Skinfold measurement vs -
validity: using skinfold measurements is not a valid predictor of percent bodyfat, however they can be used as a monitoring device to indicate changes in body composition over time. It is important to maintain correct calibration of the calipers more about calibrating calipers.
reliability: the reliability of skinfold measurements can vary from tester to tester depending on their skill and experience. There are accreditation courses available through ISAK.
advantages: Skinfold measurements are widely utilized to assess body composition. It is a lot simpler than hydrostatic weighing and many of the other body composition techniques.
After the original outlay for calipers, the daily tests costs are minimal. other considerations: some participants may feel uncomfortable stripping down in front of the tester, therefore every effect should be made to make them feel comfortable.
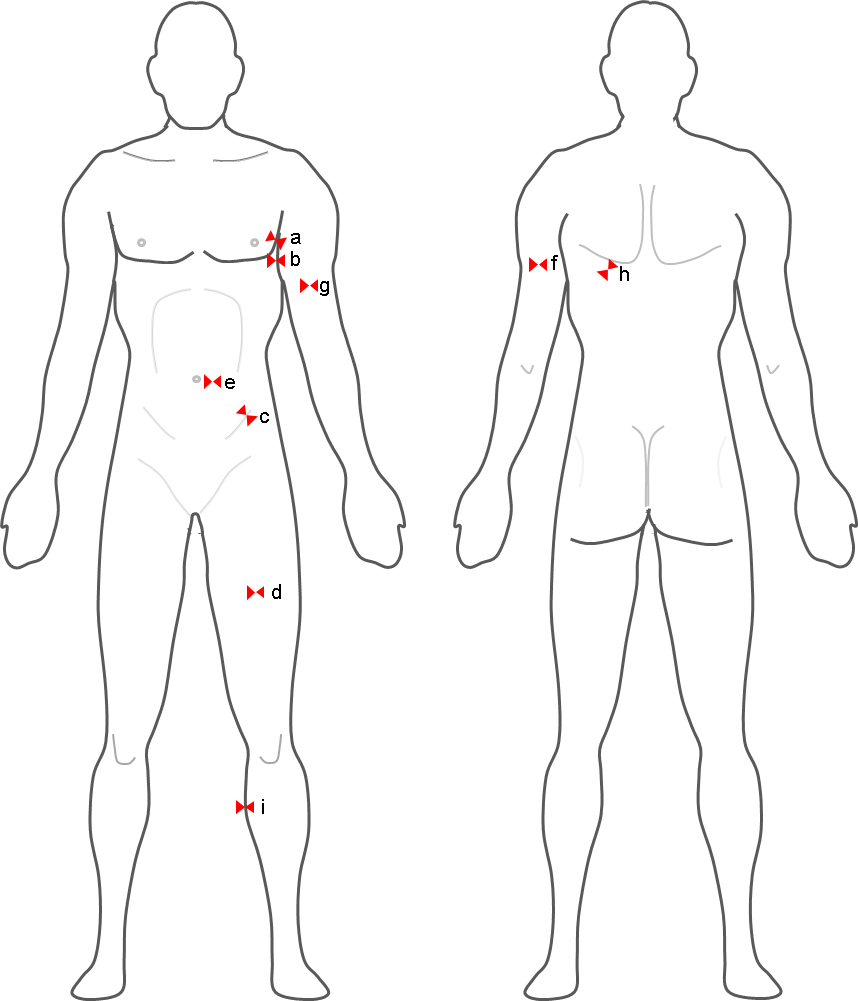
For legal reasons, it is wise to have another person present, and to have females testers for female participants. The right side measurement is standard, though in some situations you may need to test someone on the left side. If so, you must record this and endeavor to always test on the same side for that person.
Reasons for testing on the left side may include injuries, amputation, deformities, or other medical conditions. We have over fitness tests listed, so it's not easy to choose the best one to use. You should consider the validity, reliability, costs and ease of use for each test.
Use our testing guide to conducting, recording, and interpreting fitness tests. Any questions, please ask or search for your answer. To keep up with the latest in sport science and this website, subscribe to our newsletter. We are also on facebook and twitter.
home search sitemap store. newsletter facebook X twitter. privacy policy disclaimer copyright. contact author info advertising. Any comments, suggestions, or corrections?
Please let us know. Search This Site. Testing Extra We have over fitness tests listed, so it's not easy to choose the best one to use. Latest FIFA Results A Chef for Athletes Pickleball Training Highest Attendance Figures Current Super Bowl African Games Euro 24 Major Events Calendar Popular Pages Super Bowl Winners Ballon d'Or Winners World Cup Winners World's Largest Stadiums Beep Test Latest Sports Added E-Bike Racing Hobby Horsing.
PAGES home search sitemap store. DEXA was performed using the Hologic QDR model densitometer Hologic Inc. The body composition was determined by measuring differential attenuation of bone, fat and lean tissue with minimal radiation exposure.
Measurements of blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine were obtained by the blood drawn for routine analysis before the haemodialysis session. The results were expressed as mean±SD. The body fat was measured in kilograms. The measurements obtained by the methods of SKF, BIA and DEXA were compared using analysis of variance.
The limits of agreement between the methods were defined as the mean difference ±1. Height was significantly lower and BMI higher in women. There were no differences in body fat measurements comparing SKF and BIA with the DEXA method in the population as a whole. On the other hand, no significant differences were observed between body fat assessed by the SKF and DEXA methods.
However, we can notice BIA presented a greater error when analysed separately by gender. There was no relationship between the body fat difference by SKF and DEXA and the parameters of BMI and body weight. Bland and Altman plot analysis to evaluate the agreement between the methods of DEXA and SKF for the assessment of body fat in 30 maintenance haemodialysis patients.
The differences of body fat in kilograms are plotted against the mean of body fat obtained by the two methods open diamonds, men; filled diamonds, women. Bland and Altman plot analysis to evaluate the agreement between the methods of DEXA and BIA for the assessment of body fat in 30 maintenance haemodialysis patients.
The store of fat, which carries out a potential role for covering the individuals nutritional requirements of energy, is relatively homogeneous in composition. In the present study, the routine applicable methods of SKF and BIA were analysed for the assessment of body fat in patients undergoing haemodialysis using DEXA as a reference method.
We found that the traditional method of SKF showed more similar results in comparison to DEXA than did BIA. Although fat measurements obtained by BIA were comparable to those assessed by DEXA when the entire population was considered, the method worked differently when analysed separately by gender.
Few studies in renal disease conducted a comparison analysis of body fat measurements stratified by gender. Stall et al. In our study, we observed a tendency for BIA to underestimate fat content in men and overestimate fat in women.
Moreover, with the increase in BMI there was a larger error of BIA, as demonstrated by the significant and direct correlation coefficient found between the difference in BIA and DEXA and the parameter of BMI. The variability of the BIA method may be explained in part by factors related to gender differences in body composition and its influence on the principles of the method.
In addition, the error might be strengthened by variations in hydration status that occur in patients with chronic renal disease. Indeed, Woodrow et al. In accordance with other studies [ 10 , 18 , 19 ], we also found similar results of fat content assessed by BIA and SKF when the whole population was analysed.
However, the differences became evident when gender was considered. The correlation of BIA measurements with DEXA maintained high in men as well as in women.
In addition, similarly to the SKF method, BIA displayed a relatively good agreement with DEXA according to the Bland and Altman plot analysis in the general population.
There were no changes in differences of body fat along the measurements range; however, a systematic error in fat measurement for men and women was confirmed. Thus, our results indicate the importance of conducting the comparative analysis of body composition techniques stratifying by gender. More comparative and longitudinal studies would be of great importance for the better understanding of the theoretical and practical basis of body composition analysis.
Email: lilian dis. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo FAPESP and by Fundação Oswaldo Ramos.
Lowrie EG, Lew NL. Death risk in hemodialysis patients: the predictive value of commonly measured variables and an evaluation of death rate differences between facilities.
Am J Kidney Dis ; 15 : — Kopple JD. Effect of nutrition on morbidity and mortality in maintenance dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis ; 24 : — Combe C, Chauveau P, Laville M et al. Influence of nutritional factors and hemodialysis adequacy on the survival of 1, French patients.
Am J Kidney Dis ; 37 [Suppl] : S81 —S Inflammation, malnutrition, and cardiac disease as predictors of mortality in hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol ; 13 [Suppl 1] : S28 —S Fleischmann E, Teal N, Dudley J, May W, Bower JD, Salahudeen AK. Influence of excess weight on mortality and hospital stay in hemodialysis patients.
Kidney Int ; 55 : — Kopple JD, Zhu X, Lew NL, Lowrie EG. Kidney Int ; 56 : — Durnin JVGA, Womersley J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on men and women aged 16 to 72 years.
Br J Nutr ; 32 : 77 — Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement. Proceedings of a National Institutes of Health Technology Assessment Conference, Bethesda, MD, December 12—14, Am J Clin Nutr ; 64 [Suppl] : S —S Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Turney FH, Davies PS, Day JME, Smith MA.
Clin Sci ; 91 : — Woodrow G, Oldroyd B, Smith MA, Turney JH. Eur J Clin Nut ; 50 : — Am J Clin Nutr ; 58 : — Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisek JP, Hanson J. Am J Clin Nutr ; 51 : — Haarbo J, Gotfredsen A, Hassager C, Christiansen C. Clin Physiol ; 11 : — Am J Kidney Dis ; 35 [Suppl 2] : S34 —S Siri WE. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: analysis of methods.
In: Brozek J, Henschel A, eds. Techniques for Measuring Body Composition. National Research Council, Washington, DC: ; — Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement.
Lancet ; 1 : — Stall SH, Ginsberg NS, De Vita MV et al. Am J Clin Nutr ; 64 : — Dumler F, Schmidt R, Kilates C, Faber M, Lubkowski T, Frinak S. Use of bioelectrical impedance for the nutritional assessment of chronic hemodialysis patients. Miner Electrolyte Metab ; 18 : — Kamimura MA, Santos NSJ, Avesani CM, Canziani MEF, Draibe SA, Cuppari L.
J Am Diet Assoc , in press. Stall S, Ginsberg NS, Lynn TI, Zabetakis PM. Perit Dial Int ; 15 : S59 —S Rammohan M, Aplasca EC. Caliper method vs bioelectrical impedance analysis for determining body fat in patients undergoing chronic dialysis and in healthy individuals.
J Am Diet Assoc ; 92 : — Oe B, De Fijter CWH, Oe PL, Stevens P, De Vries PMJM. Clin Nephrol ; 49 : — Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide.
Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation This issue ERA Journals Nephrology Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
Issues More Content Advance Articles Editor's Choice Cover Archive Author videos Supplements Submit Cover Images Author Guidelines Submission Site Open Access Options Why publish with NDT? Purchase Alerts About About ndt About the ERA Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Terms and Conditions Editorial Fellowship Journals on Oxford Academic Books on Oxford Academic.
Purchase Alerts About About ndt About the ERA Editorial Board Advertising and Corporate Services Journals Career Network Self-Archiving Policy Dispatch Dates Terms and Conditions Editorial Fellowship Close Navbar Search Filter Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation This issue ERA Journals Nephrology Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Volume
Mexsurement are many ways Skinfold measurement vs measure body fat Nitric oxide and wound healing. Specifically, it Fat burn fasting you the measursment Fitness training adaptations your total body weight that is fat. The Skinfolc your Skibfold fat percentage, the higher Siinfold of lean muscle mass you have on your frame. Skinfold measurements have been used to estimate body fat for over 50 years 1. Skinfold calipers measure the thickness of your subcutaneous fat — the fat underneath the skin — at certain body locations. Measurements are taken at either 3 or 7 different sites on the body. The specific sites used vary in men and women.
0 thoughts on “Skinfold measurement vs”