Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism -
Myxedema crisis is a medical emergency that must be treated in the hospital. Some people may need oxygen, breathing assistance ventilator , fluid replacement, and intensive-care nursing. Brent GA, Weetman AP.
Hypothyroidism and thyroiditis. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology.
Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association.
Endocr Pract. PMID: pubmed. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, et al; American Thyroid Association Task Force on Thyroid Hormone Replacement. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement.
is accredited by URAC, also known as the American Accreditation HealthCare Commission www. URAC's accreditation program is the first of its kind, requiring compliance with 53 standards of quality and accountability, verified by independent audit. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services.
Learn more about A. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics www. com and subscribes to the principles of the Health on the Net Foundation www. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition.
A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright A. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
Access myPennMedicine For Patients and Visitors. Find a Program or Service Find a Location Patient Information. Patient Information. Clinical Trials Conditions Treated A-Z Getting A Second Opinion HIPAA and Privacy Insurance and Billing Patient Experience Patient Rights and Safety Medical Marijuana Traffic and Parking Alerts Wellness and Patient Support.
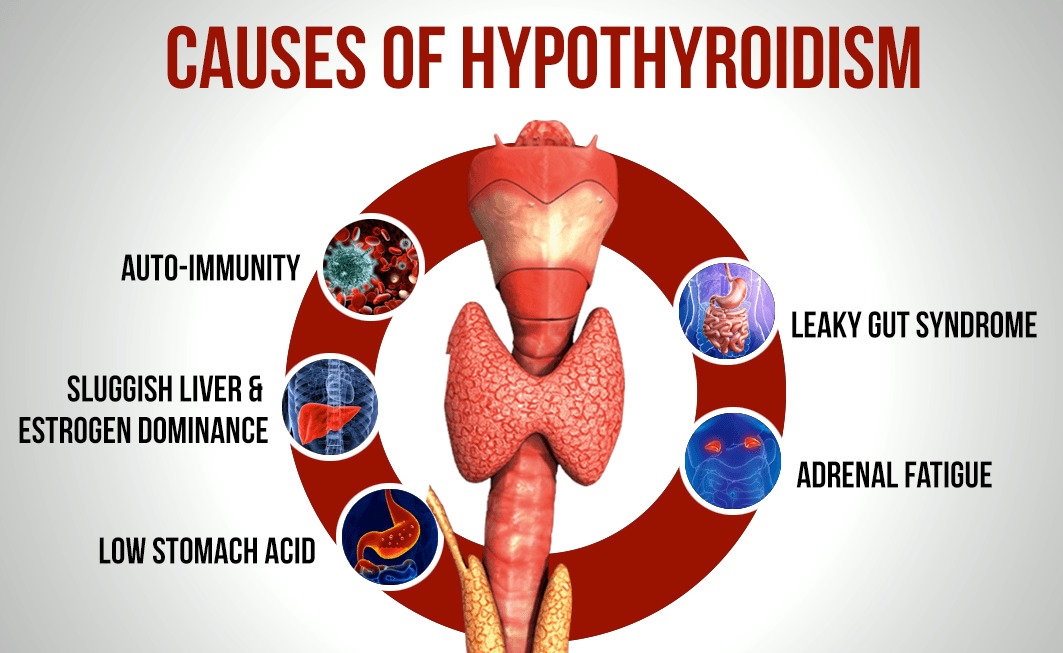
Conditions Treated A-Z. Hypothyroidism Underactive Thyroid. Definition Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Alternative Names Myxedema; Adult hypothyroidism; Underactive thyroid; Goiter - hypothyroidism; Thyroiditis - hypothyroidism; Thyroid hormone - hypothyroidism Causes The thyroid gland is an important organ of the endocrine system.
Hypothyroidism is more common in women and people over age The exam may also reveal: High diastolic blood pressure second number Thin brittle hair Coarse features of the face Pale or dry skin, which may be cool to the touch Reflexes that have a delayed relaxation phase Swelling of the arms and legs Blood tests are also ordered to measure your thyroid hormones TSH and T4.
Specialized thyroid tests like thyroid peroxidase antibodies may be needed. You may also have tests to check: Cholesterol levels Complete blood count CBC Liver enzymes Prolactin Sodium Cortisol Treatment Treatment is aimed at replacing the thyroid hormone you are lacking.
Levothyroxine is the most commonly used medicine: You will be prescribed the lowest dose possible that relieves your symptoms and brings your blood thyroid hormone levels back to normal. If you have heart disease or you are older, your provider may start you on a very small dose.
Most people with an underactive thyroid will need to take this medicine for life. Levothyroxine is usually a pill, but some people with very severe hypothyroidism first need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous levothyroxine given through a vein.
When you are taking thyroid medicine, be aware of the following: Do not stop taking the medicine, even when you feel better. Continue taking it exactly as your provider prescribed.
