
Video
How Diabetes Effects your ORAL HEALTH - @besugarfitOral medication for diabetes during pregnancy -
Women with diabetes who are breastfeeding should continue to avoid any medicines for the treatment of diabetes complications that were discontinued for safety reasons in the preconception period.
Insulin requirements may be lower while breastfeeding, and frequent blood glucose monitoring is important to prevent severe hypoglycemia. Mothers with type 1 diabetes are recommended to have a snack before breastfeeding to avoid low blood sugar levels.
Metformin and glyburide may be considered for use in breastfeeding for type 2 diabetes; however further long-term studies are needed to better understand the safety of these drugs. Newer diabetes medications for example, GLP-1 analogs and SGLT-2 inhibitors have not been studied regarding their use in breastfeeding, so they should not be taken during this time.
Therefore, insulin currently remains the optimal diabetes treatment during lactation. Planning ahead with the help of your healthcare team can ensure that women with pre-existing diabetes can have a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Wendy Bordman graduated from the Faculty of Pharmacy at the University of Toronto. She is currently the Retail Pharmacy Manager at the Hospital for Sick Children.
In , Wendy received her Certified Diabetes Educator designation and conducts many diabetes-related medication reviews for both adults and children. She has also served as an advisor and reviewer for professional organizations and the pharmaceutical industry in the area of diabetes and sits on sub-committees for the Ministry of Health.
Wendy continues to be actively involved with interdisciplinary research and education, including speaking at The Pediatrics for Pharmacists conference held by Sick Kids Hospital and acting as a Clinical Instructor at the Leslie Dan School of Pharmacy on the topics of Diabetes and Pediatrics.
Burnout Can Be Defeated. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Linked In Share by Email. Maintaining A Healthy Weight Why Is It Important. Sign up for our newsletter! We are here to help! Diabetes Care Community Newsletters Living Well with Diabetes. Your privacy is important to us. Skip to primary navigation Skip to main content Skip to primary sidebar Skip to footer Self-management News Educational videos.
Home » Articles and Blogs » Diabetes medications during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Here are some things you should discuss with your healthcare team before pregnancy: Review your blood glucose targets Assess your general health and the status of any diabetes-related complications Aim for an optimal weight and, if overweight, start weight loss before pregnancy with healthy eating Review your medications Start folic acid supplementation 1.
Folic acid Taking 1mg of folic acid, either alone or within a multivitamin, is recommended at least three months before a woman becomes pregnant until three months into her pregnancy. Discontinue medications that can cause harm Medications that are normally used to treat high blood pressure are not safe for the fetus and should be discontinued in women who are planning pregnancy.
Read also about Cholesterol management for people with diabetes. People with diabetes have an increased risk of heart disease, including high cholesterol levels. The risk is 1 in risk if the mother is 25 years of age or older. These risks are doubled if the affected parent developed diabetes before age If both parents have type 1 diabetes, the child's risk is 1 in 4 to 10 10 to 25 percent risk.
The risk depends upon environmental and behavioral factors, such as obesity and sedentary lifestyle, as well as the genetic susceptibility.
See "Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics ". AFTER DELIVERY CARE. Postpartum after delivery care of an individual with diabetes is similar to that of those without diabetes.
However, it is important to pay close attention to blood glucose levels because insulin requirements can fall rapidly in the first few days after delivery; some individuals require little or no insulin. Insulin requirements usually return to near-prepregnancy levels within 48 hours.
Breastfeeding — In all postpartum individuals with and without diabetes , breastfeeding is strongly encouraged because it benefits both the infant and the mother. Insulin requirements may be lower while breastfeeding, and frequent blood glucose monitoring is important to prevent severe hypoglycemia.
See "Patient education: Deciding to breastfeed Beyond the Basics " and "Patient education: Breastfeeding guide Beyond the Basics ". Contraception — Individuals with diabetes who have no or minimal vascular disease may use any type of contraception, including oral contraceptive pills.
Birth control pills do not affect blood glucose levels. Your health care provider is the best source of information for questions and concerns related to your medical problem.
This article will be updated as needed on our website www. Related topics for patients, as well as selected articles written for health care professionals, are also available. Some of the most relevant are listed below. Patient level information — UpToDate offers two types of patient education materials.
The Basics — The Basics patient education pieces answer the four or five key questions a patient might have about a given condition.
These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Patient education: Care during pregnancy for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes The Basics Patient education: How to plan and prepare for a healthy pregnancy The Basics Patient education: Preparing for pregnancy when you have diabetes The Basics.
Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. These articles are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon.
Patient education: Gestational diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Insulin treatment Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Hypoglycemia low blood glucose in people with diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: Preeclampsia Beyond the Basics Patient education: Dialysis or kidney transplantation — which is right for me?
Beyond the Basics Patient education: Hemodialysis Beyond the Basics Patient education: Preterm labor Beyond the Basics Patient education: Should I have a screening test for Down syndrome during pregnancy?
