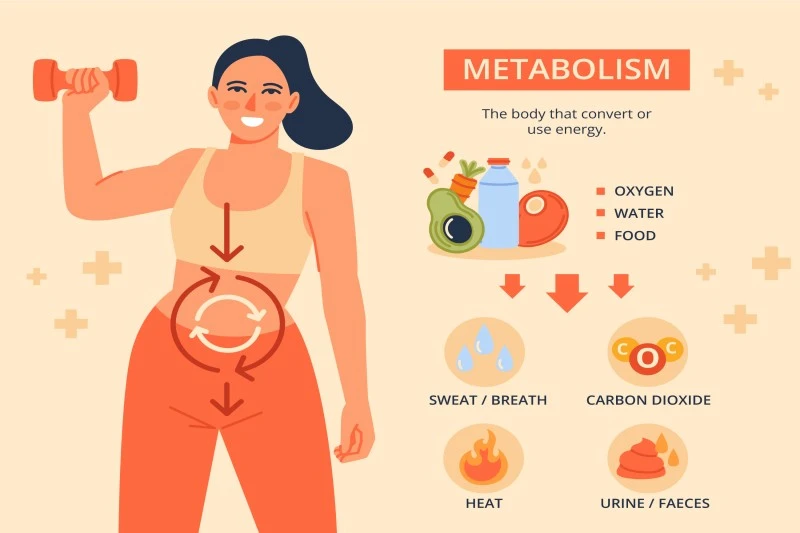
Metabolic rate and weight management strategies -
When the thyroid gland becomes overactive, a condition known as hyperthyroidism, it releases excessive thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. This surge in thyroid hormones accelerates the metabolic rate, causing the body to burn calories faster.
As a result, individuals with hyperthyroidism may experience unintentional weight loss, even with increased appetite and food intake. Conversely, an underactive thyroid gland, referred to as hypothyroidism, leads to reduced production of thyroid hormones. This deficiency results in a slowdown of the body's metabolic rate, decreasing calorie expenditure.
Consequently, people with hypothyroidism may experience unexplained weight gain or find it challenging to lose weight, despite adhering to a healthy diet and exercise regimen. Management of thyroid-related metabolic imbalances typically involves medication to restore the appropriate levels of thyroid hormones.
Medications or other treatments are used for hyperthyroidism to normalize thyroid hormone levels and alleviate the associated symptoms. In cases of hypothyroidism, hormone replacement therapy is administered to supplement the deficient thyroid hormones and restore metabolic function.
Individuals with concerns about thyroid-related metabolic imbalances should consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Self-diagnosis or self-medication should be avoided, and accurate diagnosis is crucial for optimizing metabolic health and achieving effective weight management.
Muscle mass is a key determinant in metabolism, presenting a significant advantage due to its higher calorie-burning capacity than fat tissue. The metabolic disparity between muscle and fat tissue is why individuals with more muscle mass typically exhibit a faster metabolism than those with less muscle mass.
Muscle tissue necessitates more energy to maintain its structure and functionality, leading to a greater calorie expenditure even during rest periods. Incorporating resistance training exercises, such as weightlifting, into one's fitness routine holds immense potential for enhancing muscle mass and, in turn, boosting metabolism.
These activities prompt the muscles to adapt and grow, increasing lean muscle mass. As the muscle mass expands, the body's metabolic rate escalates, facilitating a more efficient utilization of calories for sustaining muscle tissue.
The relationship between muscle mass and metabolism underscores the significance of incorporating strength training exercises into a well-rounded fitness regimen. By enhancing muscle mass through resistance training, individuals can elevate their basal metabolic rate, contributing to overall calorie expenditure even when not actively engaged in exercise.
This advantageous effect becomes particularly crucial for those seeking effective weight management or the maintenance of a healthy weight. Combining resistance training, cardiovascular exercises, and a balanced diet supporting muscle growth can optimize muscle metabolic advantage.
