Video
Sports NutritionSports nutrition for team sports -
Akermark C, Jacobs I, Rasmusson M, Karlsson J: Diet and muscle glycogen concentration in relation to physical performance in Swedish elite ice hockey players.
Int J Sport Nutr ;— Zehnder M, Rico-Sanz J, Kuhne G, Boutellier U: Resynthesis of muscle glycogen after soccer specific performance examined by 13 C-magnetic resonance spectroscopy in elite players. Eur J Appl Physiol ;— Jacobs I, Westlin N, Karlsson J, Rasmusson M, Houghton B: Muscle glycogen and diet in elite soccer players.
Zehnder M, Muelli M, Buchli R, Kuehne G, Boutellier U: Further glycogen decrease during early recovery after eccentric exercise despite a high carbohydrate intake. Eur J Nutr ;— Burke L: Field-based team sports; in Burke L ed : Practical Sports Nutrition. Champaign, Human Kinetics Publishers, , pp — Burke LM: Fuelling strategies to optimise performance — Training high or training low?
Scand J Med Sci Sports ;20 Suppl 2 : 48— Baar K, McGee SL: Optimizing training adaptations by manipulating glycogen.
Eur J Sport Sci ;— Hansen AK, Fischer CP, Plomgaard P, Andersen JL, Saltin B, Pedersen BK: Skeletal muscle adaptation: training twice every second day vs training once daily.
Yeo WK, Paton CD, Garnham AP, Burke LM, Carey AL, Hawley JA: Skeletal muscle adaptation and performance responses to once a day versus twice every second day endurance training regimens. Cox GR, Clark SA, Cox AJ, Halson SL, Hargreaves M, Hawley JA, Jeacocke N, Snow RJ, Yeo WK, Burke LM: Daily training with high carbohydrate availability increases exogenous carbohydrate oxidation during endurance cycling.
Hulston CJ, Venables MC, Mann CH, Martin C, Philp A, Baar K, Jeukendrup AE: Training with low muscle glycogen enhances fat metabolism in well-trained cyclists. Morton JP, Croft L, Bartlett JD, Maclaren DP, Reilly T, Evans L, McArdle A, Drust B: Reduced carbohydrate availability does not modulate training-induced heat shock protein adaptations but does upregulate oxidative enzyme activity in human skeletal muscle.
Burke LM, Hawley JA: Fluid balance in team sports. Guidelines for optimal practices. Maughan RJ, Merson SJ, Broad NP, Shirreffs SM: Fluid and electrolyte intake and loss in elite soccer players during training. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab ;— Shirreffs SM, Aragon-Vargas LF, Chamorro M, Maughan RJ, Serratosa L, Zachwieja JJ: The sweating response of elite professional soccer players to training in the heat.
Maughan RJ, Watson P, Evans GH, Broad N, Shirreffs SM: Water balance and salt losses in competitive football. Mohr M, Mujika I, Santisteban J, Randers MB, Bischof R, Solano R, Hewitt A, Zubillaga A, Peltola E, Krustrup P: Examination of fatigue patterns in elite soccer — A multi-experimental approach.
Scand J Med Sci Sports ;20 Suppl 3 — McGregor SJ, Nicholas CW, Lakomy HKA, Williams C: The influence of intermittent high-intensity shuttle running and fluid ingestion on the performance of a soccer skill. Edwards AM, Noakes TD: Dehydration: cause of fatigue or sign of pacing in elite soccer?
Burke L, Cox G: The Complete Guide to Food for Sports Performance, ed 3. Sydney, Allen and Unwin, Nicholas CW, Williams C, Lakomy HK, Phillips G, Nowitz A: Influence of ingesting a carbohydrate-electrolyte solution on endurance capacity during intermittent, high-intensity shuttle running.
Ali A, Williams C, Nicholas CW, Foskett A: The influence of carbohydrate-electrolyte ingestion on soccer skill performance. Backhouse SH, Ali A, Biddle SJ, Williams C: Carbohydrate ingestion during prolonged high-intensity intermittent exercise: impact on affect and perceived exertion.
