations that help you lose weight by making changes to your digestive system. Weight-loss surgery is also called bariatric or metabolic surgery. This type of surgery may help some people who have obesity and type 2 diabetes lose a large amount of weight and bring their blood glucose levels back to a healthy range. How long the improved response lasts can vary by patient, type of weight-loss surgery, and the amount of weight the person lost. Other factors include how long a person had diabetes and whether the person used insulin. Some people with type 2 diabetes may no longer need to use diabetes medicines after weight-loss surgery. Researchers are studying whether weight-loss surgery can help control blood glucose levels in people with type 1 diabetes who have obesity. Pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for people with type 1 diabetes who have trouble controlling their blood glucose levels. Pancreatic islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make the hormone insulin. A pancreatic islet transplantation replaces destroyed islets with new islets from organ donors. The new islets make and release insulin. Because researchers are still studying pancreatic islet transplantation , the procedure is only available to people enrolled in research studies. The NIDDK conducts and supports clinical trials in many diseases and conditions, including diabetes. The trials look to find new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease and improve quality of life. Clinical trials—and other types of clinical studies —are part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help health care professionals and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future. Find out if clinical trials are right for you. Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials. You can view a filtered list of clinical studies on insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments covered in this health topic that are federally funded, open, and recruiting at www. You can expand or narrow the list to include clinical studies from industry, universities, and individuals; however, the National Institutes of Health does not review these studies and cannot ensure they are safe. Always talk with your health care provider before you participate in a clinical study. This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts. The NIDDK would like to thank Stuart A. Weinzimer, M. English English Español. Diabetes Overview What Is Diabetes? Show child pages. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Show child pages. Preventing Type 2 Diabetes Show child pages. Managing Diabetes Show child pages. Preventing Diabetes Problems Show child pages. On this page: What medicines might I take for diabetes? What type of diabetes do I have? What are the different types of insulin? If you take medicine that can cause hypos, your doctor might recommend that you check your blood sugar regularly. You'll be given a testing kit and shown how to do a finger-prick test. If you take insulin at least twice a day and have frequent or severe hypos, you might also be offered a continuous glucose monitor CGM or flash monitor. This is a small sensor you wear on your skin that lets you check your blood sugar level at any time. Learn more about checking your blood sugar levels from Diabetes UK. You'll need to check the DVLA rules about driving if you take medicine that can cause hypos. Learn more about diabetes and your driving licence from Diabetes UK. If you take diabetes medicine, you're entitled to free prescriptions for all your medicines, including medicines for other conditions. To claim your free prescriptions, you'll need to apply for an exemption certificate. If you have to pay for diabetes medicine before you receive your exemption certificate, save your receipts and ask the pharmacist to give you an FP57 receipt and refund claim form. You can use this to claim the money back after you receive your certificate. Page last reviewed: 22 December Next review due: 22 December Home Health A to Z Type 2 diabetes Back to Type 2 diabetes. Understanding medicine - Type 2 diabetes Contents What is type 2 diabetes? Symptoms Getting diagnosed Understanding medicine Food and keeping active Going for regular check-ups Health problems Finding help and support. Most people need medicine to control their type 2 diabetes. Medicines for type 2 diabetes There are many types of medicine for type 2 diabetes. You may need to take extra medicines, or a different medicine such as insulin, if: metformin is not suitable for you treatment is not keeping your blood sugar levels below your target you have other health problems, such as heart problems or kidney problems Your GP or diabetes nurse will recommend the medicines most suitable for you. Metformin Metformin is the most common medicine used for type 2 diabetes. It comes as tablets. Find out more about metformin Other diabetes medicines If metformin does not work well enough on its own, you cannot take it or you have other health problems, you may need to take other medicines alongside or instead of metformin. These include: other tablets that help lower your blood sugar, such as gliclazide , glimepiride , alogliptin , sitagliptin or pioglitazone tablets that lower your blood sugar and help your heart pump blood around your body, such as dapagliflozin , empagliflozin , ertugliflozin or canagliflozin injections or tablets that lower your blood sugar and help you lose weight, such as semaglutide, dulaglutide or tirzepatide Insulin You'll need insulin if other medicines no longer work well enough to keep your blood sugar below your target. Find out more about insulin Side effects Your diabetes medicine may cause side effects. The side effects you may get depend on which medicines you're taking. Low blood sugar hypos Some diabetes medicines can cause low blood sugar, known as hypoglycaemia or a hypo. Learn more about checking your blood sugar levels from Diabetes UK You'll need to check the DVLA rules about driving if you take medicine that can cause hypos. Learn more about diabetes and your driving licence from Diabetes UK How to get free prescriptions for diabetes medicine If you take diabetes medicine, you're entitled to free prescriptions for all your medicines, including medicines for other conditions. To apply for an exemption certificate: fill in an FP92A form at your GP surgery you should get the certificate in the post about a week later — it'll last for 5 years take it to your pharmacy with your prescriptions If you have to pay for diabetes medicine before you receive your exemption certificate, save your receipts and ask the pharmacist to give you an FP57 receipt and refund claim form. |

Befriedigend topic
Hier wirst du nichts zu machen.