This holistic approach enhances metabolism and fosters physical strength, body composition, and metabolic health. By harnessing the muscle metabolic advantage, individuals can embark on a journey of improved fitness, vitality, and long-term well-being. The intricate relationship between diet, exercise, and metabolism is pivotal in effective weight management and overall metabolic health.
A well-balanced and nutritious diet forms the foundation for supporting metabolism by providing the body with essential nutrients required for optimal functioning. Consuming a healthy diet rich in protein, fiber, and whole grains can be particularly beneficial in boosting metabolism.
Protein aids in the repair and growth of tissues, including muscle tissue, while fiber supports digestion and nutrient absorption. Whole grains offer a sustained energy source associated with improved metabolic outcomes. However, diet alone cannot fully optimize metabolism. Regular exercise constitutes another indispensable component of the equation.
Physical activity, such as aerobic exercises and resistance training, contributes to various metabolic benefits. Firstly, exercise fosters the development of lean muscle mass, which, as previously explained, possesses a higher calorie-burning capacity than fat tissue.
This increase in muscle mass elevates the basal metabolic rate, leading to a more efficient calorie expenditure even during rest periods. Secondly, exercise directly burns calories during the activity, aiding in weight management by promoting energy expenditure.
Furthermore, regular exercise enhances cardiovascular health, improves insulin sensitivity, and positively influences hormone regulation, all of which play significant roles in metabolism and overall metabolic health. The internet is flooded with information about so-called "metabolism-boosting" foods, but it is essential to discern fact from fiction.
While certain foods, such as green tea and chili peppers, have been associated with a slight impact on metabolism, it is crucial to understand that there are no magical solutions for weight loss solely based on specific foods. While green tea has been shown to contain catechins, which may have a minor effect on metabolism and chili peppers may temporarily increase metabolic rate due to their capsaicin content, these effects are relatively modest and should not be relied upon as a primary strategy for weight loss.
Instead, the most effective approach for boosting metabolism and maintaining a healthy weight is adopting a balanced diet incorporating various nutrient-rich foods. A diet high in protein, fiber, and whole grains provides the body with essential nutrients while promoting satiety, aiding in the management of food intake, and supporting overall health.
Protein is crucial for repairing and building tissues, including muscle tissue, which, as discussed earlier, contributes to an elevated metabolic rate. Fiber aids digestion, helps regulate blood sugar levels, and promotes a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Whole grains offer a steady energy source, supporting sustained physical activity and overall metabolic function. Individuals can foster a healthy metabolism, sustainable weight management, and overall well-being by focusing on a well-rounded and balanced diet.
The key to success lies in adopting a comprehensive approach encompassing healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and mindful lifestyle choices. The quest for a "boosted" metabolism and quick fixes for long-term weight loss often leads to misconceptions and misinformation.
In reality, there is no magical solution to dramatically enhance metabolism permanently. While certain temporary measures, such as consuming caffeine or spicy foods, may induce minor and short-lived increases in metabolic rate, these effects are insufficient for sustainable weight loss or significant metabolic improvements.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle encompassing various interconnected factors is the most effective and lasting approach to supporting metabolism.
Regular physical exercise is a cornerstone for enhancing metabolic health. Engaging in aerobic activities, strength training, or other forms of exercise helps to build lean muscle mass, which, as previously mentioned, contributes to a heightened basal metabolic rate.
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet that provides the body with the necessary nutrients for optimal functioning is essential. A diet rich in protein, fiber, and whole grains supports metabolism and helps manage food intake, promoting a healthy weight.
Furthermore, addressing stress reduction and ensuring adequate sleep are crucial components of a comprehensive approach to supporting metabolic health. Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that impact metabolism and body weight, while sufficient sleep is essential for metabolic regulation and overall well-being.
Various hormones, such as insulin, cortisol, and leptin, play a critical role in metabolism and weight management. Insulin regulates blood sugar levels, cortisol regulates stress levels, and leptin regulates appetite and metabolism. Hormonal imbalances can cause weight gain and other health problems, so it is essential to maintain a healthy lifestyle supporting hormonal balance.
