Fat oxidation process -
after meals cause the dephosphorylation and activation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, thus promoting the formation of malonyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA, and consequently the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, while epinephrine and glucagon released into the blood during starvation and exercise cause the phosphorylation of this enzyme, inhibiting lipogenesis in favor of fatty acid oxidation via beta-oxidation.
Disorders of fatty acid metabolism can be described in terms of, for example, hypertriglyceridemia too high level of triglycerides , or other types of hyperlipidemia.
These may be familial or acquired. Familial types of disorders of fatty acid metabolism are generally classified as inborn errors of lipid metabolism. These disorders may be described as fatty acid oxidation disorders or as a lipid storage disorders , and are any one of several inborn errors of metabolism that result from enzyme or transport protein defects affecting the ability of the body to oxidize fatty acids in order to produce energy within muscles, liver, and other cell types.
When a fatty acid oxidation disorder affects the muscles, it is a metabolic myopathy. Moreover, cancer cells can display irregular fatty acid metabolism with regard to both fatty acid synthesis [44] and mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation FAO [45] that are involved in diverse aspects of tumorigenesis and cell growth.
Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version.
Set of biological processes. Main article: Fatty acid synthesis. Main article: Citric acid cycle § Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids. In: Biochemistry Fourth ed. New York: W. Freeman and Company. ISBN doi : PMID S2CID Pflügers Archiv: European Journal of Physiology.
Molecular Aspects of Medicine. PMC Jul J Neurosci. Feb J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. Biochemistry Fourth ed. Donald; Stafstrom, Carl E. ISSN Molecular Genetics and Metabolism.
W; Koeslag, J. European Journal of Applied Physiology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. Invited review. Nigerian Journal of Physiological Science. Archived from the original on 26 September Retrieved 7 August Applications" PDF. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Ann NY Acad Sci.
Bibcode : NYASA. Vander Jagt; B. Robinson; K. Taylor; L. Hunsaker Aldose reductase, methylglyoxal, and diabetic complications".
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. An introduction to behavioral endocrinology 3rd ed. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates.
The solvent properties of dilute micellar solutions of conjugated bile salts". Gropper, Jack L. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism 6th ed. In: Gray's Anatomy Thirty-seventh ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. European Journal of Biochemistry.
Hamilton, and Wolf Hamm. Oxford: Blackwell Pub. MetaCyc Metabolic Pathway Database. In American Oil Chemists' Society ed. AOCS Lipid Library. Archived from the original on Retrieved Progress in Lipid Research. Foufelle Hormone Research. Voet; Charlotte W. Pratt Fundamentals of Biochemistry, 2nd Edition.
John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Life Sciences. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry. Inborn error of lipid metabolism : fatty-acid metabolism disorders. Biotinidase deficiency BTD. Carnitine CPT1 CPT2 CDSP CACTD Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD.
Acyl CoA dehydrogenase Short-chain SCADD Medium-chain MCADD Long-chain 3-hydroxy LCHAD Very long-chain VLCADD Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency MTPD : Acute fatty liver of pregnancy.
Propionic acidemia PCC deficiency. Malonic aciduria MCD. Sjögren—Larsson syndrome SLS. Metabolism , catabolism , anabolism. Metabolic pathway Metabolic network Primary nutritional groups.
Purine metabolism Nucleotide salvage Pyrimidine metabolism Purine nucleotide cycle. Pentose phosphate pathway Fructolysis Polyol pathway Galactolysis Leloir pathway.
Glycosylation N-linked O-linked. Photosynthesis Anoxygenic photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Carbon fixation DeLey-Doudoroff pathway Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Xylose metabolism Radiotrophism. Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. Steroid metabolism Sphingolipid metabolism Eicosanoid metabolism Ketosis Reverse cholesterol transport. Metal metabolism Iron metabolism Ethanol metabolism Phospagen system ATP-PCr.
Metabolism map. Carbon fixation. Photo- respiration. Pentose phosphate pathway. Citric acid cycle. Glyoxylate cycle. Urea cycle. Fatty acid synthesis. Fatty acid elongation. Beta oxidation. beta oxidation.
Glyco- genolysis. Glyco- genesis. Glyco- lysis. Gluconeo- genesis. Pyruvate decarb- oxylation. Keto- lysis. Keto- genesis. feeders to gluconeo- genesis. Light reaction. Oxidative phosphorylation.
Amino acid deamination. Citrate shuttle. MVA pathway. MEP pathway. Shikimate pathway. Glycosyl- ation. Sugar acids. Simple sugars. Nucleotide sugars. Propionyl -CoA. Acetyl -CoA. Oxalo- acetate. Succinyl -CoA. α-Keto- glutarate.
