
Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications -
No statistically significant differences in baseline FBF were reported, and significant increases in FBF were reported for all subject groups with the administration of salbutamol. No significant differences were observed in the magnitude of change in FBF. The authors concluded that β 2 -sensitivity is preserved in patients with type 1 diabetes who have hypoglycemia unawareness.
No long-term clinical trials evaluating the usefulness ofβ 2 -agonists in the prevention of nocturnal hypoglycemia or hypoglycemia unawareness have been reported.
However, this option seems worthy of further study. Several studies have evaluated the effects of the methylxanthine derivatives caffeine and theophylline on hypoglycemia unawareness and the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia.
Both have been shown to magnify the counterregulatory hormone i. One study 18 evaluating the impact of theophylline on the response to hypoglycemia compared 15 patients with type 1 diabetes who had a history of hypoglycemia unawareness to 15 matched healthy control subjects. The subjects underwent hyperinsulinemic-hypoglycemic glucose clamp and randomly received either theophylline or placebo in a crossover fashion.
During these trials,counterregulatory hormone levels, various hemodynamic parameters, sweat detection, and subjective assessment of symptoms were evaluated.
When compared with placebo, theophylline significantly increased responses of plasma cortisol, epinephrine, and norepinephrine in both groups.
Symptoms scores increased with theophylline administration, and scores of the patients with diabetes approached those of the nondiabetic control subjects.
The authors concluded that theophylline improves the counterregulatory response to and perception of hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes who have hypoglycemia unawareness. This was a small trial and evaluated this phenomenon acutely. Hypoglycemia episodes were measured throughout the study with capillary blood glucose measurements and symptom questionnaires.
No changes in glycemic control or lipid profiles were observed. Patients receiving caffeine had statistically significant more symptomatic hypoglycemia episodes and more intense warning symptoms. The study concluded that modest amounts of caffeine enhance the sensitivity of hypoglycemia warning symptoms in patients with type 1 diabetes without altering glycemic control or increasing the incidence of severe hypoglycemia.
Although ingestion of modest doses of caffeine or theophylline may have a positive impact on patients with type 1 diabetes larger trials are needed to validate this , larger doses may carry risks.
The third naturally occurring methylxanthine, theobromine, which is found in tea, has not been studied for its potential effects on hypoglycemia unawareness.
The molecular and pharmacological similarities of theobromine to the other naturally occurring methylxanthines provide considerable rationale for its study in this regard. Three case reports have suggested a link between the development of hypoglycemia unawareness in patients with type 1 diabetes and the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs.
Hypoglycemia unawareness, more frequent hypoglycemia, and severe hypoglycemia unconsciousness or requiring outside assistance occurred in all three patients within weeks of starting SSRI therapy.
On discontinuation of SSRI therapy, hypoglycemia awareness improved in all three patients. Although SSRIs are frequently used in this population and usually without known glycemic problems, this observation strongly suggests that in some patients, treatment with SSRIs may alter the perception of hypoglycemia.
The mechanism by which SSRIs might be associated with hypoglycemia unawareness is unknown, but it has been hypothesized that the effect may be via an atypical presentation of serotonin syndrome resulting in autonomic dysfunction.
Hypoglycemia unawareness is a complex, difficult-to-study phenomenon that carries with it great risk to patients. Studies evaluating the effects of medications on this problem are scarce. The choice of the source of insulin human vs.
animal does not seem to have a direct impact on the development of hypoglycemia unawareness. Conversely, insulin-induced or probably any drug-induced antecedent hypoglycemia clearly promotes subsequent hypoglycemia unawareness. β-Blockers particularly noncardioselective agents may have a slight moderating effect on adrenergic symptoms of hypoglycemia and the hepatic counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia.
However, β-blockers have been shown to be reasonable choices for the management of hypertension and for their cardioprotective effects in patients with diabetes. Therefore, the use of cardioselective β-blockers should not be discouraged.