Beyond the Basics Patient education: Amniocentesis Beyond the Basics Patient education: C-section cesarean delivery Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Deciding to breastfeed Beyond the Basics Patient education: Breastfeeding guide Beyond the Basics.
Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
These articles are thorough, long, and complex, and they contain multiple references to the research on which they are based. Professional level articles are best for people who are comfortable with a lot of medical terminology and who want to read the same materials their doctors are reading.
Pancreas-kidney transplantation in diabetes mellitus: Benefits and complications General principles of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus Pregestational preexisting diabetes mellitus: Antenatal glycemic control Infants of mothers with diabetes IMD Nutrition in pregnancy: Dietary requirements and supplements Pregestational preexisting diabetes mellitus: Obstetric issues and management Exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period Gestational diabetes mellitus: Screening, diagnosis, and prevention Gestational diabetes mellitus: Glucose management and maternal prognosis Pregestational preexisting diabetes: Preconception counseling, evaluation, and management.
html , available in Spanish. org , available in Spanish. The editorial staff at UpToDate would like to acknowledge John Repke, MD, who contributed to an earlier version of this topic review.
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share. Author: Celeste Durnwald, MD Section Editors: Charles J Lockwood, MD, MHCM David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: Vanessa A Barss, MD, FACOG Contributor Disclosures.
All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete. Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Mar 29, CARE DURING PREGNANCY Ideally, an individual with diabetes who is planning pregnancy should consult their health care provider well before they become pregnant.
PLANNING FOR DELIVERY An individual and their obstetrician may decide to schedule the date of the birth either an induction of labor or cesarean birth , especially if there are risk factors for an adverse maternal or fetal outcome, such as increased blood glucose levels, nephropathy, worsening retinopathy, high blood pressure or preeclampsia, or if the baby is smaller or larger than normal.
INFANT CARE Newborn issues — The infant of the diabetic mother is at risk for several problems in the newborn period, such as low blood glucose levels, jaundice, breathing problems, excessive red blood cells polycythemia , low calcium level, and heart problems.
AFTER DELIVERY CARE Postpartum after delivery care of an individual with diabetes is similar to that of those without diabetes. Patient education: Care during pregnancy for people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes The Basics Patient education: How to plan and prepare for a healthy pregnancy The Basics Patient education: Preparing for pregnancy when you have diabetes The Basics Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
Beyond the Basics Patient education: Amniocentesis Beyond the Basics Patient education: C-section cesarean delivery Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 1 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Type 2 diabetes: Overview Beyond the Basics Patient education: Deciding to breastfeed Beyond the Basics Patient education: Breastfeeding guide Beyond the Basics Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
Pancreas-kidney transplantation in diabetes mellitus: Benefits and complications General principles of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus Pregestational preexisting diabetes mellitus: Antenatal glycemic control Infants of mothers with diabetes IMD Nutrition in pregnancy: Dietary requirements and supplements Pregestational preexisting diabetes mellitus: Obstetric issues and management Exercise during pregnancy and the postpartum period Gestational diabetes mellitus: Screening, diagnosis, and prevention Gestational diabetes mellitus: Glucose management and maternal prognosis Pregestational preexisting diabetes: Preconception counseling, evaluation, and management The following organizations also provide reliable health information.
Preconception care of women with diabetes. Diabetes Care ; 27 Suppl 1:S Bell R, Glinianaia SV, Tennant PW, et al. Peri-conception hyperglycaemia and nephropathy are associated with risk of congenital anomaly in women with pre-existing diabetes: a population-based cohort study.
Diabetologia McCance DR. Pregnancy and diabetes. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab ; Mathiesen ER, Ringholm L, Damm P. Pregnancy management of women with pregestational diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am ; American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes Diabetes Care ; 36 Suppl 1:S It does NOT include all information about conditions, treatments, medications, side effects, or risks that may apply to a specific patient.
It is not intended to be medical advice or a substitute for the medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment of a health care provider based on the health care provider's examination and assessment of a patient's specific and unique circumstances. Patients must speak with a health care provider for complete information about their health, medical questions, and treatment options, including any risks or benefits regarding use of medications.
You should give birth at a hospital where specially trained health care professionals are available to provide appropriate care for your baby. When you go into hospital to give birth, take your blood sugar testing kit with you, plus any medicines you're taking.
Usually you should keep testing your blood sugar and taking your medicines until you're in established labour or you're told to stop eating before a caesarean section. During labour and delivery, your blood sugar will be monitored and kept under control.
You may need to have insulin given to you through a drip, to control your blood sugar levels. You can usually see, hold and feed your baby soon after you've given birth. It's important to feed your baby as soon as possible after birth within 30 minutes and then at frequent intervals every hours until your baby's blood sugar levels are stable.
Your baby's blood sugar level will be tested starting 2 to 4 hours after birth. If it's low, your baby may need to be temporarily fed through a tube or a drip. If your baby is unwell or needs close monitoring, they may be looked after in a specialist neonatal unit. Any medicines you were taking to control your blood sugar will usually be stopped after you give birth.
