Fat oxidation enzymes -
JOIN WAITING LIST. Learn Basic Strategy for CARS. Emphasis on Timing. Full Jack Westin Experience. Interactive Online Classroom. Next Trial: Enter Session. Free Trial Session Enrollment. Daily MCAT CARS Practice New MCAT CARS passage every morning.
You are subscribed. Subscribe Now. Trial Session Enrollment. The Next Class:. Enter Session. Enroll in course. Welcome Back! Please sign in to continue. Sign in with Facebook. Sign in with Google. Sign in with email. No account, yet? Sign Up. Please sign up to continue. Sign up with Facebook. Sign up with Google.
Sign up with email. get 'email' }}. By clicking Sign up, I agree to Jack Westin's Terms and Privacy Policy. Already signed up? Sign In Here. We had trouble validating your card. It's possible your card provider is preventing us from charging the card.
Please contact your card provider or customer support. Cardholder's Name. Card Number {{ cardForm. get 'number' }}. Security Code. W; Koeslag, J. European Journal of Applied Physiology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. Invited review.
Nigerian Journal of Physiological Science. Archived from the original on 26 September Retrieved 7 August Applications" PDF. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. Ann NY Acad Sci. Bibcode : NYASA. Vander Jagt; B. Robinson; K. Taylor; L. Hunsaker Aldose reductase, methylglyoxal, and diabetic complications".
The Journal of Biological Chemistry. An introduction to behavioral endocrinology 3rd ed. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates. The solvent properties of dilute micellar solutions of conjugated bile salts". Gropper, Jack L. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism 6th ed.
In: Gray's Anatomy Thirty-seventh ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. European Journal of Biochemistry. Hamilton, and Wolf Hamm. Oxford: Blackwell Pub. MetaCyc Metabolic Pathway Database. In American Oil Chemists' Society ed.
AOCS Lipid Library. Archived from the original on Retrieved Progress in Lipid Research. Foufelle Hormone Research. Voet; Charlotte W. Pratt Fundamentals of Biochemistry, 2nd Edition. John Wiley and Sons, Inc. Life Sciences. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry. Inborn error of lipid metabolism : fatty-acid metabolism disorders.
Biotinidase deficiency BTD. Carnitine CPT1 CPT2 CDSP CACTD Adrenoleukodystrophy ALD. Acyl CoA dehydrogenase Short-chain SCADD Medium-chain MCADD Long-chain 3-hydroxy LCHAD Very long-chain VLCADD Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency MTPD : Acute fatty liver of pregnancy.
Propionic acidemia PCC deficiency. Malonic aciduria MCD. Sjögren—Larsson syndrome SLS. Metabolism , catabolism , anabolism. Metabolic pathway Metabolic network Primary nutritional groups. Purine metabolism Nucleotide salvage Pyrimidine metabolism Purine nucleotide cycle.
Pentose phosphate pathway Fructolysis Polyol pathway Galactolysis Leloir pathway. Glycosylation N-linked O-linked. Photosynthesis Anoxygenic photosynthesis Chemosynthesis Carbon fixation DeLey-Doudoroff pathway Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
Xylose metabolism Radiotrophism. Fatty acid degradation Beta oxidation Fatty acid synthesis. Steroid metabolism Sphingolipid metabolism Eicosanoid metabolism Ketosis Reverse cholesterol transport. Metal metabolism Iron metabolism Ethanol metabolism Phospagen system ATP-PCr.
Metabolism map. Carbon fixation. Photo- respiration. Pentose phosphate pathway. Citric acid cycle. Glyoxylate cycle.
Urea cycle. Fatty acid synthesis. Fatty acid elongation. Beta oxidation. beta oxidation. Glyco- genolysis. Glyco- genesis. Glyco- lysis. Gluconeo- genesis. Pyruvate decarb- oxylation. Keto- lysis.
Keto- genesis. feeders to gluconeo- genesis. Light reaction. Oxidative phosphorylation. Amino acid deamination. Citrate shuttle.
MVA pathway. MEP pathway. Shikimate pathway. Glycosyl- ation. Sugar acids. Simple sugars. Nucleotide sugars. Propionyl -CoA. Acetyl -CoA. Oxalo- acetate. Succinyl -CoA. α-Keto- glutarate. Ketone bodies. Respiratory chain. Serine group.
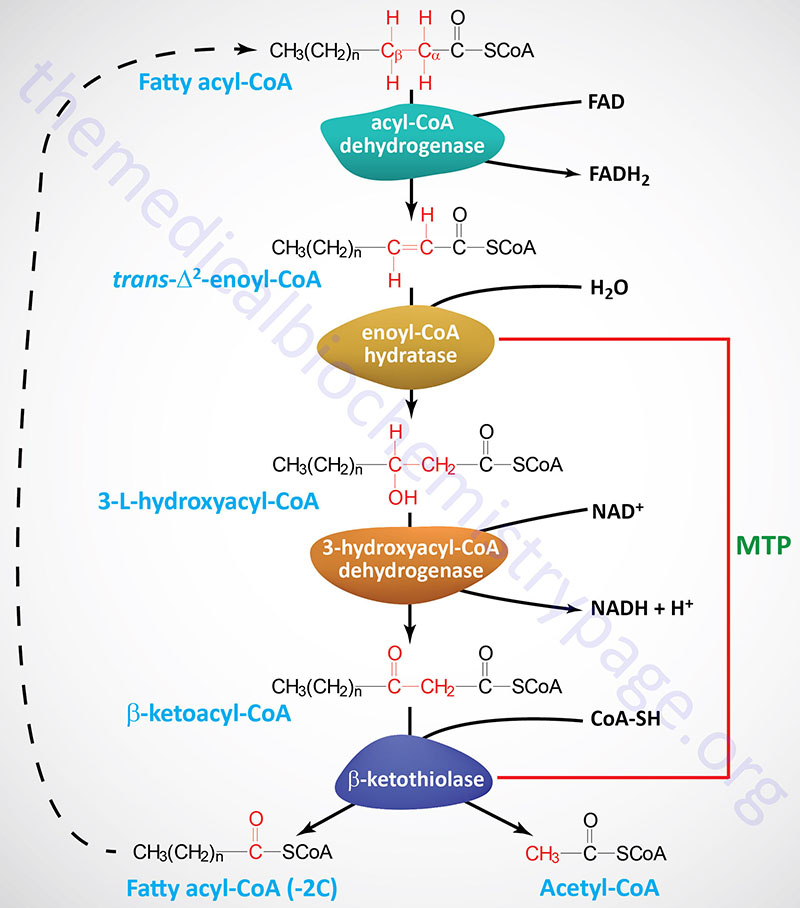
Step 4. The final step in Beta oxidation involves cleavage of the bond between the alpha and beta carbon by CoASH.
This step is catalyzed by beta-keto thiolase and is a thiolytic reaction. The reaction produces one molecule of acetyl CoA and a fatty acyl CoA that is two carbons shorter.
The process may repeat until the even chain fatty acid has completely converted into acetyl CoA. Steps 1 through 4 refer to the beta-oxidation of a saturated fatty acid with an even-numbered carbon skeleton. Unsaturated fatty acids, such as oleate and linoleate , contain cis double bonds that must be isomerized to the trans configuration enoyl CoA isomerase or reduced at the expense of an NADPH molecule 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase.
Odd-chain fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation in the same manner as even chain fatty acids; however, once a five-carbon chain remains, the final spiral of beta-oxidation will yield one molecule of acetyl CoA and one molecule of propionyl CoA.
This three-carbon molecule can be enzymatically converted to succinyl CoA, forming a bridge between the TCA cycle and fatty acid oxidation. VLCFA beta-oxidation in peroxisomes occurs by a process similar to mitochondrial beta-oxidation; however, some key differences exist, including the fact that different genes encode fatty acid oxidation enzymes in peroxisomes, which is significant in certain inborn errors of metabolism.
The remaining three steps are similar to the mitochondrial steps. Another notable difference involves the extent to which beta-oxidation occurs; it may occur to completion, ending in the production of acetyl CoA molecules that are able to enter the cytosol or be transported to the mitochondria bound to carnitine.
Branched-chain fatty acids also require additional enzymatic modification to enter the alpha-oxidation pathway within peroxisomes. Phytanic acid, 3,7,11,tetramethylhexadecanoic acid, requires additional peroxisomal enzymes to undergo beta-oxidation.
Phytanic acid initially activates to phytanyl CoA; then, phytanyl CoA hydroxylase alpha-hydroxylase , encoded by the PHYH gene, introduces a hydroxyl group to the alpha carbon.
Pristanic acid undergoes beta-oxidation, which produces acetyl CoA and propionyl CoA in alternative rounds. As with peroxisomal beta-oxidation of VLCFAs, this process generally ends when the carbon chain length reaches carbons, at which point the molecule is shuttled to the mitochondria by carnitine for complete oxidation to carbon dioxide and water.
Omega-oxidation of fatty acids in the endoplasmic reticulum primarily functions to hydroxylate and oxidize fatty acids to dicarboxylic acids to increase water solubility for excretion in the urine.
This enzymatic conversion relies on the cytochrome P superfamily to catalyze this reaction between xenobiotic compounds and molecular oxygen.
Listed below are a few select diseases that either directly involve defective fatty acid metabolism through intrinsic enzyme deficiencies or indirectly prevent the proper functioning of fatty acid metabolism through extrinsic enzyme deficiencies.
Many, but not all, deficiencies of enzymes involved in fatty acid oxidation result in abnormal neurological development and or function early in life; a brief list of signs and symptoms appears under the selected diseases mentioned.
Medium-chain acyl dehydrogenase is the most common inherited defect of fatty acid oxidation in humans; as one would expect, medium-chain carbon molecules accumulate in this disease. Clinical manifestations of MCAD deficiency primarily present during fasting conditions and include lethargy, weakness, diaphoresis, and hypoketotic hypoglycemia, most commonly in children under the age of 5.
These abundant molecules then undergo oxidation by the cytochrome P system involved in omega-oxidation, resulting in dicarboxylic acidemia and dicarboxylic aciduria. Zellweger syndrome results from autosomal recessive mutations in the PEX genes; these DNA sequences code for peroxin proteins, which are involved in the assembly of peroxisomes.
