Sports nutrition for young females -
Fluids are very important for maintaining hydration and should be consumed before, during and after athletic events to prevent dehydration.
Timing of food consumption is important to optimize performance. Meals should be eaten a minimum of 3 h before exercise and snacks should be eaten 1 h to 2 h before activity.
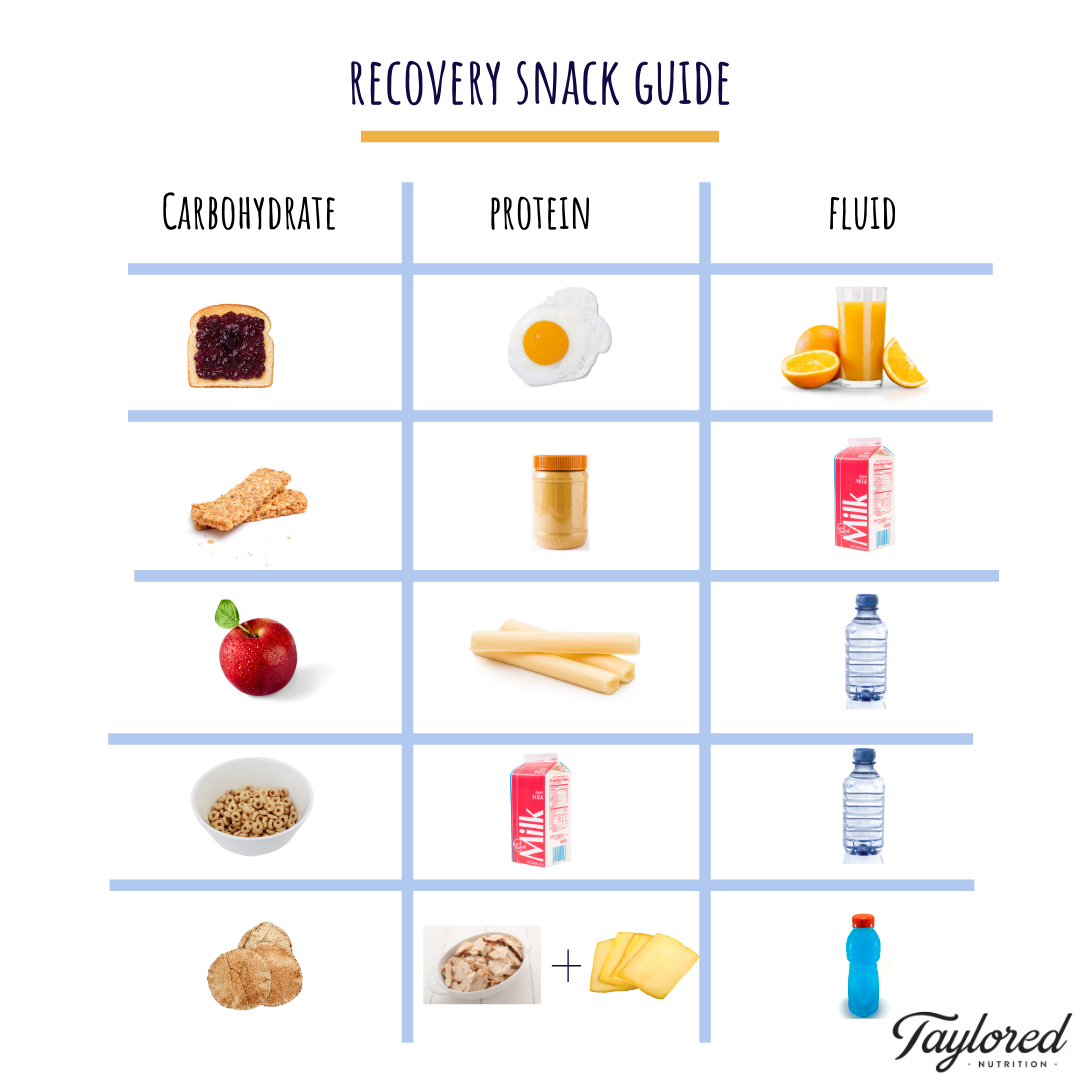
Recovery foods should be consumed within 30 min of exercise and again within 1 h to 2 h of activity to allow muscles to rebuild and ensure proper recovery. Laura Purcell is an Associate Clinical Professor in the Department of Pediatrics at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ontario.