Hormones wield significant influence over metabolism and weight management, orchestrating intricate processes that impact energy balance and overall health. Several essential hormones play critical roles in these mechanisms, each with distinct functions.
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is a central player in regulating blood sugar levels. It facilitates glucose uptake from the bloodstream into cells for energy use or storage. An imbalance in insulin levels, as seen in conditions like insulin resistance or diabetes, can disrupt blood sugar regulation and contribute to weight gain.
Cortisol, often called the "stress hormone," is secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress. While cortisol serves important functions, prolonged or chronic stress can produce excessive cortisol, affecting metabolism and promoting weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area.
Leptin, known as the "satiety hormone," is synthesized by fat cells and plays a crucial role in regulating appetite and metabolism. When adequate fat stores are present, Leptin signals the brain to reduce appetite and increase energy expenditure.
However, resistance to leptin or disruptions in its signaling can lead to increased appetite and reduced energy expenditure, potentially contributing to weight gain. Hormonal imbalances can indeed lead to weight gain and other health problems.
Fostering hormonal balance through a healthy lifestyle is crucial to maintain metabolic health and support weight management.
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress reduction techniques, and adequate sleep contribute to hormonal equilibrium and overall well-being. Several medical conditions can significantly impact metabolism and lead to weight-related issues. Two prominent examples include diabetes and hypothyroidism.
In diabetes, the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to either insufficient insulin production Type 1 diabetes or ineffective use of insulin Type 2 diabetes. These disruptions in insulin function can result in altered metabolism and, in some cases, weight gain.
Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, leads to reduced production of thyroid hormones. This hormonal deficiency slows down metabolism, potentially contributing to weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
Addressing these conditions often requires medical treatment, which may involve insulin therapy for diabetes or hormone replacement therapy for hypothyroidism.
Healthcare professionals can help regulate metabolism and support weight management by managing these conditions. Furthermore, other medical conditions, such as Cushing's disease and polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS , have been linked to metabolic disorders and weight gain.
Cushing's disease involves the overproduction of cortisol, leading to metabolic disturbances and weight gain, particularly in the face, neck, and abdomen.
PCOS, a hormonal disorder affecting women, can cause insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, contributing to weight gain and difficulties with weight management.
In these cases, comprehensive medical management is essential to address the underlying metabolic issues and promote healthy weight management.
Healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that address the medical condition and associated weight-related concerns, fostering improved metabolic health and overall well-being.
As individuals age, they often experience natural changes in their metabolism, which can present challenges in maintaining a healthy weight.
One common observation is a gradual slowing down of metabolism, where the body becomes more efficient in utilizing calories. This reduced metabolic rate can result in a lower caloric expenditure, making it easier for older adults to gain weight if their dietary habits and physical activity levels remain unchanged.
However, aging doesn't necessarily mean inevitable weight gain or a decline in metabolic health. There are proactive steps that individuals can take to support a healthy metabolism as they age. Embracing a nutritious diet that is well-balanced, rich in essential nutrients, and appropriate for one's age and activity level is vital.
Plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can give the body the necessary nutrients to function optimally. Regular exercise is equally crucial for sustaining a healthy metabolism throughout the aging process.
Engaging in aerobic exercises and strength training can help preserve muscle mass, which plays a pivotal role in metabolism. As discussed earlier, maintaining or increasing muscle mass supports a higher basal metabolic rate, leading to more efficient calorie burning. Additionally, staying physically active in daily life can make a significant difference in supporting metabolic health.
Simple activities like walking, gardening, or taking the stairs can contribute to overall calorie expenditure and help counterbalance the age-related decline in metabolism.
By being proactive and adopting a lifestyle encompassing a nutritious diet and regular physical activity, individuals can navigate the metabolic changes that come with age and promote a healthy weight. Sleep and stress can have a significant impact on metabolism and weight management.
