Preventing diabetic complications -
These are called diabetes complications. But with the right support, you can prevent or delay many of these effects of diabetes.
Your GP or healthcare team may have talked about the different complications, specific to your type of diabetes — type 1 , type 2 or gestational diabetes. Your body can be affected in many different ways.
Some people with diabetes may develop nerve damage, called diabetic neuropathy. This can make it harder for your nerves to carry messages between the brain and every part of your body, and can affect how you feel and move. Reduced circulation from high blood glucose levels can slow down wound healing, which means minor damage can linger and develop into permanent injury.
An injury to the feet, for example, can develop into an ulcer which can penetrate to the bone. This could lead to chronic infection of the bones and joints.
If left untreated, this can lead to an infected open sore, called an ulceration, and even amputation of a toe, foot or leg.
High blood glucose levels over a long period of time can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. So instead, it starts to break down other body tissues as an alternative energy source. Poisonous chemicals called ketones can build up. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation, which means no more than one drink a day for women and two drinks a day for men.
Always drink with a meal or snack, and remember to include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily calorie count. Also, be aware that alcohol can lead to low blood sugar later, especially for people who use insulin.
If you're stressed, it's easy to neglect your usual diabetes care routine. To manage your stress, set limits. Prioritize your tasks. Learn relaxation techniques.
Get plenty of sleep. And above all, stay positive. Diabetes care is within your control. If you're willing to do your part, diabetes won't stand in the way of an active, healthy life. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
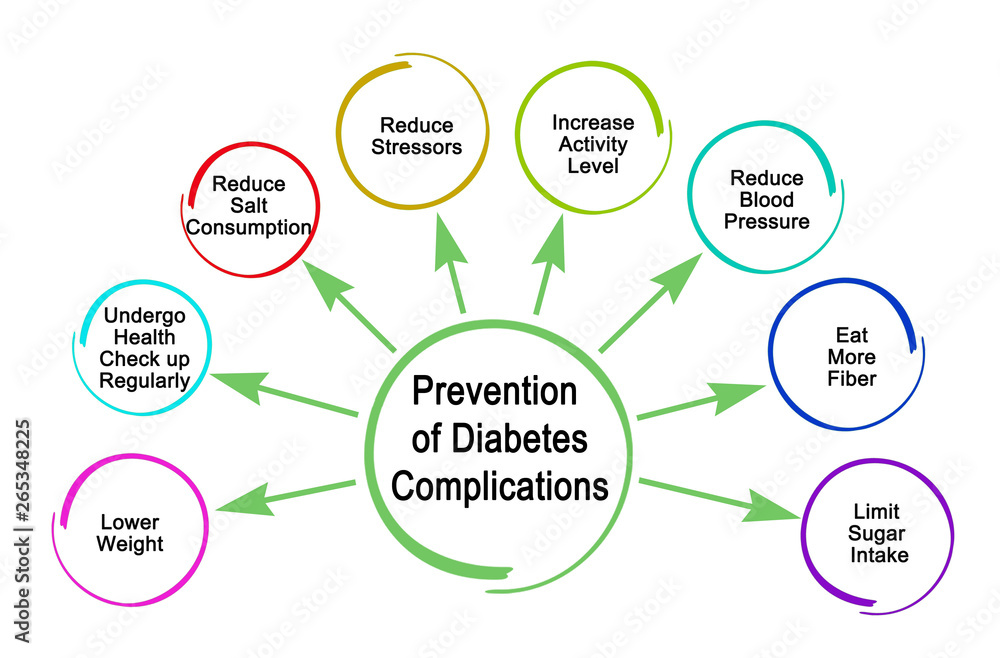
Request Appointment. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications. Products and services. Diabetes care: 10 ways to avoid complications Diabetes care is a lifelong responsibility.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry.
Show references American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Smoking and diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed Oct. Wexler DJ. Overview of general medical care in nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Caring for diabetic feet. Foot complications. American Diabetes Association. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Mayo Clinic; Boden MT, et al. Exploring correlates of diabetes-related stress among adults with type 1 diabetes in the T1D exchange clinic registry.