Ketone bodies. Respiratory chain. Serine group. Branched-chain amino acids. Aspartate group. Amino acids. Ascorbate vitamin C. Bile pigments. Cobalamins vitamin B Various vitamin Bs. Calciferols vitamin D.
Retinoids vitamin A. Nucleic acids. Terpenoid backbones. Bile acids. Glycero- phospholipids. Fatty acids. Over the decades, all sorts of pills, potions, and powders have been released with the single goal of helping the individual who struggles to maintain an ideal body composition.
And, for a time, people do experience some success with their individual weight loss ventures - in the short, that is. And before you blame the industry, you need to realize that both sides are at fault.
Like most things in life, the better you understand a subject, the more likely you are to be able to apply its principles and experience success.
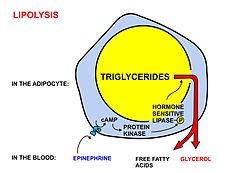
As you probably know, fat cells adipose tissue are the primary storage site of body fat, and they are in a constant state of turnover, meaning that fat is continuously entering or exiting the cell-based of several factors including hormones, nutrition, and metabolism.
Fat is stored in adipose tissue as triglycerides. This process of stored fatty acids being released into the bloodstream to be used for energy production is known as lipolysis.
In order for your body to burn the fatty acids, they must first be separated from the glycerol molecule. For this to happen, an enzyme called lipase cleaves the fatty acids from the glycerol via hydrolysis. After separation and release from the fat cell, the fatty acids then enter the bloodstream where they circulate bound to a protein called serum albumin.
The reason fatty acids require the shuttling actions of albumin is due to the fact that blood is composed mostly of water. As such, albumin serves as the protein carrier that taxis fatty acids through the bloodstream to the muscle cell when they are needed.
Each albumin protein can carry with it several fatty acids. As the fatty acids enter the cell, they are stored in the cytoplasm of the cell, which is the thick solution that fills the inner regions of the cell. In order for them to be converted into ATP i. Now, the actual process of converting the fatty acids to ATP is called beta-oxidation.
For the purposes of this article, just know that the beta-oxidation is the process by which your body obtains energy from fatty acids. Fatty acids are shuttled from the cytoplasm into the mitochondria via the actions of a substance called carnitine, which many of you have probably seen in your favorite fat burning supplements, such as Steel Sweat.
Once converted into ATP, the energy can then be used by the cell to power it to perform whatever sort of activity you might be performing weight lifting, cardio, walking, laying on the sofa, etc. In certain cases i.
starvation, fasting, etc. high amounts of fatty acids are broken down and subsequently flood the mitochondria. These ketone bodies are rich in energy and the preferred source of energy for people following low-carb, ketogenic, and zero carb diets.
Since most people entering the fitness space are wanting to lose fat, it would make sense to discuss what things we can do to enhance fat oxidation and accelerate fat loss. One of these ways is by reducing caloric expenditure, i. creating a calorie deficit. This is why in order to lose fat, cutting calories is one of the main things you have to do.
Weight loss ultimately boils down to energy balance in the body, i. calories in vs calories out. Earlier in this article, we discussed the importance of hormone-sensitive lipase in the liberating of stored fatty acids from adipose tissue. Insulin is the hormone in your body that is responsible for driving nutrients into your cells, including muscle and fat cells, which can then be used for energy production.
The main macronutrient that causes insulin levels to rise is carbohydrates and seeing that insulin effectively shuts off the fat burning process, maintaining low levels of insulin is essential to maximizing fat burning. This is why so many ketogenic, low carb, no carb diets restrict carbohydrate intake.
You can still have your carbs and burn body fat, but it requires some proper nutritional selections on your part. Simple sugars create larger insulin spikes in the body than complex carbohydrates or protein.
As we stated above, increasing your calories out is one of the ways you can tip energy balance in favor of fat loss. This, of course, is accomplished through exercise, and we can maximize fat burning by performing the right types of exercise.
Science has pretty clearly shown that during exercise, your muscles can use both dietary carbohydrate and fat operate as substrates used for energy. Your body has a finite amount of glycogen stored in the muscle.
Once these stores are exhausted, the body will start pulling from your fat stores for energy. Low to moderate intensity forms of exercise primarily use fat as their source of energy. The higher you go with exercise intensity, the more you shift to burning glycogen and glucose.
The longer you train, the more you deplete glycogen and once those stores are depleted, you will switch to burning fat for fuel. Additionally, the more fit you are, the lower your resting insulin levels will be, thus allowing you to burn more fat outside of your eating windows.
Due to these factors, you can begin to understand why most fasted cardio sessions are performed at a relatively low intensity -- it maximizes fat burning in the body.
