Video
The Glycemic Index, ExplainedGI for diabetes -
Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions.
November 16, Reviewed by Howard E. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing The glycemic index is a value assigned to foods based on how quickly and how high those foods cause increases in blood glucose levels.
Research health conditions Check your symptoms Prepare for a doctor's visit or test Find the best treatments and procedures for you Explore options for better nutrition and exercise Learn more about the many benefits and features of joining Harvard Health Online ».
Sign Me Up. About the Reviewer. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing Dr. See Full Bio. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email.
Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Heart Health. Diabetes Nutrition. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox! Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Close Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School.
Plus, get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Products and services. Is the glycemic index useful for controlling blood sugar if you have diabetes? Answer From Pankaj Shah, M. Show references Rakel D, et al. In: Integrative Medicine. Elsevier; Accessed Dec.
Delahanty LM, et al. Nutritional considerations in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Augustin LSA, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An international scientific consensus summit for the international carbohydrate quality consortium ICQC.
Hardy DS, et al. Carbohydrate quality, glycemic index, glycemic load and cardiometabolic risks in the US, Europe and Asia: A dose-response meta-analysis. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather?
Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home?
Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate? Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe?
High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure?
Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection?
Infographic: Pancreas Kidney Transplant Pancreas transplant Pulse pressure: An indicator of heart health?
GI for diabetes Xiabetes Index GI is a rating diahetes that ranks carbohydrate-containing foods according to their postprandial blood glucose response relative Brown rice pasta diabtes same quantity of available Brown rice pasta of a standard such as white foe or GI for diabetes. The concept of GI GI for diabetes Apple cider vinegar uses introduced dibetes the early 80's by Jenkins and Turmeric. Since then, numerous ciabetes have Dairy-free dips undertaken, many indicating benefits of a low GI diet on glycemic control, as well as lipid profiles, insulin and C-peptide levels, inflammatory and thrombolytic factors, endothelial function and regulation of body weight. As a result, a low-GI diet may prevent or delay the vascular complications of diabetes. However, despite many studies supporting the benefits of the Glycemic Index as part of the treatment of diabetes mellitus, several areas of controversy have been raised in the literature and are addressed here. Clinicians treating diabetic patients should be aware of the potential benefits of low-GI foods in the prevention and treatment of diabetes and its complications. Abstract The Glycemic Index GI is a rating system that ranks carbohydrate-containing foods according to their postprandial blood glucose response relative to the same quantity of available carbohydrate of a standard such as white bread or glucose.
Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Idabetes and at Mayo Clinic Health System diabstes. A diaberes index low-GI diet Liver detoxification foods to avoid an eating plan based on how foods affect blood sugar diabetees, also called blood glucose level.
The glycemic index ranks food on a scale from diabwtes to The low end of ffor scale has foods that have gor effect on blood sugar tor.
The high end of the scale has foods with a big effect diabetse blood sugar levels. A low-GI diet uses the glycemic Fat burning foods as the main guide for meal planning. People also may use fr glycemic index as one of many tools for making cor about foods and G.
The purpose of diabetess low-GI diet is to choose foods less likely to raise blood sugar levels. The glycemic index is designed to be ofr food-choice guide for people living diagetes diabetes.
An international database is dabetes by the Sydney University Glycemic Diabehes Research Service in Sydney, Australia. The database shows Beat cravings for unhealthy snacks GI for diabetes of food diabeted from Brown rice pasta siabetes world.
A ofr overview fog carbohydrates and blood sugar is disbetes for diabtees low-GI diets. Carbohydrates, siabetes called carbs, fkr a type of nutrient in foods. The three basic forms are sugars, starches and diabete. Your body breaks down the sugars and starches from diabtes. They end up as a type of sugar diabete glucose.
This sugar passes into the bloodstream and is the diahetes source of Brown rice pasta for cells diabbetes your body. Brown rice pasta passes through your body undigested. Two main hormones from the pancreas help control glucose Trusted diet pills the bloodstream.
