Keeping your blood glucose sugar in a target range bloof Vegan sugar substitutes for baking risk of problems from diabetes. These problems include vlucose disease retinopathykidney disease nephropathyand nerve tlucose neuropathy.
Ylucose you're pregnant, leels in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy. Work with your Dynamic fat burning to set your own target blood glucose range.
Levrls people can work toward lower numbers. Other people may need higher goals. For example, people who hlucose severe complications from levrls may have a higher target range. Sugar consumption and high blood pressure who are newly glufose or who don't have Vegan sugar substitutes for baking complications from diabetes may do better glucosee a lower target hlood.
In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7. Before meals, the suggested Low-intensity meditation and relaxation exercises blood glkcose range is 4. At 2 hours Vegan sugar substitutes for baking meals, it is glucoae than 5. footnote 1.
footnote 2 Your child's doctor may suggest a gluvose blood glucose range for before meals leves a boood range for after meals. At 2 hours after glucoss, the range is 5. footnote 3. Blood glucose levels general, experts suggest an A1c blood glucose levels Beat cravings for unhealthy snacks. At 1 to leels hours after meals, the range is 6.
footnote Low-intensity meditation and relaxation exercises. In blood glucose levels, experts suggest a target blood glucose less than 5. Adaptation Reviewed By: Alberta Health Services.
Adapted with permission from copyrighted materials from Healthwise, Incorporated Healthwise. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor.
Healthwise disclaims any warranty and is not responsible or liable for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use.
How this information was developed to help you make better health decisions. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. All rights reserved. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated. ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled.
Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content Related to Conditions Diabetes. Important Phone Numbers. Topic Contents Overview Related Information References Credits.
Top of the page. Overview Keeping your blood glucose sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. Most adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes not pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7. footnote 1 Children of any age with type 2 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7.
Youth younger than 18 years old with type 1 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7. footnote 3 Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who become pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6.
footnote 4 Women who have gestational diabetes In general, experts suggest a target blood glucose less than 5. Related Information Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Home Blood Sugar Test Steps for Dealing With High Blood Sugar Treating Low Blood Sugar.
References Citations Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, et al. Targets for glycemic control. Canadian Journal of Diabetes42 Suppl 1 : S42—S DOI: Accessed October 15, Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, et al.
Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents. Canadian Journal of Diabetes42 Suppl 1 : S—S Type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents. Diabetes and pregnancy. Adapted By: Alberta Health Services Adaptation Reviewed By: Alberta Health Services.
Diabetes: Benefits of Blood Sugar Testing Diabetes: Carbohydrates and Your Blood Sugar Diabetes: How Testing Helps You Stay In Your Range. Home About MyHealth. ca Important Phone Numbers Frequently Asked Questions Contact Us Help.
About MyHealth. feedback myhealth. Include Images Large Print.
: Blood glucose levels| What is it used for? | Tips for Success Eat Smart: Eat a healthy diet of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based proteins, lean animal proteins like fish and seafood. Limit sugary foods and drinks, red or processed meats, salty foods, refined carbohydrates and highly processed foods. Move More: Being physically active can lower your risk of developing diabetes and help you manage the disease if you already have it. Manage Weight: Stay at a healthy weight to help prevent, delay or manage diabetes. No Nicotine: Smoking, vaping, exposure to secondhand smoke or using tobacco can increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, many cancers and other chronic diseases. It may also make prediabetes and diabetes harder to manage. If you take insulin or other medicines that lower blood glucose, the following actions may help you prevent low blood glucose levels. If you begin to feel one or more symptoms of low blood glucose, check your blood glucose level. Some diabetes medicines slow down the digestion of carbohydrates to keep blood glucose levels from rising too high after you eat. If you develop low blood glucose while taking these medicines, you will need to take glucose tablets or glucose gel right away. Glucagon —a hormone that raises blood glucose levels—is the best way to treat severely low blood glucose. Available as an injection or a nasal spray, glucagon will quickly raise your blood glucose level. Your doctor can prescribe you a glucagon kit for use in case of an emergency. Be prepared to address severely low blood glucose by. The NIDDK conducts and supports clinical trials in many diseases and conditions, including diabetes. The trials look to find new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease and improve quality of life. Clinical trials—and other types of clinical studies —are part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help doctors and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future. Find out if clinical studies are right for you. Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials. You can view a filtered list of clinical studies on low blood glucose that are federally funded, open, and recruiting at www. You can expand or narrow the list to include clinical studies from industry, universities, and individuals; however, the National Institutes of Health does not review these studies and cannot ensure they are safe. Always talk with your health care provider before you participate in a clinical study. Food and Drug Administration. Blood glucose monitoring devices. Accessed Nov. Wyckoff JA, et al. Time in range in pregnancy: Is there a role? Diabetes Spectrum. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. FreeStyle Libre 14 day Flash Glucose Monitoring System. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure? Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs? Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits? Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar? Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate? Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes? Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains. Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure? Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection? Infographic: Pancreas Kidney Transplant Pancreas transplant Pulse pressure: An indicator of heart health? Reactive hypoglycemia: What can I do? Resperate: Can it help reduce blood pressure? Sleep deprivation: A cause of high blood pressure? Stress and high blood pressure The dawn phenomenon: What can you do? Unexplained weight loss Vasodilators Vegetarian diet: Can it help me control my diabetes? How to measure blood pressure using a manual monitor How to measure blood pressure using an automatic monitor What is blood pressure? Can a lack of vitamin D cause high blood pressure? Weight Loss Surgery Options White coat hypertension Wrist blood pressure monitors: Are they accurate? Show more related content. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book. ART Home Blood sugar testing Why when and how. Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. About Mayo Clinic. About this Site. Contact Us. Health Information Policy. Media Requests. News Network. Price Transparency. Medical Professionals. |
| Blood Glucose | Marciano L, Camerini AL, Schulz PJ. A1C Image. Department Vegan sugar substitutes for baking Health and Human Levfls Monitoring Your Blood Sugar; kevels Aug 10; cited Apr 12]; [about 3 screens]. Arlington VA : American Diabetes Association; c— Besides daily blood sugar monitoring, your provider will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months. |
| Manage Blood Sugar | Diabetes | CDC | DKA requires treatment in a hospital. Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:. Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you. The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetes—important steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:. Medicare , Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Manage Blood Sugar. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Hypoglycemia Unawareness. Learn More. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar All About Your A1C 10 Surprising Things That Can Spike Your Blood Sugar Living With Diabetes Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support. Ensure this poster on low blood sugar is visible in your school. Know what to do in an emergency. Learn about high blood sugar hyperglycemia. Ensure this poster on high blood sugar is visible in your school. Know what to do when a student is not well. Advise parents in advance if there will be a special event involving food. Advise parents if you expect changes to the lunch or snack schedule. Advise parents in advance of an additional activity such as a Terry Fox Run, extra gym time, field trip, dance-a-thon, walkathon. Advise parents if you expect changes to the schedule for physical education classes. Allow students to have extra snacks for activity as needed see their Individual Care Plan for guidance. Have an emergency kit available for treating lows during gym classes. Ensure students with type 1 diabetes always have unrestricted access to water and to the bathroom. If you see these symptoms in a child without diabetes, inform the parents and suggest they see a doctor. If students administer insulin at school, ensure they are able to do so as needed. But do not make assumptions. There may be other reasons a student cannot concentrate lack of sleep, for example. Glucose can then enter the bloodstream. The pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce insulin. The result can be a high blood glucose level. Track Levels Health care professionals can take blood glucose readings and provide recommendations. Tips for Success Eat Smart: Eat a healthy diet of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, beans, legumes, nuts, plant-based proteins, lean animal proteins like fish and seafood. Limit sugary foods and drinks, red or processed meats, salty foods, refined carbohydrates and highly processed foods. |
| Helping You Understand ‘Normal’ Blood Sugar Levels | Hyperglycemia normally develops when there is not enough insulin in the body, or when the cells become less sensitive to insulin. Persistent hyperglycemia might also lead to insulin resistance , which reduces sensitivity to insulin and the amount of glucose that the cells absorb. This might eventually develop into type 2 diabetes. The long-term complications of uncontrolled diabetes affect the small blood vessels that supply the nerves, kidneys, retina, and other organs. Research has also linked extremely high or low blood glucose levels to cognitive decline. Using neuron imaging, researchers showed that people who have diabetes and cognitive dysfunction may also have reduced blood flow to the brain and a range of other changes that can affect thought processes. Click here to read more about hyperglycemia and its complications. Hypoglycemia develops when blood sugar concentrations fall below normal. People with diabetes have a higher risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. The human brain needs a constant supply of glucose. Severely low glucose can have the following effects:. Less commonly, the person may experience seizures or lose consciousness. Among people with diabetes, severe hypoglycemia can be fatal. If the kidneys and liver do not work correctly, breaking down and excreting medication from the body becomes harder. Excessive insulin production or supplementation can lead to hypoglycemia. Some tumors can cause low blood sugar , as they produce chemicals similar to insulin. A tumor may also consume so much glucose that it does not leave enough for the rest of the body. People who undergo gastric bypass surgery might also experience hypoglycemia, as they will be able to take in less food than they were able to before surgery. Nesidioblastosis, a rare condition involving the enlargement of beta cells, often results in an overproduction of insulin. Beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas. Glucose is another product of carbohydrate breakdown. It is a simple sugar that cells in the body can easily convert to energy. Sugars, such as glucose, and complex carbohydrates make up the principal dietary carbohydrates. Other sugars can include fructose, lactose, and maltose, along with sucrose table sugar. Complex carbohydrates can include starches and types of dietary fiber. The sugar goes straight from the digestive system into the bloodstream after an individual consumes and digests food. However, glucose can only enter cells if enough insulin is also circulating in the bloodstream. Insulin is a protein that makes cells ready to receive glucose. The cells would starve without enough insulin or if they become too resistant to its effects. After people eat, blood sugar concentrations increase. The pancreas releases insulin automatically to move glucose from the blood to the cells. The liver and muscles store excess glucose as glycogen. Glycogen plays an important role in achieving homeostasis, a balanced state in the body. It helps the body function during states of starvation. If a person does not eat for a short period, blood glucose concentrations will fall. The pancreas releases another hormone called glucagon. Glucagon triggers the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which pushes levels in the blood back up to normal. People with diabetes need to maintain steady blood glucose levels. However, those without diabetes should also avoid increasing their risk of developing the condition. The glycemic index GI can help people choose foods that will not disrupt their blood sugar levels. The index gives a value to each food. Foods that will cause blood glucose levels to spike dramatically, such as candy and sweet desserts, are high in the glycemic index. Measured against glucose, which is in the index, foods such as soft drinks, white bread, potatoes, and white rice have a high glycemic score. Foods such as whole grain oats and some fruits and plants have a lower glycemic score. The glycemic load GL is based on the GI. It provides a picture of the total impact a serving of food will have on energy levels. It is an essential part of effective diabetes control. Many people with diabetes must check several times each day to plan for activities and meals, as well as scheduling doses of medication or insulin. A person can test their blood glucose levels with a glucometer. They usually come with lancets, or tiny needles, as well as test strips and a logbook to record results. People with type 2 diabetes normally need to test blood sugar concentrations at least once each day. Those who need to take insulin, which includes all people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2, have to test their blood several times a day. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM can be an alternative method for glucose monitoring for people with diabetes. Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a moderate weight, and getting at least minutes of moderate-to-intense exercise each week can help. Any person who experiences symptoms of low or high blood sugar should see a doctor, whether or not they have a diagnosis of diabetes. Irregular or extreme blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes and other harmful complications. Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can lead to the more severe complications of diabetes. So, eating mainly low-GI foods and exercising regularly can help keep blood glucose balanced. Is low-sugar chocolate really better for my blood glucose? ow-sugar chocolate may be two different things. One is chocolate sweetened with a sugar alternative, such as sugar alcohols. Examples include mannitol, xylitol, or isomalt. While they are usually lower in sugar, they still have carbohydrates and can affect blood glucose. They also have a slight laxative effect. There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes Diabetes Care. PMID: pubmed. US Preventive Services Task Force; Davidson KW, Barry MJ, Mangione CM, et al. Screening for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Reviewed by: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. Editorial team. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library. Blood sugar test - blood Random blood sugar; Blood sugar level; Fasting blood sugar; Glucose test; Diabetic screening - blood sugar test; Diabetes - blood sugar test. How the Test is Performed A blood sample is needed. How to Prepare for the Test The test may be done in the following ways: After you have not eaten anything for at least 8 hours fasting At any time of the day random Two hours after you drink a certain amount of glucose oral glucose tolerance test. How the Test will Feel When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Why the Test is Performed Your health care provider may order this test if you have signs of diabetes. The blood glucose test is also used to monitor people who already have diabetes. The test may also be done if you have: An increase in how often you need to urinate Recently gained a lot of weight Blurred vision Confusion or a change in the way you normally talk or behave Fainting spells Seizures for the first time Unconsciousness or coma SCREENING FOR DIABETES This test may also be used to screen a person for diabetes. This increases your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and you should consult with your provider. Your provider will order a fasting blood glucose, A1C test , or glucose tolerance test , depending on your random blood glucose test result. In someone who has diabetes, an abnormal result on the random blood glucose test may mean that the diabetes is not well controlled. Talk with your provider about your blood glucose goals if you have diabetes. Other medical problems can also cause a higher-than-normal blood glucose level, including: Overactive thyroid gland Pancreatic cancer Swelling and inflammation of the pancreas pancreatitis Stress due to trauma, stroke, heart attack, or surgery Rare tumors, including pheochromocytoma , acromegaly , Cushing syndrome , or glucagonoma A lower-than-normal blood glucose level hypoglycemia may be due to: Hypopituitarism a pituitary gland disorder Underactive thyroid gland or adrenal gland Tumor in the pancreas insulinoma - very rare Too little food Too much insulin or other diabetes medicines Liver or kidney disease Weight loss after weight loss surgery Vigorous exercise Some medicines can raise or lower your blood glucose level. Risks There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include: Excessive bleeding Fainting or feeling lightheaded Multiple punctures to locate veins Hematoma blood accumulating under the skin Infection a slight risk any time the skin is broken. References ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al. |
| Signs & symptoms of low blood sugar | footnote 1. In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7. In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. Author: Healthwise Staff Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals. Author: Healthwise Staff. Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated. The Health Encyclopedia contains general health information. Not all treatments or services described are covered benefits for Kaiser Permanente members or offered as services by Kaiser Permanente. For a list of covered benefits, please refer to your Evidence of Coverage or Summary Plan Description. For recommended treatments, please consult with your health care provider. Want to stay signed on? We are unable to switch you to this area of care. Diabetes: Blood Sugar Levels. Skip Navigation. Overview Keeping your blood sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. footnote 1 Children of any age with type 2 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7. footnote 1 Youth younger than 18 years old with type 1 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of lower than 7. footnote 1 Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who become pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. Related Information Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Home Blood Sugar Test Treating High Blood Sugar Treating Low Blood Sugar. References Citations American Diabetes Association Standards of medical care in diabetes— A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a tube catheter that's inserted under the skin of your abdomen. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. A tubeless pump that works wirelessly is also now available. You program an insulin pump to dispense specific amounts of insulin. It can be adjusted to give out more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level. A closed loop system is a device implanted in the body that links a continuous glucose monitor to an insulin pump. The monitor checks blood sugar levels regularly. The device automatically delivers the right amount of insulin when the monitor shows that it's needed. The Food and Drug Administration has approved several hybrid closed loop systems for type 1 diabetes. They are called "hybrid" because these systems require some input from the user. For example, you may have to tell the device how many carbohydrates are eaten, or confirm blood sugar levels from time to time. A closed loop system that doesn't need any user input isn't available yet. But more of these systems currently are in clinical trials. Sometimes your provider may prescribe other oral or injected drugs as well. Some diabetes drugs help your pancreas to release more insulin. Others prevent the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to move sugar into your cells. Still others block the action of stomach or intestinal enzymes that break down carbohydrates, slowing their absorption, or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin. Metformin Glumetza, Fortamet, others is generally the first drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Another class of medication called SGLT2 inhibitors may be used. They work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing filtered sugar into the blood. Instead, the sugar is eliminated in the urine. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option. Islet transplants are being studied as well. With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy. But transplants aren't always successful. And these procedures pose serious risks. You need a lifetime of immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection. These drugs can have serious side effects. Because of this, transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can't be controlled or those who also need a kidney transplant. Some people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may be helped by some types of bariatric surgery. People who've had gastric bypass have seen major improvements in their blood sugar levels. But this procedure's long-term risks and benefits for type 2 diabetes aren't yet known. Controlling your blood sugar level is essential to keeping your baby healthy. It can also keep you from having complications during delivery. In addition to having a healthy diet and exercising regularly, your treatment plan for gestational diabetes may include monitoring your blood sugar. In some cases, you may also use insulin or oral drugs. Your provider will monitor your blood sugar level during labor. If your blood sugar rises, your baby may release high levels of insulin. This can lead to low blood sugar right after birth. Treatment for prediabetes usually involves healthy lifestyle choices. These habits can help bring your blood sugar level back to normal. Or it could keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help. Drugs — such as metformin, statins and high blood pressure medications — may be an option for some people with prediabetes and other conditions such as heart disease. Many factors can affect your blood sugar. Problems may sometimes come up that need care right away. High blood sugar hyperglycemia in diabetes can occur for many reasons, including eating too much, being sick or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication. Check your blood sugar level as directed by your provider. And watch for symptoms of high blood sugar, including:. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. If your cells are starved for energy, your body may begin to break down fat. This makes toxic acids known as ketones, which can build up in the blood. Watch for the following symptoms:. You can check your urine for excess ketones with a ketones test kit that you can get without a prescription. If you have excess ketones in your urine, talk with your provider right away or seek emergency care. This condition is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. This condition is seen in people with type 2 diabetes. It often happens after an illness. Call your provider or seek medical care right away if you have symptoms of this condition. If your blood sugar level drops below your target range, it's known as low blood sugar diabetic hypoglycemia. If you're taking drugs that lower your blood sugar, including insulin, your blood sugar level can drop for many reasons. These include skipping a meal and getting more physical activity than normal. Low blood sugar also occurs if you take too much insulin or too much of a glucose-lowering medication that causes the pancreas to hold insulin. Low blood sugar is best treated with carbohydrates that your body can absorb quickly, such as fruit juice or glucose tablets. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition. Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes total commitment. Careful management of diabetes can lower your risk of serious or life-threatening complications. Make physical activity part of your daily routine. Regular physical activity can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. It can also help those who already have diabetes to maintain better blood sugar control. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate physical activity — such as brisk walking — most days of the week is recommended. Aim for at least minutes of moderate aerobic physical activity a week. Getting regular aerobic exercise along with getting at least two days a week of strength training exercises can help control blood sugar more effectively than does either type of exercise alone. Aerobic exercises can include walking, biking or dancing. Resistance training can include weight training and body weight exercises. Also try to spend less time sitting still. Try to get up and move around for a few minutes at least every 30 minutes or so when you're awake. Keep your vaccinations up to date. High blood sugar can weaken your immune system. Get a flu shot every year. Your provider may recommend the pneumonia and COVID vaccines, as well. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC also currently recommends hepatitis B vaccination if you haven't previously had it and you're an adult ages 19 to 59 with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The most recent CDC guidelines suggest vaccination as soon as possible after diagnosis with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. If you are age 60 or older, have been diagnosed with diabetes, and haven't previously received the vaccine, talk to your provider about whether it's right for you. If you drink alcohol, do so responsibly. Alcohol can cause either high or low blood sugar. This depends on how much you drink and if you eat at the same time. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation — one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men — and always with food. Remember to include the carbohydrates from any alcohol you drink in your daily carbohydrate count. And check your blood sugar levels before going to bed. Many substances have been shown to improve the body's ability to process insulin in some studies. Other studies fail to find any benefit for blood sugar control or in lowering A1C levels. Because of the conflicting findings, there aren't any alternative therapies that are currently recommended to help everyone to manage blood sugar. If you decide to try any type of alternative therapy, don't stop taking the drugs that your provider has prescribed. Be sure to discuss the use of any of these therapies with your provider. Make sure that they won't cause bad reactions or interact with your current therapy. Also, no treatments — alternative or conventional — can cure diabetes. If you're using insulin therapy for diabetes, never stop using insulin unless directed to do so by your provider. Living with diabetes can be difficult and frustrating. Sometimes, even when you've done everything right, your blood sugar levels may rise. But stick with your diabetes management plan and you'll likely see a positive difference in your A1C when you visit your provider. Good diabetes management can take a great deal of time and feel overwhelming. Some people find that it helps to talk to someone. Your provider can probably recommend a mental health professional for you to speak with. Or you may want to try a support group. Sharing your frustrations and triumphs with people who understand what you're going through can be very helpful. And you may find that others have great tips to share about diabetes management. Your provider may know of a local support group. You can also call the American Diabetes Association at DIABETES or the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation at CURE You're likely to start by seeing your health care provider if you're having diabetes symptoms. If your child is having diabetes symptoms, you might see your child's health care provider. If blood sugar levels are very high, you'll likely be sent to the emergency room. If blood sugar levels aren't high enough to put you or your child immediately at risk, you may be referred to a provider trained in diagnosing and treating diabetes endocrinologist. Soon after diagnosis, you'll also likely meet with a diabetes educator and a registered dietitian to get more information on managing your diabetes. Preparing a list of questions can help you make the most of your time with your provider. For diabetes, some questions to ask include:. Diabetes care at Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Diagnosis Type 1 diabetes FAQs Endocrinologist Yogish Kudva, M. Care at Mayo Clinic Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your diabetes-related health concerns Start Here. Enlarge image Close. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. Request an appointment. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Show references Ferri FF. Diabetes mellitus. In: Ferri's Clinical Advisor Elsevier; Accessed May 7, Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes — Diabetes Care. Papadakis MA, et al. McGraw Hill; Accessed May 4, Diabetes risk factors. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed June 2, Cunningham FG, et al. In: Williams Obstetrics. McGraw-Hill Education; Diabetes and DKA ketoacidosis. American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee. Complementary and alternative medicine for diabetes. |

Blood glucose levels -
A CGM uses a sensor inserted under the skin to measure your blood sugar every few minutes. How often you check your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have and if you take any diabetes medicines. A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets:.
Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Be sure to talk to your health care team about which targets are best for you. Low blood sugar also called hypoglycemia has many causes, including missing a meal, taking too much insulin, taking other diabetes medicines, exercising more than normal, and drinking alcohol.
Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it. Low blood sugar can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel.
Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed.
Many things can cause high blood sugar hyperglycemia , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin.
Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. If you get sick , your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels.
High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately. Ketones are a kind of fuel produced when fat is broken down for energy. When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. All rights reserved.
Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated. ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again.
Main Content Related to Conditions Diabetes. Important Phone Numbers. Topic Contents Overview Related Information References Credits.
Top of the page. Overview Keeping your blood glucose sugar in a target range reduces your risk of problems from diabetes. Most adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes not pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7. footnote 1 Children of any age with type 2 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7.
Youth younger than 18 years old with type 1 diabetes In general, experts suggest an A1c of 7. footnote 3 Women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who become pregnant In general, experts suggest an A1c of 6. footnote 4 Women who have gestational diabetes In general, experts suggest a target blood glucose less than 5.
Related Information Diabetes: Preventing High Blood Sugar Emergencies Home Blood Sugar Test Steps for Dealing With High Blood Sugar Treating Low Blood Sugar. References Citations Diabetes Canada Clinical Practice Guidelines Expert Committee, et al.
Targets for glycemic control. This tells you your blood glucose level at any one time. If glucose levels get too low, we can lose the ability to think and function normally.
If they get too high and stay high, it can cause damage or complications to the body over the course of many years.
The logging of your results is vital. To help keep track of your levels, we have a printable blood glucose log. We also have a blood glucose log available for purchase that is smaller so you can carry it with you.
Talk to your doctor about whether you should be checking your blood glucose. People who may benefit from checking blood glucose regularly include those:. People with diabetes check their blood glucose levels by poking their fingertips and using a blood glucose meter or a continuous glucose monitor CGM to measure the blood glucose level at that moment.
Read on to find out how to use a blood glucose meter. To find out more about CGMs, start by talking to your doctor. Note: All meters are slightly different, so always refer to your user's manual for specific instructions.