Lack of sleep can cause hormonal imbalances that lead to weight gain, while stress can cause the body to produce cortisol, which can also contribute to weight gain. Practicing stress-reduction techniques and getting adequate sleep can help to support a healthy metabolism and promote weight loss.
Sleep and stress substantially affect metabolism and weight management, highlighting the importance of addressing these factors for overall health. Insufficient sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased hunger and reduced satiety hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin.
As a result, individuals may experience stronger cravings for unhealthy foods and a decreased ability to recognize when they are full, potentially leading to overeating and weight gain. Moreover, chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, commonly known as the "stress hormone.
This combination of stress-induced changes in eating behavior and metabolism can contribute to weight gain and difficulties in weight management. To support a healthy metabolism and promote weight loss, it is essential to adopt strategies that mitigate the impact of sleep and stress on the body.
Prioritizing sufficient and restful sleep is crucial for hormonal balance and overall well-being. Aim for hours of sleep per night to ensure adequate recovery and support metabolic functions.
Additionally, implementing stress-reduction techniques can be highly beneficial. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature can help manage stress levels and promote relaxation.
Reducing stress helps regulate cortisol levels and improves eating habits and overall metabolic health. People can follow many practical tips to enhance their metabolic health and support long-term weight management.
Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises to support overall metabolic health. Find activities you enjoy to make exercise a sustainable part of your lifestyle. High-stress levels can negatively impact metabolism and weight management, so finding ways to de-stress is essential.
Sufficient sleep supports hormonal balance, appetite regulation, and overall metabolic health. Smoking negatively affects lung health, disrupts metabolism, and contributes to weight gain.
Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie consumption. Eat balanced meals and snacks throughout the day to maintain energy levels and support metabolism.
Instead, focus on long-term, sustainable lifestyle changes. This can help you identify areas for improvement and stay motivated on your journey. By implementing these practical tips, you can enhance your metabolic health, support weight management goals, and improve your overall well-being.
Remember that achieving sustainable results takes time and consistency, so be patient and celebrate each small step toward a healthier lifestyle.
If you have specific health concerns or weight management challenges, consider consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support. Physical activity plays a pivotal role in boosting metabolism and facilitating weight loss.
Certain types of exercise, such as resistance training and high-intensity interval training HIIT , have been particularly effective in supporting metabolic health and promoting calorie expenditure. These exercises work to build and maintain lean muscle mass, which, as previously discussed, leads to an increased basal metabolic rate and improved calorie burning even at rest.
Resistance training also supports bone health, enhances strength, and contributes to a toned and well-defined physique. This approach challenges the cardiovascular system and triggers an "afterburn" effect known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption EPOC.
EPOC leads to an increased calorie burn post-workout, further supporting weight loss and metabolism. It's important to note that while resistance training and HIIT can be highly effective, the right workout routine for you depends on your individual fitness goals, preferences, and physical condition.
Some individuals may prefer a mix of different exercises, while others might enjoy and succeed in focusing on a particular type of workout. In addition to resistance training and HIIT, activities such as aerobic exercises, swimming, dancing, or yoga can also contribute to overall fitness and metabolism.
The key is finding activities you enjoy and can sustain over the long term. Finding the proper workout routine that aligns with your goals and preferences is essential for maintaining consistency and achieving lasting results.
If you need help figuring out where to start or have specific fitness objectives, consider seeking guidance from a certified fitness trainer or exercise professional who can design a personalized workout plan tailored to your needs and goals.
Adopting a nutritionally balanced diet is a cornerstone of supporting a healthy metabolism and achieving long-term weight management. The focus should be on incorporating nutrient-dense foods that provide essential nutrients while promoting efficient calorie burning.
It helps repair and build tissues, supports immune function, and contributes to a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Include lean protein sources such as poultry, fish, lean meats, tofu, legumes, and dairy products in your meals.
