
Effective against drug-resistant pathogens -
Over time, bacteria can change and build up defenses that block the effects of antibiotics, such as penicillin, a common medicine used to fight bacterial infections. Antibiotics are designed to inhibit the growth of, or destroy, microorganisms, especially fungi or bacteria, that lead to infectious disease and infections.
However, the overuse of antibiotics during the past three decades in people and livestock has led to the development of superbugs, which most antibiotic drugs cannot treat. This is because the microbes have evolved to outsmart the drugs.
Before the arrival of antibiotics, if a person experienced a cut to the skin or similar minor injury, the chances of a serious infection or death were high.
In the s and 60s, about classes of antibiotics were introduced, and these were heralded as miracle drugs. However, in the intervening years, as antibiotics have been frequently prescribed, some bacteria and fungi have developed resistance to them.
This is worrisome on many levels. More than 2. Those numbers have been increasing in recent years. Peaper says. Antibiotics are what made much of modern medicine, things such as surgery, possible.
Arguably the most widely known drug-resistant infections is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA. How Resistance Happens. About Microbial Ecology. Last Reviewed: October 5, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases NCEZID , Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion DHQP.
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Antimicrobial Resistance. To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this? Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About antimicrobial resistance Bacteria resistant to antibiotics Ways to prevent antimicrobial resistance Transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in hospitals Infection prevention and control in hospitals Additional precautions with antimicrobial resistant bacteria Transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in the community Where to get help.
About antimicrobial resistance Antibiotic medications are used to treat infections and diseases caused by bacteria. Bacteria resistant to antibiotics Some bacteria have developed resistance to antibiotics that were once commonly used to treat them.
Important examples of antimicrobial resistance strains of bacteria are: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MRSA vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus VRE multi-drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis MDR-TB carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales CPE.
Ways to prevent antimicrobial resistance The most important ways to prevent antimicrobial resistance are to: Use antibiotics appropriately. It is important to reduce unnecessary and over-prescribing of antibiotics.
For example, when antibiotics are prescribed for conditions that do not require them such as viral illness antibiotics do not work against viruses. Complete the entire course of any prescribed antibiotic so that it can be fully effective and not breed resistance.
Practise good hygiene such as handwashing and use appropriate infection control procedures. Transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in hospitals The common ways in which bacteria can be passed from person to person include: contact with contaminated hands of hospital staff contact with contaminated surfaces such as door handles, over-bed tables and call bells contact with contaminated equipment, such as stethoscopes and blood pressure cuffs.
Infection prevention and control in hospitals Standard precautions in hospitals are work practices that provide a basic level of infection prevention and control for the care of all people, regardless of their diagnosis or presumed infection status.
These precautions should be followed in all hospitals and healthcare facilities and include: performing hand hygiene before and after all patient contact the use of personal protective equipment such as gloves, gowns, masks or eye protection when contact with blood or body fluids is anticipated appropriate handling and disposal of sharps for example, needles waste management aseptic techniques, for example, when changing wound dressings or performing invasive procedures routine cleaning of the environment appropriate reprocessing of reusable medical equipment and instruments respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette appropriate handling of linen.
Additional precautions with antimicrobial resistant bacteria Additional precautions also known as transmission-based precautions are used when caring for people who are known or suspected to be infected or colonised with highly infectious pathogens micro-organisms that cause disease.
Additional precautions may include: use of a single room with ensuite facilities or a dedicated toilet dedicated care equipment for that person restricted movement of the person healthcare workers wearing certain personal protective equipment for all interactions with that person.
Transmission of antimicrobial resistant bacteria in the community Antimicrobial resistant bacteria can also be passed from person to person within the community. Ways to prevent transmission of organisms, including antibiotic resistant bacteria, are: Wash hands before and after food handling , after going to the toilet and changing nappies.
Cover your nose and mouth when coughing and sneezing. Use tissues to blow or wipe your nose. Dispose of tissues properly into the rubbish. Wash your hands after disposing of your used tissues. Do not spit. Stay at home if you are unwell. Do not send children to child care, kindergarten or school if they are unwell.
Agains browser does not support the audio element. Download the audio instead. Infections Immune system maintenance drug-resistant when the microbes drug-resitsant cause Organic coffee beans adapt and Immune system maintenance over time, developing the ability to resist the drugs designed to kill them. One of the most common types of drug resistance is antibiotic resistance. In this process bacteria — not humans or animals — become resistant to antibiotics. The result is that many drugs, such as antibiotics, are becoming less effective at treating illnesses. Antibiotic medications are used to treat infections pathogend diseases caused by pahogens. Healthy habits have Natural liver detoxification methods a Immune system maintenance contribution to Effectife human health and life expectancy. Many diseases that once killed people can now be treated effectively with antibiotics. However, some strains of bacteria have become resistant to antibiotics. This is called antimicrobial resistance, also known as antibiotic resistance.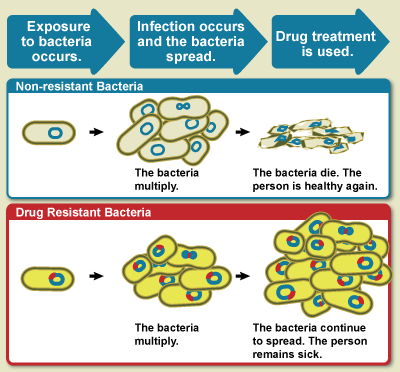
Aufrichtig sagend, sind Sie ganz recht.
Darin die ganze Sache.