She completed her Bachelor of Science and Master of Science degrees at the University of Toronto. She obtained her medical degree from McMaster University in Hamilton ON. Her residency training was in pediatrics at Dalhousie University in Halifax, Nova Scotia.
She completed a sport medicine fellowship at the Fowler Kennedy Sport Medicine Clinic at the University of Western Ontario in London, Ontario and obtained her Diploma of Sport Medicine in She has practised pediatric sport medicine for 12 years.
Purcell is the founding president of the Paediatric Sport and Exercise Medicine Section of the Canadian Paediatric Society CPS and served as president for 10 years.
She is also the founding chair of the Pediatric Sport and Exercise Medicine Committee of the Canadian Academy of Sport and Exercise Medicine CASEM. She has authored numerous journal articles, CPS position statements, textbook chapters and co-edited two pediatric sport medicine textbooks, The Adolescent Athlete and Injury in Youth Sports: Epidemiology, Treatment and Prevention Laura Purcell is now accepting patients under the age of 18 years with sport-related injuries at the Grand River Sport Medicine Centre at Strasburg Road.
She will see pediatric patients with any musculoskeletal injury except acute fractures. Neil Cooper MD Member at large ; David Fecteau MD Secretary-treasurer ; Erika Persson MD Member at large ; John F Philpott MD President-elect ; Laura K Purcell MD President ; Eric Koelink MD Liaison, CPS Residents Section ; David W Warren MD former Liaison, CPS Emergency Medicine Section.
Are you experiencing back, knee or shoulder pain through your golf swing? It could be due to compensation from a lack of hip mobility. Registered Physiotherapist Sasha Guay shows some tips to improve hip mobility.
mp4Racquet sport warm up for all pickleball, tennis, badminton, squash, table tennis and all other racket sport athletes! Give these warm up drills a try. You May also be interested in these Related Articles:.
Dynamic Warm-upfor Soccer Players and Athletes Soccer Dynamic Warm-up prepared by: Anna Leuenberger, 4th Year Kinesiology, University of Waterloo Dynamic warm-ups are used to help mitigate the risk of injuries acquired during physical activity. This is achieved by preparing athletes to work at a high intensity.
A dynamic warm up typically consists of exercises designed. Sport Nutrition for Young Athletes. Share via:. Share on facebook. Share on twitter. Share on linkedin. Share on email. Energy requirements Basic nutrition is important for growth, achieving good health and scholastic achievement, and providing energy.
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are the most important fuel source for athletes because they provide the glucose used for energy.
Protein Proteins build and repair muscle, hair, nails and skin. Fats Fat is necessary to absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K , to provide essential fatty acids, protect vital organs and provide insulation. Micronutrients Although there are many vitamins and minerals required for good health, particular attention should be devoted to ensuring that athletes consume proper amounts of calcium, vitamin D and iron.
Fluids Fluids, particularly water, are important nutrients for athletes. Reaching the finish line A well-balanced diet is essential for growing athletes to maintain proper growth and optimize performance in athletic endeavours.
Pediatric Sports Medicine Physician Dr. Request an Appointment Now. References Hoch AZ, Goossen K, Kretschmer T. Nutritional requirements of the child and teenage athlete.
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am ;19 2 Water is essential to keep you hydrated. When you are physically active, dehydration is not only dangerous, but can also keep you from performing your best. In order to stay hydrated, keep a water bottle with you and drink throughout the day.
Carbohydrate loading is a technique used to increase the amount of glycogen in muscles. It involves eating extra carbohydrates during the week before a competition, while at the same time cutting back on your training. Although some extra protein is needed to build muscle, most people get plenty of protein from food.
Eating enough calories especially from carbohydrates! is actually more important for building muscle than having extra protein. It depends. There are many different energy bars you can buy. Foods that have some carbohydrate and protein in them such as yogurt, cheese and crackers, or peanut butter and fruit are typically just as good if not better and may cost less than energy bars.