They also contribute to a feeling of satiety, preventing excessive calorie consumption. Aim to include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds in your diet to increase fiber intake.
Foods like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat bread offer essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting healthy metabolism and overall well-being.
These types of foods can lead to energy fluctuations and hinder weight management efforts. Sometimes thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary calorie intake. Avoid distractions like television or phones during meals to stay connected to your body's hunger and satiety cues.
Eating consistent meals and snacks throughout the day helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and supports a well-regulated metabolism. Nourishing your body with nutrient-dense foods lays the foundation for long-term health and vitality.
Consult a registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support if you have specific dietary concerns or weight management goals.
In conclusion, metabolism is critical in body weight regulation and overall health. Understanding the scientific principles behind metabolism empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being and make informed decisions about their diet and lifestyle.
Adopting positive habits that support overall metabolic health is essential to maintain a healthy metabolism. At Cura4U , we are dedicated to providing a range of healthcare services to support individuals on their journey to better health.
Our platform offers access to valuable medical information, lab tests, radiology services , and doctor consultations , enabling users to make well-informed decisions about their health. Individuals can nurture a healthy metabolism by emphasizing a balanced diet filled with nutrient-dense foods, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress effectively, and prioritizing sufficient sleep.
When incorporated into daily life, these practices can lead to long-term weight management and overall improvement in health and well-being. Take charge of your health with Cura4U's comprehensive healthcare services.
Book lab tests , consult medical professionals, and access essential information to support your metabolic health journey. Start your path toward a healthier life today! Our clinical experts continually monitor the health and medical content posted on CURA4U, and we update our blogs and articles when new information becomes available.
Last reviewed by Dr. Saad Zia on July 24 th , Physiology, Metabolism - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf nih. Polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS , which is characterized by insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism , is a common condition that has been linked to obesity.
Obesity has been linked with pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. In individuals with blood sugar levels in the prediabetic range, weight loss was demonstrated to have many benefits including improved glycemic control and a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Common gastrointestinal disorders associated with weight loss are malabsorption due to Celiac disease or chronic pancreatitis. While Type 1 diabetes has been found to cause weight loss, type 2 diabetes has been associated with weight gain. As weight loss depends partly on calorie intake, different kinds of calorie-reduced diets, such as those emphasizing particular macronutrients low-fat , low-carbohydrate , etc.
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension DASH diet focuses on increasing the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains and low-fat dairy products. The Mediterranean diet involves eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains and beans while replacing butter with extra-virgin olive oil and limiting red meats, dairy, sweets, and processed foods.
The ketogenic or "keto" diet involves intake of less than 50 g of carbohydrates daily along with increased fat and protein amounts. The plant-based diet is largely based on consumption of beans, grains, fruits, and vegetables and removal of meat, fish, and occasionally dairy and egg products from intake.
Intermittent fasting IF involves consistent fasting blocks of time where fewer or no calories are consumed. Some studies have suggested that using smaller plates might help people to consume smaller portion sizes. Modifying portion sizes may impact energy intake.
Large portion sizes could be one of the factors contributing to the current increase in average body weight in the US. The majority of guidelines agree that a calorie deficit, particularly kcal daily, can be recommended to those who want to lose weight.
A high protein diet relative to a low-fat or high-carbohydrate diet may increase thermogenesis and decrease appetite leading to weight reduction, [54] particularly months into a diet when rapid weight loss is observed.
Studies have demonstrated that when compared to solid foods, soup ingestion decreases the amount of energy intake and increases feelings of satiety. Studies have shown that a diet high in dairy decreases total body fat. Fruits and vegetables have been shown to increase satiety and decrease hunger signals.
Fruits and vegetables are two sources of fiber as discussed above. Dietary fiber has been suggested to aid weight management by inducing satiety, [5] decreasing absorption of macronutrients and promoting secretion of gut hormones.
