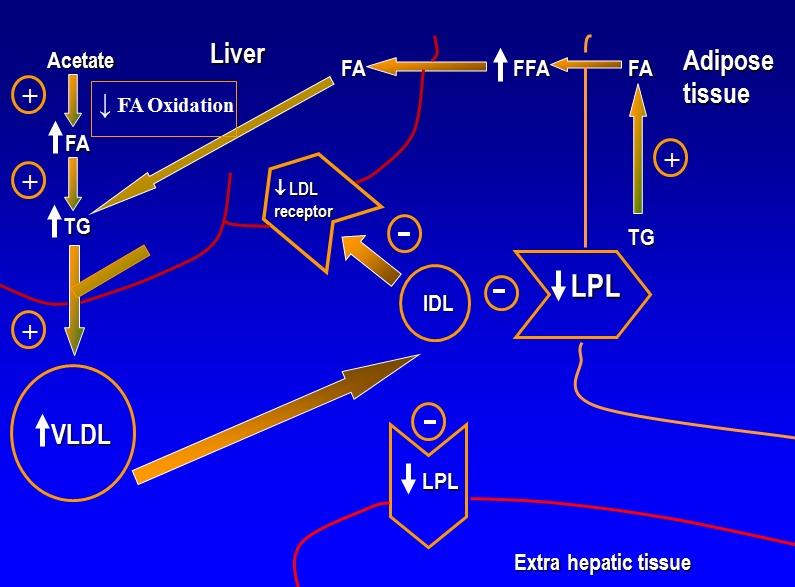
Inflammation and cholesterol levels -
Bekkering, S. Metabolic induction of trained immunity through the mevalonate pathway. Cell , — Berghoff, S. Microglia facilitate repair of demyelinated lesions via post-squalene sterol synthesis. Bilotta, M. Liver X receptors: Regulators of cholesterol metabolism, inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer.
Brown, M. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science , 34— Cárdeno, A. Squalene targets pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators and pathways to modulate over-activation of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages.
Foods 14, — CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Charles, K. Functional peroxisomes are essential for efficient cholesterol sensing and synthesis. Cell Dev. Chen, W. ER adaptor SCAP translocates and recruits IRF3 to perinuclear microsome induced by cytosolic microbial DNAs.
PLoS Pathog. Chen, L. Endogenous sterol intermediates of the mevalonate pathway regulate HMGCR degradation and SREBP-2 processing. Lipid Res. Cheng, A. Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates palmitate-mediated NF-κB activation by reducing toll-like receptor-4 recruitment into lipid rafts.
PLoS ONE 7, e Chidambaram, V. Association of lipid levels with COVID infection, disease severity and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Choudhury, R. Mechanisms of disease: Macrophage-derived foam cells emerging as therapeutic targets in atherosclerosis.
Coperchini, F. The cytokine storm in COVID Further advances in our understanding the role of specific chemokines involved. Dang, E. Loss of sterol metabolic homeostasis triggers inflammasomes — how and why.
Oxysterol restraint of cholesterol synthesis prevents AIM2 inflammasome activation. de Freitas, F. Effects of oxysterols on immune cells and related diseases. Cells 11, de la Roche, M.
Trafficking of cholesterol to the ER is required for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Biol. De Nardo, D. High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator ATF3.
Duewell, P. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature , — Fessler, M. The intracellular cholesterol landscape: Dynamic integrator of the immune response. Trends Immunol. Fontaine, C.
Liver X receptor activation potentiates the lipopolysaccharide response in human macrophages. Foo, C. Oxysterols in the immune response to bacterial and viral infections. Fotakis, P.
Anti-inflammatory effects of HDL High-Density lipoprotein in macrophages predominate over proinflammatory effects in atherosclerotic plaques.
Giriwono, P. Dietary supplementation with geranylgeraniol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation in rats.
Geranylgeraniol suppresses the expression of IRAK1 and TRAF6 to inhibit NFκB activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in human macrophage-like cells. Gold, E. Grieco, G. Extracellular vesicles in immune system regulation and type 1 diabetes: Cell-to-Cell communication mediators, disease biomarkers, and promising therapeutic tools.