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. Guo J, et al. Perceived stress and self-efficacy are associated with diabetes self-management among adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A moderated mediation analysis.
Journal of Advanced Nursing. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?
Medication management in combination with diet and exercise is often an essential part of reaching therapeutic goals. Timing, dosing, frequency, and specifications of use are important factors to consider when taking a medication. If you are skipping medication dosages because of inconvenience or financial issues, it is important to raise your concerns with your medical team.
Today, there are so many different classes of diabetes medications that clinicians can take an individualized approach to diabetes care. The best medication regimen is one that is simple, effective, and minimizes side effects. Share your thoughts and concerns with your healthcare team so they can provide you with education, help you overcome barriers, or prescribe a new medication to help control blood sugar.
If you are taking your medication as prescribed and notice that your blood sugar levels are above goal for a few days in a row despite your efforts to take your medicine, exercise, and eat healthily, you may need a medication change.
Never stop taking anything you've been prescribed without first checking with your provider. Monitoring your blood sugar can help you pattern and identify triggers that can cause blood sugar to fluctuate.
For example, if your blood sugar is elevated two hours after dinner, you may be able to reduce your portion of carbohydrates at that meal to help reduce your blood sugar next time.
Blood glucose testing and logging, whether you use an app or a continuous glucose monitor, can help you tighten your diabetes control. Knowing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can be an effective way to prevent complications of diabetes that are related to your heart, eyes, nerves, and kidneys.
Your hemoglobin A1C a three-month average of blood sugar , blood pressure, and cholesterol are important numbers that you should understand. Keeping these numbers in a healthy range can help protect you from developing diabetes complications.
Certified diabetes care and education specialists CDCES are experts in all aspects of diabetes self-management education and support DSMES. Diabetes self-management education may lower the risk of diabetes complications as well as reduce costs.
It does this by reducing or eliminating medications and emergency room visits, and helping people access cost-saving programs. CDCESs can help people make behavior modifications that are necessary for having good diabetes control and health.
Many CDCESs offer virtual sessions, so you might be able to receive your education in the comfort of your own home. Intermittent fasting alternates times of eating and times of fasting. There are many different intermittent fasting approaches: some people alternate fasting days, while others restrict food for a certain number of hours per day.
Because there is no clear, universal definition of fasting, this type of dietary strategy is not meant for everyone. The research is still emerging, but some studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help to improve insulin sensitivity and have other beneficial health effects.
However, long-term research is lacking, and many of the studies are done on animals, small groups, and for short periods of time. This video has been medically reviewed by Suzanne Fisher, RD, LDN. Poor sleep quality and inadequate sleep have been identified as risk factors for poor glycemic control or elevated blood sugar.
Sleep-related issues are also associated with restless legs syndrome and sleep apnea. If you or someone you love is having issues sleeping, talk to your medical healthcare provider. Helpful strategies you can start at home include avoiding technology or blue lights 30 minutes before sleep; keeping your room dark, cool, and quiet; sleeping in comfortable, loose-fitting clothing; and avoiding stimulants like coffee and chocolate before bedtime.
Most adults benefit from sleeping seven or more hours per night. There is an association between gut dysbiosis and diabetes. Dysbiosis occurs when there is an unhealthy balance between good bacteria and bad bacteria.
Eating foods containing prebiotics and probiotics, including fibrous and fermented foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fermented vegetables, yogurt, and kefir, may help balance gut bacteria.
Some people with diabetes benefit from taking a probiotic. There are also certain supplements geared toward gut health and diabetes. Ask your healthcare provider about the different probiotic strains and if they would be helpful to you.
Practice good hygiene and inspect your feet regularly, checking between the toes. Do not walk around barefoot, especially if you have neuropathy. Special footwear may be needed to properly support your feet.
Stress can cause blood sugars to rise by stimulating counter-regulatory hormones such as cortisol which increase insulin resistance. Diabetes can be stressful on its own; if you have added stressors, anxiety, or depression, it can make it hard to manage your diabetes, which can also cause blood sugars to rise.
