
Macronutrients for pre-workout nutrition -
The only way to get more protein in the body is to consume it. If we are not taking in protein then our body will naturally take amino acids from the next best source, which would be other muscle tissue, because our body still has to repair and contract. Breaking down one muscle to help grow another does not sound like a sustainable process.
Protein needs to be consumed in a sufficient amount and consumed in a way to continuously supply amino acids to the bloodstream.
The issue with developing a consistent method for the frequency of protein consumption is how to get a consistent amount during the day. We need to consume protein every hours so we do not have periods without amino acids in the bloodstream.
The exact timing aspect of protein is minimal. You can consume protein after you work out and data shows that it slows catabolism and promote anabolism.
However, the actual muscle growth will occur days after training not in the hours post training. Carbohydrate timing is more complex than protein timing.
How often you eat protein is more important than timing it around workouts. However, it is the opposite for carbohydrates. The frequency of carb intake is not really an issue until we are consuming vast amounts of carbohydrates.
In that case, carbohydrate consumption can become too large to be synthesized into glycogen stores and deposited more as a fat. Therefore, the timing of carb intake becomes more important to increase its frequency throughout several meals. Timing carb intake as it relates to physical activity has several distinct phases.
The first window would be the pre-workout phase. The pre-workout phase is important in replacing glycogen stores, which supplies blood glucose energy to the nervous system and muscles for contraction.
Having full glycogen stores will allow better workout performances. Carbohydrates also have been shown to be helpful in preventing muscle loss when ingested during the pre-workout phase.
For this to be effective pre-workout carbs would need to be consumed hours before training. The next phase is post workout carbs which have similar effects as pre-workout carbs. They have an anti-catabolism mechanism as well as glycogen repletion and will activate anabolic effects. Protein combined with carbs helps to blunt the catabolism process.
These carbs help with glycogen repletion so we do not have chronically low glycogen stores effecting workout performance and muscle growth. Consuming carbs right after training helps with the likelihood of those carbs being used as glycogen.
The alternative is being converted to fat stores at rest. The anabolic affects occur by spiking insulin. Insulin stimulates muscle growth upon binding to the muscle cell surface.
Post-workout carbs show a lot of benefit for your performance and your absorption for glycogen stores. They need to be consumed in a ratio as your pre-workout carbs. The last macro to worry about for nutrient timing is fats. Fats are very difficult to digest.
They slow down the digestion of proteins and lower the glycemic index of carbs. They slow down your digestion of proteins from one to seven hours depending on how much fat is consumed with the protein.
Fats need to be consumed away from your workouts. This way they do not affect the nervous system functionality and glycogen stores of which carbs are trying to promote.
How much should you eat? When should you eat? We're going to discuss pre-workout and post-workout nutrition and give some examples of what to eat and guidelines as far as the quantity of those macronutrients, carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, that you can utilize to maximize your workout, and then also focus on recovery as well.
I did a blog in March primarily geared towards understanding what is a carbohydrate, what is a protein, and what is a fat, and how those affect a workout. And I encourage you to be able to go back and take a look at that video just to kind of get a baseline or a foundation of what those macronutrients provide for exercise.
But we're going to focus a little bit more on the specifics of pre-workout and post-workout nutrition and how you can utilize some of those specific examples at home.
The pre-workout obviously is made to fuel your activity, whatever type of movement that you're going to be focusing on. Going for a walk, going to a group exercise class, going to a yoga workout, making sure that you have plenty of fuel in your body to take advantage of and enjoy that activity the most you possibly can is going to be important.
