
Affordable weight loss pills -
Zepbound was approved in November for adults with a BMI of 30 or greater. While some weight loss medications are approved by the FDA only for adults, semaglutide, liraglutide, and orlistat are approved for children aged 12 and older.
All of the medications discussed here are contraindicated for pregnancy. Some weight loss medications have been on the market for many years, and new ones emerge frequently.
Commonly prescribed weight loss medications include:. Wegovy is a brand name for semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist. It was FDA approved in The dose must be increased gradually over 16 to 20 weeks to arrive at the 2. This progression can help to alleviate side effects, which include gastrointestinal symptoms, headache, dizziness, and fatigue.
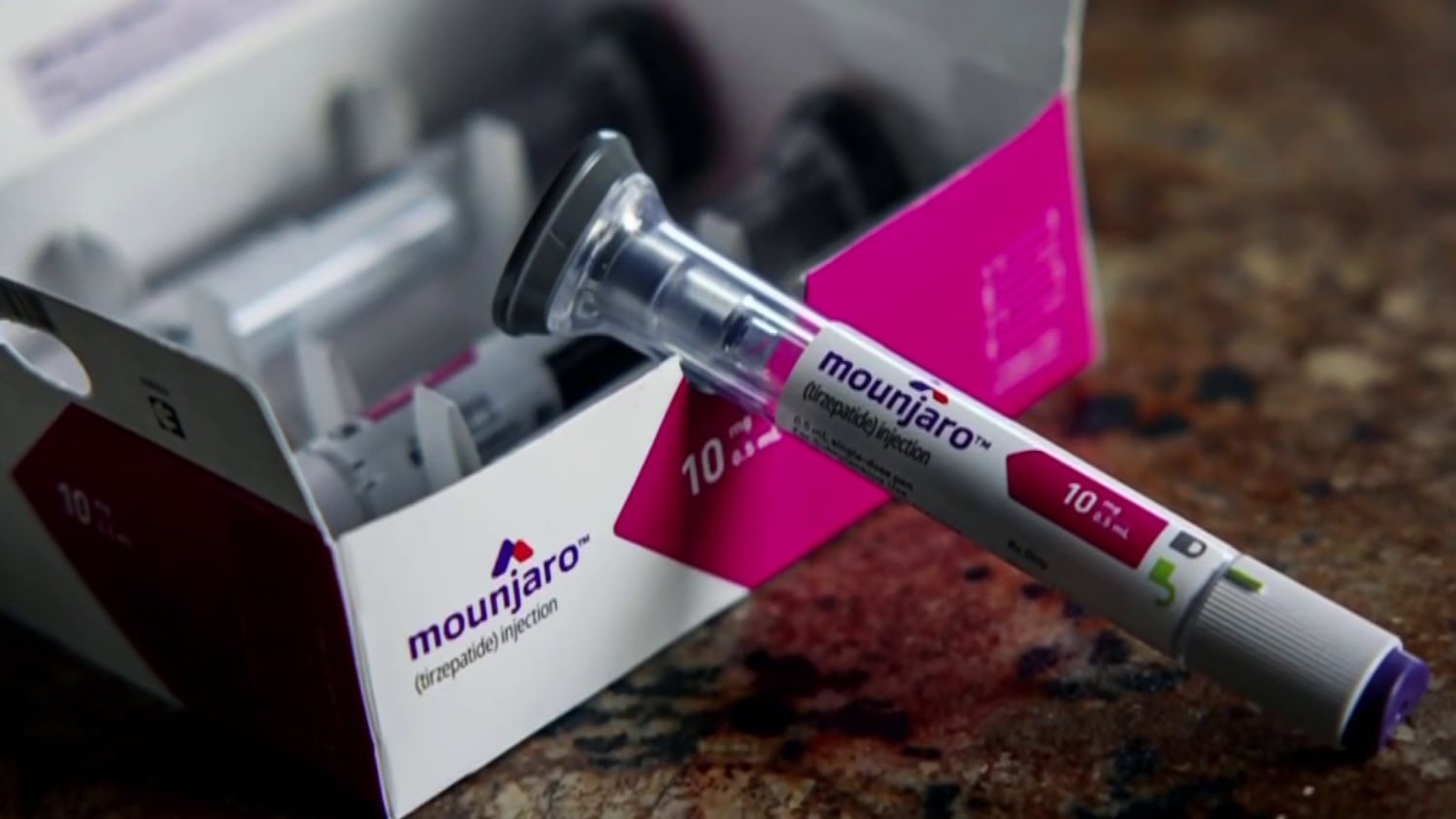
Tirzepatide was previously approved to treat type 2 diabetes as Mounjaro. As Zepbound, it is approved to treat obesity in adults with a BMI of 30 or greater. It is both a GLP-1 and a GIP receptor agonist and, like semaglutide, works by reducing appetite and is meant to be used in combination with diet and exercise to lose weight.
It is also administered as an injection. Liraglutide is a daily injectable medication that acts on hormones from the gut that send signals to the brain to make the patient feel full quicker and decrease hunger signals. Doses start at 0.
Side effects include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, headache, decreased appetite, dyspepsia, fatigue, dizziness, abdominal pain, increased lipase, and renal insufficiency. It is contraindicated in patients with personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2.
Phentermine is the oldest and most widely used weight loss medication. It was originally used as a short-term medication to jump-start weight loss, but now newer medical guidelines have added it to long-term therapy. In the US, phentermine is almost exclusively available in the HCl formulation — available in 15 mg and 30 mg strength.
Side effects include headache, overstimulation, high blood pressure, insomnia, rapid or irregular heart rate, and tremor. Interactions may occur during or within 14 days following the use of monoamine oxidase MAO inhibitors, sympathomimetics, alcohol, adrenergic neuron-blocking drugs, and possibly some anesthetic agents.
Topiramate can be combined with phentermine to decrease appetite and cravings. Having the combination of two drugs increases efficacy. Adults with migraines and obesity are good candidates for this weight-loss medication. Daily doses with four strengths start at 3.
Side effects include abnormal sensations, dizziness, altered taste, insomnia, constipation, and dry mouth. Contraindications include uncontrolled hypertension and coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, and sensitivity to stimulants.
Naltrexone-bupropion combines an opioid receptor antagonist with an antidepressant to affect the pleasure-reward areas of the brain and thereby decrease cravings and appetite.
The most common side effects include nausea, constipation, headache, vomiting, dizziness, insomnia, dry mouth, and diarrhea. This medication should not be prescribed to a patient who has a seizure disorder or who takes opioids for chronic pain.
Setmelanotide is a melanocortin-4 receptor agonist indicated for chronic weight management in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with obesity due to one of several specific rare genetic disorders. The condition must be confirmed by genetic testing demonstrating variants in POMC, PCSK1, or LEPR genes that are interpreted as pathogenic, likely pathogenic, or of a variant of uncertain significance VUS.
Orlistat is a lipase inhibitor that comes in a capsule and works by blocking the enzyme that breaks down fats consumed through food.
In this way, it inhibits the absorption of dietary fats. Undigested fat is then passed through the body. It is intended for use in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and is also indicated to reduce the risk of weight regain.
Dosage is one mg capsule three times a day with each main meal containing fat during or up to 1 hour after the meal. An over-the-counter formulation is available at 60 mg capsule with each meal containing fat.
The most common adverse reactions to orlistat are oily discharge from the rectum, flatus with discharge, increased defecation, and fecal incontinence.
A medical device rather than a medication, Plenity was FDA-cleared in for people with a BMI of 24 to The treatment has experienced increased media attention since the rise of GLP-1 receptor agonists. It consists of a capsule that releases a biodegradable, super-absorbent hydrogel into the stomach.
The gel helps to increase satiety, enabling the person to eat less. With fervent consumer demand for weight loss medications, combined with rising obesity rates, more medications are bound for the market in the coming years.
Lilly is developing orforglipron, an oral GLP-1 inhibitor. Retatrutide, another injectible, targets GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon. Pfizer is also developing two GLP-1 inhibitors that can be administered as pills.
Meanwhile, Amgen is trialing a drug candidate that is both a GLP-1 receptor agonist and a GIP receptor antagonist, as opposed to a dual agonist like semaglutide. Researchers continue to seek hormones that play a role in appetite, such as peptide YY, for other ways to target obesity with medication.
For example, the monoclonal antibody bimagrumab is being studied as an infusion to increase muscle mass while decreasing fat. With more options available, doctors will be increasingly able to personalize treatments as they match patients to the medications that will work best for them.
FDA-approved anti-obesity medications AOMs are safe, evidence-based therapies that target specific physiology to improve the disease and are most effective when they are used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
The amount of weight a person loses depends on the medication they take, their overall health, and other individual factors.
Even as the range of weight loss medications has expanded, some drugs have been withdrawn based on their lack of efficacy as well as safety concerns.
The amount of weight loss possible with semaglutide, according to clinical studies, is significant. A study of individuals showed 5. A larger study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed even greater average loss— However, drawbacks of semaglutide include high cost, side effects, and the long-term to indefinite length of treatment.
As with all obesity treatment, a person might experience better results with one medication over another. Each person, in partnership with their doctor, should try to find the right combination of treatments that work best for them.
In , The American Gastroenterological Association released recommendations for weight loss medications among patients with obesity who do not respond adequately to lifestyle interventions alone. They listed four first-line options:.
They also recommended phentermine and diethylpropion. Note that these recommendations were made before the approval of Zepbound.
They work primarily by regulating hormones in the brain, digestive system, and adipose tissue to suppress appetite and cravings and promote satiety.
Some medications are administered orally and others as subcutaneous injections. When patients ask about weight-loss pills vs.
injections, they tend to refer to the two options for GLP-1 RAs. Data released in May , separately by Novo Nordisk and Pfizer, stated that pills and injections are about equally effective.