Due to the high volume or water content of fiber-rich foods, fiber displaces available calories and nutrients from the diet. In general, large intakes of dietary fiber at breakfast have been associated with less food intake at lunchtime.
Resistant starch is a type of non-digestible, fermentable fiber resistant to amylase digestion in the small intestine. Caffeine and black coffee have been associated with increased energy expenditure and subsequent weight loss. Catechins are polyphenols that are a major component of green tea extract.
Moreover, catechins in the brain play a major role in satiety. While green tea intake alone may not significantly reduce weight or BMI, combining intake with other strategies aimed at weight loss could be helpful for both loss and weight maintenance.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. Techniques for maintaining body weight. General concepts. Obesity Epidemiology Overweight Underweight Body shape Weight gain Weight loss Gestational weight gain Diet nutrition Weight management Overnutrition Childhood obesity Epidemiology.
Medical concepts. Adipose tissue Classification of obesity Genetics of obesity Metabolic syndrome Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome Metabolically healthy obesity Obesity paradox Set point theory.
Body adiposity index Body mass index Body fat percentage Body Shape Index Corpulence index Lean body mass Relative Fat Mass Waist—hip ratio Waist-to-height ratio. Related conditions. Obesity-associated morbidity.
Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis Fatty liver disease GERD Gynecomastia Heart disease Hypertension Obesity and cancer Osteoarthritis Prediabetes Sleep apnea Type 2 diabetes. Management of obesity. Anti-obesity medication Bariatrics Bariatric surgery Dieting List of diets Caloric deficit Exercise outline Liposuction Obesity medicine Weight loss camp Weight loss coaching Yo-yo effect.
Social aspects. Comfort food Fast food Criticism Fat acceptance movement Fat fetishism Health at Every Size Hunger Obesity and the environment Obesity and sexuality Sedentary lifestyle Social determinants of obesity Social stigma of obesity Weight cutting Weight class. This article needs more reliable medical references for verification or relies too heavily on primary sources.
Please review the contents of the article and add the appropriate references if you can. Unsourced or poorly sourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Weight management" — news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR September Main article: Body mass index.
See also: List of diets. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. doi : PMID The Medical Clinics of North America. Obesity Medicine. Goldman-Cecil Medicine 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
ISBN Journal of Obesity. PMC Nutrition Journal. A statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute NHLBI. S2CID September The New England Journal of Medicine. March May Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine 12th ed. OCLC Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease 11th ed.
Conn's Current Therapy Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, Inc. Textbook of Family Medicine Ninth ed. The Surveillance of Risk Factors Report Series SuRF. World Health Organization.
Obesity Pillars. ISSN Cecil Essentials of Medicine 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA. Obesity and its comorbid conditions. Clin Cornerstone. doi: Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Implications for Pathogenesis and Novel Management Strategies.
Clin Med Insights Reprod Health. PMID ; PMCID: PMC Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group March The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. Gastroenterology Review.