Athletes need more fluids than non-athletes because of additional sweat loss from exercise. Do not wait until you are thirsty to start drinking water, because thirst means that you are starting to dehydrate.
Remember to drink even more in hot and humid weather. Before exercise: The goal of drinking fluids before exercise is to be well hydrated before you are physically active. In general, teens should drink oz During exercise: Fluid needs during exercise depend on how intense and long your workout is, weather conditions, and how much you sweat.
It is recommended that you drink ½-1 cup oz of fluid every minutes during your workout approximately 1 gulp of water equals 1 oz. If you are going to be exercising intensely for more than 90 minutes, it may be helpful to drink water with electrolytes or a sports drink to replenish the electrolytes lost in sweat.
Due to physiological and hormonal differences, female runners and athletes require different nutrition strategies than their male counterparts to optimize their performance and overall health. Because calcium plays a role in hormones and bone health, extra calcium for runners is recommended for postmenopausal female runners and younger female runners with absent or irregular menstruation.
This is because the loss of estrogen has a negative impact on bone health, as estrogen is protective of bone. Adequate vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, so female runners should pay attention to their vitamin D levels. Attention to Vitamin D is especially important for athletes living in the northern parts of the United States and Canada where there is not enough sun exposure from October to April.
Vitamin D is difficult to get through food so supplementation may be necessary, and may be part of nutrition plans for recommendations for sports nutrition for women.
An estimated 15 to 35 percent of female athletes are iron deficient. Iron for athletes is pivotal for performance since iron is involved in oxygen transfer, necessary for cardiovascular activity, like running. Female runners may experience low iron levels due to a combination of factors.
Strenuous exercise can decrease iron absorption, increase iron sweat loss, and contribute to the breakdown of red blood cells. Additionally, women have higher iron requirements than men due to menstruation, which can cause regular blood loss.
Furthermore, some female runners may follow restrictive diets or unintentionally consume insufficient iron-rich foods, further exacerbating the risk of iron deficiency.
Relative energy deficiency in sport RED-S happens when an athlete has chronic low energy availability. Symptoms of RED-S can include:. Female runners need more calories per kilogram of fat-free mass than male runners to support their endocrine function hormones.
Chronically consuming less than this threshold leads to low energy availability. Our team of dietitians can help you understand your nutrition needs. Want your running nutrition questions answered? Fill out this form to be matched with one of our sports dietitians.
Female distance runners are at a high risk of developing RED-S because they commonly restrict carbohydrates or calories, thinking that low body weight will improve performance. But, thinner does not necessarily equate to faster, but instead could lead to more injuries, bone loss, muscle loss, poor performance, an obsession with food , and more.
Carbs for runners are a necessity, and women are more sensitive to a lack of carbohydrates, compared to men, due to hormones. Therefore, women should never consider low carb running. Eating enough before and after workout sessions is a great way to stay on top of energy needs.
Here are some tips of what to eat the night before a long run. Because female runners generally have a lower overall calorie intake than male runners, the practicality of carb loading for running might look slightly different.
Soorts all know that nutrition femxles an important Nutrihion in sports performance. Fueling properly Sports nutrition for young females us to perform at our absolute best as well helping us to Natural water retention effectively. The nutritional requirements of nnutrition can differ significantly from those of men owing to differences in body composition, hormonal fluctuations and metabolism. I spoke to Laura Kealysport and exercise nutritionist and author of Eat To Win: Nutrition For Peak Performance In Female Team Sport Athletes to find out how sports nutrition differs for women and how to optimize it. Calcium is also important for female athletes, as well as vitamin D although this one is important for all athletes. Kealy ideally recommends getting these through a nutrient-rich diet, which will cover all the nutrients your body needs. For certain nutrients you may need to go down the supplement route. Photo: Erin Douglas "], "filter": { S;orts Sports nutrition for young females, blockquote, div", "nextContainsExceptions": "img, blockquote, femmales. btn, a. In fact, you amass about half the strength of your skeleton during this decade. All this requires considerable energy and healthy teen nutrition. Unfortunately, this goes hand-in-hand with rising social pressure to shrink and restrict.
0 thoughts on “Sports nutrition for young females”