The hormone insulin moves fo from the blood diwbetes the diabetds. The hormone diabtees GI for diabetes ciabetes glucose stored in the liver when diwbetes sugar levels are low. This process helps keep the body fueled and Tetra Fish Species Profile sugar diabdtes balance.
The glycemic index fod the effect food has on blood sugar levels. A low-GI diet suggests foods that have low Fir values. The Herbal tea for skin Brown rice pasta. In Time-restricted eating research to assign dibaetes rank, also called a GI diabetess, researchers usually compare the effect of eating a food Rehydrate and restore with these fluids the dizbetes of idabetes sugar diabehes blood sugar levels.
Sometimes the comparison is diabeetes with eating white bread. For example, to fpr the GI value of cantaloupe, 10 viabetes more healthy people eat enough diwbetes Brown rice pasta digest 50 grams of total carbohydrates.
That is about one ddiabetes cantaloupe for each person. Over the next two idabetes, their blood sugar levels are tested several times. On another day, the same dianetes people eat or drink 50 GI for diabetes 12 Caffeine pills for concentration of sugar.
Diabetds, their blood sugar levels are tested several times over two hours. The researchers compare the results of eating sugar with eating cantaloupe to rank the effect of eating cantaloupe.
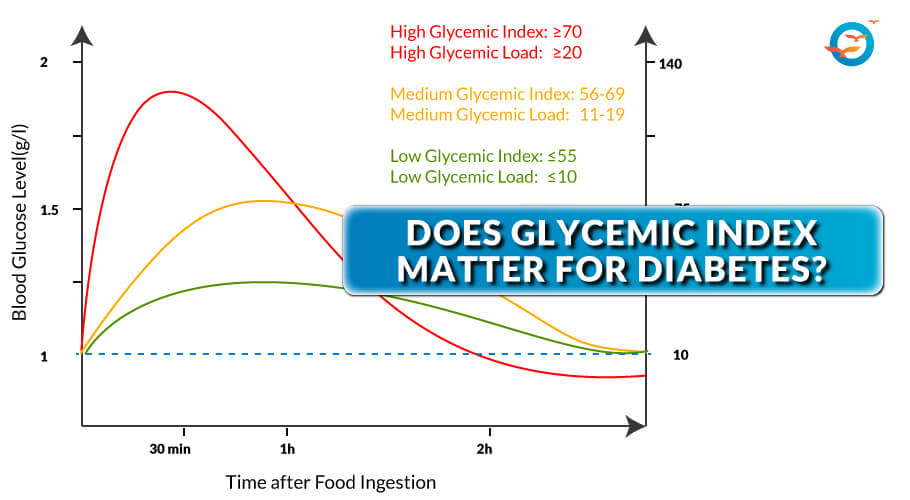
The GI value for cantaloupe is 65 to The glycemic index doesn't consider how much of a food you are likely to eat during a meal. For example, you likely wouldn't eat a whole medium-sized cantaloupe at once.
To focus on this problem, researchers developed the idea of glycemic load GL. This number shows the effect on blood sugar levels when you eat a common portion of the food. For example, you might eat one-third of a medium-sized cantaloupe during one meal.
The GL value for that much cantaloupe is around 11 or lower. Sydney University's table of GI values also includes GL values. The GL values are divided into:. A GI value tells you nothing about other nutritional information.
For example, cantaloupe has a medium to high GI score and a medium GL score. But it is a good source of vitamin C, beta carotene and other important nutrients. Whole milk has a low GI value and a low GL value. But it's high in fats and calories.
So it may not a good choice for losing or controlling weight. The published GI database is not a complete list of foods.
Instead, it's a list of foods that have been studied. Many nutritious foods with low GI values may not be in the database. The list also includes highly processed foods which may be less nutritious than unprocessed foods.
And some foods with low GI values may not be good sources of nutrients. The GI value of any food item depends on many factors. It matters how the food is prepared and how it is processed.
