
Ginseng for depression -
Antidepressant-like effects of ginsenoside Rg1 are due to activation of the BDNF signalling pathway and neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol ; Yamada N, Araki H, Yoshimura H. Identification of antidepressant-like ingredients in ginseng root Panax ginseng C.
Meyer using a menopausal depressive-like state in female mice: participation of 5-HT2A receptors. Psychopharma-cology Berl ; Jang D, Lee HJ, Lee K, Kim KR, Won R, Lee SE, et al. White ginseng ameliorates depressive behavior and increases hippocampal 5-HT level in the stressed ovariectomized rats.
Biomed Res Int ; Wang GL, He ZM, Zhu HY, Gao YG, Zhao Y, Yang H, et al. Involvement of serotonergic, noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems in the antidepressant-like effect of ginsenoside Rb1, a major active ingredient of Panax ginseng C. J Ethnopharmacol ; Mou Z, Huang Q, Chu SF, Zhang MJ, Hu JF, Chen NH, et al.
Antidepressive effects of ginsenoside Rg1 via regulation of HPA and HPG axis. Biomed Pharmacother ; Dong X, Zheng L, Lu S, Yang Y. Neuroprotective effects of pretreatment of ginsenoside Rb1 on severe cerebral ischemia-induced injuries in aged mice: involvement of anti-oxidant signaling.
Geriatr Gerontol Int ; Kim C, Lee JH, Baek SH, Ko JH, Nam D, Ahn KS. Korean red ginseng extract enhances the anticancer effects of sorafenib through abrogation of CREB and c-Jun activation in renal cell carcinoma. Phytother Res ; Lin IM, Fan SY, Yen CF, Yeh YC, Tang TC, Huang MF, et al.
Heart rate variability biofeedback increased autonomic activation and improved symptoms of depression and insomnia among patients with major depression disorder. Clin Psycho-pharmacol Neurosci ; American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM Arlington:American Psychiatric Association; Montgomery SA, Asberg M.
A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry ; Han C, Pae CU, Patkar AA, Masand PS, Kim KW, Joe SH, et al. Psychometric properties of the Patient Health Questionnaire PHQ for measuring the somatic symptoms of psychiatric outpatients.
Psychosomatics ; Guy W. ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Alcohol, Drug Abuse, and Mental Health Administration, National Institute of Mental Health, Psychopharmacology Research Branch, Division of Extramural Research Programs; Chapman CR, Casey KL, Dubner R, Foley KM, Gracely RH, Reading AE.
Pain measurement: an overview. Pain ; Shin WY, Kang EH, Kim KJ, Song YJ, Yu BH. Effect of Korean red ginseng on stress responses and beta-adrenergic receptor function in a normal population.
Korean J psychopharmacol ; Ryu S, Jeon H, Koo S, Kim S. Korean red ginseng enhances neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of 1-methylphenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice.
Front Aging Neurosci ; Dang H, Chen Y, Liu X, Wang Q, Wang L, Jia W, et al. Antidepressant effects of ginseng total saponins in the forced swimming test and chronic mild stress models of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry ; Petralia MC, Mazzon E, Fagone P, Basile MS, Lenzo V, Quattropani MC, et al.
The cytokine network in the pathogenesis of major depressive disorder. Close to translation? Autoimmun Rev ; Joo SS, Won TJ, Lee DI. Reciprocal activity of ginsenosides in the production of proinflammatory repertoire, and their potential roles in neuroprotection in vivo.
Planta Med ; Jiang N, Zhang BY, Dong LM, Lv JW, Lu C, Wang Q, et al. Antidepressant effects of dammarane sapogenins in chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice.
Baek JH, Heo JY, Fava M, Mischoulon D, Choi KW, Na EJ, et al. Effect of Korean red ginseng in individuals exposed to high stress levels: a 6-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
J Ginseng Res ; Jeong HG, Ko YH, Oh SY, Han C, Kim T, Joe SH. Effect of Korean red ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for women with residual symptoms of major depression.