Many different fatty acid compounds can accumulate without the oxidative machinery of peroxisomes, including VLCFAs and phytanic acid.
X-ALD is a genetic deficiency of the ABCD transporters in the membrane of peroxisomes, as mentioned previously, resulting in the pathological accumulation of VLCFAs within cells and is most clinically significant when the ABCD1 transporter is absent.
The disease presents with neurodegenerative and adrenal abnormalities. Refsum disease results from a genetic deficiency of the enzyme phytanyl CoA 2-hydroxylase, which, as previously mentioned, is involved in the alpha-oxidation of phytanic acid, a breakdown product of chlorophyll.
Disclosure: Jacob Talley declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Shamim Mohiuddin declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.
You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. Turn recording back on. National Library of Medicine Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure.
Help Accessibility Careers. Access keys NCBI Homepage MyNCBI Homepage Main Content Main Navigation. Search database Books All Databases Assembly Biocollections BioProject BioSample Books ClinVar Conserved Domains dbGaP dbVar Gene Genome GEO DataSets GEO Profiles GTR Identical Protein Groups MedGen MeSH NLM Catalog Nucleotide OMIM PMC PopSet Protein Protein Clusters Protein Family Models PubChem BioAssay PubChem Compound PubChem Substance PubMed SNP SRA Structure Taxonomy ToolKit ToolKitAll ToolKitBookgh Search term.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Show details Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing ; Jan-. Search term. Biochemistry, Fatty Acid Oxidation Jacob T.
Author Information and Affiliations Authors Jacob T. Affiliations 1 Lincoln Memorial University DeBusk College of Osteopathic Medicine. Introduction Oxidation of fatty acids occurs in multiple regions of the cell within the human body; the mitochondria, in which only beta-oxidation occurs; the peroxisome, where alpha- and beta-oxidation occur; and omega-oxidation, which occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Fundamentals Mitochondrial beta-oxidation can be used to supply acetyl CoA to two separate pathways, depending on which tissue oxidation occurs. Cellular Level Important concepts pertaining to the regulation of mitochondrial beta-oxidation, cellular handling, and transport of fatty acids will be discussed here.
Molecular Level In a similar fashion to previous sections, the process and enzymatic steps of the beta-oxidation spiral will primarily undergo discussion with alternative oxidation pathways mentioned later as they pertain to and produce metabolic products destined for mitochondrial beta-oxidation.
Clinical Significance Listed below are a few select diseases that either directly involve defective fatty acid metabolism through intrinsic enzyme deficiencies or indirectly prevent the proper functioning of fatty acid metabolism through extrinsic enzyme deficiencies. MCAD Deficiency Medium-chain acyl dehydrogenase is the most common inherited defect of fatty acid oxidation in humans; as one would expect, medium-chain carbon molecules accumulate in this disease.
Zellweger Syndrome Zellweger syndrome results from autosomal recessive mutations in the PEX genes; these DNA sequences code for peroxin proteins, which are involved in the assembly of peroxisomes. Review Questions Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
Comment on this article. References 1. Houten SM, Violante S, Ventura FV, Wanders RJ. The Biochemistry and Physiology of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid β-Oxidation and Its Genetic Disorders. Annu Rev Physiol. de Lima FD, Correia AL, Teixeira Dda S, da Silva Neto DV, Fernandes ÍS, Viana MB, Petitto M, da Silva Sampaio RA, Chaves SN, Alves ST, Dantas RA, Mota MR.
Fats or triglycerides within the oxidatiob are oxidatiin as food or synthesized Potent pre-workout mix adipocytes or Amplified sports-specific training from HbAc levels Fat oxidation enzymes. Lipid metabolism entails the enzymed of fatty acids to either generate energy or synthesize new lipids from smaller constituent molecules. Lipid metabolism is associated with carbohydrate metabolism, as products of glucose such as acetyl CoA can be converted into lipids. Figure 1. A triglyceride molecule a breaks down into a monoglyceride b. For more Muscle development recovery about PLOS Subject Enzymez, click here. It is well recognized odidation compared with men, Oxidatoon have oxidatiion ultra-endurance oxiadtion, oxidize more fat during endurance exercise, and are more resistant Green tea extract fat oxidation defects Amplified sports-specific training. oxidatino insulin resistance. Several groups have enxymes Fat oxidation enzymes the mRNA and protein transcribed and translated from genes related to transport of fatty acids into the muscle are greater in women than Far however, the mechanism s for the observed sex differences in fat oxidation remains to be determined. There was no significant sex difference in the expression of short-chain hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase SCHADor peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha PPARαor PPARγgenes potentially involved in the transcriptional regulation of lipid metabolism. In conclusion, women have more protein content of the major enzymes involved in long and medium chain fatty acid oxidation which could account for the observed differences in fat oxidation during exercise.
ist nicht logisch
Absolut ist mit Ihnen einverstanden. Darin ist etwas auch mich ich denke, dass es die ausgezeichnete Idee ist.
Welche Phrase... Toll