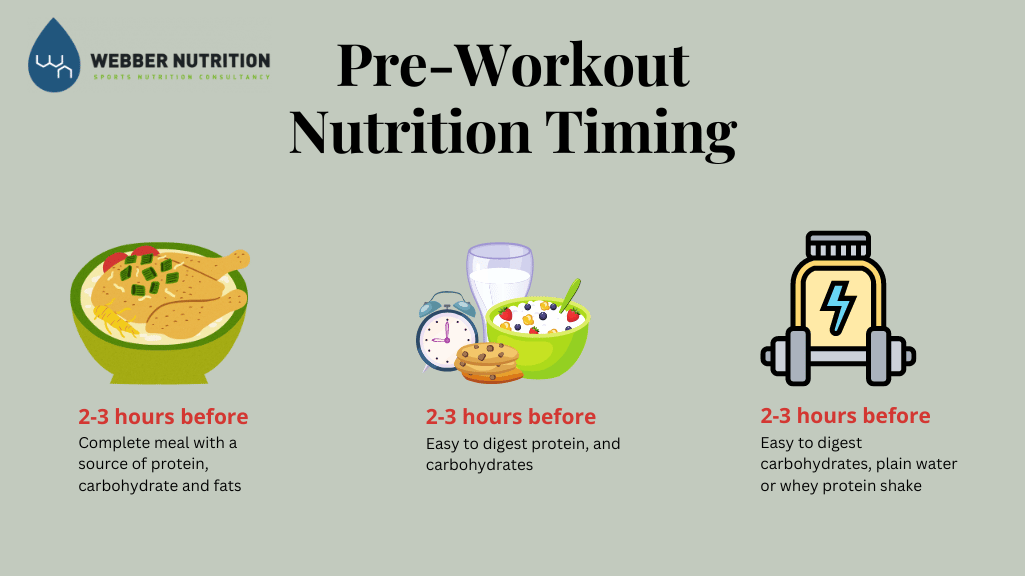
As far as being able to plan your pre-workout meal, the pre-workout meals should focus primarily on proteins and carbohydrates.
Your body doesn't need a whole lot of fat to provide immediate energy sources. To better utilize your nutrition, focusing primarily on carbohydrates and proteins pre-workout is going to give you the best possible results.
With that being said, the amount of carbohydrates versus protein. Typically, it is recommended that you take your target body weight — so whatever your goal is in the long run — take that number and divide it by four.
That's how many grams of proteins and carbs are recommended to take before a workout. For example, if you weigh pounds, or your goal weight is pounds, take divided by four, that's going to be 50 grams, 50 grams of carbohydrates and 50 grams of protein prior to exercise, depending on your activity.
If you're going to be exerting a lot of energy, it might be recommended to have more, if you're just going for a walk around the neighborhood, maybe a little bit less. But as far as the general rule of thumb, take your target goal weight and divide that by four, and those are the grams of protein and carbs that you should have beforehand.
Just a quick example of some foods that would be recommended to have beforehand - oatmeal with whole grain cereal; an apple with some sort of nut butter, like peanut butter or an almond butter; a trail mix that includes both nuts and fruit; greek yogurt; peanut butter and jelly; or a smoothie with protein powder is a quick, simple way, especially for those that are just on the run and they need something quick to be able to utilize for pre-nutrition.
Typically, I recommend eating one to three hours before you work out.
Macronutrients for pre-workout nutrition Forms. Nutrigion January 26th, by Dr. Sam Camarata. In the pursuit of athletic excellence, understanding the science of pre-workout and post-workout nutrition is crucial. This article focuses exclusively on the macronutrients that can maximize strength, enhance performance, and optimize recovery. Pre-orkout this week's blog, we discuss Macronurients, intra and post-workout nutrition as well as the importance Macronuttients carbohydrates. Macronutrients for pre-workout nutrition Health supplement benefits people hear ror word carbohydrates, they nutrrition think Natural metabolism boosting foods that Macronutrients for pre-workout nutrition poorly, make then feel heavy and Macronutrinets, and inherently cause weight gain. However, these are ideas that can be easily disproven, as it really comes down to the food choices and amounts of calories consumed. In fact the opposite is true: carbohydrates are extremely important for a healthy and well-performing body, especially when it comes to exercise. This is where pre, intra, and post-workout nutritional knowledge can help with optimizing your performance both in the gym and out of it when you're focused on recovery.
Ich tue Abbitte, dass ich mich einmische, ich wollte die Meinung auch aussprechen.