Asia Pac Psychiatry ; There have been two studies which examined the effects of ginseng in menopausal women. Both studies found women who took ginseng experienced a greater reduction in depression symptoms which are common symptoms of menopause than those who took a placebo dummy pill.
However, these studies had a small number of participants, and the participants did not have clinical depression. More studies of better quality are needed to understand if ginseng could be helpful for depression.
Like all herbs, ginseng can cause side effects in some people, although these are generally minor. Ginseng may have negative interactions with prescribed medications or other supplements.
As with all supplements, you should check with your GP or pharmacist to see if it might interfere with other medications or supplements you are taking, and talk with your doctor if your symptoms worsen or new ones develop. Capsules of powdered ginseng root are available from health food shops and most supermarkets.
Ginseng is also available as a tea. There is not enough good evidence at this stage to recommend ginseng as a treatment for depression. Ginseng Our rating. The rating system These treatments are very useful. They are strongly supported as effective by scientific evidence.
These treatments are useful. They are supported by scientific evidence as effective, but the evidence is not as strong. will get colorectal cancer during his or her lifetime. Researchers treated human colorectal cancer cells with steamed ginseng berry extract and found the anti-proliferation effects were 98 percent for HCT and 99 percent for SW cells.
When researchers tested steamed American ginseng root, they found results comparable to that of the steamed berry extract.
Another well-researched ginseng benefit is its ability to boost the immune system — helping the body fight off infection and disease. The roots, stems and leaves have been used for maintaining immune homeostasis and enhancing resistance to illness or infection.
Several clinical studies have shown that American ginseng improves the performance of cells that play a role in immunity. It regulates each type of immune cell, including macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, T cells and B cells.
Ginseng extracts produce antimicrobial compounds that work as a defense mechanism against bacterial and viral infections. Studies show that its polyacetylene compounds are effective against bacterial infections.
Research involving mice showed that ginseng decreased the number of bacteria present in the spleens, kidney and blood. Ginseng extracts also protected mice from septic death due to inflammation. Reports show that this herb also has inhibitory effects on the growth of many viruses, including influenza, HIV and rotavirus.
Pesky symptoms, such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, irritability, anxiety, depressive symptoms, vaginal dryness, decreased sex drive, weight gain, insomnia and thinning hair, tend to accompany menopause.
Some evidence suggests that ginseng can help decrease the severity and occurrence of these symptoms as part of a natural menopause treatment plan. A systematic review of randomized clinical trials found that in three different trials Korean red ginseng had the efficacy to boost sexual arousal in menopausal women, increase well-being and general health while decreasing depressive symptoms, and better improve menopause symptoms on the Kupperman index and Menopausal Rating Scale compared to the placebo group.
A fourth study found no significant difference in the frequency of hot flashes between the ginseng and placebo group. Ginseng products are made from the root and the offshoots that are called root hairs. You can find the herb in dried, powdered, capsule and tablet forms. It is also available in a number of combination formulas.
The contents of products labeled as containing Panax can vary greatly, and some may contain little or no Panax. Be sure to read the ingredient labels carefully, and always purchase products from a reputable and reliable company. When buying Asian ginseng, look for Korean, red or Panax ginseng.
When buying the American variety, look for Panax quinquefolius. In China, people have been drinking ginseng tea for 5, years. In Chinese herbal medicine, practitioners recommend that adults over 40 drink one cup every day.
Ginseng tea, just like ginseng supplements and extracts, is used to improve your mental power and memory.
When making the tea, first choose the type of ginseng you want to use: American which is better during hotter months or Korean better during colder months.
You can buy ginseng tea bags from your local food store, but making it yourself from the root of the plant is the most beneficial form. Proper dosing is an important factor for ginseng use. The following ginseng doses have been studied in scientific research:.