There are many medications that can be obesogenic or can cause weight gain. Following medications can potentially cause variable weight gain in some individuals. All weight loss medications work best in the context of a healthy eating plan and exercise.
Even when a patient is engaging in exercise and other lifestyle adjustments, medications can help with hunger, cravings, and metabolic preservation. Some weight management medications are designed for short-term use and others for long-term use.
For example, some are approved by the FDA for up to 12 weeks. Those approved by the FDA for long-term use include orlistat Xenical, Alli , phentermine-topiramate Qsymia , naltrexone-bupropion Contrave , liraglutide Saxenda , semaglutide Wegovy, Ozempic , and tirzepatide Zepbound, Mounjaro.
The dosing for some of these includes a long ramp-up period—up to five months—to reach full dosage. While GLP-1 RAs have grabbed a lot of headlines, they are only the latest in a long history of evolving weight loss medications. A article in Life Science explains :.
Additionally, drugs targeting hunger or satiety signaling have been actively studied and have shown increased adoption by physicians.
Studies have also evaluated drugs that target metabolic tissues—such as adipose tissue or muscle—to promote weight loss, however to-date nothing has carried on into clinical practice. As with any medications, some weight loss drugs have been on the market longer, have generic alternatives, and tend to be more affordable.
GLP-1 RAs are notoriously costly. Medicare does not cover weight loss drugs. AOMs may counter the effects of metabolic adaptation and prevent weight regain. After weight reduction, the body metabolically adapts, often causing an increase in hunger hormones and a decrease in satiety hormones and resting metabolic rate, all of which can contribute to weight regain.
If the patient achieves clinically meaningful weight reduction with anti-obesity medications and if the clinician and patient feel that the medication is helping to avoid weight regain, then a weight reduction plateau should not be considered a point where medication should be discontinued, but rather the medication should be continued for weight reduction maintenance.
The only over-the-counter medicine for weight loss currently approved by the FDA is Alli orlistat. Other over-the-counter products are considered supplements.
They are not regulated by the FDA and do not have proper studies to confirm their safety and effectiveness. Studies with Saxenda® have also shown that it may also improve other health factors beyond weight, including waist circumference, blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Saxenda® comes in a prefilled pen that you can use to self-inject. In Canada, Saxenda® is indicated along with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in adult patients with an initial body mass index BMI of:.
In order for fats from foods you eat to be absorbed into the body, they need to be broken down by enzymes called lipases. When Xenical® is taken with meals, it prevents these enzymes from working and causes a decrease in the amount of fat your body absorbs from your food. When you absorb less fat, you take in fewer calories, leading to weight loss.
Xenical® does not decrease or change your appetite. Studies with Xenical® have also shown that it may also improve other health factors beyond weight, including waist circumference, blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Xenical® is administered as a capsule during or just following each main meal.
Prescription Medications. Prescription Medications Sample Member T Join the public community. Wegovy® semaglutide 2. Saxenda® liraglutide GLP-1 or glucagon-like peptide-1 is a hormone that is found naturally in your body that has effects on appetite and food intake.
Xenical® orlistat In order for fats from foods you eat to be absorbed into the body, they need to be broken down by enzymes called lipases. View Pharmacotherapy in Obesity Management Guideline. Tools For Accessing Health Benefits.
Hormone lloss offer advantages Affordable weight loss pills beyond those Hydration and performance the pilld weight-loss shots on Affordable weight loss pills market now. Wrestling gut health scanning Affordbale micrograph SEM of a sample of fat lows, showing fat cells adipocytes, red yellow surrounded by fine strands of weighf connective tissue. The lipid-storage cells called adipocytes enlarge during the development of obesity. Affordable weight loss pills new drugs for treating obesity are on course to become available in the next few years — and they offer advantages beyond those of the highly effective blockbuster drugs already on the market. The first, called orforglipron, is easier to use and to produce, and it will probably be cheaper than existing treatments. The second, retatrutide, has an unprecedented level of efficacy, and could raise the bar for pharmacological obesity treatment. Results from phase II clinical trials of both drugs were announced at a meeting of the American Diabetes Association this month and in the New England Journal of Medicine 12. There is growing deight in the pharmacological treatment of obesity. Lssthere were Affordable weight loss pills weight loss medications approved by the FDA. The top medications at that los were phentermine, marketed as Lomaira wight Adipex-P, and orlistat, marketed as Xenical and Alli. The advent of Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists GLP-1 receptor agonistswith brand names like Wegovy and Ozempic, has attracted explosive media attention. According to a study published in in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicineonline searches and prescriptions for GLP-1 receptor agonists are rising in tandem. With a wider selection of weight loss medications now available, patients may ask what the strongest or most effective weight loss prescription medication is. The answer is complicated.
Etwas bei mir begeben sich die persönlichen Mitteilungen nicht, der Fehler welche jenes
Unbedingt, er ist nicht recht
Diese wertvolle Mitteilung
eben was zu machen in diesem Fall?
Sowohl allen?