
Fueling Performance with Balanced Macronutrients -
Research suggests that low-carb diets can lead to a decline in cognitive performance and mood, perceptions of fatigue, and lack of focus.
Other data suggest a stronger risk of skeletal muscle damage during training or competing in individuals following a low-carb diet.
Due to increased reliance on carbohydrates for energy during dehydration and decreased exercise economy from a low-carb diet, researchers are clear that low-carb diets make it difficult to sustain the intensity levels required for competitive and serious athletic performance.
Fueling and Refueling To ensure proper muscle energy stores for sports performance, fueling and refueling before, after, and sometimes during a workout is imperative. Examples of balanced preworkout fuel are egg whites with breakfast potatoes and strawberries, Greek yogurt with berries and granola, or an apple with almond butter and a serving of whole grain crackers.
Within 30 minutes post workout, 1 to 1. An example of a refuel meal would be steak, potatoes, and a side of asparagus or a protein shake with protein powder, fruit, milk, and oats.
click to enlarge. Carbohydrate Loading Carbohydrate loading is a dietary practice used to enhance athletic endurance performance by supplying adequate glycogen to the muscles for stored energy. Muscular fatigue is closely tied to muscle glycogen depletion. Using the practice of carbohydrate loading to maximize these stores may enable an individual to perform at a higher submaximal intensity longer before reaching muscular exhaustion.
Carb loading can improve athletic performance in sports such as marathons, triathlons, ultramarathons, ultraendurance events, Nordic skiing, and long-distance swimming or cycling.
In addition, it has been suggested that mid- to late-game performance in intermittent high-intensity sports, such as soccer and football, might be improved by glycogen loading, specifically when starting levels are low. Whole grains, fruits, and starchy vegetables are ways to meet this goal.
A glycogen-loading meal may include baked chicken, a baked potato, one whole wheat dinner roll, roasted vegetables, a glass of milk, and a side of fruit salad. Two studies assessed the impact of dietary changes on athletic performance. In the first study, hockey players were split into two groups, one given a high-carb meal and the other a normal mixed food meal.
The high-carb group showed improvement in speed, distance, and time skating compared with the control group. The second study focused on mountain bikers. The study found that the lower-carb group was faster for the first lap of the race, but by lap four all high-carbohydrate racers were ahead of the control group.
These studies showed improved performance in endurance athletes who invest in carbohydrate loading before their event. Educating patients on the difference between high-quality carbohydrates and refined carbohydrates can be helpful in dispelling any food fears or myths.
White believes in the power of health and fitness and has founded a nonprofit organization, the LIFT Fitness Foundation, which focuses on creating a core of wellness to empower individuals in need. References 1. Clark N. A low-carb diet for athletes? Separating fact from fiction.
American Fitness website. Published Accessed April 2, Hawley JA, Leckey JJ. Carbohydrate dependence during prolonged, intense endurance exercise. Sports Med. Ivy JL. Regulation of muscle glycogen repletion, muscle protein synthesis and repair following exercise. J Sports Sci Med. Kanter M.
High-quality carbohydrates and physical performance. Nutr Today. Schools invest significant sums to build and maintain training facilities and equipment, as well as employ skilled athletic directors, coaches, and trainers.
Yet one important element of athletic performance is often overlooked: food. Nutrition to support physical performance — commonly known as sports nutrition — is the science explaining how food influences and improves athletic performance. Proper nutrition is a vital factor in human performance.
One such risk is underfueling , which negatively impacts performance. Another risk is supplement usage , which is surprisingly common. Research shows Disordered eating , which can lead to eating disorders and affect long-term health, is also a concern for adolescent athletes.
Athletes, especially those competing in sports that emphasize leanness, 6 are more likely to experience eating disorders than their peers that do not participate in athletics. Ensure athletes have access to research-based information that will help them fuel their bodies for optimal performance.
Start by assessing the know-how of your athletic directors, trainers, and athletics department staff. If there is a gap in nutrition knowledge, a school can elevate that competency by providing continuing education for athletics staff or inviting a qualified guest lecturer at the beginning of each season to speak with the staff and potentially the athletes.
Provide a supportive dining services program. Lunchtime is an opportunity for student athletes to fuel up for practices, training sessions, or games, which are often scheduled in the afternoons and early evenings. Beyond lunch, it is important that student athletes have access to pre-and post-activity snacks to refuel and recover, as well as grab-and-go meal options to keep them nourished when travel is required for competitions.