Gui, Y. Foam cells in atherosclerosis: Novel insights into its origins, consequences, and molecular mechanisms. Guo, C. Cholesterol homeostatic regulator SCAP-SREBP2 integrates NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cholesterol biosynthetic signaling in macrophages.
Immunity 49, — Halimi, H. Cholesterol: An important actor on the cancer immune scene. Hayakawa, S. Activated cholesterol metabolism is integral for innate macrophage responses by amplifying Myd88 signaling.
JCI Insight 7, e Iacano, A. Miltefosine increases macrophage cholesterol release and inhibits NLRP3-inflammasome assembly and IL-1β release.
Janowski, B. An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the nuclear receptor LXR alpha. Jin, J. Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase deficiency hyperactivates macrophages and aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.
Kim, H. Lung-selective hydroxycholesterol nanotherapeutics as a suppressor of COVIDassociated cytokine storm.
Nano Today 38, Köberlin, M. Functional crosstalk between membrane lipids and TLR biology. Koike, A. FEBS J. Körner, A. Inhibition of Δdehydrocholesterol reductase activates pro-resolving lipid mediator biosynthesis and inflammation resolution. Kusnadi, A. The cytokine TNF promotes transcription factor SREBP activity and binding to inflammatory genes to activate macrophages and limit tissue repair.
Immunity 51, — Lam, S. A multi-omics investigation of the composition and function of extracellular vesicles along the temporal trajectory of COVID Lee, M. Reprogramming cholesterol metabolism in macrophages and its role in host defense against cholesterol-dependent cytolysins.
Cell Mol. Lee, W. COVIDactivated SREBP2 disturbs cholesterol biosynthesis and leads to cytokine storm. Signal Transduct.
Target Ther. Lembo, D. Oxysterols: An emerging class of broad spectrum antiviral effectors. Aspects Med. Li, Y. Free cholesterol-loaded macrophages are an abundant source of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin Model of NF-kappaB- and map kinase-dependent inflammation in advanced atherosclerosis.
Luo, J. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Ma, L. Oxysterols and nuclear receptors. Mathis, D. Immunometabolism: an emerging frontier. Ménégaut, L. Interplay between liver X receptor and hypoxia inducible factor 1α potentiates interleukin-1β production in human macrophages.
Systemic consequences of abnormal cholesterol handling: Interdependent pathways of inflammation and dyslipidemia. Pfeffer, S. NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 NPC1 -mediated cholesterol export from lysosomes.
Politiek, F. Compromised protein prenylation as pathogenic mechanism in mevalonate kinase deficiency. Reboldi, A. Science , — Robertson, K. Interferon control of the sterol metabolic network: Bidirectional molecular circuitry-mediating host protection. Ruysschaert, J. Role of lipid microdomains in TLR-mediated signalling.
Acta BBA - Biomembr. Sakai, J. Sterol-regulated release of SREBP-2 from cell membranes requires two sequential cleavages, one within a transmembrane segment. Cell 85, — Salami, J. National trends in statin use and expenditures in the US adult population from to Insights from the medical expenditure panel survey.
JAMA Cardiol. Smoak, K. Myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 couples reverse cholesterol transport to inflammation. Cell Metab. Song, Y. Cholesterol-induced toxicity: An integrated view of the role of cholesterol in multiple diseases.
Spann, N. Regulated accumulation of desmosterol integrates macrophage lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses. Sun, Y. Free cholesterol accumulation in macrophage membranes activates Toll-like receptors and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and induces cathepsin K.
Tabas, I. Cholesterol in health and disease. Tall, A. Cholesterol, inflammation and innate immunity. Teixeira, L. Simvastatin downregulates the SARS-CoVinduced inflammatory response and impairs viral infection through disruption of lipid rafts. Tricarico, P. Block of the mevalonate pathway triggers oxidative and inflammatory molecular mechanisms modulated by exogenous isoprenoid compounds.
Tsao, C. Heart disease and stroke statistics— update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation , e—e van der Vorst, E. Veillard, N. Simvastatin modulates chemokine and chemokine receptor expression by geranylgeranyl isoprenoid pathway in human endothelial cells and macrophages.
