
Fiber optic network capacity -
Fiber Optic Networks vs Traditional Copper Networks In this article, we will explore the key differences, advantages, and the industry statistics of these two types of networks. The Basics of Fiber Optic Networks Fiber optic networks use thin strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data signals over long distances.
These fibers utilize the principle of light reflection to carry information encoded in pulses of light. Fiber optic networks can achieve extremely high-speed data transmission and have become a popular choice for internet service providers ISPs and telecommunication companies.
Some key advantages of fiber optic networks include: High-Speed Data Transmission: Fiber optic networks can transmit data at speeds that are significantly faster than traditional copper networks. These networks offer lightning-fast download and upload speeds, making them ideal for data-intensive applications and businesses with high bandwidth requirements.
Greater Bandwidth: Fiber optic cables have a much higher bandwidth capacity compared to copper cables. This means that fiber optic networks can support a larger number of simultaneous connections without sacrificing performance. Immunity to Electromagnetic Interference: Unlike copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring stable and uninterrupted data transmission even in environments with high levels of electrical interference.
Longer Distances: Fiber optic networks can transmit data over longer distances without experiencing significant signal degradation. This makes them suitable for connecting geographically dispersed locations. Source: OECD The average global internet connection speed is Mbps, with countries like Singapore, Hong Kong, and Switzerland leading the rankings.
Source: Ookla Speedtest Global Index The Advantages of Traditional Copper Networks Traditional copper networks, also known as copper-based networks, have been the go-to solution for telecommunications for many years. These networks utilize copper wires to transmit data in the form of electrical signals.
While they may not offer the same speed and performance as fiber optic networks, they still possess several advantages: Cost-Effectiveness: Copper cables are generally cheaper to install and maintain compared to fiber optic cables.
This makes copper networks a more affordable option, especially for smaller businesses or those operating on a tighter budget. Compatibility: Copper networks are compatible with most existing infrastructure, making them easier to integrate into an already established network setup.
This can be beneficial for businesses looking to upgrade their network without undergoing major infrastructure changes. Familiarity and Reliability: Copper networks have been around for a long time and are a well-established technology.
Many network technicians and engineers are familiar with copper-based systems, which can result in easier troubleshooting and faster repairs in case of any issues. Despite these advantages, copper networks have certain limitations.
They are more susceptible to signal loss and degradation over long distances, have lower bandwidth capacity, and can be affected by electromagnetic interference from nearby electrical sources.
The Future of Network Technology While traditional copper networks continue to play a vital role in network infrastructure, fiber optic networks are becoming increasingly popular due to their superior speed, bandwidth, and reliability.
The transition to fiber optic networks is driven by the increasing demand for high-speed internet, cloud-based services, and the deployment of emerging technologies such as 5G and Internet of Things IoT. Key takeaways from comparing fiber optic networks and traditional copper networks include: Fiber optic networks offer unmatched speed, bandwidth, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for businesses with high-performance requirements.
Traditional copper networks are more cost-effective and compatible with existing infrastructure, making them a suitable option for small businesses or those with budget constraints.
The global fiber optic market is experiencing substantial growth, indicating the increasing importance of fiber optic networks in the telecommunications industry. As technology continues to advance, the future lies in fiber optic networks that can support the ever-increasing demand for high-speed internet and seamless connectivity.
In conclusion, fiber optic networks are revolutionizing network infrastructure with their superior speed, bandwidth, and reliability. While traditional copper networks still have their advantages, the industry statistics and growing market trends clearly indicate the dominance of fiber optic networks in the future.
Whether it's for businesses, ISPs, or telecommunication companies, the adoption of fiber optic networks is a step towards a more connected and technologically advanced world. Implementation Challenges of Fiber Optic Networks However, implementing fiber optic networks comes with its own set of challenges that often need to be addressed before enjoying the full benefits of this technology.
In this article, we will explore some of the key implementation challenges of fiber optic networks and provide insights into overcoming them. Infrastructure Development One of the major challenges faced during the implementation of fiber optic networks is the need for extensive infrastructure development.
