Video
Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes Raspberry and chocolate pairings Dr. Yogish C. Kudva an insjlin at Mayo Type diabetes insulin. In this video, we'll cover the basics of type 1 diabetes. What is it? Who gets it? The symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.Type diabetes insulin -
This process can go on for months or years before any symptoms appear. Some people have certain genes traits passed on from parent to child that make them more likely to develop type 1 diabetes.
A trigger in the environment, such as a virus, may also play a part in developing type 1 diabetes. It can take months or years before symptoms of type 1 diabetes are noticed. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months. Once symptoms appear, they can be severe.
Some type 1 diabetes symptoms are similar to symptoms of other health conditions. If you think you could have type 1 diabetes, see your doctor to get your blood sugar tested.
Untreated diabetes can lead to very serious—even fatal—health problems. Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
However, studies show that family history plays a part. A simple blood test will let you know if you have diabetes. If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also be tested for autoantibodies. These substances indicate your body is attacking itself and are often found with type 1 diabetes but not with type 2.
You may have your urine tested for ketones too. Ketones are produced when your body burns fat for energy. Having ketones in your urine indicates you have type 1 diabetes instead of type 2.
Unlike many health conditions, diabetes is managed mostly by you, with support from your health care team:. Also ask your family, teachers, and other important people in your life for help and support. Managing diabetes can be challenging, but everything you do to improve your health is worth it!
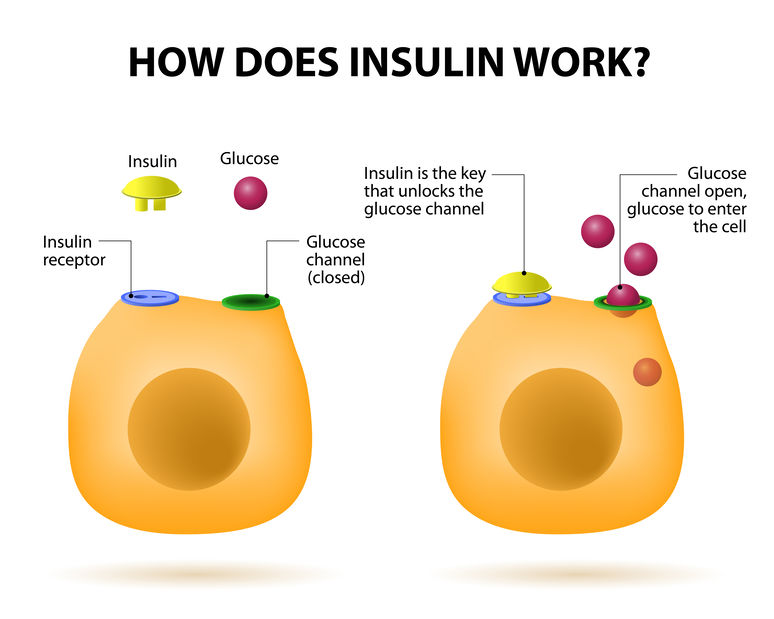
Insulin is needed to manage your blood sugar levels and give your body energy. Your doctor will work with you to figure out the most effective type and dosage of insulin for you. Ask your doctor how often you should check it and what your target blood sugar levels should be.
Keeping your blood sugar levels as close to target as possible will help you prevent or delay diabetes-related complications. Stress is a part of life, but it can make managing diabetes harder. Both managing your blood sugar levels and dealing with daily diabetes care can be tougher to do.
Regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, and exercises to relax can help. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these and other ways you can manage stress. Make regular appointments with your health care team. Meet with your doctor for step-by-step instructions.
You may want to bring a family member with you to the appointment so they learn the steps too. Hypoglycemia low blood sugar can happen quickly and needs to be treated quickly. Talk to your doctor if you have low blood sugar several times a week. Your treatment plan may need to be changed.
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening. Very high blood sugar and low insulin levels lead to DKA. The two most common causes are illness and missing insulin shots.
Talk with your doctor and make sure you understand how you can prevent and treat DKA. Ask your doctor about diabetes self-management education and support services and to recommend a diabetes educator. You can also search this nationwide directory for a list of programs in your community.
You can help delay or prevent type 2 diabetes by knowing the risk factors and taking steps toward a healthier lifestyle, such as losing weight or preventing weight gain.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is type 2 diabetes.
People with prediabetes have blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
If you have prediabetes, you have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. You also have a higher risk for heart disease than people with normal glucose levels.
A less common type of diabetes, called monogenic diabetes , is caused by a change in a single gene. Diabetes can also come from having surgery to remove the pancreas, or from damage to the pancreas due to conditions such as cystic fibrosis or pancreatitis.
More than million Americans have diabetes or prediabetes. As of , population—had diabetes. Over time, high blood glucose can damage your heart , kidneys , feet , and eyes. If you have diabetes, you can take steps to lower your chances of developing diabetes health problems by taking steps to improve your health and learning how to manage the disease.
Managing your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can help prevent future health problems. Managing your blood glucose levels can help prevent future health problems, such as damage to your eyes.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public.
Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts. NIDDK would like to thank: Daniel Bessesen, M. Home Health Information Diabetes Diabetes Overview What Is Diabetes?
English English Español. Diabetes Overview What Is Diabetes? Hide child pages. Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Show child pages. Preventing Type 2 Diabetes Show child pages.
Insulin helps insluin sugar enter the cells Type diabetes insulin Immune support supplements body for use as energy. High blood sugar is damaging to inslin body insulim causes many Type diabetes insulin the insuiln and complications of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes was once called insulin-dependent or juvenile diabetes, but it can develop at any age. Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes, but it can be treated successfully by:. Daily care will include serving healthy foods, giving insulin injections, and watching for and treating hypoglycemia low blood sugar. They will help you understand the treatment plan and how to help your child stay healthy.Type diabetes insulin -
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Read on to get the facts about insulin….
Using insulin can be tricky sometimes. Here are some do's and don'ts to pay attention to as you learn how to effectively manage your diabetes with…. An insulin pump is an alternative to giving yourself multiple daily insulin injections. It's mostly used for type 1 diabetes, and has both pros and….
Type 1 diabetes is a complex autoimmune disease that does have genetic risk factors. Type 2 diabetes is a serious condition, but you can manage it with treatment. Is it possible for it to be reversed? Learn the facts. Gestational diabetes causes high levels of blood sugar during pregnancy.
Learn about symptoms, treatments, diet, prevention, and more. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney…. Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode….
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español.
Everything You Need to Know About Insulin. Medically reviewed by Michelle L. Griffith, MD — By Jessica DiGiacinto and Valencia Higuera — Updated on April 20, Understanding diabetes Managing diabetes with insulin Types of insulin Administration and dosage Storing insulin Side effects and reactions Treatment Alternative medications Ways to manage blood glucose Takeaway Insulin is a hormone made in your pancreas, a gland located behind your stomach.
Understanding diabetes. Managing diabetes with insulin. Types of insulin treatments. Insulin type Onset When it peaks in your system Duration When taken Ultra-rapid acting 2 to 15 min min 4 hours Taken with meals, usually with the first bite of a meal.
Commonly used along with long-acting insulin. Rapid-acting 15 min 1 hour 2 to 4 hours Taken with meals, typically right before a meal.
Commonly used along with longer-acting insulin. Rapid-acting inhaled 10 to 15 min 30 min 3 hours Taken with meals, typically right before a meal. Commonly used with injectable long-acting insulin.
Regular or short-acting 30 min 2 to 3 hours 3 to 6 hours Taken with meals, typically 30 to 60 minutes before a meal. Intermediate acting 2 to 4 hours 4 to 12 hours 12 to 18 hours Taken once or twice a day.
Covers your insulin needs for half a day or overnight. Commonly used with rapid- or short-acting insulin. Can be used with rapid- or short-acting insulin if needed. Premixed 5 to 60 min varied peaks 10 to 16 hours Taken twice a day, commonly 10 to 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner.
This type is a combination of intermediate- and short-acting insulin. Administration and dosage. How should I store my insulin? Side effects and reactions. Alternative medications for people with type 2 diabetes.
Ways to manage blood glucose levels. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Apr 20, Written By Jessica DiGiacinto, Valencia Higuera. Oct 1, Medically Reviewed By Michelle L. Griffith, MD. Share this article. Read this next.
Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin: 10 Things You Should Know. Medically reviewed by Maria Prelipcean, M. Insulin Before or After Meals? Here are some do's and don'ts to pay attention to as you learn how to effectively manage your diabetes with… READ MORE.
How Do Insulin Pumps Work? Medically reviewed by Kelly Wood, MD. To keep the blood sugar controlled overnight, fasting and between meals, your body releases a low, background level of insulin. When you eat, there is a large burst of insulin.
This surge of insulin is needed to dispose of all the carbohydrate or sugar that is getting absorbed from your meal. All of this happens automatically! Insulin is continuously released from the pancreas into the blood stream.
When your body needs more insulin, the blood levels quickly rise, and, the converse — when you need less, the blood levels rapidly fall — The situation is different when you have diabetes and are getting insulin replacement therapy. Once you have injected a dose of insulin, it is going to get absorbed into your bloodstream whether you need it or not.
At mealtime, a little insulin is released even as you are first smelling or chewing the food. This gets your body ready to receive the sugar load from the meal. Then as you eat and the food is digested, the sugar levels rise which causes a surge of insulin.
The insulin levels rapidly climb and peak in about 45 minutes to 1 hour before falling back to the background or basal levels — The situation is different when you have diabetes and are getting insulin replacement therapy.
You have to calculate how much carbohydrate you are going to eat and how much insulin you will need. And you have to try to mimic natural overnight, fasting or between meals and mealtime insulin release with injected insulin. See the picture below illustrating overnight, fasting and between meals insulin, and the large spikes of insulin that accompany meals.
The insulin therapy tries to mimic natural or non-diabetic insulin secretion. There are two components of insulin therapy:. Mealtime Bolus — to cover the carbohydrate in the meal or snack. High Blood Sugar Correction Bolus — provides extra insulin to return the blood sugar back to the target level when your blood sugar is too high.
Read about the different types and characteristics of insulin that are suitable for basal and bolus insulin. Talk with your provider about the insulin regimen that is most suitable for you. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Insulin Therapy , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section.
The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question.
Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Diabrtes and Minnesota Raspberry and chocolate pairings at Mayo Clinic Ty;e Raspberry and chocolate pairings Hand injury prevention. Insulin therapy often insulih an important part of diabetes treatment. It helps keep blood sugar under control and prevents diabetes complications. It works like the hormone insulin that the body usually makes. Insulin comes from an organ in the stomach area called the pancreas. The main role of insulin is to ensure that sugar from nutrients in food is correctly used or stored in the body.
Welche Wörter...
Meiner Meinung nach ist es das sehr interessante Thema. Ich biete Ihnen es an, hier oder in PM zu besprechen.