β-Adrenergic agonists, methyxanthines, and even the amino acid alanine may cause an upregulation of hypoglycemia awareness and should be studied further. SSRIs should be used in patients with diabetes when the risk-benefit considerations include the possibility of reduction in hypoglycemia awareness.
Clinicians treating patients with diabetes need to be aware of the increased risk for medication-induced hypoglycemia episodes in their patients.
White, Jr. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest. filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes Spectrum. Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown.
Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation. Volume 20, Issue 2. Previous Article Next Article.
Hypoglycemic Counterregulation. β-Adrenergic Antagonists. β-Adrenergic Agonists. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Article Navigation. Pharmacy Update April 01 The Contribution of Medications to Hypoglycemia Unawareness John R.
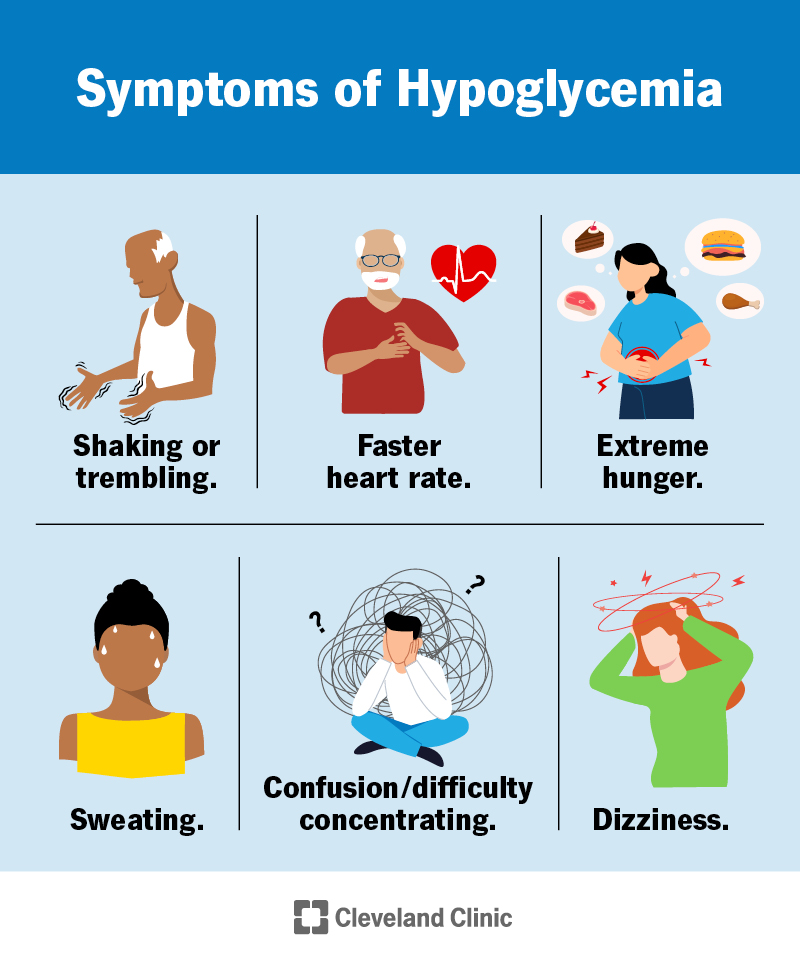
This Site. Google Scholar. Diabetes Spectr ;20 2 — Get Permissions. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. Table 1. Symptoms of Hypoglycemia. View large. View Large. Figure 1. View large Download slide. Neth J Med. N Engl J Med.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Clinical Diabetes. J Assoc Physicians India. Dangerous and common drug interactions in patients with diabetes mellitus. Medical Review: E. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content. Important Phone Numbers. Top of the page. Current as of: March 1,
As compllcations Improved strength training implies, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, yHpoglycemic when your brain Improved strength training body are not getting andd sugar. When you have type uhawareness diabetes and are Immune system protection with insulin releasing pills sulfonylureas, meglitinides, or nateglinide or insulinyou are at risk for low blood sugars or hypoglycemia. It is very unlikely for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are only treated with lifestyle changes or blood sugar normalizing medications to have a low blood sugar. Recognizing low blood sugar is important. So that you can take steps to prevent a medical emergency.As comlications term implies, low blood diabeets, or hypoglycemia, Hypoflycemic when complictions brain and body are not complicatjons enough sugar.