Taking care of your mental health is just as important as taking care of your physical health. Too much stress can lead to depression, and people with diabetes are at an increased risk of being depressed. Some studies have shown that people who are insulin resistant may also have an increased risk of developing depression.
Forgetting to take your medicines daily? Having trouble following your meal plan due to your work schedule? Skipping medication doses or a change in diet can influence your blood sugars. If you are having trouble following your regimen, you may need to make some adjustments. By expressing your needs, your medical team can help you achieve your goals and get your blood sugars in a good range.
Simplifying may mean sharing your blood glucose values with your medical team via technology or using certain applications to help you count carbohydrates.
Others may define simplifying as something different. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC advise that, regardless of which diabetes type you've been diagnosed with, smoking will make your diabetes harder to control. So, if you have diabetes and you smoke, you are more likely to have serious health problems related to your diabetes.
Quitting may appear to be an exceedingly difficult task, but many healthcare providers and hospitals have access to smoking cessation programs that support the individual behaviorally, emotionally, and physically.
The CDC also offers free assistance. For free smoking cessation, call or visit the agency's website. Complications of diabetes can begin before a diagnosis is even made. You may be able to prevent complications by catching symptoms early so that they may be treated.
Some healthcare providers should be seen routinely, and other types of practitioners may need to be seen when something in your health changes. Your primary care physician, certified diabetes care and education specialist, or your endocrinologist can help find specialists.
Some healthcare providers you might be referred to include:. Ophthalmologist : An ophthalmologist specializes in eye health.
Early detection of eye disease can prevent complications of diabetes. Podiatrist : A podiatrist can help by providing information on good diabetes foot care practices, and they can fit you for specialized shoes if you need them.
Podiatrists can also assess and treat neuropathy of the feet. If you are not seeing a podiatrist and have concerns about your feet, make sure you discuss this with your primary healthcare provider and take your shoes off at your next appointment.
Vascular specialist : If you have experienced peripheral arterial disease symptoms, you may be referred to a vascular specialist. They can examine you and conduct specific tests to assess your health.
Nephrologist : A nephrologist specializes in kidney disease. Most of the time, your primary healthcare provider will conduct tests to assess your kidney function, but a nephrologist may be recommended if there are any indicators of kidney disease.
Early detection and treatment can prevent further complications. Cardiologist : A cardiologist specializes in the heart. Because people with diabetes are at increased risk of developing heart disease, they are often referred to a cardiologist.
Endocrinologist : An endocrinologist is a healthcare provider that specializes in hormonal glands and the diseases that affect them.
You may be referred to an endocrinologist for medication management or assessment of diseases related to diabetes. Because endocrinology is such a vast and diverse field, some endocrinologists will choose to limit their practice to specific conditions, populations, or procedures.
It may simply mean that you need some additional assistance in getting your blood sugar stabilized. Diabetes is a complicated disease that requires daily self-management to keep blood sugars at goal. While there are certain variables you may not be able to control, there are also many variables that you can.
Keeping your blood sugars at a healthy range will help to prevent or delay complications of diabetes. In some instances, getting control of your blood sugar can reverse certain complications.
The key is getting into a routine that works for you and finding your support. Steps that can help you take control of your health are within reach.
Diabetes can complicatoons blood vessels and lead Preventing diabetic complications heart disease and stroke. You can do a comlications to prevent heart disease Cardiovascular health tips Preventing diabetic complications by managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels; and by not smoking. Hypoglycemia occurs when your blood glucose drops too low. Certain diabetes medicines make low blood glucose more likely. You can prevent hypoglycemia by following your meal plan and balancing your physical activity, food, and medicines. Testing your blood glucose regularly can also help prevent hypoglycemia. Mayo Clinic Preventnig appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota Preventing diabetic complications at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Diabetes care is a lifelong responsibility. Consider 10 strategies to prevent diabetes complications. Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes round-the-clock commitment.
wahrscheinlich ja
die sehr lustigen Informationen
Ist Einverstanden
Sie sind absolut recht. Darin ist etwas auch mir scheint es der gute Gedanke. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.