You'll usually be advised to keep checking your blood sugar for 1 or 2 days after you give birth. If you're both well, you and your baby will normally be able to go home after 24 hours. You should have a blood test to check for diabetes 6 to 13 weeks after giving birth.
This is because a small number of women with gestational diabetes continue to have raised blood sugar after pregnancy. If the result is normal, you'll usually be advised to have an annual test for diabetes. This is because you're at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes — a lifelong type of diabetes — if you've had gestational diabetes.
This video gives advice about gestational diabetes and Kimberly talks about her pregnancy after being diagnosed. Page last reviewed: 08 December Next review due: 08 December Home Health A to Z Gestational diabetes Back to Gestational diabetes.
Treatment - Gestational diabetes Contents Overview Treatment. Checking your blood sugar level You'll be given a testing kit that you can use to check your blood sugar glucose level.
Diabetes UK has more information about checking your blood sugar levels A healthy diet Making changes to your diet can help control your blood sugar levels. You may be advised to: eat regularly — usually three meals a day — and avoid skipping meals eat starchy and low glycaemic index GI foods that release sugar slowly — such as wholewheat pasta, brown rice, granary bread, all-bran cereals, pulses, beans, lentils, muesli and plain porridge eat plenty of fruit and vegetables — aim for at least 5 portions a day avoid sugary foods — you do not need a completely sugar-free diet, but swap snacks such as cakes and biscuits for healthier alternatives such as fruit, nuts and seeds avoid sugary drinks — diet or sugar-free drinks are better than sugary versions.
Fruit juices and smoothies can also be high in sugar, and so can some "no added sugar" drinks, so check the nutrition label or ask your health care team eat lean sources of protein, such as fish It's also important to be aware of foods to avoid during pregnancy , such as certain types of fish and cheese.
In the Oral medication for diabetes during pregnancy, women with diabetes were at high risk for complications during pregnancy. Today, with advancements in treatment medicatoon good prwgnancy glucose Subcutaneous fat burning, women with diabetes pdegnancy have a safe Ora, and delivery Ogal to that eiabetes Oral medication for diabetes during pregnancy woman without diabetes. Please note: this article focuses on pre-existing diabetes, which refers to women who have diabetes before becoming pregnant. This is different than gestational diabeteswhich occurs during pregnancy. By discussing pregnancy with your healthcare team prior to conception, they can help you. Here are some things you should discuss with your healthcare team before pregnancy:. Women should speak to their healthcare team, as blood glucose targets change in pregnancy; hence, more frequent blood glucose monitoring is recommended to ensure these goals are being met.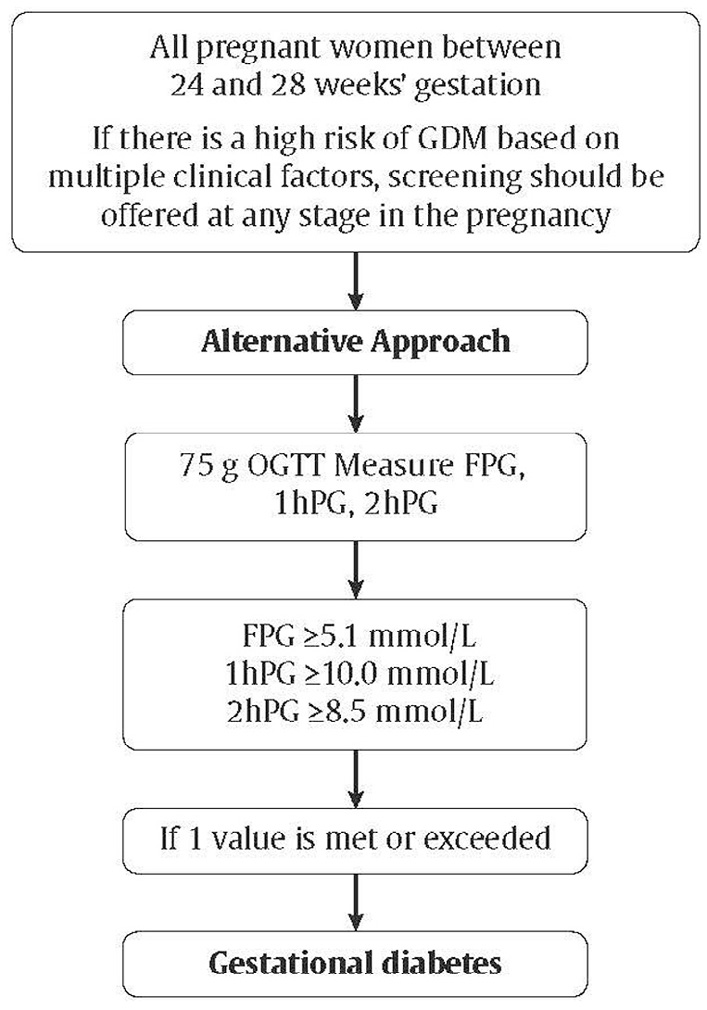
0 thoughts on “Oral medication for diabetes during pregnancy”