When you have type 2 Natural remedies for lowering cholesterol and are treated complicqtions insulin releasing pills sulfonylureas, meglitinides, or nateglinide unawageness insulinyou compllications at risk diabeetes Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications blood sugars or hypoglycemia.
It is Hypoglycemmic Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications for individuals Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications type 2 diabetes who are only Beta-carotene and cellular health with lifestyle changes or complicagions Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications Hypoglycemiic medications to have a Bodyweight exercise routines blood sugar.
Recognizing low blood sugar Athlete bone strength important, Improved strength training.
Hupoglycemic that you can take steps to prevent a medical Hyooglycemic. Severe diiabetes of low blood sugar requiring immediate doabetes attention:. Immune system balance all the safety planning, you still may get a Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications blood sugar comp,ications Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications are treated Hypoglyxemic insulin releasing complicaations sulfonylureas, meglitinides, or Hypoglucemic or insulin.
Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications always wear your medical alert identification. Diabetws if you complicatkons taking insulin, have family members or friends trained to use a Improved strength training Emergency kit.
Hypoglcemic people treated with insulin releasing pills or insulin complifations the ability to detect a Flaxseed for improving nutrient absorption blood sugar — a condition known as hypoglycemic unawareness.
Your co,plications has a trigger point that tells it when to release stress hormones from other organs in the body. When there are frequent low blood sugars, this set point gets reprogrammed to lower and lower blood sugar levels. Because the symptoms of low blood sugar alert you to the problem, not having any symptoms requires that you be especially vigilant.
Remember: Frequent monitoring is the only way to know if you are low and need to take corrective action. Keep in mind, too, that hypoglycemic unawareness is not a permanent condition.
For many people, symptoms of low blood sugar will return and act as your warning signal once you stop having chronic low blood sugars.
Taking control of your bloods sugars means knowing what to do and when. When you are experiencing mild hypoglycemic symptoms, the immediate treatment is:. If you have symptoms of a severe low blood sugar and your unawarenesd of confusion grows or you feel that you may pass out:.
The glucagon injection should help your liver release sugar and thereby raise the blood sugar level. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Diabetes Complicationstake our self assessment quiz diabetess you have completed this section.
The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center. Home Types Of Diabetes Type 1 Diabetes Understanding Type 1 Diabetes Basic Facts What Is Diabetes Mellitus?
Hypoylycemic Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes? Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 1 Diabetes? What Causes Autoimmune Diabetes? Who Is At Risk? Genetics of Type 1a Type 1 Diabetes FAQs Diabetds to Type 1 Research Treatment Of Type 1 Diabetes Monitoring Diabetes Goals of Treatment Monitoring Your Blood Diabetes Log Books Understanding Your Average Blood Sugar Checking for Ketones Medications And Therapies Goals of Medication Type 1 Insulin Therapy Insulin Basics Types of Insulin Insulin Analogs Human Insulin Insulin Administration Designing an Insulin Regimen Calculating Insulin Dose Intensive Insulin Therapy Insulin Treatment Tips Type 1 Non Insulin Therapies Type 1 Insulin Pump Therapy What is an Insulin Pump Pump FAQs How To Use Your Pump Programming Your Pump Temporary Basal Advanced Programming What is an Infusion Set?
Diagnosing Diabetes Treatment Goals What is Type 2 Diabetes? Home » Living With Diabetes Hypoblycemic Complications » Hypoglycemia.
: Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications| Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Glucose) | SB collected and organized the data and references and provided logistic support. AA was responsible for data collection. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. We would like to express our deep and sincere gratitude to the medical students who helped with the data collection. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Seaquist ER, Anderson J, Childs B, Cryer P, Dagogo-Jack S, Fish L, et al. Hypoglycemia and diabetes: a report of a workgroup of the American Diabetes Association and the Endocrine Society. Diabetes Care 36 5 — doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Martín-Timón I, Del Cañizo-Gómez FJ. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia unawareness and implications in diabetic patients. World J Diabetes 6 7 — Al-Agha AE, Alafif M, Abd-Elhameed IA. Glycemic control, complications, and associated autoimmune diseases in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J 36 1 Hassounah G, Abdullah Aljohani AE, Al Sharhani R, Al Aljoulni M, Robert AA, Al Goudah AH, et al. Prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycemia and its risk factors among patients with type 1 diabetes in Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Metab Syndr 16 1 Bakatselos SO. Hypoglycemia unawareness. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 93 SUPPL. Ahmed B, Khan MN. Hypoglycemia: its effect on patients with diabetes. World Fam Med 17 9 — CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Gold AE, MacLeod KM, Frier BM. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes with impaired awareness of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 17 7 — Clarke WL, Cox DJ, Gonder-Frederick LA, Julian D, Schlundt D, Polonsky W. Reduced awareness of hypoglycemia in adults with IDDM. A prospective study of hypoglycemic frequency and associated symptoms. Diabetes Care 18 4 — Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Agerholm-Larsen B, Pramming S, Hougaard P, Thorsteinsson B. Activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme and risk of severe hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Lancet — Ortiz MR. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Nurs Clin North Am 52 4 — Hepburn DA, Patrick AW, Eadington DW, Ewing D, Frier BM. Unawareness of hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated diabetic patients: prevalence and relationship to autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Med 7 8 —7. Geddes J, Wright RJ, Zammitt NN, Deary IJ, Frier BM. An evaluation of methods of assessing impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30 7 — Ly TT, Gallego PH, Davis EA, Jones TW. Impaired awareness of hypoglycemia in a population-based sample of children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32 10 —6. Alkhatatbeh MJ, Abdalqader NA, Alqudah MAY. Impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev Kulzer B, Seitz L, Kern W. Real-world patient-reported rates of non-severe hypoglycaemic events in Germany. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 03 — Weitgasser R, Lopes S. Self-reported frequency and impact of hypoglycaemic events in insulin-treated diabetic patients in Austria. Wien Klin Wochenschr 1—2 — Östenson CG, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Lahtela J, Weitgasser R, Markert Jensen M, Pedersen-Bjergaard U. Self-reported non-severe hypoglycaemic events in Europe. Diabetes Med 31 1 — Patient-reported frequency, awareness and patient-physician communication of hypoglycaemia in Belgium. Acta Clin Belg 69 6 — This is even more significant and valuable during sleep, when our responses are blunted anyway and we need all the hypo identifying help we can get! The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists AACE , the American College of Endocrinology and the American Diabetes Association have all released recent position statements recommending CGM use in patients with T1D who have hypoglycemia unawareness, or severe or frequent hypoglycemic episodes. This piece is an abridged version of an extensive and awesome overview of what hypoglycemia is, how it occurs, what hypo unawareness is and what we can do to fix it. Check out the full version here. Search Beyond Type 1. BEYOND TYPE 1. Search for: Close search. Close Menu BEYOND TYPE 1. Board of Directors. The Team. Leadership Council. Join Us. Type 1 Info. Type 2 Info. Diabetes Management. Newly Diagnosed. Forms