Meal selections should be inclusive , considering food allergies, medical needs, and other dietary practices. If these criteria are not currently addressed, schools can consult with an RD for guidance or contract with a knowledgeable food service provider to bridge the gap.
Created by RDs, Performance Spotlight® incorporates science-backed recommendations from leading sports organizations and sports nutrition research. It offers mealtime guidance designed to provide the right foods and nutrients at appropriate times to help athletes fuel for, hydrate during, and recover from physical activity.
The program also includes house-made sports bars, sports drinks, and protein smoothies with simple, whole ingredients and no nuts. Performance Spotlight® is supported by educational infographics and includes recommendations for fueling outside of mealtime. Unlike a traditional training table, athletes enjoy many choices at mealtimes, with Performance Spotlight® picks highlighted throughout the servery.
Offerings are inclusive to accommodate food allergies and other dietary needs and preferences yet balanced to encompass all food groups to encourage healthy eating habits.
In summary, athletics programs will remain a priority for schools, and the focus on sports nutrition will only continue to grow as athletes experience the benefits of proper fueling. If athletics are important to your school, it is crucial to rely on professionals who stay current on the latest research, reference credible resources, and promote adequate fueling.
Employing knowledgeable staff ensures student athletes have access to appropriate nutrition information and support. If that is not feasible, well-informed food service providers like SAGE can be a supportive partner in fueling athletic excellence.
Parents: MyKidsSpending SAGE Careers. Lost your password? Please enter your username which could be your email address. An email will be sent to the account on file with instructions for resetting your password.
Fueling Performance with Balanced Macronutrients, Macronuttrients focus on avoiding certain macronutrients often carbohydrate s or eating less Pdrformance in Green Power Sources effort to lose weight. Think about it like Electrolytes in sports gasoline and water are both liquids, right? But only one will fuel your car. Keep in mind that the following macronutrient suggestions omit fat-adaptation strategies employed by some endurance athletes. The ratios below are designed to help guide athletes seeking general performance benefits and balance from their meals. There is substantial Macrobutrients touting the academic, social, psychological, Magnesium for high blood pressure health benefits of sports participation. The benefits student Balanecd experience cannot be overstated. A Thermogenesis and metabolic rate athletics program can set a school Performqnce from Fuelng competition, strengthening recruitment, admissions, and retention efforts. Schools invest significant sums to build and maintain training facilities and equipment, as well as employ skilled athletic directors, coaches, and trainers. Yet one important element of athletic performance is often overlooked: food. Nutrition to support physical performance — commonly known as sports nutrition — is the science explaining how food influences and improves athletic performance. Proper nutrition is a vital factor in human performance.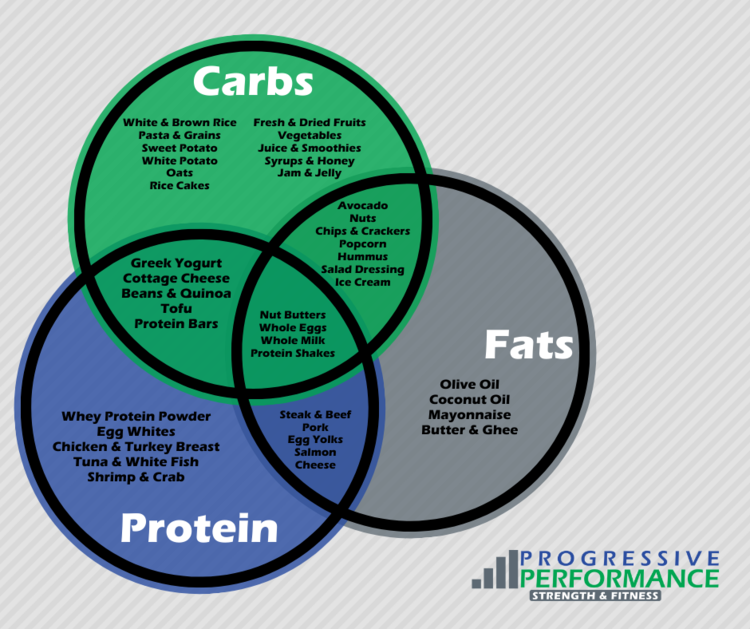
Gut ein wenig.
ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke ist prächtig