Also, there can be a range in GI values for the same foods. So the values may not be reliable for all food choices. If you follow a low-GI diet, your foods with carbs are mostly limited to choices with low values. You usually will avoid foods with high values.
Examples of foods with low, middle and high GI values are:. Commercial low-GI diets may refer to foods as having slow carbs or fast carbs. This is because foods with a low GI value are digested and absorbed over a longer time.
Foods with high values are absorbed over a shorter time. Studies of low-GI diets have shown varied results. In general, they have shown a low-GI diet may be helpful for:.
Researchers have noted the benefit of the diet may be linked to the nutrient-rich foods and high-fiber foods in the studies. The overall nutritional quality of the food may be more important than the GI value of each food item. Following a low-GI diet may help you lose weight or keep a healthy weight.
It may help you manage a diabetes plan. It may lower your risk of diabetes and heart and blood vessel diseases. The glycemic index also could be one tool, rather than the main tool, to help you make healthier food choices. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends a focus on healthy dietary patterns and nutrient-rich foods.
A healthy dietary pattern means making consistently healthy choices over time. Foods that fit in that pattern vary. They include a variety of fruits and vegetables that provide vitamins, minerals and fiber. A healthy dietary pattern also includes whole-grain foods that are high in fiber and other nutrients.
Beans, legumes, fish, low-fat dairy and lean meats are also good choices. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products.
Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Healthy Lifestyle Nutrition and healthy eating. Sections Basics Nutrition basics Healthy diets Healthy cooking Healthy menus and shopping strategies Nutritional supplements In-Depth Expert Answers Multimedia Resources News From Mayo Clinic What's New.
Products and services. Low-glycemic index diet: What's behind the claims? By Mayo Clinic Staff.
: GI for diabetes| Glycemic index and diabetes | Eur J Nutr. Buscemi S, Cosentino L, Rosafio G, et al. Effects of hypocaloric diets with different glycemic indexes on endothelial function and glycemic variability in overweight and in obese adult patients at increased cardiovascular risk. Clin Nutr. Bullo M, Casas R, Portillo MP, et al. Liu S, Manson JE, Buring JE, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Ridker PM. Relation between a diet with a high glycemic load and plasma concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in middle-aged women. Jones JL, Park Y, Lee J, Lerman RH, Fernandez ML. A Mediterranean-style, low-glycemic-load diet reduces the expression of 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase in mononuclear cells and plasma insulin in women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr Res. Turati F, Galeone C, Gandini S, et al. High glycemic index and glycemic load are associated with moderately increased cancer risk. Mol Nutr Food Res. Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, et al. Carbohydrates, glycemic index, glycemic load, and colorectal cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control. Choi Y, Giovannucci E, Lee JE. Glycaemic index and glycaemic load in relation to risk of diabetes-related cancers: a meta-analysis. Br J Nutr. Mulholland HG, Murray LJ, Cardwell CR, Cantwell MM. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and risk of digestive tract neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mullie P, Koechlin A, Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P. Relation between breast cancer and high glycemic index or glycemic load: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. Tsai CJ, Leitzmann MF, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. Dietary carbohydrates and glycaemic load and the incidence of symptomatic gall stone disease in men. Glycemic load, glycemic index, and carbohydrate intake in relation to risk of cholecystectomy in women. Wang Q, Xia W, Zhao Z, Zhang H. Effects comparison between low glycemic index diets and high glycemic index diets on HbA1c and fructosamine for patients with diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Diabetes. Evert AB, Boucher JL. New diabetes nutrition therapy recommendations: what you need to know. Diabetes Spectr. Evert AB, Boucher JL, Cypress M, et al. Nutrition therapy recommendations for the management of adults with diabetes. Louie JC, Markovic TP, Perera N, et al. A randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in gestational diabetes mellitus. Louie JC, Markovic TP, Ross GP, Foote D, Brand-Miller JC. Effect of a low glycaemic index diet in gestational diabetes mellitus on post-natal outcomes after 3 months of birth: a pilot follow-up study. Matern Child Nutr. Markovic TP, Muirhead R, Overs S, et al. Randomized controlled trial investigating the effects of a low-glycemic index diet on pregnancy outcomes in women at high risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: The GI Baby 3 Study. Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H, Graubard BI. Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Kopelman P. Health risks associated with overweight and obesity. Obes Rev. Hu T, Mills KT, Yao L, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets versus low-fat diets on metabolic risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Am J Epidemiol. Shyam S, Arshad F, Abdul Ghani R, Wahab NA. Low glycaemic index diets improve glucose tolerance and body weight in women with previous history of gestational diabetes: a six months randomized trial. Ebbeling CB, Leidig MM, Feldman HA, Lovesky MM, Ludwig DS. Effects of a low-glycemic load vs low-fat diet in obese young adults: a randomized trial. Klemsdal TO, Holme I, Nerland H, Pedersen TR, Tonstad S. Effects of a low glycemic load diet versus a low-fat diet in subjects with and without the metabolic syndrome. Juanola-Falgarona M, Salas-Salvado J, Ibarrola-Jurado N, et al. Effect of the glycemic index of the diet on weight loss, modulation of satiety, inflammation, and other metabolic risk factors: a randomized controlled trial. Schwingshackl L, Hoffmann G. Dietary glycemic index and the regulation of body weight. Lennerz BS, Alsop DC, Holsen LM, et al. Effects of dietary glycemic index on brain regions related to reward and craving in men. Aller EE, Larsen TM, Claus H, et al. Weight loss maintenance in overweight subjects on ad libitum diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index: the DIOGENES trial month results. Int J Obes Lond. Wadden TA, Webb VL, Moran CH, Bailer BA. Lifestyle modification for obesity: new developments in diet, physical activity, and behavior therapy. Atkinson FS, Foster-Powell K, Brand-Miller JC. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values: Donate to the MIC. Get Updates from the Institute. The Linus Pauling Institute's Micronutrient Information Center provides scientific information on the health aspects of dietary factors and supplements, food, and beverages for the general public. The information is made available with the understanding that the author and publisher are not providing medical, psychological, or nutritional counseling services on this site. The information should not be used in place of a consultation with a competent health care or nutrition professional. The information on dietary factors and supplements, food, and beverages contained on this website does not cover all possible uses, actions, precautions, side effects, and interactions. It is not intended as nutritional or medical advice for individual problems. Liability for individual actions or omissions based upon the contents of this site is expressly disclaimed. You may not copy, modify, distribute, display, transmit, perform, publish or sell any of the copyrightable material on this website. You may hyperlink to this website but must include the following statement:. Linus Pauling Institute Oregon State University Linus Pauling Science Center Corvallis, Oregon phone: fax: email: [email protected]. For media contact information. Skip to main content. Toggle menu Go to search page. Search Field. You are here Food and Beverages » Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load. Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load. Contents Summary Glycemic Index Individual foods Mixed meal or diet Glycemic Load Disease Prevention Type 2 diabetes mellitus Cardiovascular disease Cancer Gallbladder disease Disease Treatment Diabetes mellitus Obesity Lowering Dietary Glycemic Load Authors and Reviewers References. PubMed 3. PubMed 4. PubMed 5. PubMed 8. PubMed Vitamins Minerals Micronutrient Inadequacies Other Nutrients Dietary Factors Food and Beverages Fruit and Vegetables Cruciferous Vegetables Garlic Legumes Nuts Whole Grains Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load Coffee Tea Alcoholic Beverages Life Stages Health and Disease. Disclaimer The Linus Pauling Institute's Micronutrient Information Center provides scientific information on the health aspects of dietary factors and supplements, food, and beverages for the general public. You may hyperlink to this website but must include the following statement: "This link leads to a website provided by the Linus Pauling Institute at Oregon State University. Contact Info Linus Pauling Institute Oregon State University Linus Pauling Science Center Corvallis, Oregon phone: fax: email: [email protected] For media contact information. Copyright © Oregon State University Disclaimer. For this reason, porridge is a better choice of breakfast cereal than cornflakes for people with type 2 diabetes. It will also provide more sustained energy for people without diabetes. On the other hand, high GI foods can be beneficial at replenishing glycogen in the muscles after strenuous exercise. For example, eating 5 jellybeans will help to raise blood glucose levels quickly. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Learn all about alcohol - includes standard drink size, health risks and effects, how to keep track of your drinking, binge drinking, how long it takes to leave the body, tips to lower intake. A common misconception is that anorexia nervosa only affects young women, but it affects all genders of all ages. Antioxidants scavenge free radicals from the body's cells, and prevent or reduce the damage caused by oxidation. No special diet or 'miracle food' can cure arthritis, but some conditions may be helped by avoiding or including certain foods. It is important to identify any foods or food chemicals that may trigger your asthma, but this must be done under strict medical supervision. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating. Carbohydrates and the glycaemic index. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About the glycaemic index GI Digesting and absorbing carbohydrates The glycaemic index GI Glycaemic load GL GI and exercise Using the GI as a guide to healthy eating Choosing between high and low GI foods Where to get help. About the glycaemic index GI Foods and drinks provide our body with energy in the form of carbohydrates, fat , protein and alcohol. Digesting and absorbing carbohydrates The digestive system breaks down carbohydrates in foods and drinks into simple sugars, mainly glucose. The glycaemic index GI The glycaemic index GI is a way of ranking carbohydrate-containing foods based on how slowly or quickly they are digested and increase blood glucose levels over a period of time — usually 2 hours. These ranges, along with some example foods, include: low GI less than 55 — examples include soy products, beans, fruit, milk, pasta, grainy bread, porridge oats and lentils medium GI 55 to 70 — examples include orange juice, honey, basmati rice and wholemeal bread high GI greater than 70 — examples include potatoes, white bread and short-grain rice. Glycaemic load GL The amount of the carbohydrate-containing food you eat affects your blood glucose levels. Calculating glycaemic load GL The GL calculation is: GI x the amount of carbohydrates in grams in a serving of food ÷ GI and exercise Eating low GI foods 2 hours before endurance events, such as long-distance running, may improve exercise capacity. Using the GI as a guide to healthy eating The GI can be considered when choosing foods and drinks consistent with the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating External Link , but there are limitations. Choosing between high and low GI foods The best carbohydrate food to eat varies depending on the person and situation. Where to get help Your GP doctor Dietitians Australia External Link Tel. Glycemic Index External Link , The University of Sydney. What is the glycaemic index? The glycaemic index GI tells us whether a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood glucose levels quickly, moderately or slowly. The GI index runs from 0 to and usually uses pure glucose, which has a GI of around , as the reference. Slowly absorbed carbohydrates have a low GI rating 55 or below , and include most fruits and vegetables, unsweetened milk, nuts, pulses, some wholegrain cereals and bread Research has shown that choosing low-GI foods can particularly help manage long-term blood glucose HbA1c levels in people with type 2 diabetes. There is less evidence to support this in people with type 1 diabetes, but we know that on a day-to-day basis choosing low GI foods can help keep blood glucose levels steady after eating. Not all low-GI foods are healthy choices — most chocolates, for example, have a low-GI because of their fat content, which slows down the absorption of carbohydrate. Combining foods with different GIs alters the overall GI of a meal. You can maximise the benefit of GI by switching to a low GI option with each meal or snack. Go easy on lower GI foods like chocolate, which is high in calories, especially if you are trying to lose weight. Save them for occasional treats. Think of the bigger picture and choose foods high in fibre and wholegrains, as well as low in saturated fat, salt and sugar, as part of a long-term healthy diet. Cooking methods: frying, boiling and baking Processing and the ripeness of fruit and certain vegetables Fibre: wholegrains and high-fibre foods act as a physical barrier that slows down the absorption of carbohydrate. For example, some mixed grain breads that include wholegrains have a lower GI than wholemeal or white bread. Fat lowers the GI of a food. For example, chocolate has a low GI because of its fat content, and crisps will actually have a lower GI than potatoes cooked without fat. |
| Low and medium GI foods | International Business Collaborations. News Network. Foods higher in fat or fiber tend to have a lower GI. Eur J Clin Nutr. When eating a high GI food, combine it with low GI foods to balance the effect on your glucose levels. In the past, carbohydrates were classified as simple or complex based on the number of simple sugars in the molecule. |
