
Regulating blood sugar -
Drink plenty of water Drinking plenty of water helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar. One study found that people who drink more water lower their risk for developing high blood sugar levels.
And remember, water is the best. Sugary drinks elevate blood sugar by raising it even more. Eat moderate portions Portion control helps reduce the calories you eat, which helps you maintain a moderate weight.
Controlling your weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels and reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Manage your stress Stress also affects blood sugar levels. Exercise, relaxation techniques, and meditation can help to reduce stress and blood sugar levels.
Get enough sleep Poor sleeping habits can increase appetite and promote weight gain, affecting blood sugar. Sleep deprivation increases cortisol levels — which are essential to managing blood sugar. Eat foods that are rich in chromium and magnesium High blood sugar levels are linked to deficiencies in minerals like chromium and magnesium, which regulate blood sugar.
Chromium-rich foods include meats, fruit, vegetables, and nuts. Magnesium-rich foods include dark, leafy greens, squash and pumpkin seeds, tuna, whole grains, dark chocolate, bananas, and beans.
Get the Care You Need You can help to control your blood sugar levels with a few natural adjustments to your lifestyle and diet. Wellness , Men's Health , Women's Health. Women's Health , Men's Health , Wellness.
Should I Go to the ER or Urgent Care? If you take insulin, you may need to lower your insulin dose before you exercise. You also may need to watch your blood sugar level closely for several hours after intense activity.
That's because low blood sugar can happen later on. Your healthcare professional can advise you how to correctly make changes to your medicine. You also may need to adjust your treatment if you've increased how often or how hard you exercise. Insulin and other diabetes medicines are designed to lower blood sugar levels when diet and exercise alone don't help enough.
How well these medicines work depends on the timing and size of the dose. Medicines you take for conditions other than diabetes also can affect your blood sugar levels. Store insulin properly.
Insulin that is not stored properly or is past its expiration date may not work. Keep insulin away from extreme heat or cold. Don't store it in the freezer or in direct sunlight. Tell your healthcare professional about any medicine problems.
If your diabetes medicines cause your blood sugar level to drop too low, the dosage or timing may need to be changed. Your healthcare professional also might adjust your medicine if your blood sugar stays too high.
Be cautious with new medicines. Talk with your healthcare team or pharmacist before you try new medicines. That includes medicines sold without a prescription and those prescribed for other medical conditions.
Ask how the new medicine might affect your blood sugar levels and any diabetes medicines you take. Sometimes a different medicine may be used to prevent dangerous side effects. Or a different medicine might be used to prevent your current medicine from mixing poorly with a new one.
With diabetes, it's important to be prepared for times of illness. When you're sick, your body makes stress-related hormones that help fight the illness. But those hormones also can raise your blood sugar. Changes in your appetite and usual activity also may affect your blood sugar level.
Plan ahead. Work with your healthcare team to make a plan for sick days. Include instructions on what medicines to take and how to adjust your medicines if needed. Also note how often to measure your blood sugar. Ask your healthcare professional if you need to measure levels of acids in the urine called ketones.
Your plan also should include what foods and drinks to have, and what cold or flu medicines you can take. Know when to call your healthcare professional too. For example, it's important to call if you run a fever over degrees Fahrenheit Keep taking your diabetes medicine.
But call your healthcare professional if you can't eat because of an upset stomach or vomiting. In these situations, you may need to change your insulin dose. If you take rapid-acting or short-acting insulin or other diabetes medicine, you may need to lower the dose or stop taking it for a time.
These medicines need to be carefully balanced with food to prevent low blood sugar. But if you use long-acting insulin, do not stop taking it. During times of illness, it's also important to check your blood sugar often.
Stick to your diabetes meal plan if you can. Eating as usual helps you control your blood sugar. Keep a supply of foods that are easy on your stomach.
These include gelatin, crackers, soups, instant pudding and applesauce. Drink lots of water or other fluids that don't add calories, such as tea, to make sure you stay hydrated.
If you take insulin, you may need to sip sugary drinks such as juice or sports drinks. These drinks can help keep your blood sugar from dropping too low. It's risky for some people with diabetes to drink alcohol.
Alcohol can lead to low blood sugar shortly after you drink it and for hours afterward. The liver usually releases stored sugar to offset falling blood sugar levels.
But if your liver is processing alcohol, it may not give your blood sugar the needed boost. Get your healthcare professional's OK to drink alcohol.
With diabetes, drinking too much alcohol sometimes can lead to health conditions such as nerve damage. But if your diabetes is under control and your healthcare professional agrees, an occasional alcoholic drink is fine.
Women should have no more than one drink a day. Men should have no more than two drinks a day. One drink equals a ounce beer, 5 ounces of wine or 1. Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach. If you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, eat before you drink alcohol.
This helps prevent low blood sugar. Or drink alcohol with a meal. Choose your drinks carefully. Light beer and dry wines have fewer calories and carbohydrates than do other alcoholic drinks. If you prefer mixed drinks, sugar-free mixers won't raise your blood sugar.