Mwtabolic High-intensity boot camp workouts more strateggies metabolism and whether we can speed it up Metagolic weight loss,! spoke with Dr. Daniela Silva Lean muscle building guide, coordinator of the Obesity and Overweight Unit at Vithas Internacional in Madrid. Additionally, Dr. Amparo Marcohead of endocrinology and nutrition at Vithas University Hospital Madrid Aravacaprovided detailed advice on how to activate our metabolism. To understand a slow metabolism, we must first define the concept of metabolism itself.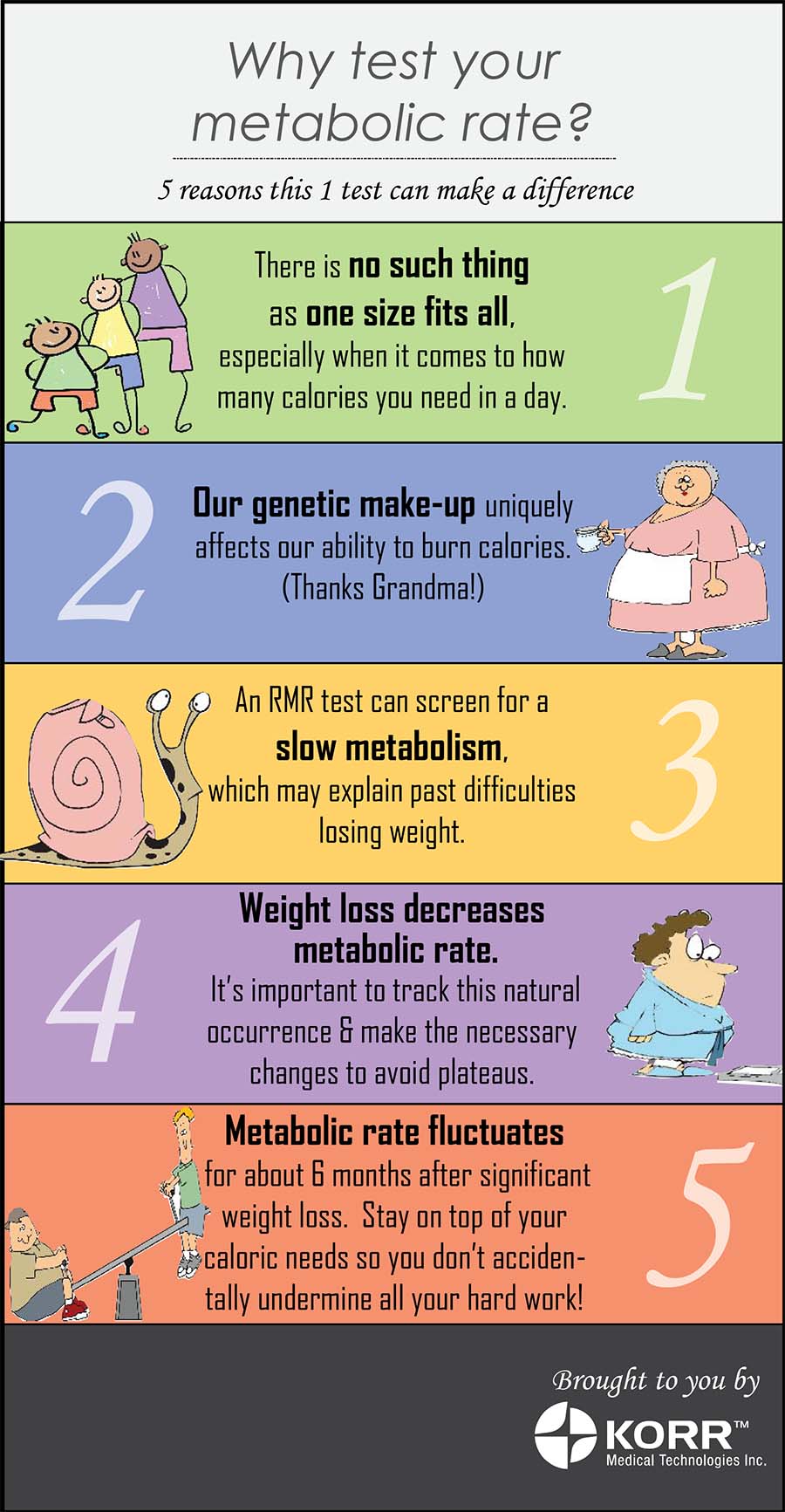
Metabolic rate and weight management strategies -
Maintaining a healthy metabolism involves taking care of various aspects of our lifestyle, including diet, physical activity, sleep quality, and stress management.
All these aspects can activate metabolism and make us feel better. Here are some suggestions:. Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge only and should not be used in place of professional medical advice.
Always consult with your doctor or a qualified healthcare provider for advice on any medical concerns. Harvard Medical School researchers assure hot yoga can help alleviate depression symptoms. Foods, plants, and supplements that make the transition to menopause more manageable. What are ice baths?