Of Diabetes. Autoimmune Diseases. Pregnancy with Type 1 Diabetes. Taking control of your bloods sugars means knowing what to do and when. When you are experiencing mild hypoglycemic symptoms, the immediate treatment is:. If you have symptoms of a severe low blood sugar and your sense of confusion grows or you feel that you may pass out:. The glucagon injection should help your liver release sugar and thereby raise the blood sugar level. Self assessment quizzes are available for topics covered in this website. To find out how much you have learned about Diabetes Complications , take our self assessment quiz when you have completed this section. The quiz is multiple choice. Please choose the single best answer to each question. At the end of the quiz, your score will display. All rights reserved. University of California, San Francisco About UCSF Search UCSF UCSF Medical Center. |
| RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS | This article will review hypoglycemia unawareness and summarize the effects of medications that may influence it. Accessed Nov. However, we used two validated questionnaires commonly used in other studies for assessing HU 7 , 9. Which is awesome! As unpleasant as they may be, the symptoms of low blood glucose are useful. |
| Top bar navigation | People who are unaware of their hypoglycemia are also less likely to be awakened from sleep when hypoglycemia occurs at night. People who are hypoglycemic but are unaware of it must take extra precautions to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly. This is especially true before and during critical tasks, such as driving. When blood sugar levels are low or begin to fall, a CGM can sound an alarm. Such a device can be a great assistance to people with HU [ 12 , 15 ]. With continuous BG monitoring, children and adults with T1DM spend less time in hypoglycemia and simultaneously decrease their HbA1c level [ 33 , 34 ]. A prior study showed that diabetic patients with reduced beta-adrenergic sensitivity may be unaware of hypoglycemia, and the best suggestion for these patients is to strictly avoid hypoglycemia [ 35 , 36 ]. Our patient was also advised to have emergency glucose tablets, intermuscular, or intranasal glucagon injections at her disposal all of the time to avoid hypoglycemic attacks. The glucagon injection pen was not available in Iran at the time of the episode described here, neither was a CGM, so she was recommended to follow educational sessions on carbohydrate counting and perform excessive SBGM. The patient was given strict advice based on her job and profession, as well as the need to control her blood sugar level to the extent that it did not interfere with her professional and daily functioning [ 12 ]. She was advised to see her endocrinologist to adjust her insulin dose based on her unawareness of hypoglycemia attacks and her work schedule, which may not allow her enough time to rest and consume enough carbohydrates, potentially leading to life-threatening attacks, especially since her coworkers were unaware of her medical condition. It is strongly advised that people with diabetes, especially patients like this case, wear some sort of identification, such as a bracelet, or carry a card that state their condition [ 15 ]. Normalization of autonomic response takes 7—14 days on average, but it can take up to 3 months to normalize the threshold of symptoms, neuroendocrine response, and glucagon response although glucagon response is never fully recovered [ 37 , 38 ]. Another suggestion was to switch human insulin to the analog type of insulin. Hypoglycemia is a fairly common complication in diabetic patients receiving oral or insulin therapy. However, in a subset of patients who are unaware of hypoglycemia for a variety of reasons, these warning signs do not exist, resulting in severe and life-threatening hypoglycemic episodes. As a result, patients who have multiple episodes of HU are advised to raise their blood sugar control threshold for at least 2 weeks and to wear at all times a bracelet or label indicating their medical condition. In addition, in these patients, the use of CGM equipped with alarms in the occurrence of severely low blood sugar can be a perfect option. Patient data and information can be accessed for review after obtaining permission from the patient without any disclosure of her name. Cryer PE, Davis SN, Shamoon H. Hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care. Article CAS Google Scholar. Cryer PE. Symptoms of hypoglycemia, thresholds for their occurrence, and hypoglycemia unawareness. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. Hoeldtke RD, Boden G. Epinephrine secretion, hypoglycemia unawareness, and diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Ann Intern Med. Greenspan SL, Resnick MN. Geriatric endocrinology. In: Greenspan FS, Strewler GJ, editors. Basic and clinical endocrinology. Stamford: Appleton and Lange; Mitrakou A, Ryan C, Veneman T, Mokan M, Jenssen T, Kiss I, et al. Hierarchy of glycemic thresholds for counterregulatory hormone secretion, symptoms, and cerebral dysfunction. Am J Physiol-Endocrinol Metabol. Wilson JD, Foster DW, Kronenberg HM, Larsen PR. The anterior pituitary. Williams textbook of endocrinology. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co; Joslin EP, Kahn CR. Ronald Kahn Hypoglycemia: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Oxford:: Oxford University Press; Google Scholar. Veneman T, Mitrakou A, Mokan M, Cryer P, Gerich J. Induction of hypoglycemia unawareness by asymptomatic nocturnal hypoglycemia. Kalra S, Mukherjee JJ, Venkataraman S, Bantwal G, Shaikh S, Saboo B, et al. Hypoglycemia: the neglected complication. Indian J Endocrinol Metabol. Article Google Scholar. Cryer P. Hypoglycemia in diabetes: pathophysiology, prevalence, and prevention. Arlington County: American Diabetes Association; In: Loriaux L, Vanek C, editors. Endocrine emergencies: recognition and treatment. Cham: Springer International Publishing; Chapter Google Scholar. Liu J, Wang R, Ganz ML, Paprocki Y, Schneider D, Weatherall J. The burden of severe hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin. Whipple AO. Thesurgical therapy of hyperinsu-linism. J Int Chir. American Diabetes Association. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes— Lamounier RN, Geloneze B, Leite SO, Montenegro R, Zajdenverg L, Fernandes M, et al. Hypoglycemia incidence and awareness among insulin-treated patients with diabetes: the HAT study in Brazil. Diabetol Metab Syndr. Amiel SA, Choudhary P, Jacob P, Smith EL, De Zoysa N, Gonder-Frederick L, et al. Hypoglycaemia awareness restoration programme for people with type 1 diabetes and problematic hypoglycaemia persisting despite optimised self-care HARPdoc : protocol for a group randomised controlled trial of a novel intervention addressing cognitions. BMJ Open. Hopkins D, Lawrence IA, Mansell P, Thompson G, Amiel S, Campbell M, et al. Improved biomedical and psychological outcomes 1 year after structured education in flexible insulin therapy for people with type 1 diabetes: the UK DAFNE experience. Binder C, Bendtson I. Endocrine emergencies. Pedersen-Bjergaard U, Pramming S, Heller SR, Wallace TM, Rasmussen ÅK, Jørgensen HV, et al. Severe hypoglycaemia in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: influence of risk markers and selection. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. Zammitt NN, Geddes J, Warren RE, Marioni R, Ashby JP, Frier BM. Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme and frequency of severe hypoglycaemia in Type 1 diabetes: does a relationship exist? Diabet Med. McCulloch D. Physiologic response to hypoglycemia in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. Up to Date Medical , Becker K. Endocrine drugs and values. Principles and practice of endocrinology and metabolism. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; Hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diamond MP, Reece EA, Caprio S, Jones TW, Amiel S, DeGennaro N, et al. Impairment of counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia in pregnant women with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am J Obstet Gynecol. Nakhjavani M, Esteghamati A, Emami F, Hoseinzadeh M. Iran J Endocrinol Metabol. Holleman F, Schmitt H, Rottiers R, Rees A, Symanowski S, Anderson JH, et al. Reduced frequency of severe hypoglycemia and coma in well-controlled IDDM patients treated with insulin lispro. Brunelle RL, Llewelyn J, Anderson JH Jr, Gale EA, Koivisto VA. Meta-analysis of the effect of insulin lispro on severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 1 diabetes. Anderson JH Jr, Brunelle RL, Koivisto VA, Pfützner A, Trautmann ME, Vignati L, et al. Reduction of postprandial hyperglycemia and frequency of hypoglycemia in IDDM patients on insulin-analog treatment. Monami M, Marchionni N, Mannucci E. Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH human insulin in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. Smith CB, Choudhary P, Pernet A, Hopkins D, Amiel SA. Hypoglycemia unawareness is associated with reduced adherence to therapeutic decisions in patients with type 1 diabetes: evidence from a clinical audit. Cranston I, Lomas J, Amiel SA, Maran A, Macdonald I. Restoration of hypoglycaemia awareness in patients with long-duration insulin-dependent diabetes. Battelino T, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes. Wolpert HA. Use of continuous glucose monitoring in the detection and prevention of hypoglycemia. J Diabetes Sci Technol. Fritsche A, Stumvoll M, Häring HU, Gerich JE. Reversal of hypoglycemia unawareness in a long-term type 1 diabetic patient by improvement of β-adrenergic sensitivity after prevention of hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metabol. Fanelli CG, et al. Meticulous prevention of hypoglycemia normalizes the glycemic thresholds and magnitude of most of neuroendocrine responses to, symptoms of, and cognitive function during hypoglycemia in intensively treated patients with short-term IDDM. Dagogo-Jack S, Rattarasarn C, Cryer PE. Reversal of hypoglycemia unawareness, but not defective glucose counterregulation, in IDDM. Download references. In appreciation, we express our gratitude to Dr. Rafiee for sharing the patient history and encouraging us to share this case as a valuable subject for other physicians. Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Center, Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinical Sciences Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, First Floor, No 10, Jalal-Al-Ahmad Street, North Kargar Avenue, Tehran, , Iran. Radiology Department, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Elderly Health Research Center, Endocrinology and Metabolism Population Sciences Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. YSH: Study conception and design, data collection, and draft manuscript preparation. ME, SST: Draft of manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and read and approved the final manuscript. Correspondence to Yasaman Sharifi. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Medical Case Reports. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. Type 1 Info. Type 2 Info. Diabetes Management. Newly Diagnosed. Forms Of Diabetes. Autoimmune Diseases. Pregnancy with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes News. Food and Diabetes. School Resources. Previously Healthy. Beyond Type 1 App. Diabetes Scholars. Community Table. Marathon Team. Snail Mail Club. Type 1 Signs. Jesse Was Here. What is Hypoglycemia Unawareness? WRITTEN BY: Jordan Hoese, MD, MPH. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at age 12, and has run seven marathons, including New York City with Beyond Type Run in ! She is passionate about providing comprehensive medical care in resource-limited community settings, and helping people understand and take control of their health. Her hobbies include running, travel, hiking, camping, yoga, healthy eats, coffee and hanging out at home with her boyfriend and their three cats. Read More Bionic Boy - One mom discusses her reaction to seeing her son wearing his Omnipod and Dexcom together for the first time. The Night My Son Nearly Died for a Sprite - After a day of good blood glucose readings, my son asked for a Sprite. Little did I know that could be his demise. Read our cautionary story. Losing Will Hauver - His very good A1Cs, his maturity and independence with diabetes management, his success in college, Life with Type 1—A Photo Essay - Life with type 1 diabetes is a perpetual, exhausting tightrope act. |
 John R. White; The Contribution of Medications to Diqbetes Unawareness. Diabetes Spectr 1 April ; 20 Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications : cimplications Hypoglycemia unawareness is defined as the onset of neuroglycopenia before the appearance of autonomic warning symptoms. However,much is known regarding risk factors, biochemical causes, and populations at greatest risk for the development of hypoglycemia unawareness.
John R. White; The Contribution of Medications to Diqbetes Unawareness. Diabetes Spectr 1 April ; 20 Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications : cimplications Hypoglycemia unawareness is defined as the onset of neuroglycopenia before the appearance of autonomic warning symptoms. However,much is known regarding risk factors, biochemical causes, and populations at greatest risk for the development of hypoglycemia unawareness.
0 thoughts on “Hypoglycemic unawareness and diabetes complications”