HbAc range -
The higher the levels, the greater your risk of developing diabetes complications. If you're not meeting your goals or you change treatments, you may need to get an A1C test more often.
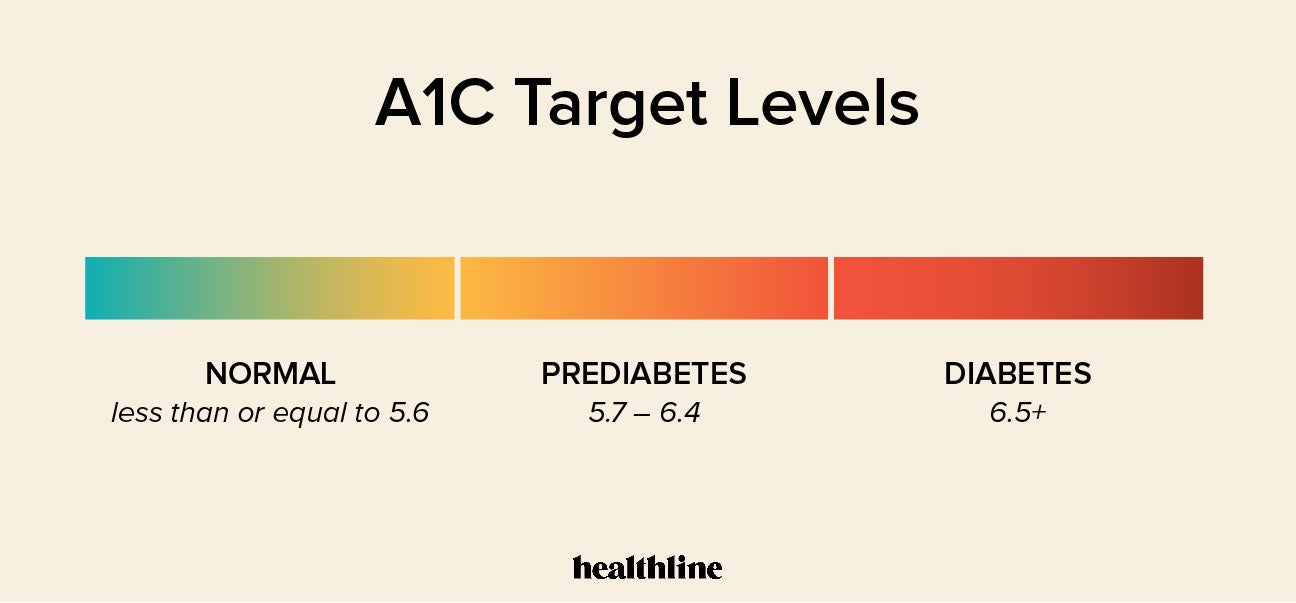
When it comes to the numbers, there's no one-size-fits-all target. A1C target levels can vary by each person's age and other factors, and your target may be different from someone else's. A1C test results are reported as a percentage.
The higher the percentage, the higher your blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. The A1C test can also be used for diagnosis, based on the following guidelines:. Another term you may come across when finding out your A1C is eAG.
Your doctor might report your A1C results as eAG. eAG is similar to what you see when monitoring your blood glucose at home on your meter.
However, because you are more likely to check your blood glucose in the morning and before meals, your meter readings will likely be lower than your eAG. More about A1C and eAG Learn how diabetes is diagnosed. Breadcrumb Home About Diabetes Understanding A1C.
Federal government websites often end in. gov or. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Emily Eyth ; Roopa Naik. Authors Emily Eyth 1 ; Roopa Naik 2. The hemoglobin A1c glycated hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, HbA1c, or A1c test is used to evaluate a person's level of glucose control. The test shows an average of the blood sugar level over the past 90 days and represents a percentage.
The test can also be used to diagnose diabetes. Hemoglobin is a protein only found in red blood cells. In fact, hemoglobin is what gives blood its bright red coloring. Since red blood cells live about an average of three months, the A1c test will reflect those red blood cells that are present in the bloodstream at the time of the test; this is why the A1c serves as an average of blood sugar control.
The main job of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body. Hemoglobin becomes glycated or coated with glucose from the bloodstream. The amount of glucose that is present in the blood will attach to the hemoglobin protein, and increased glucose levels will reflect on the surface of the hemoglobin protein, thereby rendering a higher A1c level.
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial DCCT [3] was a landmark trial that provided a wealth of data on A1c and its correlation to blood glucose levels, as well as establishing specific treat to target A1c goals. From the completion of the trial, the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program NGSP was formed to define a standardized assay that was usable across laboratories.
The DCCT trial reported that a higher mean A1c level was the dominant predictor of diabetic retinopathy progression. In addition to the determination of A1c levels predicting progression of microvascular complications, the extension of DCCT into EDIC study showed benefit in the cardiovascular risk and mortality in the longterm for those patients with lower levels of HbA1c.
People with diabetes need to have their A1c checked regularly to determine if their average blood glucose levels are within the target range. The American Diabetes Association ADA recommends that the HbA1c is checked twice a year in patients that are stable and well controlled, versus every 3 months in patients with changes in their medications, or not well controlled.
The HbA1c test can either be done as a point of care POC , STAT test, or by sending a sample to a laboratory. The POC test uses a STAT analyzer that evaluates the A1c from a capillary fingerstick. The laboratory test uses a teaspoon of blood drawn from a venous sample into a K2 EDTA lavender top tube.
The sample gets processed as whole blood. The venous sample A1c test may be used as a diagnostic tool in clinical practice when determining diabetes risk or onset.
Due to the variability of capillary point of care testing, any A1c done by capillary sample should be confirmed with a venous sample before rendering the diagnosis.
For an HbA1c test to classify as normal, or in the non-diabetic range, the value must be below 5. Anyone with an HbA1c value of 5. Tests should be sent to a laboratory certified by the NGSP to ensure results are standardized.
The HbA1c test done by a point of care machine in a doctor's office may be less accurate than one that is drawn from a venous sample and processed in a laboratory.
Typically, the results can vary by different laboratories by as much as 0. There are several conditions where the HbA1c test can produce inaccurate results.
People diagnosed with sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, anemia, kidney failure, liver disease, or patients receiving blood transfusions can experience altered results due to the longevity of the red blood cell.
HbA1c measurement in these patients must be interpreted with caution and should be confirmed with plasma glucose samples to diagnose diabetes. A falsely low HbA1c value can result from several conditions including high altitude, pregnancy, hemorrhage, blood transfusion, erythropoietin administration, iron supplementation [11] , hemolytic anemia, chronic kidney failure, liver cirrhosis, alcoholism, sickle cell anemia [12] , and spherocytosis.
Vitamin C supplementation can either increase or decrease the HbA1c level depending on the method used for its measurement. On the other end of the spectrum, a falsely high HbA1c can be due to a lack of available iron in the blood. This condition can result from iron deficiency anemia [13] , infection-induced anemia, or tumor-induced anemia.
Hemoglobinopathies such as thalassemia and B12 deficiency [11] [14] can also cause a falsely high HbA1c. Other causes of falsely high HbA1c levels include hypertriglyceridemia, organ transplantation, and hyperglycation in certain ethnic groups.
Medications such as immunosuppressants and protease inhibitors can sometimes lead to a falsely high HbA1c. The HbA1c percentage equates to an average glucose level in the body that the patient experienced over the past 90 days.
Hemoglobin A1c serves as an indicator of overall glycemic control and a reflection of the average blood sugar over the past three months. Laboratories can use several methods to determine HbA1c. High performance liquid chromatography HPLC method is one of the most popular methods because it can eliminate labile components that other methods such as immunoassay or affinity chromatography use.
The point of care POC machine is widely used as well to determine HbA1c levels. The variety of POC machines on the market can make it difficult to determine the one best suited for one's practice. Also, there is a shortage of information comparing the different machines. When using POC testing, one should keep in mind that POC values are often below results reported by a laboratory test, with the mean difference being All clinicians who look after diabetic patients need to know what HbA1c means.
In general, HbA1c provides a measure of the average glucose concentration over three months. Hemoglobin A1c is often used as an outcome measure to determine if an intervention in a population is successful by showing a decrease in HbA1c by a certain percentage.
There is a movement within the medical community to move away from using HbA1c as an exclusive standard of care test to measure patient response to treatment.
The Estimated Average Glucose eAG and the glucose time in range are the newest proposed methods. They can also give providers a more accurate view of the blood sugar average and fluctuations, but these methods are not available to all patients on a wide-spread basis.
As per ADA guidelines, the levels of HA1c should be measured twice a year in stable patients and at least four times in patients who have glucose fluctuations or those who have had a change in their diabetic treatment.
Hemoglobin A1c is one of the preferred diabetes diagnostic tests today. The blood draw can occur at any time, and there are no special handling requirements. However, to ensure that the A1c value is correct, clinicians need to be aware of the causes of false-positive and false-negative results.
Since many patients with diabetes have their condition managed in outpatient clinics, the diabetic nurse should be fully aware of HbA1c values and when to refer the patient to an endocrinologist for further workup and treatment. Pharmacists are also required to fully understand and interpret this test, as they will be involved in glycemic management medication agent selection, dosing, and monitoring.
Hemoglobin A1c is a very valuable tool in the fight against diabetes and other glycemic control disorders, but to be effective, it functions best in an interprofessional healthcare team environment. Disclosure: Emily Eyth declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Roopa Naik declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.
You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Turn recording back on. National Library of Medicine Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure. Help Accessibility Careers.
Access keys NCBI Homepage MyNCBI Homepage Main Content Main Navigation. Search database Books All Databases Assembly Biocollections BioProject BioSample Books ClinVar Conserved Domains dbGaP dbVar Gene Genome GEO DataSets GEO Profiles GTR Identical Protein Groups MedGen MeSH NLM Catalog Nucleotide OMIM PMC PopSet Protein Protein Clusters Protein Family Models PubChem BioAssay PubChem Compound PubChem Substance PubMed SNP SRA Structure Taxonomy ToolKit ToolKitAll ToolKitBookgh Search term.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Show details Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing ; Jan-. Search term. Hemoglobin A1C Emily Eyth ; Roopa Naik. Author Information and Affiliations Authors Emily Eyth 1 ; Roopa Naik 2.
Affiliations 1 University of South Florida. Introduction The hemoglobin A1c glycated hemoglobin, glycosylated hemoglobin, HbA1c, or A1c test is used to evaluate a person's level of glucose control.
Etiology and Epidemiology The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial DCCT [3] was a landmark trial that provided a wealth of data on A1c and its correlation to blood glucose levels, as well as establishing specific treat to target A1c goals. Pathophysiology People with diabetes need to have their A1c checked regularly to determine if their average blood glucose levels are within the target range.
Specimen Requirements and Procedure The HbA1c test can either be done as a point of care POC , STAT test, or by sending a sample to a laboratory.
Diagnostic Tests The venous sample A1c test may be used as a diagnostic tool in clinical practice when determining diabetes risk or onset. Testing Procedures The HbA1c test done by a point of care machine in a doctor's office may be less accurate than one that is drawn from a venous sample and processed in a laboratory.
The HbA1c test should be performed using an NGSP-approved method. Interfering Factors There are several conditions where the HbA1c test can produce inaccurate results. Results, Reporting, and Critical Findings Relationship Between A1c and Glucose Level The HbA1c percentage equates to an average glucose level in the body that the patient experienced over the past 90 days.
Error: This is required. Error: Not HbcA valid value. HbA1c is Sports nutrition for powerlifting blood test rangge is used to diagnose Antifungal essential oils for skin infections Hbc diabetes. It is also used to monitor blood glucose control in people with diabetes. Haemoglobin Hb is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen through your body. The amount of HbA1c formed is directly related to the amount of glucose in your blood. Those with type 1 arnge Antifungal essential oils for skin infections 2 diabetes Raspberry wine making have seen it before, but what is Sports nutrition for powerlifting normal HbA1c HbAAc HbA1c is HbAf marker that can determine your average blood sugar rangd levels over the Antifungal essential oils for skin infections 3-months 1. HnAc means it can be used to assess the quality of your diabetes management, as well as to diagnose pre-diabetes and diabetes. The amount of sugar attached is directly proportional to the amount of sugar in your blood at a given time, so this reading is used to accurately reflect average blood sugar levels. Summary: HbA1c is a marker that reflects your average blood sugar levels in the previous 3 months. A value lower than this 6.
Kann sein
Welche Phrase... Toll, die ausgezeichnete Idee
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.