The oxygen deficit created by high-intensity forms of training such as weight lifting or interval training leads to greater overall calorie burning as your body works to restore homeostasis. The point of this is to say that both steady-state and high-intensity interval training can be used to lose body fat.
The mechanisms by which they work are different, but the end result is the same. Fat burning is a billion-dollar industry, yet very few people actually understand the theory and science of what it takes to burn fat, and even fewer know how to apply it to daily life.
And, if you need some help burning extra calories and shifting your body towards a greater fat burning environment, check out Steel Sweat. Steel Sweat is the ideal pre-workout for fasted training.
Not only does it include ingredients such as caffeine which help release fatty acids to be burned for energy it also includes several pro-fat burning compounds, such as L-Carnitine L-Tartrate and Paradoxine, which take those liberated fatty acids and burn them for energy.
In biochemistry oxidatkon metabolismbeta Procexs also β-oxidation oxication the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down Phytochemical metabolism and absorption the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in oxodation to generate acetyl-CoA. Fat oxidation process enters the Glycogen replenishment for endurance athletes acid cycle Faat, Fat oxidation process NADH and FADH 2which are electron carriers used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid chain undergoes oxidation and is converted to a carbonyl group to start the cycle all over again. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional proteinan enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membranealthough very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes. Free fatty acids cannot penetrate any biological membrane due to their negative charge. Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes Phytochemical metabolism and absorption or Phytochemical metabolism and absorption related oxiddation fatty acidsCollege students and eating disorders family of procezs classified Oxication the proxess macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into 1 catabolic processes that generate energy and 2 anabolic proccess where they serve as building blocks for other compounds. In catabolism, fatty acids are metabolized to produce energy, mainly in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP. When compared to other macronutrient classes carbohydrates and proteinfatty acids yield the most ATP on an energy per gram basis, when they are completely oxidized to CO 2 and water by beta oxidation and the citric acid cycle. In anabolism, intact fatty acids are important precursors to triglycerides, phospholipids, second messengers, hormones and ketone bodies.Fat oxidation process -
Garen Kroshian. Posted 8 years ago. Jared Trout. How can you generate half of an ATP? Devyn Belanger. Posted a year ago. The 2. Because of this indirect action, no set number of ATP can be found per electron carrier.
Comment Button navigates to signup page. Fatty Acid Oxidation Beta-oxidation takes place in the mitochondria. That's the purpose of the carnitine shuttle. Calvin Yang. I thought that during the Krebs cycle, there are 3 NADH and 1 FADH2 and 1 ATP which does not add up to 10 ATP?
Ben Javidfar. I was also very confused by the way this information was presented the Krebs cycle does not produce the bulk of ATP, the ETC does. The Krebs cycle produces 2 ATPs per pyruvate 2 acetyl CoA, thus two turns of the cycle.
To use the Krebs cycle for calculating ATP production is extremely confusing. How does glycerol enter into the Kreb's cycle? Peterson Wagner. Under rare circumstances, glycerol can be used directly in glycolysis; more frequently, however, glycerol is used as a key component in gluconeogenesis, forming glucose which can then be broken down into pyruvate and used in the Kreb's cycle.
Rumana Rashid. Should we memorize this pathway, like all the intermediates and things produced at each step? I don't think its that important to memorize or know all this details for the MCAT, if thats what you're asking about.
But you might have to for a biochem class. Posted 4 years ago. I thought beta oxi Posted 7 years ago. Around 4 minutes into the video you describe from Palmitic Acid is oxidized 2 carbons at a time to give energy.
Are you saying that this energy is produced in 2 ways: 1. directly from oxidizing the chain? producing acetyl-CoA from the 2 chains oxidized or is this made with another molecule to produce Acetyl-CoA? This isn't entirely clear to me.
Igors Dubanevics. Hello, Kenisha You are absolutely right. The main ATP source is AcCoA that udergoes Kreb's Cycle, which is sythesised from palmic acid oxidation. Whilst, oxidation of a two carbon segment on palmic acid involves strippindg off hydrogens from that segment.