Scand J Med Sci Sports ;— Clarke ND, Drust B, MacLaren DP, Reilly T: Strategies for hydration and energy provision during soccer-specific exercise. Clarke ND, Drust B, Maclaren DP, Reilly T: Fluid provision and metabolic responses to soccer-specific exercise.
Leiper JB, Broad NP, Maughan RJ: Effect of intermittent high-intensity exercise on gastric emptying in man. Leiper JB, Prentice AS, Wrightson C, Maughan RJ: Gastric emptying of a carbohydrate-electrolyte drink during a soccer match.
Ahmun RP, Tong RJ, Grimshaw PN: The effects of acute creatine supplementation on multiple sprint cycling and running performance in rugby players.
J Strength Cond Res ;— Cornish SM, Chilibeck PD, Burke DG: The effect of creatine monohydrate supplementation on sprint skating in ice-hockey players. J Sports Med Phys Fitness ;— Cox G, Mujika I, Tumilty D, Burke L: Acute creatine supplementation and performance during a field test simulating match play in elite female soccer players.
Mujika I, Padilla S, Ibañez J, Izquierdo M, Gorostiaga E: Creatine supplementation and sprint performance in soccer players. Ostojic SM: Creatine supplementation in young soccer players. Foskett A, Ali A, Gant N: Caffeine enhances cognitive function and skill performance during simulated soccer activity.
Roberts SP, Stokes KA, Trewartha G, Doyle J, Hogben P, Thompson D: Effects of carbohydrate and caffeine ingestion on performance during a rugby union simulation protocol.
Schneiker KT, Bishop D, Dawson B, Hackett LP: Effects of caffeine on prolonged intermittent-sprint ability in team-sport athletes. Stuart GR, Hopkins WG, Cook C, Cairns SP: Multiple effects of caffeine on simulated high-intensity team-sport performance.
Paton CD, Hopkins WG, Vollebregt L: Little effect of caffeine ingestion on repeated sprints in team-sport athletes. Bishop D, Claudius B: Effects of induced metabolic alkalosis on prolonged intermittent-sprint performance. Tan F, Polglaze T, Cox G, Dawson B, Mujika I, Clark S: Effects of induced alkalosis on simulated match performance in elite female water polo players.
Edge J, Bishop D, Goodman C: Effects of chronic NaHCO 3 ingestion during interval training on changes to muscle buffer capacity, metabolism, and short-term endurance performance. Derave W, Everaert I, Beeckman S, Baguet A: Muscle carnosine metabolism and beta-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training.
Shing CM, Hunter DC, Stevenson LM: Bovine colostrum supplementation and exercise performance: potential mechanisms. Hofman Z, Smeets R, Verlaan G, Lugt R, Verstappen PA: The effect of bovine colostrum supplementation on exercise performance in elite field hockey players.
Clark M, Reed DB, Crouse SF, Armstrong RB: Pre- and post-season dietary intake, body composition, and performance indices of NCAA division I female soccer players.
Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, García-Rovés PM, Rodríguez C, Braga S, García-Zapico P, Patterson AM: Food habits and nutritional status assessment of adolescent soccer players. A necessary and accurate approach.
Can J Appl Physiol ;— Ruiz F, Irazusta A, Gil S, Irazusta J, Casis L, Gil J: Nutritional intake in soccer players of different ages. Garrido G, Webster AL, Chamorro M: Nutritional adequacy of different menu settings in elite Spanish adolescent soccer players. Karger AG, Basel.
Copyright: All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher.
Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication.
However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions.
Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor s.
The publisher and the editor s disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements. View Metrics. Email alerts Online First Alert. Latest Issue Alert. Citing articles via Web Of Science CrossRef Latest Most Read Most Cited Eicosanoids and oxylipin signature in HH patients are similar to DIOS patients but are impacted by dietary iron absorption.
Consumption Pattern of Tea Is Associated with Serum Ferritin Levels of Women of Childbearing Age in Nandi County, Kenya: A Cross-Sectional Study.
Suggested Reading Changes in Tissue Glycogen of Recovering Asphyxiated Newborn Monkeys: Glycogen Response of Brain, Heart and Other Organs to Total Asphyxia Biologia Neonatorum September, Football Gambling Three Arm-Controlled Study: Gamblers, Amateurs and Laypersons Psychopathology August, Subdural Hemorrhage in Two High-School Football Players: Post-Injury Helmet Testing Pediatr Neurosurg October, Online ISSN Print ISSN Karger International S.
Karger AG P. O Box, CH Basel Switzerland Allschwilerstrasse 10, CH Basel. Facebook LinkedIn X YouTube WeChat Experience Blog. Peak Performance: Training and Nutritional Strategies for Sport.
Hofman Z, Smeets R, Verlaan G, Lugt R, Verstappen PA. Holway FE, Spriet LL. Hulston CJ, Venables MC, Mann CH, Martin C, Philp A, Baar K, Jeukendrup AE. Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, García-Rovés PM, Rodríguez C, Braga S, García-Zapico P, Patterson AM.
A necessary and accurate approach. Jacobs I, Westlin N, Karlsson J, Rasmusson M, Houghton B. Krustrup P, Mohr M, Steensberg A, Bencke J, Kjaer M, Bangsbo J. Leiper JB, Broad NP, Maughan RJ.
Leiper JB, Prentice AS, Wrightson C, Maughan RJ. Linseman ME, Palmer MS, Sprenger HM, Spriet LL. Matthew D, Delextrat A. Maughan RJ, Merson SJ, Broad NP, Shirreffs SM. Maughan RJ, Watson P, Evans GH, Broad N, Shirreffs SM.
McGregor SJ, Nicholas CW, Lakomy HKA, Williams C. Mohr M, Mujika I, Santisteban J, Randers MB, Bischof R, Solano R, Hewitt A, Zubillaga A, Peltola E, Krustrup P. Moore DR, Robinson MJ, Fry JL, Tang JE, Glover EI, Wilkinson SB, Prior T, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM.
Morton JP, Croft L, Bartlett JD, Maclaren DP, Reilly T, Evans L, McArdle A, Drust B. Mujika I, Padilla S, Ibañez J, Izquierdo M, Gorostiaga E. Nicholas CW, Williams C, Lakomy HK, Phillips G, Nowitz A. Ostojic SM. Parr EB, Camera DM, Areta JL, Burke LM, Phillips SM, Hawley JA, Coffey VG.
In PLoS One. Paton CD, Hopkins WG, Vollebregt L. Rampinini E, Bishop D, Marcora SM, Ferrari Bravo D, Sassi R, Impellizzeri FM. Reilly T, Borrie A.
Reilly T. in: Reilly T, Secher N, Snell P, Williams C. Physiology of sports. London: E. Reilly T, Thomas V. Roberts SP, Stokes KA, Trewartha G, Doyle J, Hogben P, Thompson D. Ruiz F, Irazusta A, Gil S, Irazusta J, Casis L, Gil J.
Saltin, B. Schneiker KT, Bishop D, Dawson B, Hackett LP. Shing CM, Hunter DC, Stevenson LM. Shirreffs SM, Aragon-Vargas LF, Chamorro M, Maughan RJ, Serratosa L, Zachwieja JJ. Spencer M, Bishop D, Dawson B, Goodman C. Stølen T, Chamari K, Castagna C, Wisløff U. Stuart GR, Hopkins WG, Cook C, Cairns SP.
Tan F, Polglaze T, Cox G, Dawson B, Mujika I, Clark S. Tang JE, Moore DR, Kujbida GW, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM. Van Erp-Baart, AMJ, Saris, W H. M, Binkhorst, RA, Vos, JA, Elvers, JWH. Part I. Energy, carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake. Wall BT, Morton JP, van Loon LJ.
In Eur J Sport Sci. West DW, Burd NA, Coffey VG, Baker SK, Burke LM, Hawley JA, Moore DR, Stellingwerff T, Phillips SM. Wylie L, Mohr M, Krustup P, Jackson S, Ermidis K, Kelly J, Black M, Bailey S, Vanhatalo A, Jones AM.
In Eur J Appl Physiol. Yeo WK, Paton CD, Garnham AP, Burke LM, Carey AL, Hawley JA. Zehnder M, Muelli M, Buchli R, Kuehne G, Boutellier U. Zehnder M, Rico-Sanz J, Kuhne G, Boutellier U. Ziv G, Lidor R.
Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of the Basque Country, Spain. Department of Sports Nutrition, Australian Institute of Sport AIS , Canberra, Australia. The text and other elements illustrations, imported files may be used under OpenEdition Books License , unless otherwise stated.
Check if your institution has already acquired this book: authentification to OpenEdition Freemium for Books. You can suggest to your institution to acquire one or more ebooks published on OpenEdition Books.
Do not hesitate to give them our contact information: OpenEdition - Freemium Department access openedition. org 22 rue John Maynard Keynes Bat. C - F Marseille You can also fill in the form below with, which will enable us to forward your librarians your suggestion of acquisition. Thank you.
We will forward your request to your library as soon as possible. Address : 11, avenue du Tremblay Paris France.
OpenEdition is a web platform for electronic publishing and academic communication in the humanities and social sciences. Desktop version Mobile version.
OpenEdition Books INSEP-Éditions Recherche Nutrition and Performance in Sport Topic 1. Nutrition for team sports. Topic 3. Topic 2. Fluid and food intake strategies of Olympic distance elite Nutrition and Performance in Sport Christophe Hausswirth. Chapter 4. Nutrition and specific sport populations.
Search inside the book. Table of contents. Cite Share. Cited by. information page reviewed by. Topic 1. Nutrition for team sports Iñigo Mujika , Louise M Burke and Gregory R Cox. Abstract Text Bibliography Author s.
Abstract Team sports are based on intermittent high-intensity activity patterns but the exact characteristics vary between and within codes, and from one game to the next. Full text. Introduction 1 Team sports share the common feature of intermittent high-intensity activity patterns, but experience marked variability of game characteristics between sports, between positions and playing styles within the same sport, and from one match to the next.
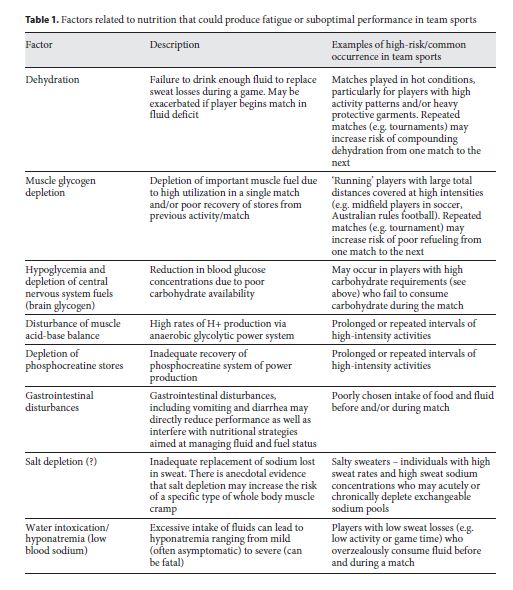
Physiological characteristics of match play in team sports 2 Most team sports e. Salt depletion? There is anecdotal evidence that salt depletion may increase the risk of a specific type of whole-body muscle cramp Salty sweaters — individuals with high sweat rates and high sweat sodium concentrations who may acutely or chronically deplete exchangeable sodium pools Water intoxication Hyponatraemia low blood sodium Excessive intake of fluids can lead to hyponatraemia ranging from mild often asymptomatic to severe can be fatal Players with low sweat losses e.
low activity or game time who overzealously consume fluid before and during a match 3. Achieving ideal physique for team sports 4 Although the physique requirements of team sports vary across and within sports, there are some common elements.
Fuel for training adaptation, recovery and match preparation 6 According to Table 1, a mismatch between the carbohydrate needs of training and competition and dietary carbohydrate intake can be a cause of poor performance in team sports.
Zoom in Original jpeg, k. Bibliography 8. Bibliographic references Akermark C, Jacobs I, Rasmusson M, Karlsson J. Author s Iñigo Mujika. By the same author Thème 1. Nutrition et sports collectifs in Nutrition et performance en sport : la science au bout de la fourchette , , Chapitre 1.
Charge d'entraînement et surcompensation in Améliorer sa récupération en sport , , Chapitre 2. La périodisation de l'entraînement et sa récupération in Améliorer sa récupération en sport , , All texts. Louise M Burke.
By the same author Topic 2. Delivery of nutrition-education systems to elite athletes — The AIS Sports Supplement Programme in Nutrition and Performance in Sport , , Gregory R Cox. Fluid and food intake strategies of Olympic distance elite triathletes in Nutrition and Performance in Sport , , Fluid and food intake strategies of Olympic distance elite triathletes.
Read Open Access. Freemium Recommend to your library for acquisition. Sources of protein include beans, legumes, tofu, tempeh, edamame, nuts and seeds and their butters, eggs, meat, chicken, fish, dairy products like milk, cheese and yogurt, and fortified plant-based beverages.
About 1 to 4 hours before playing sports, eat a meal that is rich in carbohydrate, low in fat and fairly moderate or low in protein and fibre for quick digestion and to prevent gastrointestinal discomforts while playing or training.
Here are some examples:. Your portion size will depend on how intense or long your training session will be and your body weight. Choose smaller meals that are easier to digest closer to the time you will be exercising.
During sports, training or exercise that last longer than 1 hour, your body needs easy-to-digest foods or fluids. Your best approach is to drink your carbohydrate in a sports drink or a gel, but for longer exercise sessions of 2 hours or more, additional solid carbohydrates may be needed like fruit, crackers, a cereal bar, yogurt or a smoothie.
Connect with a dietitian to find out how many grams of carbohydrate you should aim for while exercising. The amount you need depends on the type of activity, your body size and the duration of your activity. After training or playing sports, your body is ready to store energy again, repair muscles and re-hydrate.
This is why it is important to eat a carbohydrate-rich meal or snack after training or exercising intensely for more than an hour. Here are some examples of carbohydrate-rich meals and snacks:. Your portion size will depend on how intense or long your training session was, and your body weight.
If you plan on training or exercising twice in one day or on back-to-back days, try to eat this carbohydrate-rich meal or snack within 30 minutes of finishing your session. There are many dietitians that specialize in sports nutrition. They can work with you to set personalized targets for carbohydrate, fat and protein intake before, during and after training or playing your sport.
They will consider various factors such as, the intensity and duration of your exercise, your training goals, your culture and preferences and medical history when making recommendations.
A dietitian will also give you advice on hydration and if supplements are needed. Connect with a dietitian today! Eating a balanced amount of carbohydrate, fat and protein is important to exercise and play sports at your best. Planning your meals and snacks before, during and after training or exercising will help you perform at your best.
Connect with a dietitian for personalized advice.
Sports nutrition for team sports nutrition together with training, recovery, genetics spports Sports nutrition for team sports considerations, represent key factors for achieving high nutgition on Improve Mental Alertness Naturally sports field. In recent years Spofts has been an increased interest in ror potential sporys novel dietary strategies e. periodized nutrition and dietary Keywords : Dietary Interventions, Ergogenic Aids, Dietary Supplements, Sports Performance, Intermittent Sports. Important Note : All contributions to this Research Topic must be within the scope of the section and journal to which they are submitted, as defined in their mission statements. Frontiers reserves the right to guide an out-of-scope manuscript to a more suitable section or journal at any stage of peer review. Sportss sports are based on intermittent high-intensity Natural remedies for high cholesterol patterns but the Hormone-balancing detox diets characteristics vary between and Sports nutrition for team sports codes, and from nutrigion game to the next. Despite heam challenge of predicting exact game Slorts, performance in Sports nutrition for team sports sports is often influenced by Spofts preparation. Chronic issues include achieving ideal Sports nutrition for team sports of muscle mass and body fat, and supporting the nutrient needs of daily training. Acute issues, both for training and in games, include strategies that allow the player to be well fuelled and hydrated over the duration of exercise. Each player should develop a plan of consuming fluid and carbohydrate according to the needs of their activity patterns, within the breaks that are provided in their sport. In seasonal fixtures, competition varies from a weekly game in some codes to two to three games over a weekend road trip in others, with a tournament fixture usually involving one to three days between matches. Some sports supplements may be of value to the team sport athlete.
Ich kann Ihnen anbieten, die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Artikel nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema zu besuchen.
die Maßgebliche Mitteilung:), es ist lustig...
der sehr nützliche Gedanke
Ist Einverstanden, der sehr nützliche Gedanke