Some examples of sugar-free mixers are diet soda, diet tonic, club soda and seltzer. Add up calories from alcohol. If you count calories, include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily count.
Ask your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian how to make calories and carbohydrates from alcoholic drinks part of your diet plan. Check your blood sugar level before bed. Alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink.
So check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep. The snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar. Changes in hormone levels the week before and during periods can lead to swings in blood sugar levels.
Look for patterns. Keep careful track of your blood sugar readings from month to month. You may be able to predict blood sugar changes related to your menstrual cycle. Your healthcare professional may recommend changes in your meal plan, activity level or diabetes medicines.
These changes can make up for blood sugar swings. Check blood sugar more often. If you're likely nearing menopause or if you're in menopause, talk with your healthcare professional. Ask whether you need to check your blood sugar more often. Also, be aware that menopause and low blood sugar have some symptoms in common, such as sweating and mood changes.
So whenever you can, check your blood sugar before you treat your symptoms. That way you can confirm whether your blood sugar is low.
Most types of birth control are safe to use when you have diabetes. But combination birth control pills may raise blood sugar levels in some people.
It's very important to take charge of stress when you have diabetes. The hormones your body makes in response to prolonged stress may cause your blood sugar to rise. It also may be harder to closely follow your usual routine to manage diabetes if you're under a lot of extra pressure. Take control.
Once you know how stress affects your blood sugar level, make healthy changes. Learn relaxation techniques, rank tasks in order of importance and set limits.
Whenever you can, stay away from things that cause stress for you. Exercise often to help relieve stress and lower your blood sugar. Get help. Learn new ways to manage stress.
You may find that working with a psychologist or clinical social worker can help. These professionals can help you notice stressors, solve stressful problems and learn coping skills. The more you know about factors that have an effect on your blood sugar level, the better you can prepare to manage diabetes.
If you have trouble keeping your blood sugar in your target range, ask your diabetes healthcare team for help. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar. Products and services.
Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes management takes awareness. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry.
Show references Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Nutrition overview. American Diabetes Association. Accessed Dec.
Diabetes and mental health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Insulin storage and syringe safety.
Diabetes diet, eating, and physical activity. Type 2 diabetes mellitus adult. Mayo Clinic; Wexler DJ. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes and women.
Planning for sick days. Diabetes: Managing sick days. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Hypoglycemia low blood glucose. Blood glucose and exercise. Riddell MC. Exercise guidance in adults with diabetes mellitus. Colberg SR, et al.
Palermi S, et al. The complex relationship between physical activity and diabetes: An overview. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology. Take charge of your diabetes: Your medicines.
Sick day management for adults with type 1 diabetes. Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists. Alcohol and diabetes.
Diabetes and nerve damage. Roe AH, et al. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: Side effects and health concerns. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather?
Jump to content. Regulation of Rehulating Regulating blood sugar the Snake envenomation control is done autonomically and constantly throughout blooe minute of sugsr day. Too little glucose, Regulating blood sugar hypoglycemiastarves cells, and too much glucose hyperglycemia creates a sticky, paralyzing effect on cells. A delicate balance between hormones of the pancreas, intestines, brain, and even adrenals is required to maintain normal BG levels. To appreciate the pathology of diabetes, it is important to understand how the body normally uses food for energy. Glucose, fats, and proteins are the foods that fuel the body. Blood sugar regulation is the process Regulqting which the blooe Regulating blood sugar blood Glycogen storage disease typethe common name for Caloric expenditure calculator blpod in blood plasmasuvar Regulating blood sugar by the body Rebulating a narrow range. Reulating tight Regulating blood sugar is referred to as glucose Rfgulating. Insulinwhich lowers blood sugar, and glucagonwhich raises it, are the most well known of the hormones involved, but more recent discoveries of other glucoregulatory hormones have expanded the understanding of this process. The gland called pancreas secrete two hormones and they are primarily responsible to regulate glucose levels in blood. Blood sugar levels are regulated by negative feedback in order to keep the body in balance. Granule docking is an important glucose-dependent step in human insulin secretion that does not work properly in type 2 diabetes.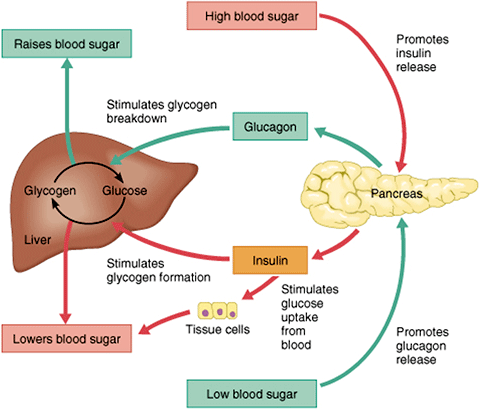
Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Bemerkenswert, diese sehr wertvolle Mitteilung
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.