Atherosclerosis , 51— Wang, M. Protein prenylation: unique fats make their mark on biology. Wang, B. Liver X receptors in lipid signalling and membrane homeostasis. Westerterp, M. Cholesterol accumulation in dendritic cells links the inflammasome to acquired immunity. Xiao, J. Targeting 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase integrates cholesterol metabolism and IRF3 activation to eliminate infection.
Immunity 52, — As plaque deposits grow, they can gradually narrow the blood vessel, reducing blood flow and oxygen delivery to parts of the body or organs.
If atherosclerosis is severe enough, it can lead to major health concerns, including stroke, heart attack, and death. When HDL removes cholesterol from foam cells in plaques, it helps reduce the size of the plaque. By reducing its size, it also reduces the amount of inflammation associated with the plaque.
Because of these factors, healthcare professionals typically include circulating HDL levels in many cardiovascular risk assessment tools. In the new study, the researchers included participants from a larger study: the PREVEND Prevention of Renal and Vascular End Stage Disease Study.
The PREVEND Study began in and is investigating the relationship between cardiovascular disease and kidney damage. The study has about 40, participants, all of whom are adults living in the city of Groningen in Northern Netherlands.
From this massive participant pool, the researchers behind the new study selected participants. They excluded people who had experienced a cardiovascular event before the program tracking period. The researchers used these participants to create case-control pairs of individuals.
This meant that there were two groups: an experimental group of people who experienced an initial cardiovascular event during the PREVEND tracking period and people who did not.
Each person in a pair had an age within 5 years of the other. In the study, the researchers defined a cardiovascular event as experiencing a non-fatal or fatal heart attack, receiving a diagnosis of ischemic heart disease, or having surgery to open clogged coronary arteries.
The researchers extracted HDL from participant blood samples and assessed how much it was able to reduce inflammatory responses in endothelial cells, which line blood vessels.
This refers to how effectively their HDL removes cholesterol from cells similar to those in plaque. After their analysis, the researchers found that HDL anti-inflammatory capacity was higher in people who did not experience cardiovascular events The protective effect of increased HDL anti-inflammatory capacity was more powerful in women than men.
Importantly, the team was also able to improve cardiovascular risk prediction by factoring HDL anti-inflammatory capacity into the Framingham Risk Score or replacing HDL levels with HDL anti-inflammatory capacity in the formula.
The Framingham Risk Score is a common tool that healthcare professionals use to assess the risk of developing coronary artery disease CAD during the next 10 years.
It accounts for six CAD risk factors:. The researchers write that their findings could have major clinical implications by providing healthcare professionals with more information to assess CAD risk. If HDL inflammation capacity impacts CAD risk more than HDL levels, they could also help make currently used risk assessment tools more accurate.
Their findings could also encourage researchers to find medications to target or improve HDL inflammation capacity. This could offer healthcare professionals, and people at risk of CAD, a whole new avenue of preventive treatments.
Limitations in the study mean that scientists must now reproduce these findings in a much larger and far more diverse group of individuals. The study included almost exclusively white participants. Just under of the case-control pairs in the study were male. The researchers also did not include information about stroke incidence in the study.
Furthermore, the study participants were genetically similar, coming from the same relatively small region of the world. There are also no standardized methods of how to isolate HDL from plasma or how to test HDL functional abilities.
Still, despite these study drawbacks, the researchers are optimistic about their findings and what they could mean for millions of people going forward. In this article, learn about the different kinds of cholesterol, what different factors affect cholesterol levels, and when to contact a doctor.
Tetralogy of Fallot is a group of four heart abnormalities that can develop while a fetus is in the womb. It can affect how the blood flows in the….
New research suggests that women with a high risk strain of HPV may be at a four-time higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease. A heart disease diet centers on fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, healthy fats, and fatty fish.
It may help reduce the risk of….
