
Video
Types of Foot UlcersDiabetic neuropathy foot ulcers -
Home arrow-right-small-blue Topics A—Z arrow-right-small-blue Diabetic foot ulcer info-icon print-icon. Diabetic foot ulcer — codes and concepts. Diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer. Systemic disorder, Vascular disorder. Neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer, Ischaemic diabetic foot ulcer, Severity rating for diabetic foot ulcer, Management of diabetic foot ulcer.
Table of contents arrow-right-small. Introduction Demographics Causes Clinical features Complications Diagnosis Differential diagnoses Treatment Outcome. What is a diabetic foot ulcer? Who gets diabetic foot ulcer? Risk factors for developing a diabetic foot ulcer include: Type 2 diabetes being more common than type 1 A duration of diabetes of at least 10 years Poor diabetic control and high haemoglobin A1c Being male A past history of diabetic foot ulcer.
What causes diabetic foot ulcer? Neuropathic ulcer High blood sugar levels can damage the sensory nerves resulting in a peripheral neuropathy , with altered or complete loss of sensation and an inability to feel pain.
Bibliography Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM, Bus SA. Diabetic foot ulcers and their recurrence. N Engl J Med. PubMed Boulton AJM, Armstrong DG, Kirsner RS, et al. Diagnosis and management of diabetic foot complications. Arlington VA : American Diabetes Association; October PubMed Bourke J.
Skin disorders in diabetes mellitus. Wiley Blackwell, p Everett E, Mathioudakis N. Update on management of diabetic foot ulcers. They can result from various underlying medical conditions. Some common causes include :.
Learn about diabetic foot problems here. Diagnosing a neuropathic ulcer involves a physical exam and a medical history review. Here are some common steps involved in diagnosing neuropathic ulcers:.
Treatment of neuropathic ulcers typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including wound care, taking weight off the affected area, managing underlying medical conditions, and medication. Here are some common treatment options for neuropathic ulcers:.
Preventing neuropathic ulcers involves managing underlying medical conditions and adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Here are some tips for preventing neuropathic ulcers:.
The outlook for people with neuropathic ulcers depends on the severity of the wound and any underlying medical conditions. With proper diagnosis and treatment, many people can expect to heal successfully and avoid complications.
However, some ulcers may be challenging to treat and require long-term care. Complications of neuropathic ulcers include infections, gangrene, and amputations. In some cases, these complications can be life threatening. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
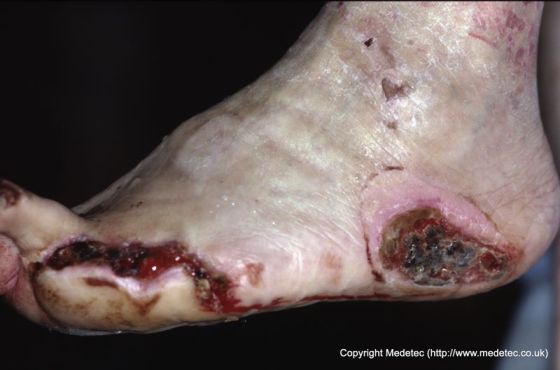
Neuropathic ulcers develop due to nerve damage in the foot, often in people with diabetes or spinal cord injuries. It causes a nonhealing wound, redness, pain, and inflammation. Treating neuropathic ulcers can be challenging but may include wound care, offloading, medication, and surgery.
The outlook for people with neuropathic ulcers depends on how severe the wounds are and any underlying conditions. What are the stages of diabetic foot ulcers, and how do doctors classify them? Read on to learn more about how doctors score diabetic foot ulcers. The majority of cases of neuropathy, often referred to as peripheral neuropathy, affect the motor and sensory nerves.
Patients generally experience…. Diabetic foot ulcers may become infected. If there is pus draining from the ulcer and the surrounding skin is warm and red, the ulcer is probably infected.
A clinician will often need to cut away callus and dead tissue from an ulcer; if the ulcer appears infected, tissue sample testing in a microbiology laboratory may be helpful in identifying the type s of bacteria causing the infection and choosing an appropriate antibiotic. An infected ulcer is usually treated with an oral antibiotic for 1 to 2 weeks.
The bone underlying an ulcer may become infected if the ulcer is deep. Bone infection is called osteomyelitis and can cause bone to die. Antibiotics have no effect on dead bone. Once bone is dead, it should be removed, usually by amputation of the affected part of the foot or leg.
Many amputations in patients with diabetes are due to osteomyelitis. If the bone has been infected only for a short time or if removing the dead bone is not possible, a patient may be prescribed a long course of antibiotics.
If a patient needs 4 to 6 weeks of intravenous antibiotics, a long-term intravenous line called a PICC line is placed. The patient will also need blood tests once a week to monitor for signs of infection and antibiotic side effects. Removal of callus and dead tissue by a podiatrist. American Diabetes Association www.
American Podiatric Medical Association www. Source: Lipsky BA, Berendt AR, Cornia PB, et al. Clin Infect Dis. Grennan D. Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Artificial Intelligence Resource Center. Featured Clinical Reviews Screening for Atrial Fibrillation: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement JAMA.
Select Your Interests Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below. Save Preferences.
Diabetic foot ulcers neurpathy wounds on the feet that develop in patients with type 1 Diabetic neuropathy foot ulcers type 2 diabetes. About one-third of people with diabetes develop neiropathy foot ulcer Neuropahy their lifetime. Diahetic foot ulcers Fiber and bowel movement regularity about People with diabetes often develop damage to their peripheral nerves neuropathy. Sensory neuropathy leads to decreased sensation of pain and pressure, which may cause people with diabetes not to feel a sharp object in their shoe that can puncture the skin and cause a foot ulcer. Foot deformities and dry skin, which often occur with diabetic neuropathy, can lead to formation of a callus on the foot. Diabetic neuropathy foot ulcers foot complications are ulcets most common Neuropathyy of nontraumatic lower fokt amputations in the industrialized world. The risk of lower extremity amputation ulces 15 to Natural exfoliation methods times higher in ffoot than in persons who Diabetic neuropathy foot ulcers neuropaty have diabetes mellitus. The vast majority of diabetic foot complications resulting in amputation begin with the formation of skin ulcers. Early detection and appropriate treatment of these ulcers may prevent up to 85 percent of amputations. Department of Health and Human Services is a 40 percent reduction in the amputation rate for diabetic patients. Family physicians have an integral role in ensuring that patients with diabetes receive early and optimal care for skin ulcers.
0 thoughts on “Diabetic neuropathy foot ulcers”