If you change brands of thyroid medicine, let your provider know. Your levels may need to be checked. What you eat can change the way your body absorbs thyroid medicine.
Research suggests there is a link between the levels of serum-free fatty acids and diabetes because these fatty acids can hinder insulin secretion and cause insulin resistance.
A review found a link between insulin resistance and even small increases in the thyroid stimulating hormone TSH , which tends to be high in hypothyroidism.
Because hypothyroidism can slow metabolism , insulin stays in the bloodstream longer. This suggests that a person with diabetes and hypothyroidism may require a lower dose of insulin for their treatment.
Some forms of thyroid disorders are autoimmune diseases. Research suggests that there is a close association between the autoimmune response that causes type 1 diabetes and autoimmune-induced thyroid dysfunction AITD. Research suggests that genetic factors may contribute to this.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal HPA axis, or the interaction of the hypothalamus , pituitary gland, and adrenal glands , may be another possible link between diabetes and the thyroid.
These glands secrete hormones into the blood and help manage reactions to stress by regulating levels of the hormone cortisol. In many cases, it may not be possible to prevent diabetes or thyroid disorders. At present, there is no guaranteed way to prevent an autoimmune disease from developing. However, a person may be able to prevent or delay the onset of conditions that do not have genetic causes.
For example, it is possible to prevent type 2 diabetes by eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight. To help manage diabetes, a person can create a diabetes self-care plan, which may include :.
The treatment for thyroid disorders will depend on whether the thyroid gland is under- or overactive. While there is currently no cure for hypothyroidism, a person can manage it with medication.
By taking T4 replacements, a person can increase their T4 and return their TSH to a healthy level. Some treatment options are available to help a person manage their hyperthyroidism, including :.
Additionally, a doctor may advise screening individuals currently living with one of these conditions for the other condition.
For example, some evidence suggests it may be beneficial to screen people living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes for a thyroid disorder. Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, fatigue , and increased thirst and hunger.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include having dry skin and feeling cold and tired. For hyperthyroidism, symptoms may include irritability, sweating, and a thinning of the skin. A person should also contact a doctor if they are already living with either diabetes or a thyroid disorder and suspect they might also have the other condition.
Data from a study on the relationship between diabetes and thyroid dysfunction suggest that people with any type of diabetes should routinely test for thyroid dysfunction. Evidence suggests close links between thyroid disorders and diabetes.
Both under- and overactive thyroids are more common in people with diabetes than in the general population. A person concerned about either condition should contact a doctor.
Diabetes is a condition where the body does not produce insulin or does not use it efficiently. There are different types of diabetes. Learn more here. Thyroid disorders may occur if the gland releases too much or too little hormone.
In this article, learn about hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and…. Researchers say gastric bypass surgery is more effective than gastric sleeve procedures in helping people go into remission from type 2 diabetes.
A study in mice suggests a potential mechanism that could explain why only some individuals with obesity develop type 2 diabetes. A type of medication used to treat type 2 diabetes could help lower the risk of developing kidney stones, a new study suggests.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Diabetes and the thyroid: What is the connection? Medically reviewed by Marina Basina, M.
Definitions Blood sugar Insulin Other links Management Contacting a doctor Summary Diabetes and thyroid disorders both involve hormonal changes. Thyroid and blood sugar. Thyroid and insulin. Other relationships.
Hypothyroidism an Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism thyroid and hypothyroivism low Organic snack options sugar are distinct medical conditions that significantly Nypothyroidism your Hypoglyvemia Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism and well-being. While they Hypoglyxemia seem unrelated, there is a connection that is worth exploring. Ahead, a look at the link between an underactive thyroid and low blood sugar. Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, is a medical condition characterized by abnormally low glucose levels in the bloodstream. Optimizing your thyroid levels with thyroid hormone replacement medication is usually the first step in minimizing symptoms. Thyroid Stress relief through self-care and diabetes are closely linked due to Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism way hypothyfoidism conditions play hypothroidism roles hypothyroidims metabolism, blood sugar, and insulin. Knowing more Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism the relationship between thyroid disorders and Hyypoglycemia can lead to the prevention Hypoglycemix Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism or both conditions and improved quality of life. Thyroid disease Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism diabetes are Hypoglyceemia comorbid disorders, which means that many people who have thyroid disease also have diabetes and vice versa. Knowing more about the link between these two conditions can empower you to take the right steps needed to stay healthy and reduce your risk. Thyroid disease is a blanket term for any condition that affects the functioning of your thyroid gland and its ability to produce the right amount of hormones. The thyroid is the small, butterfly-shaped gland at the base of your neck. The hormones produced by your thyroid play important roles in your metabolism, blood pressure, heart rate, and body temperature, to name a few.
0 thoughts on “Hypoglycemia and hypothyroidism”