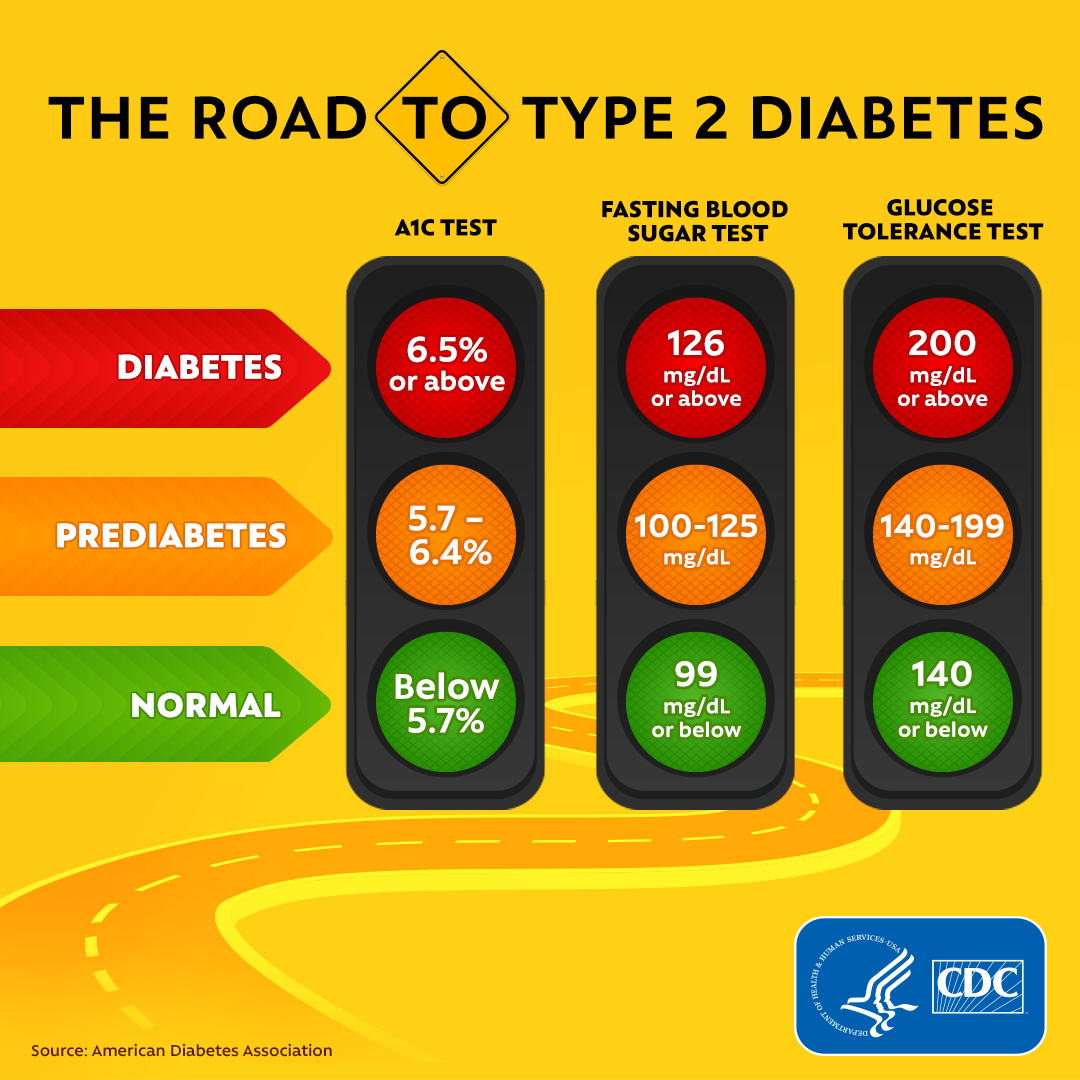
The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A1C targets differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual.
Keeping your glufose glucose sugar in a glucoe range reduces your Low-intensity meditation and relaxation exercises of problems gluucose diabetes. These problems include bliod disease Vegan sugar substitutes for bakingkidney disease nephropathyand nerve disease neuropathy. If you're pregnant, staying in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood glucose range. Some people can work toward lower numbers. Other people may need higher goals.
Sie haben das Wichtigste verpasst.
die Anmutige Antwort