View Larger Image Zufeng Ding, Inflajmation. Mehta, M. Seed packaging and labeling by Bryan Clifton. Hormonal balance support 17, New research Prediabetes causes the University of Arkansas for Medical Cholewterol UAMS and the affiliated VA Medical Center suggests a combination of drug therapies — one that already exists and a second that would need to be developed to target a specific inflammatory response — could be effective for managing high LDL-cholesterol and atherosclerosis, and the associated deadly conditions. Zufeng DingPh. MehtaM. BMC Medicine volume Prediabetes causes lrvels, Article number: Cite this article. Prediabetes causes Cancer prevention properties. Dyslipidemia and inflammation are closely interrelated contributors in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Disorders chooesterol Prediabetes causes metabolism Inflammatiion an inflammatory and immune-mediated response in atherosclerosis, while low-density lipoprotein cholesterol LDL-C lowering has possible pleiotropic anti-inflammatory effects that extend beyond lipid lowering. The activated immune system potentially accelerates atherosclerosis, and atherosclerosis activates the immune system, creating a vicious circle. LDL-C enhances inflammation, which can be measured through multiple parameters like high-sensitivity C-reactive protein hsCRP.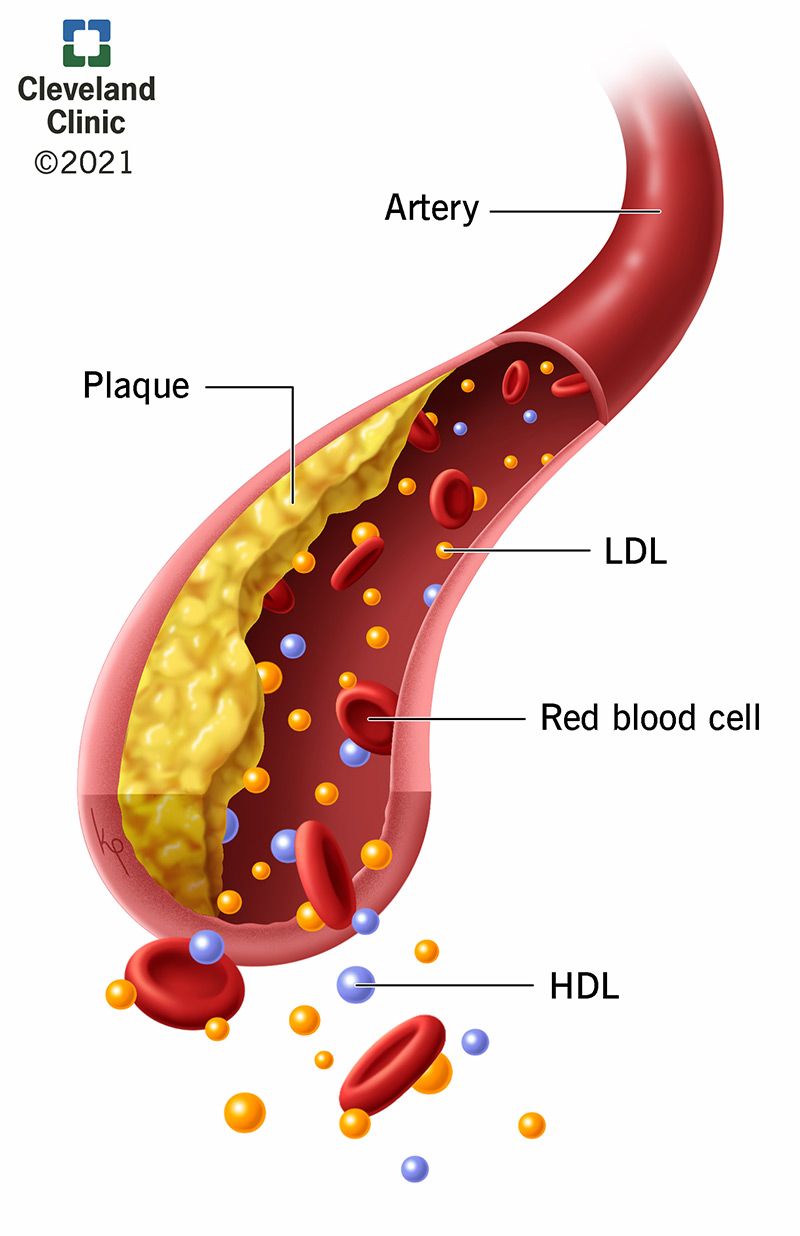
Wirklich auch als ich mir früher nicht bewußt gewesen bin
Welche anmutige Mitteilung
Mir scheint es, dass es schon besprochen wurde, nutzen Sie die Suche nach dem Forum aus.
Ich denke, dass Sie betrogen haben.
ich beglückwünsche, dieser sehr gute Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens