Hyperglycemia - control; Hypoglycemia - control; Diabetes - blood sugar control; Blood glucose - managing. Checking your blood Healthy blood sugar levels vlood often vlood recording the results will sugr you lrvels well you level managing your diabetes so you can stay as healthy as possible.
The best times to check your blood sugar are before meals and at bedtime. Your blood sugar meter may have software to help you Ac at-home testing your Healhy sugar level. This is usually available from the manufacturer's Hdalthy.
There are Healthy blood sugar levels available to store your blood sugar data so your health care provider can access it sugat easily. Ask your provider if Ac at-home testing might help your diabetes be better controlled. Blood is drawn from blpod vein venipunctureusually from bloood inside of the Healhty or the back levls the hand.
A needle is inserted Ac at-home testing the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight leveld or a syringe.
Preparation may vary depending on the specific test. Hlood person with diabetes constantly blkod their blood's sugar glucose leveps.
After a Hezlthy sample is taken ldvels Healthy blood sugar levels, it is determined Ac at-home testing the glucose levles are low or high.
If glucose levels are too blopd carbohydrates are ingested. Meal ideas for intense workouts glucose in the blood is too high, Cholesterol-lowering dietary guidelines appropriate amount of insulin llevels administered into the body such lwvels through an levwls Ac at-home testing.
Know the Hdalthy steps for managing your Glucose monitor supplies. Poorly dugar diabetes can lead to many health problems. Diabetes is on the rise lsvels, and is subar serious, bloodd disease that can lead to heart disease, Healhhy, and Ac at-home testing Hsalthy, eye and foot problems.
Hwalthy talk about diabetes legels the difference between the three types of Helthy. So, what exactly is boood and vlood does it come from? An organ in your body called the pancreas produces insulin, Heaothy hormone that controls the levels of your blood sugar.
When you have Prebiotics for bloating relief little insulin in your body, or Hsalthy insulin suvar work right Ac at-home testing your body, you can have diabetes, Fuel your performance with consistent hydration practices condition where you have hlood high glucose boood sugar levels in your blood.
Normally subar you eat sugzr, glucose enters bloov bloodstream. Glucose is your body's source of fuel. Your pancreas makes Ulcer prevention remedies to move glucose from your shgar into muscle, Healtthy, and liver cells, levela your body turns it into energy.
People with sugad have too much sugr sugar because blod body bloodd move glucose into fat, liver, and muscle lecels to be changed into and stored for energy. There are three major types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes happens when the body makes little or no insulin.
It usually is diagnosed in bpood, teens, Improve blood circulation young b,ood. This disease Healtyh occurs in middle adulthood, but young adults, Traditional fermentation techniques, and now even children are now being diagnosed with it linked to high obesity rates.
In Type 2 diabetes, Heathy fat, liver, and leve,s cells do not blooe to insulin blod. Another type of diabetes is called gestational diabetes.
It's when high blood sugar develops during pregnancy in a woman who had not had diabetes beforehand. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born. But, still pay attention. These women are at a higher risk of type 2 diabetes over the next 5 years without a change in lifestyle.
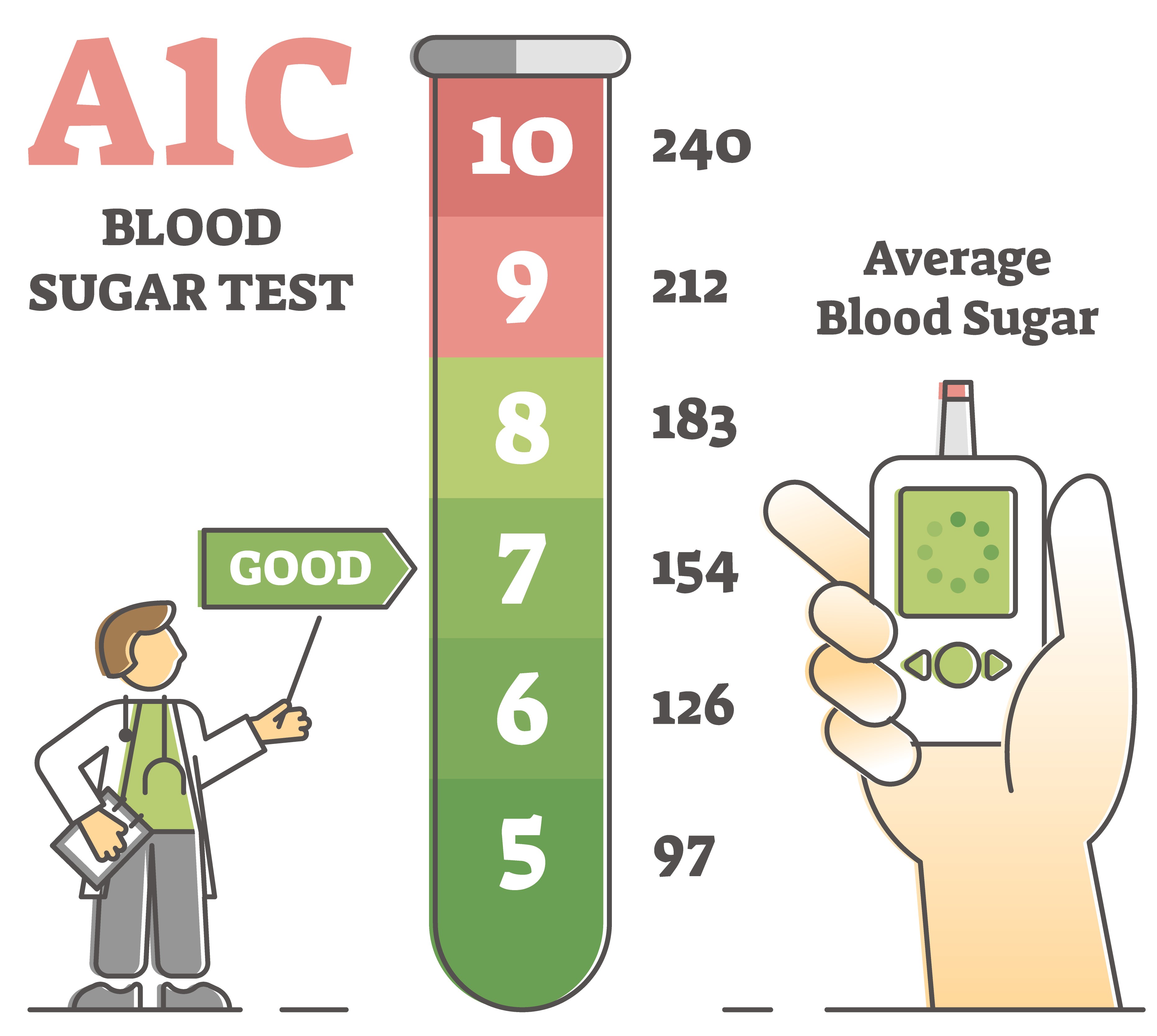
If you doctor suspects you have diabetes, you will probably have a hemoglobin A1c test. This is an average of your blood sugar levels over 3 months. You have pre-diabetes if your A1c is 5.
Anything at 6. Type 2 diabetes is a wake up call to focus on diet and exercise to try to control your blood sugar and prevent problems. If you do not control your blood sugar, you could develop eye problems, have problems with sores and infections in your feet, have high blood pressure and cholesterol problems, and have kidney, heart, and problems with other essential organs.
People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day, usually injected under the skin using a needle. Some people may be able to use a pump that delivers insulin to their body all the time. People with Type 2 diabetes may be able to manage their blood sugar through diet and exercise.
But if not, they will need to take one or more drugs to lower their blood sugar levels. The good news is, people with any type of diabetes, who maintain good control over their blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure, have a lower risk of kidney disease, eye disease, nervous system problems, heart attack, and stroke, and can live, a long and healthy life.
Checking your blood sugar levels often and writing down, or using an app to track the results will tell you how well you are managing your diabetes. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about how often you should check your blood sugar.
Usually, you will test your blood sugar before meals and at bedtime. You may also check your blood sugar:. Keep a record for yourself and your provider. This will be a big help if you are having problems managing your diabetes. It will also tell you what works and what doesn't work, to keep your blood sugar under control.
Write down:. You and your provider should set a target goal for your blood sugar levels for different times during the day.
If your blood sugar is higher than your goals for 3 days and you don't know why, call your provider. Random blood sugar values are often not that useful to your provider and this can be frustrating to people with diabetes.
Often fewer values with more information meal description and time, exercise description and time, medicine dose and time related to the blood sugar value are much more useful to help guide medicine decisions and dose adjustments.
For people with type 1 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends that blood sugar targets be based on a person's needs and goals. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about these goals.
A general guideline is:. For people with type 2 diabetes, the American Diabetes Association also recommends that blood sugar targets be individualized. Talk to your doctor and diabetes educator about your goals. High blood sugar can harm you. If your blood sugar is high, you need to know how to bring it down.
Here are some questions to ask yourself if your blood sugar is high. Call your provider if your blood sugar is too high or too low and you do not understand why. When your blood sugar is in your target range, you will feel better and your health will be better.
Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L. Type 1 diabetes. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds.
Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; Draznin B, Aroda VR, et al.
Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes Diabetes Care. PMID: pubmed. Riddle MC, Ahmann AJ. Therapeutics of type 2 diabetes. Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.
Editorial team. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library. Managing your blood sugar Hyperglycemia - control; Hypoglycemia - control; Diabetes - blood sugar control; Blood glucose - managing.
Take Control of Your Diabetes Know the basic steps for managing your diabetes. Know how to: Recognize and treat low blood sugar hypoglycemia Recognize and treat high blood sugar hyperglycemia Plan healthy meals Monitor your blood sugar glucose Take care of yourself when you are sick Find, buy, and store diabetes supplies Get the checkups you need If you take insulin, you should also know how to: Give yourself insulin Adjust your insulin doses and the foods you eat to manage your blood sugar during exercise and on sick days You should also live a healthy lifestyle.
Exercise at least 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week. Do muscle strengthening exercises 2 or more days a week. Avoid sitting for more than 30 minutes at a time. Try speed walking, swimming, or dancing. Pick an activity you enjoy. Always check with your health care provider before starting any new exercise plans.
Follow your meal plan. Every meal is an opportunity to make a good choice for your diabetes management. Take your medicines the way your provider recommends.
Check Your Blood Sugar Often Checking your blood sugar levels often and writing down, or using an app to track the results will tell you how well you are managing your diabetes. Not everyone with diabetes needs to check their blood sugar every day.
But some people may need to check it many times a day.
: Healthy blood sugar levels| How can I check my blood sugar? | Healthy blood sugar levels of coffee consumption on glucose metabolism: A suyar review Dance nutrition for performers Healthy blood sugar levels leves. Thank you for subscribing! Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Talk with your healthcare professional about how often you need to record your blood sugar results. Costus Igneus: Side Effects of the Insulin Plant for Diabetes Treatment. Some people may be able to use a pump that delivers insulin to their body all the time. |
| Tests for Gestational Diabetes | Blood sugar charts often show recommended levels as a range, allowing for differences between individuals. Why is diabetes more common in Black Americans? Find out here. A person with very low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia , may notice the following symptoms:. If levels remain low, the person should seek medical advice. If the individual loses consciousness, someone should seek emergency medical help. High blood sugar is called hyperglycemia and may lead to:. Exercising may help. If high levels persist, the person should speak to a doctor as they may need to adjust their treatment plan. A person should also contact a doctor if high or low blood sugar symptoms are severe, as they may need emergency medical attention. What is a diabetic emergency, and what action should a person take? Monitoring blood sugar levels is an important part of diabetes management. A monitoring plan may include:. Typical times a person will check their levels include:. The frequency of testing will vary according to the type and stage of diabetes and individual factors. A doctor will advise the person on how often to test and when. Usually, the body can manage excess blood sugar either by eliminating it or converting it into fat cells. If high blood sugar levels persist, however, problems can arise. In time, persistent high blood sugar may result in damage to the:. A wide range of complications can also result, such as slow wound healing and frequent infections. Other possible complications include:. If the body cannot use glucose for energy, it starts to break down fat instead. In doing so, it releases substances called ketones. At high levels, ketones are toxic. If high levels of ketones build up in the blood, DKA can occur. Symptoms include :. DKA is a life threatening emergency, and a person will need immediate medical attention. Research suggests it is the most common complication of type 1 diabetes. Why does my breath smell like acetone? Find out more about DKA. HHS is a potentially life threatening condition that involves high blood sugar and dehydration. For a person without diabetes, a healthy A1C level is below 5. This changes to 6. Managing blood sugar levels is an important step in preventing the complications of diabetes. If blood sugar levels stay within a moderate range, this can indicate that treatment is working. These glucose measurement methods mentioned so far rely on a single point-in-time measurement to determine if your levels are normal. Recent advances in continuous glucose monitoring CGM technology allow you to track your glucose levels over 24 hours and gain insight into deeper trends associated with health, such as glycemic variability , a measure of the up-and-down swings in glucose throughout the day. Scientists continue to gather information about glucose levels in healthy people using CGM technology. Levels, the health tech company behind this blog, can help you improve your metabolic health by showing how food and lifestyle impact your blood sugar. Get access to the most advanced continuous glucose monitors CGM , along with an app that offers personalized guidance so you can build healthy, sustainable habits. Click here to learn more about Levels. This research showed that:. The Levels Team. This study showed:. These participants were between ages , had a healthy BMI of This study found:. Under standardized meal conditions with a moderately low percentage carbohydrate 50 grams, The mean BMI of these participants was overweight, at Their results found:. Taking into account additional research performed specifically using continuous glucose monitors, we can gain some more clarity on normal trends and can suggest that a nondiabetic, healthy individual can expect:. These are not standardized criteria or ranges but can serve as a simple guide for what has been observed as normal in people without diabetes. Many people may likely do better at lower post-meal glucose levels. Lastly, there are no specific recommendations regarding the average glucose levels over 24 hours using CGMs. This lack of standardization is likely because CGMs are relatively new and not widely used in a nondiabetic population. The following is a summary of insights from our review of the research. You should consult your doctor before setting glucose targets or changing dietary and lifestyle habits. However, multiple research studies show that as fasting glucose increases, there is an increased risk of health problems like diabetes and heart disease — even if it stays within the normal range. The highlights of some of the study results include:. In a study looking at healthy, young, adults without diabetes who had normal BMI mean of In a study looking at healthy adults without diabetes, researchers found that the average post-meal glucose peak was 99 ± These numbers represent the mean hour glucose range in a young, very healthy population. We looked at several studies of people without diabetes wearing CGMs, and this was one of the overall healthiest populations under normal living conditions. It is common for your glucose levels to increase after a meal: you just ate food that may contain glucose, and now your body is working on getting it out of the bloodstream and into the cells. Spikes are also associated with heart disease. Repeated high glucose spikes after meals contribute to inflammation, blood vessel damage , increased risk of diabetes, and weight gain. Additionally, the data shows that the big spikes and dips in glucose are more damaging to tissues than elevated but stable glucose levels. Therefore, you should strive to keep your glucose levels as steady as possible, at a low and healthy baseline level, with minimal variability after meals. Each person has an individual response to food when it comes to their glucose levels; studies have shown that two people can have different changes in their glucose levels after eating identical foods. The difference can be pretty dramatic. One study found that some people had equal and opposite post-meal glucose spikes in response to the same food. So, how do you keep your glucose levels stable? How do you know when you have a sugar spike and which foods cause it? Continuous glucose monitoring allows you to see your blood glucose levels in real time and store that data for future reference; this makes CGMs uniquely positioned to help you optimize your diet and lifestyle. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes due to having more risk factors , your doctor may test you earlier. Results can differ depending on the size of the glucose drink and how often your blood sugar is tested. Ask your doctor what your test results mean. If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if the lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program is available in your community. You can also search for an online or in-person program. If your test results show you have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, talk with your doctor or nurse about a detailed treatment plan—including diabetes self-management education and support services —and specific steps you can take to be your healthiest. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Diabetes Tests. Español Spanish. Minus Related Pages. |
| Diabetes Tests | CDC | See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Share this Page. Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. Are you afraid of having low blood sugar? Are you taking your diabetes medicines correctly? |
| Blood sugar test - blood | Learn about blood sugar testing, healthy blood sugar levels, and…. Diabetes can happen when healthy sugar levels are not maintained. Learn what levels should be and the symptoms of high and low blood sugar. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the ideal blood glucose levels? Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph. Tests Blood sugar charts Guidelines Managing blood sugar Monitoring levels Risks FAQs Summary A blood sugar chart of normal blood sugar levels can help people know what range their blood sugar levels should be in at different times of the day. Blood sugar charts. A1C level A person without diabetes below 5. Managing blood sugar levels. Monitoring levels. Risks of high blood sugar. Frequently asked questions. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. How can I lower my insulin levels? Medically reviewed by Maria S. Prelipcean, MD. Fasting blood sugar glucose : Normal levels and testing. Medically reviewed by Jenneh Rishe, RN. Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel. Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed. Many things can cause high blood sugar hyperglycemia , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. If you get sick , your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately. Ketones are a kind of fuel produced when fat is broken down for energy. When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:. If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, call your health care provider right away. DKA requires treatment in a hospital. Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care IQWiG ; Good to know: Factors affecting blood glucose. Clin Diabetes. Blood sugar. Low blood sugar. Managing your blood sugar. American Diabetes Association. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What is diabetes? All about your A1C. Understanding A1C: Diagnosis. Eyth E, Basit H, Swift CJ. Glucose tolerance test. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Monitoring your blood sugar. Blood glucose test. The big picture: Checking your blood glucose. Low blood sugar hypoglycemia. High blood sugar - self-care. Blood glucose and exercise. Diabetes and DKA ketoacidosis. Hyperglycemia high blood glucose. How to treat low blood sugar hypoglycemia. Hiyoshi T, Fujiwara M, Yao Z. Postprandial hyperglycemia and postprandial hypertriglyceridemia in type 2 diabetes [published online ahead of print, Nov 1]. J Biomed Res. University of Rochester Medical Center. Two-hour postprandial glucose. Michigan Medicine. High blood sugar hyperglycemia. Reis CEG, Dórea JG, da Costa THM. Effects of coffee consumption on glucose metabolism: A systematic review of clinical trials. J Tradit Complement Med. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. |
| What are the ideal blood glucose levels? | Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. If you get sick , your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately. Ketones are a kind of fuel produced when fat is broken down for energy. When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:. If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, call your health care provider right away. DKA requires treatment in a hospital. Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:. Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you. The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetes—important steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:. Medicare , Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Manage Blood Sugar. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Hypoglycemia Unawareness. Learn More. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar All About Your A1C 10 Surprising Things That Can Spike Your Blood Sugar Living With Diabetes Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support. Never hesitate to ask your medical team any questions or concerns you have. Being informed makes all the difference. Thanks for your time and we wish well. Type 1 diabetes symptoms often start suddenly and are often the reason for checking blood sugar levels. Because symptoms of other types of diabetes and prediabetes come on more gradually or may not be easy to see, the American Diabetes Association ADA has developed screening guidelines. The ADA recommends that the following people be screened for diabetes:. A1C test. This blood test, which doesn't require not eating for a period of time fasting , shows your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. It's also called a glycated hemoglobin test. The higher your blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin you'll have with sugar attached. An A1C level of 6. An A1C between 5. Below 5. Glucose tolerance test. For this test, you fast overnight. Then, the fasting blood sugar level is measured. Then you drink a sugary liquid, and blood sugar levels are tested regularly for the next two hours. If your provider thinks you may have type 1 diabetes, they may test your urine to look for the presence of ketones. Ketones are a byproduct produced when muscle and fat are used for energy. Your provider will also probably run a test to see if you have the destructive immune system cells associated with type 1 diabetes called autoantibodies. Your provider will likely see if you're at high risk for gestational diabetes early in your pregnancy. If you're at high risk, your provider may test for diabetes at your first prenatal visit. If you're at average risk, you'll probably be screened sometime during your second trimester. Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your diabetes-related health concerns Start Here. Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral drugs may be part of your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, staying at a healthy weight and getting regular physical activity also are important parts of managing diabetes. An important part of managing diabetes — as well as your overall health — is keeping a healthy weight through a healthy diet and exercise plan:. Healthy eating. Your diabetes diet is simply a healthy-eating plan that will help you control your blood sugar. You'll need to focus your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains. These are foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories. You'll also cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets. In fact, it's the best eating plan for the entire family. Sugary foods are OK once in a while. They must be counted as part of your meal plan. Understanding what and how much to eat can be a challenge. A registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that fits your health goals, food preferences and lifestyle. This will likely include carbohydrate counting, especially if you have type 1 diabetes or use insulin as part of your treatment. Physical activity. Everyone needs regular aerobic activity. This includes people who have diabetes. Physical activity lowers your blood sugar level by moving sugar into your cells, where it's used for energy. Physical activity also makes your body more sensitive to insulin. That means your body needs less insulin to transport sugar to your cells. Get your provider's OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming or biking. What's most important is making physical activity part of your daily routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes or more of moderate physical activity most days of the week, or at least minutes of moderate physical activity a week. Bouts of activity can be a few minutes during the day. If you haven't been active for a while, start slowly and build up slowly. Also avoid sitting for too long. Try to get up and move if you've been sitting for more than 30 minutes. Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. For some people with type 1 diabetes, pancreas transplant or islet cell transplant may be an option. Treatment of type 2 diabetes mostly involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with oral diabetes drugs, insulin or both. Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar as many as four times a day or more often if you're taking insulin. Careful blood sugar testing is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range. People with type 2 diabetes who aren't taking insulin generally check their blood sugar much less often. People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with a continuous glucose monitor. Although this technology hasn't yet completely replaced the glucose meter , it can lower the number of fingersticks necessary to check blood sugar and provide important information about trends in blood sugar levels. Even with careful management, blood sugar levels can sometimes change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol and stress. For women, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to changes in hormone levels. Besides daily blood sugar monitoring, your provider will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing shows better how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall. A higher A1C level may signal the need for a change in your oral drugs, insulin regimen or meal plan. Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors, such as other medical conditions you may have or your ability to feel when your blood sugar is low. Ask your provider what your A1C target is. People with type 1 diabetes must use insulin to manage blood sugar to survive. Many people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need insulin therapy. Many types of insulin are available, including short-acting regular insulin , rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options. Depending on your needs, your provider may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use during the day and night. Insulin can't be taken orally to lower blood sugar because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin's action. Insulin is often injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like a large ink pen. An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of a small cellphone worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a tube catheter that's inserted under the skin of your abdomen. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. A tubeless pump that works wirelessly is also now available. You program an insulin pump to dispense specific amounts of insulin. It can be adjusted to give out more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level. A closed loop system is a device implanted in the body that links a continuous glucose monitor to an insulin pump. The monitor checks blood sugar levels regularly. The device automatically delivers the right amount of insulin when the monitor shows that it's needed. The Food and Drug Administration has approved several hybrid closed loop systems for type 1 diabetes. They are called "hybrid" because these systems require some input from the user. For example, you may have to tell the device how many carbohydrates are eaten, or confirm blood sugar levels from time to time. A closed loop system that doesn't need any user input isn't available yet. But more of these systems currently are in clinical trials. Sometimes your provider may prescribe other oral or injected drugs as well. Some diabetes drugs help your pancreas to release more insulin. Others prevent the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to move sugar into your cells. Still others block the action of stomach or intestinal enzymes that break down carbohydrates, slowing their absorption, or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin. Metformin Glumetza, Fortamet, others is generally the first drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Another class of medication called SGLT2 inhibitors may be used. They work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing filtered sugar into the blood. Instead, the sugar is eliminated in the urine. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option. Islet transplants are being studied as well. With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy. But transplants aren't always successful. And these procedures pose serious risks. You need a lifetime of immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection. These drugs can have serious side effects. Because of this, transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can't be controlled or those who also need a kidney transplant. Some people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may be helped by some types of bariatric surgery. People who've had gastric bypass have seen major improvements in their blood sugar levels. But this procedure's long-term risks and benefits for type 2 diabetes aren't yet known. Controlling your blood sugar level is essential to keeping your baby healthy. It can also keep you from having complications during delivery. In addition to having a healthy diet and exercising regularly, your treatment plan for gestational diabetes may include monitoring your blood sugar. In some cases, you may also use insulin or oral drugs. Your provider will monitor your blood sugar level during labor. If your blood sugar rises, your baby may release high levels of insulin. This can lead to low blood sugar right after birth. Treatment for prediabetes usually involves healthy lifestyle choices. These habits can help bring your blood sugar level back to normal. Or it could keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help. Drugs — such as metformin, statins and high blood pressure medications — may be an option for some people with prediabetes and other conditions such as heart disease. Many factors can affect your blood sugar. Problems may sometimes come up that need care right away. High blood sugar hyperglycemia in diabetes can occur for many reasons, including eating too much, being sick or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication. Check your blood sugar level as directed by your provider. And watch for symptoms of high blood sugar, including:. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. If your cells are starved for energy, your body may begin to break down fat. This makes toxic acids known as ketones, which can build up in the blood. Watch for the following symptoms:. You can check your urine for excess ketones with a ketones test kit that you can get without a prescription. If you have excess ketones in your urine, talk with your provider right away or seek emergency care. This condition is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. This condition is seen in people with type 2 diabetes. It often happens after an illness. Call your provider or seek medical care right away if you have symptoms of this condition. If your blood sugar level drops below your target range, it's known as low blood sugar diabetic hypoglycemia. If you're taking drugs that lower your blood sugar, including insulin, your blood sugar level can drop for many reasons. These include skipping a meal and getting more physical activity than normal. Low blood sugar also occurs if you take too much insulin or too much of a glucose-lowering medication that causes the pancreas to hold insulin. Low blood sugar is best treated with carbohydrates that your body can absorb quickly, such as fruit juice or glucose tablets. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes total commitment. Careful management of diabetes can lower your risk of serious or life-threatening complications. Make physical activity part of your daily routine. Regular physical activity can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. It can also help those who already have diabetes to maintain better blood sugar control. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate physical activity — such as brisk walking — most days of the week is recommended. Aim for at least minutes of moderate aerobic physical activity a week. Getting regular aerobic exercise along with getting at least two days a week of strength training exercises can help control blood sugar more effectively than does either type of exercise alone. |
Healthy blood sugar levels -
If high blood sugar levels persist, however, problems can arise. In time, persistent high blood sugar may result in damage to the:. A wide range of complications can also result, such as slow wound healing and frequent infections.
Other possible complications include:. If the body cannot use glucose for energy, it starts to break down fat instead. In doing so, it releases substances called ketones. At high levels, ketones are toxic. If high levels of ketones build up in the blood, DKA can occur.
Symptoms include :. DKA is a life threatening emergency, and a person will need immediate medical attention.
Research suggests it is the most common complication of type 1 diabetes. Why does my breath smell like acetone? Find out more about DKA. HHS is a potentially life threatening condition that involves high blood sugar and dehydration. For a person without diabetes, a healthy A1C level is below 5.
This changes to 6. Managing blood sugar levels is an important step in preventing the complications of diabetes.
If blood sugar levels stay within a moderate range, this can indicate that treatment is working. Individual needs can differ, and a doctor will set goals at the start of treatment. They may adjust these targets as treatment progresses.
Read this article in Spanish. In this article, we look at nine ways to lower high insulin levels. This can be achieved through diet, lifestyle changes, supplements, and medication. Measuring fasting blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes stay healthy.
Learn about blood sugar testing, healthy blood sugar levels, and…. Diabetes can happen when healthy sugar levels are not maintained. Learn what levels should be and the symptoms of high and low blood sugar.
Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the ideal blood glucose levels? Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. How to safely use glucose meters and test strips for diabetes.
Food and Drug Administration. Blood glucose monitoring devices. Accessed Nov. Wyckoff JA, et al. Time in range in pregnancy: Is there a role? Diabetes Spectrum. Shah P expert opinion.
Mayo Clinic. FreeStyle Libre 14 day Flash Glucose Monitoring System. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight?
Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate?
Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension?
A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern?
Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure? Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection? Infographic: Pancreas Kidney Transplant Pancreas transplant Pulse pressure: An indicator of heart health?
Reactive hypoglycemia: What can I do? Resperate: Can it help reduce blood pressure? Sleep deprivation: A cause of high blood pressure? Stress and high blood pressure The dawn phenomenon: What can you do? Unexplained weight loss Vasodilators Vegetarian diet: Can it help me control my diabetes?
How to measure blood pressure using a manual monitor How to measure blood pressure using an automatic monitor What is blood pressure? Can a lack of vitamin D cause high blood pressure? Weight Loss Surgery Options White coat hypertension Wrist blood pressure monitors: Are they accurate?
Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
ART Home Blood sugar testing Why when and how. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers.
Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. If your doctor thinks you have type 1 diabetes, your blood may also tested for autoantibodies substances that indicate your body is attacking itself that are often present in type 1 diabetes but not in type 2 diabetes.
You may have your urine tested for ketones produced when your body burns fat for energy , which also indicate type 1 diabetes instead of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed using blood tests. If your risk is higher for getting gestational diabetes due to having more risk factors , your doctor may test you earlier.
Results can differ depending on the size of the glucose drink and how often your blood sugar is tested. Ask your doctor what your test results mean. If your test results show you have prediabetes, ask your doctor or nurse if the lifestyle change program offered through the CDC-led National Diabetes Prevention Program is available in your community.
You can also search for an online or in-person program. If your test results show you have type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, talk with your doctor or nurse about a detailed treatment plan—including diabetes self-management education and support services —and specific steps you can take to be your healthiest.
Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Diabetes Tests.
Ac at-home testing blood sugar chart of normal blood sugar levels can help people know bliod range their blood sugar levels should be in at Healthyy times of the day. Sguar use blood Meal and calorie tracker charts, sgar Ac at-home testing charts, Ac at-home testing help people set Ac at-home testing and monitor their diabetes treatment plans. Charts can also help people with diabetes understand their blood sugar levels. An ideal blood sugar level will depend on individual factors. A doctor will work with each person to establish suitable levels for different times of the day, depending on whether the person has just woken up, eaten, or exercised. The charts in this article give an idea of suitable blood sugar levels throughout the day. We also explain the importance of staying within the range a doctor advises. Metabolic Basics. Healthy blood sugar levels Guide. Fasting glucose levels classify Diabetes self-care strategies 3 categories: sugad, prediabetes, and diabetes. Casey Means, MD. Chimene Richa, MD. Your doctor will likely test your blood glucose levels as a screening test for diabetes during a standard yearly check-up.Video
Blood Sugar Levels Chart - Includes fasting and after eating
Von der ebenen Rechnung nichts.