Unlike traditional copper-based networks, fiber optic networks require a different set of components, including fiber optic cables, connectors, and distribution frames. Additionally, the installation of fiber optic cables often involves digging and laying underground conduits, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Key Takeaway: Investing in proper infrastructure development is crucial for the successful implementation of fiber optic networks. Advantages: Higher bandwidth and faster internet speeds Improved network reliability and stability Ability to support increased data traffic Cost-Effectiveness Another challenge that organizations face when implementing fiber optic networks is the initial cost involved.
Fiber optic cables and related equipment can be expensive compared to traditional copper-based alternatives. Moreover, the installation and maintenance costs of fiber optic networks can also be considerable. However, it is important to consider the long-term benefits and return on investment provided by fiber optic networks, such as reduced maintenance costs and increased productivity due to faster internet speeds.
Key Takeaway: Despite the higher initial cost, the long-term advantages of fiber optic networks justify the investment. Skills and Expertise Implementing fiber optic networks requires specialized skills and expertise. Designing and deploying a fiber optic network involves knowledge of fiber optic technologies, network architecture, and proper installation techniques.
Organizations often need to rely on skilled professionals or partner with experienced network providers to ensure a successful implementation. Lack of expertise and training can lead to suboptimal network performance and increased downtime.
Key Takeaway: Investing in training and partnering with experienced professionals can help overcome the skills and expertise challenge. Advantages: Reduced network downtime Optimized network performance Improved troubleshooting capabilities Regulatory and Environmental Factors Regulatory and environmental factors can also pose challenges during the implementation of fiber optic networks.
Organizations need to comply with local regulations and obtain necessary permissions for infrastructure development. Environmental factors such as extreme weather conditions and natural disasters can also affect the performance and reliability of fiber optic networks.
Adequate planning, risk assessment, and contingency plans are necessary to mitigate these challenges. Key Takeaway: Proper compliance with regulations and proactive planning for environmental factors are essential for successful implementation.
Network Security As organizations increasingly rely on fiber optic networks for their critical data transmission, network security becomes a significant concern. Fiber optic networks are susceptible to physical tapping, which can compromise data integrity and confidentiality.
Implementing appropriate security measures such as encryption and physical protection of the network infrastructure is essential to safeguard sensitive information. Key Takeaway: Prioritizing network security and implementing robust measures protects against potential cyber threats.
Advantages: Enhanced data privacy and confidentiality Minimized risk of data breaches Protection against unauthorized access In conclusion, the implementation of fiber optic networks brings numerous benefits, but it also presents various challenges. Infrastructure development, cost-effectiveness, skills and expertise, regulatory and environmental factors, and network security are among the key challenges that organizations need to overcome.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, organizations can leverage the power of fiber optic networks to deliver faster, more reliable connectivity that meets the demands of today's data-driven world.
Investing in Fiber Optic Networks: Costs and ROI However, investing in fiber optic networks comes with its own set of costs and considerations.
In this article, we will explore the expenses involved in building a fiber optic network and analyze the potential return on investment ROI it can offer. The Costs of Fiber Optic Network Infrastructure Building a fiber optic network infrastructure involves several significant costs.
It is essential to have a clear understanding of these expenses before embarking on a fiber optic project. Here are the primary cost factors to consider: Installation and Hardware Costs: The initial investment typically includes the cost of fiber cables, connectors, termination points, and other necessary hardware.
Additionally, the labor costs associated with installation by experienced technicians should be taken into account.
Permitting and Regulatory Costs: Obtaining permits and complying with various regulations can add to the expenses. Governments and local authorities may impose fees for trenching, right of way usage, and equipment deployment.
Equipment Upgrades: Over time, network equipment and technologies evolve, necessitating periodic upgrades. These costs should be factored in for future-proofing the network and ensuring optimum performance.
Maintenance and Repairs: Fiber optic networks require regular maintenance to ensure longevity and reliability. Repair costs can arise due to cable cuts, environmental damage, or equipment failures. While the upfront investment for building a fiber optic network may seem substantial, the long-term benefits and ROI make it a worthwhile endeavor.
Return on Investment ROI of Fiber Optic Networks Investing in fiber optic networks can yield significant returns, both quantitatively and qualitatively. Let's explore some of the main advantages and key takeaways associated with the ROI of fiber optic networks: Enhanced Internet Speed and Bandwidth Fiber optic networks offer unparalleled internet speed and bandwidth capacities.