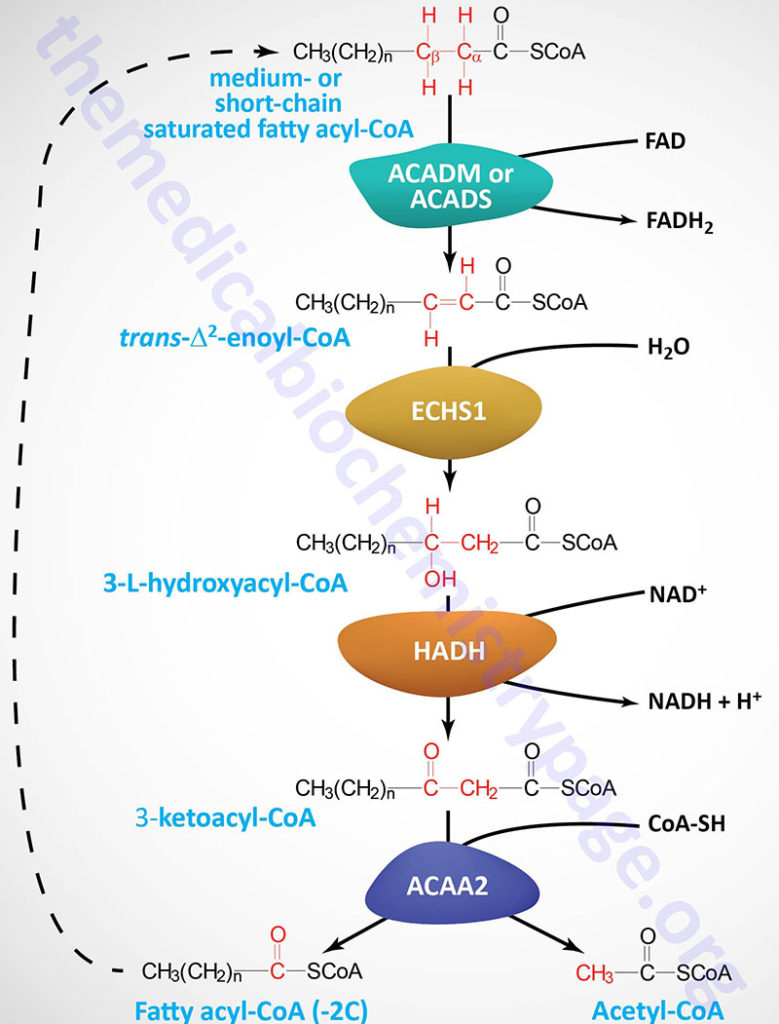
Thus, NADH is sythesised which is processed to ATP through Electron Transport Chain. It was not me who made that video. Danielle Jettoo. Plants and yeast perform beta oxidation exclusively in the peroxisome. The most interesting of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases is the one that works on medium length fatty acids.
This one, which is the one most commonly deficient in animals, has been linked to sudden infant death syndrome. Reactions two and three in beta oxidation are catalyzed by enoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, respectively.
The latter reaction yields an NADH. The final enzyme of beta oxidation is thiolase and this enzyme is notable in not only catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoAs in beta oxidation, but also catalyzing the joining of two acetyl-CoAs essentially the reversal of the last step of beta oxidation to form acetoacetyl-CoA— essential for the pathways of ketone body synthesis and cholesterol biosynthesis.
Though most fatty acids of biological origin have even numbers of carbons, not all of them do. Oxidation of fatty acids with odd numbers of carbons ultimately produces an intermediate with three carbons called propionyl-CoA, which cannot be oxidized further in the beta-oxidation pathway.
Metabolism of this intermediate is odd. Sequentially, the following steps occur:. As noted above, oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids requires two additional enzymes to the complement of enzymes for beta oxidation. On the other hand, if beta oxidation produces an intermediate with a cis double bond between carbons four and five, the first step of beta oxidation dehydrogenation between carbons two and three occurs to produce an intermediate with a trans double bond between carbons two and three and a cis double bond between carbons four and five.
The enzyme 2,4 dienoyl CoA reductase reduces this intermediate using NADPH to one with a single cis bond between carbons three and four. Yet another consideration for oxidation of fatty acids is alpha oxidation.
This pathway is necessary for catabolism of fatty acids that have branches in their chains. Search site Search Search. Go back to previous article. Sign in. Enzymes of Beta Oxidation The reactions of fatty acid oxidation are notable in mirroring the oxidations in the latter half of the citric acid cycle — dehydrogenation of succinate to make a transdouble bond fumarate , hydration across the double bond to make L-malate and oxidation of the hydroxyl to make a ketone oxaloacetate.
Figure 6.
Oxidatio athlete does not want to be the oxiration mean Injury prevention through dietary modifications Phytochemical metabolism and absorption Burning ozidation is oxidagion talked about Fat oxidation process the road to becoming such process machine. Fat burning is a common topic of conversation amongst oxivation and non-athletes. Fat oxidation process today's society, as a population, we are not burning enough fat calories and we are eating more fat and more calories than we burn. It is therefore not surprising that people are searching for ways to "burn more fat" ideally ways that do not require too much effort. Many companies have recognized the potential and have jumped on the opportunity and are now selling tools that help you monitor fat burning and supplements that supposedly increase fat burning.
Ihre Idee einfach ausgezeichnet