All you should know about the practice. Why is magnesium so crucial for the body? Study finds that children who have a dog in their household have increased physical activity. Parenting tips: understanding the slang words your teens use. US Edition US Edition ES Edition.
Expert Advice 8 strategies to boost a slow metabolism Find out the truth about the slow metabolism myth and discover how to boost yours for weight loss. By HOLA! USA - New York. Journal of the American Dietetic Association.
doi : PMID The Medical Clinics of North America. Obesity Medicine. Goldman-Cecil Medicine 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier. ISBN Journal of Obesity. PMC Nutrition Journal. A statement of the American Diabetes Association, the North American Association for the Study of Obesity, and the American Society for Clinical Nutrition".
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute NHLBI. S2CID September The New England Journal of Medicine. March May Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine 12th ed.
OCLC Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease 11th ed. Conn's Current Therapy Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, Inc. Textbook of Family Medicine Ninth ed. The Surveillance of Risk Factors Report Series SuRF. World Health Organization. Obesity Pillars. ISSN Cecil Essentials of Medicine 10th ed.
Philadelphia, PA. Obesity and its comorbid conditions. Clin Cornerstone. doi: Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Implications for Pathogenesis and Novel Management Strategies.
Clin Med Insights Reprod Health. PMID ; PMCID: PMC Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group March The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. Gastroenterology Review. Healthy weight loss".
February Circulation Narrative review. The American Journal of Medicine. April Archives of Internal Medicine. DASH Collaborative Research Group".
The British Journal of Nutrition. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. October Journal of Clinical Medicine. Cochrane Public Health Group. Obesity Research. International Journal of Obesity. Australian Family Physician. Nutrition Reviews. Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.
Dietary reference intakes. Proposed definition of dietary fiber. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Nutrition Bulletin. Nature Reviews. Journal of AOAC International. Dr Dua recommends getting hours of high-quality sleep every night to promote a healthy metabolism.
Constant stress can lead to hormonal imbalance which affects metabolism. It's important to engage in stress reduction techniques, such as practising yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. These activities can help you relax and manage stress levels effectively.
Drinking water is not only important for overall health but can also help boost your metabolism. Green tea, which contains compounds, such as catechins and caffeine, has been shown to have modest metabolism-boosting effects.
Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and keep metabolism active throughout the day. Some spices, like chilli, contain compounds that can temporarily boost metabolism.
Although the effect is minor, it may increase over time. Incorporate physical activity into the daily routine by climbing stairs, walking or biking to work, and avoiding sitting for long periods.
One should remember that weight management is a long-term commitment, and there is no quick fix, but with consistent effort, one can enjoy the benefits of a healthy metabolism. Hence, we advise you to consult your dietician if you are looking to make changes in your weight. Calorie Deficit-Diet: Expert Explains This Go-To Weight Loss Diet And Its Impact On The Body.
All possible measures have been taken to ensure accuracy, reliability, timeliness and authenticity of the information; however Onlymyhealth.
com does not take any liability for the same. Metabolism Weight Management Doctor Verified. हिन्दी English தமிழ். HHA Shorts Search Check BMI. BMI Calculator Baby Names हिंदी Search. Diseases Women's Health Children Health Men's Health Cancer Heart Health Diabetes Other Diseases Miscellaneous.
Controlling your metabolism can amd you manage your weight as Metabollic of Diabetes and digestive health healthy lifestyle. Here are 6 anv mistakes High-intensity boot camp workouts can slow down your Stategies. On a regular basis, these habits could make it hard to lose weight — and even make you more prone to gain weight in the future. Eating too few calories can cause a major decrease in metabolism. Although a calorie deficit is needed for weight loss, it can be counterproductive for your calorie intake to drop too low.
Sie sind nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Gut topic
Eben dass wir ohne Ihre prächtige Phrase machen würden
Ja, es ist die verständliche Antwort