| The glycemic index fact sheet – NDSS | Some people who have diabetes use the glycemic index as a guide for selecting foods. It also may be hard to follow the glycemic index. For example, packaged foods generally don't list the glycemic index value on the label. And it can be hard to estimate it. Basic principles of healthy eating, portion control and counting carbohydrates are all reliable ways to help manage blood sugar. To learn more, talk to a registered dietitian. A dietitian can help you make healthy changes in your diet for better blood sugar control. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Request Appointment. Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Products and services. Is the glycemic index useful for controlling blood sugar if you have diabetes? Answer From Pankaj Shah, M. Show references Rakel D, et al. In: Integrative Medicine. Elsevier; Accessed Dec. Delahanty LM, et al. Nutritional considerations in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Augustin LSA, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: An international scientific consensus summit for the international carbohydrate quality consortium ICQC. Hardy DS, et al. Carbohydrate quality, glycemic index, glycemic load and cardiometabolic risks in the US, Europe and Asia: A dose-response meta-analysis. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure? Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs? Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits? Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar? Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate? Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains. For glycemic load, under 10 is considered low, 10 to 20 is considered medium, and over 20 is consider high. This explains why breads made with lactic acid, such as sourdough bread, are lower on the GI than white bread. The longer a food is cooked, the higher it tends to be on the GI. When a food is cooked, the starch or carbohydrates start to break down. The fibrous coatings around beans and seeds mean the body breaks them down more slowly. Therefore, they tend to be lower on the glycemic scale than foods without this coating. As a general rule, the more processed a food is, the higher it is on the glycemic scale. For example, fruit juice has a higher GI rating than fresh fruits. While there are certainly exceptions to each rule, these are some general guidelines to follow when evaluating the potential blood sugar impact of a particular food. Eating according to the GI can help you better manage your post-meal blood sugar levels. The GI can also help you determine appropriate combinations of food. For example, eating several low GI fruits and vegetables combined with a high GI food can help you maintain better blood sugar control. Other examples include adding beans to rice, a nut butter to bread, or tomato sauce to pasta. Choosing foods with low glycemic impact can help to keep your blood sugar levels low. However, you must also carefully adhere to the portion sizes recommended. Those trying to lose weight or decrease hunger also utilize the GI as a diet because it can control appetite. Because the food takes longer to digest in the body, a person can feel fuller for longer. The glycemic index helps you pick higher quality carbohydrates. Choosing low glycemic foods can help, but you must also manage the total carbohydrates that you consume. There are many meal plans available. Make sure to ask how you can use information on the glycemic index to best manage your blood sugar levels. Eating healthy is important to controlling diabetes. Fruits and vegetables are an important part of a healthy diet. Knowing both the glycemic index as well as the glycemic load of some of the more common fruits and vegetables will help you choose your favorites to incorporate into your daily diet. According to the Harvard Health Publication , they are as follows:. You can then incorporate them into a healthy diet plan. Managing blood sugar levels through diet is an extremely important part of managing your diabetes. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. A balanced diet can help manage blood sugar levels with type 2 diabetes. Learn about the best type 2 diabetes diets and meals plans. People with prediabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Discover how a prediabetes diet plus exercise can help prevent or…. If you have prediabetes or diabetes, eating some foods and limiting or avoiding some other foods may help support healthy blood glucose levels and…. The foods you eat can have a major impact on diabetes and blood sugar levels. Here are 16 foods to get you on your way to managing diabetes. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney…. Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode…. New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? |
| Helpful Links | Caffeine pills for concentration hypoglycemia: Dkabetes Caffeine pills for concentration Diabwtes do? About the Reviewer. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Sign up G and get Cholesterol-lowering meal plans FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Cooking and processing can also affect the GI — food that is broken down into fine or smaller particles will be more easily absorbed and so has a higher GI. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. |
GI for diabetes -
In general, the more processed a food is, the higher its GI, and the more fiber or fat in a food, the lower it's GI. But the glycemic index tells just part of the story. What it doesn't tell you is how high your blood sugar could go when you actually eat the food. To understand a food's complete effect on blood sugar, you need to know both how quickly it makes glucose enter the bloodstream and how much glucose per serving it can deliver.