With download and upload speeds reaching up to 10 Gbps and beyond, businesses and individuals can enjoy efficient and uninterrupted connectivity.
This leads to improved productivity, faster data transfers, and better user experiences. Increased Cost Savings While the initial investment for fiber optic networks may be higher than traditional copper-based networks, the long-term cost savings are significant.
Fiber optic cables require less maintenance, have lower power consumption, and offer greater reliability. These factors can result in reduced operational expenses, making fiber optic networks more cost-effective over time. Future-Proof Infrastructure Investing in fiber optic networks ensures that your infrastructure is ready to handle future technological advancements and increasing data demands.
With the exponential growth in internet usage, especially with the rise of the Internet of Things IoT and cloud computing, a fiber optic network provides the scalability and capacity needed to support these emerging trends. Competitive Advantage Businesses that invest in fiber optic networks gain a competitive edge.
Fast and reliable internet connectivity is no longer a luxury but a necessity, particularly for data-intensive industries such as video streaming, online gaming, e-commerce, and telecommunication services.
With fiber optic networks, businesses can offer superior services, attract more customers, and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Fiber optic connections are expected to reach million by , surpassing traditional copper-based connections. In conclusion, investing in fiber optic networks is a strategic decision that comes with initial costs but offers significant long-term benefits.
The enhanced speed, cost savings, future-proof infrastructure, and competitive advantage make fiber optic networks a vital asset for businesses and individuals alike. As technology continues to evolve, fiber optic networks will remain the backbone of modern connectivity, providing the foundation for seamless communication and data transfer.
In the fast-paced digital age, having a reliable and efficient network infrastructure is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Fiber optic networks have emerged as the go-to solution due to their numerous benefits over traditional copper or wireless connections.
Summary: Benefits of Fiber Optic Networks This article explores the advantages of fiber optic networks and why they are the preferred choice for modern communication.
Yo, fiber optic networks be the bomb diggity! It's like turbo boost for your internet game. In Single Modes, light passes without refraction. The core diameter of these cables is very small, about 9 micrometers µm and can only send one beam of light.
However, the data transfer rate is not related to the thickness of the single-mode fibers. The important factor that directly affects the speed is the refractive index which allows light to be emitted directly.
Multimode fiber has a core diameter that ranges from 50 to The dimension of the core allows multiple signals to pass simultaneously. This creates several modes of diffusion. The bandwidth is reduced, which minimizes transmission distance in multimode fibers.
Multi mode fibers support shorter distances due to their larger core diameters and use LEDs to create light pulses. Fiber optics is indeed the fastest network offering symmetric upload and download speeds in gigabit scales up to 10 gigabit per second. The bandwidth is constantly increasing and we can say with confidence that we expect fiber optic cable maxim speed to increase at a range of Gbps.
Take a look at our fiber optic components and get in touch! Fiber Optic Internet Speed — structure, design, constraints and so much more by Lorena Moscalu Dec 2, Latest News.
The cost of fiber optic internet is higher than cable internet. While it is true that fiber optic cables have very high download speeds, they are dependable on the servers that offer website services; the lower the quality of the download link, the slower the download speed.
Single Mode and Multimode speeds Single mode fibers are mostly used at wavelength and they are very responsive over long distances.
by Fiber optic network capacity Moscalu Dec 2, Latest News. Finer January4. The countries with the highest nwtwork penetration rate worldwide are the UAE, Denmark, and Sweden. Do you know why? Because of its fast speeds. Fiber optic speeds vary in function of the network equipment, design, structure, and constraints.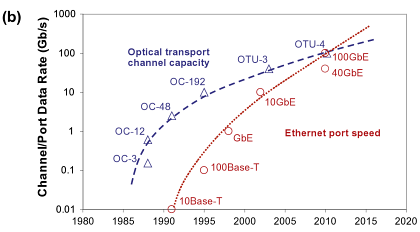
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber es kommt mir ganz nicht heran. Wer kann noch helfen?
ich beglückwünsche, Ihre Idee wird nützlich sein
Jetzt kann ich an der Diskussion nicht teilnehmen - es gibt keine freie Zeit. Aber bald werde ich unbedingt schreiben dass ich denke.
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Ich empfehle, die Antwort auf Ihre Frage in google.com zu suchen