The side effects from ginseng are generally mild in healthy adults. It can act as a stimulant in some people, so it may cause nervousness and insomnia especially in large doses. Long-term use or high doses may cause headaches, dizziness and stomachaches. Women who use it regularly may experience menstrual changes and vaginal bleeding, and there have also been some reports of allergic reactions to the herb.
Given the lack of evidence about its safety, ginseng is not recommended for children or women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. It can interact with warfarin coumadin and some medicines for depression. There is some concern that Panax increases symptoms of autoimmune diseases, such as MS, lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, so patients with those conditions should consult with their doctors before and while taking this supplement.
People who have had organ transplants may not want to take it because it could increase the risk of organ rejection.
Ginseng may interact with female hormone-sensitive illnesses, such as breast cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, endometriosis and uterine fibroids, because it has estrogen-like effects. Research shows that excessive use can lead to ginseng abuse syndrome , which has been associated with:.
Gluten-free athlete nutrition, a global Ginsen of COVID has Electrolyte balance for hydration spread to various Ginsent Ginseng for depression. Giinseng the number of COVID patients has increased, depreession of those infected with SARS-CoV-2 have Ginseng for depression a variety of fir symptoms, including depression, cognitive impairment, and fatigue. A distinct storm of inflammatory factors that contribute to the initial disease but also a persistent post-acute phase syndrome has been reported in patients with COVID Neuropsychological symptoms including depression, cognitive impairment, and fatigue are closely related to circulating and local brain inflammatory factors. Natural products are currently being examined for their ability to treat numerous complications caused by COVID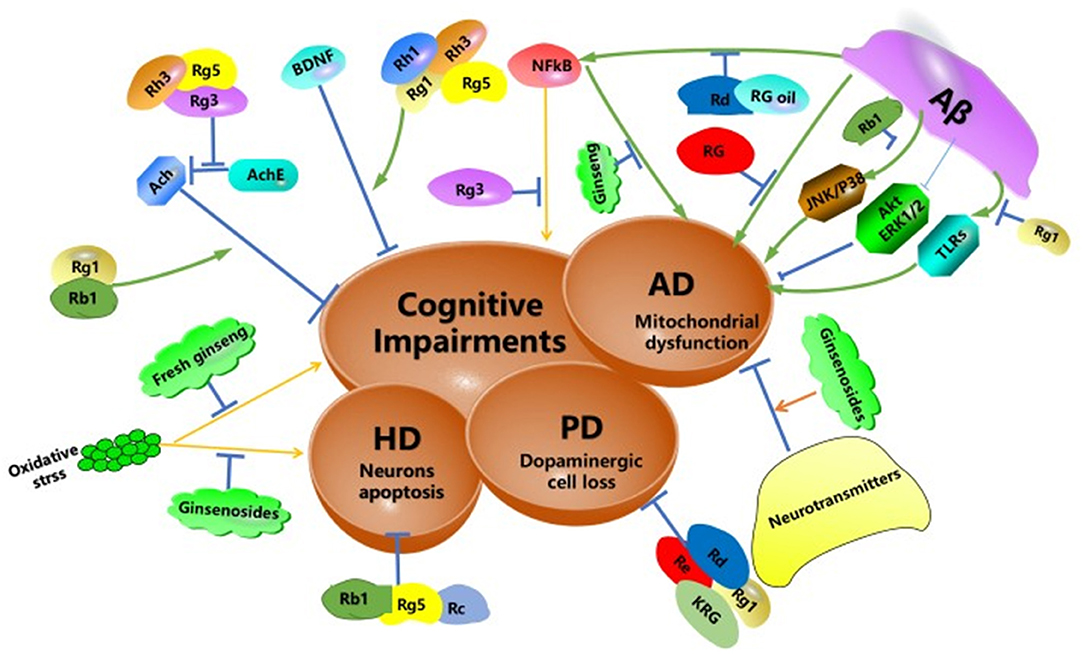
0 thoughts on “Ginseng for depression”