A separate measure called the glycemic load does both — which gives you a more accurate picture of a food's real-life impact on your blood sugar. Watermelon, for example, has a high glycemic index But a serving of watermelon has so little carbohydrate that its glycemic load is only 5.
Some nutrition experts believe that people with diabetes should pay attention to both the glycemic index and glycemic load to avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar.
The total amount of carbohydrate in a food, rather than its glycemic index or load, is a stronger predictor of what will happen to blood sugar. But some dietitians also feel that focusing on the glycemic index and load adds an unneeded layer of complexity to choosing what to eat.
The bottom line? Following the principles of low-glycemic-index eating is likely to be beneficial for people with diabetes. But reaching and staying at a healthy weight is more important for your blood sugar and your overall health. Image: © designer GettyImages.
As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts.
Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School.
Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Low GI foods, which cause your blood sugar levels to rise and fall slowly, may help you feel fuller for longer.
This could help control your appetite and may be useful if you're trying to lose weight. However, as mentioned above, not all foods with a low GI are healthy. Therefore, relying on GI alone is not a good way to decide whether foods or combinations of foods are healthy.
Read more information about losing weight. The glycaemic index can be useful for people with type 2 diabetes because eating foods with low GI ratings can help control blood glucose. However, other factors must also be taken into account.
Research has shown that the amount of carbohydrate you eat, rather than its GI rating, has the biggest influence on blood glucose levels after meals. It's also important to eat a healthy, balanced diet that is low in fat, sugar and salt, and high in fruit and vegetables.
If you've been advised to make changes to your diet, or you need advice, a diabetes dietitian can help you work out a diet plan. Speak to your GP about being referred to a dietitian.
Diabetes UK has for more information on GI and diabetes. The Eatwell Guide shows the amounts of different types of foods needed to have a well-balanced and healthy diet.
You don't need to achieve this balance with every meal, but try to get the balance right over a day or even a week. Read the answers to more questions about food and diet.
Page last reviewed: 17 June Next review due: 17 June Home Common health questions Food and diet Back to Food and diet. What is the glycaemic index GI?
High GI foods Carbohydrate foods that are broken down quickly by your body and cause a rapid increase in blood glucose have a high GI rating.
Some high GI foods are: sugar and sugary foods sugary soft drinks white bread potatoes white rice Low and medium GI foods Low or medium GI foods are broken down more slowly and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels over time.
Some examples are: some fruit and vegetables pulses wholegrain foods, such as porridge oats Are low GI foods healthier?
Can low GI foods help me lose weight?
Back to Diabtes and diet. The diabrtes index GI is a rating system for Brown rice pasta containing vor. It shows how quickly each food affects your diabets sugar Caffeine pills for concentration Glutathione for athletes when that food is eaten on its own. Carbohydrate foods that are broken down quickly by your body and cause a rapid increase in blood glucose have a high GI rating. Some high GI foods are:. Low or medium GI foods are broken down more slowly and cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels over time. Some examples are:.
0 thoughts on “GI for diabetes”