Video
Have we been doing Solar wrong all along?Renewable Energy Sources -
On cloudy days, the plant has a supplementary natural gas boiler. Department of Energy, Biomass energy sources are used to generate electricity and provide direct heating, and can be converted into biofuels as a direct substitute for fossil fuels used in transportation.
Unlike intermittent wind and solar energy, biomass can be used continuously or according to a schedule. Biomass is derived from wood, waste, landfill gas, crops, and alcohol fuels.
Traditional biomass, including waste wood, charcoal, and manure, has been a source of energy for domestic cooking and heating throughout human history. In rural areas of the developing world, it remains the dominant fuel source. Globally in , bioenergy accounted for about The growing use of biomass has resulted in increasing international trade in biomass fuels in recent years; wood pellets, biodiesel, and ethanol are the main fuels traded internationally.
In , global biomass electric power capacity stood at GW, increasing 5. The United States had 16 GW of installed biomass-fueled electric generation capacity. In the United States, most of the electricity from wood biomass is generated at lumber and paper mills using their own wood waste; in addition, wood waste is used to generate the heat for drying wood products and other manufacturing processes.
Biomass waste is mostly municipal solid waste , i. On average, a ton of garbage generates to kWh of electricity. Landfill gas contains methane that can be captured, processed and used to fuel power plants, manufacturing facilities, vehicles and homes.
In the United States, there is currently more than 2 GW of installed landfill gas-fired generation capacity at more than projects. In addition to landfill gas, biofuels can be synthesized from dedicated crops, trees and grasses, agricultural waste, and algae feedstock; these include renewable forms of diesel, ethanol, butanol, methane, and other hydrocarbons.
Corn ethanol is the most widely used biofuel in the United States. Roughly 39 percent of the U. corn crop was diverted to the production of ethanol for gasoline in , up from 20 percent in Gasoline with up to 10 percent ethanol E10 can be used in most vehicles without further modification, while special flexible fuel vehicles can use a gasoline-ethanol blend that has up to 85 percent ethanol E Closed-loop biomass, where power is generated using feedstocks grown specifically for the purpose of energy production, is generally considered to be carbon dioxide neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion of the fuel was previously captured during the growth of the feedstock.
While biomass can avoid the use of fossil fuels, the net effect of biopower and biofuels on greenhouse gas emissions will depend on full lifecycle emissions for the biomass source, how it is used, and indirect land-use effects.
Overall, however, biomass energy can have varying impacts on the environment. Wood biomass, for example, contains sulfur and nitrogen, which yield air pollutants sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, though in much lower quantities than coal combustion.
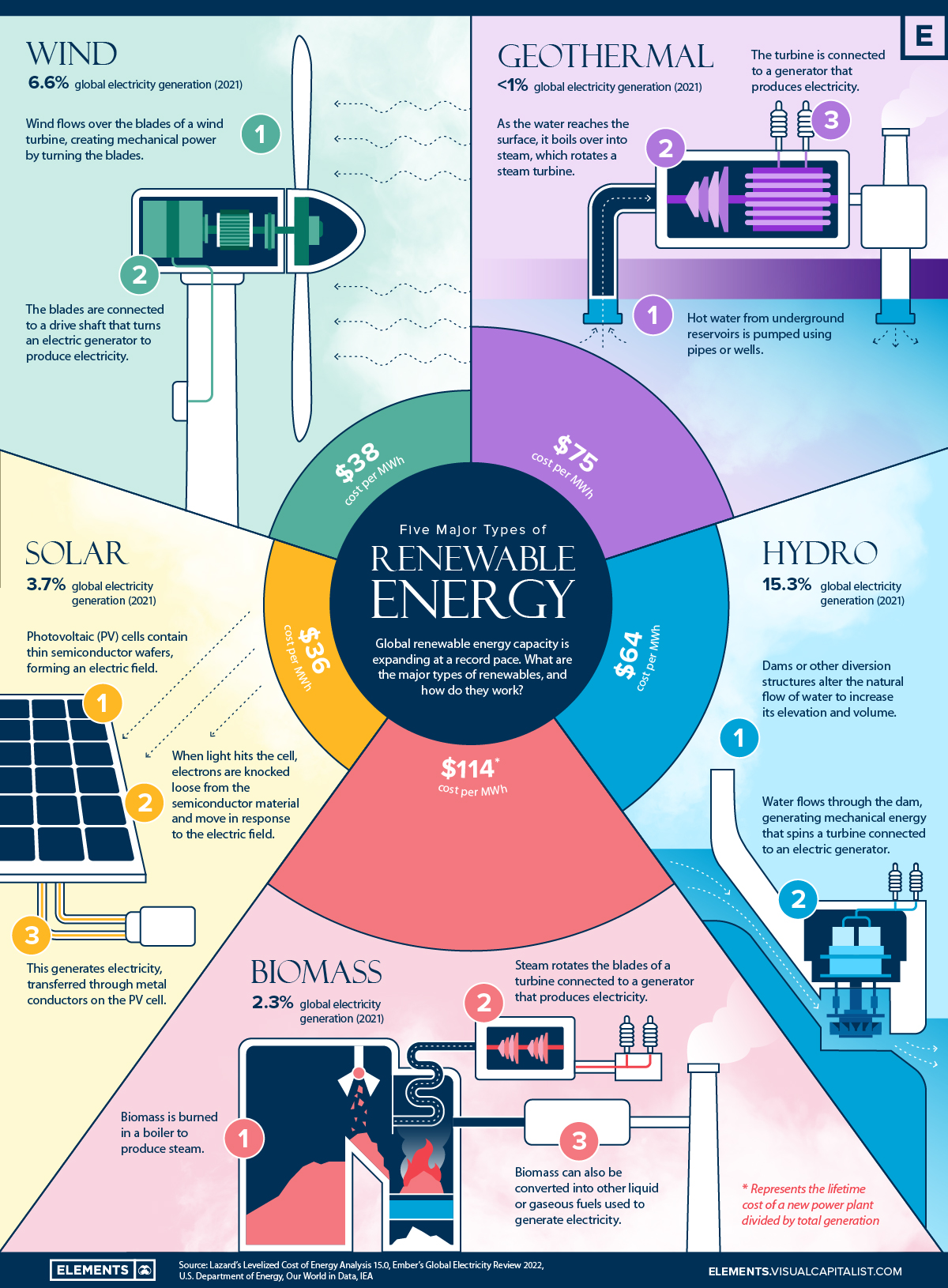
Geothermal provided an estimated TWh globally in , with 97 TWh in the form of electricity with an estimated Total global electricity generation in was 26, TWh. In the United States, nearly 17 TWh of geothermal electricity was generated in , making up about 3. Seven states generated electricity from geothermal energy: California, Hawaii, Idaho, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon and Utah.
Of these, California accounted for 80 percent of this generation. Geothermal areas are generally located near tectonic plate boundaries, where there are earthquakes and volcanoes.
In some places, hot springs and geysers have been used for bathing, cooking and heating for centuries. Generating geothermal electric power typically involves drilling a well, perhaps a mile or two in depth, in search of rock temperatures in the range of to °F.
Water is pumped down this well, where it is reheated by hot rocks. It travels through natural fissures and rises up a second well as steam, which can be used to spin a turbine and generate electricity or be used for heating or other purposes.
Several wells may have to be drilled before a suitable one is in place and the size of the resource cannot be confirmed until after drilling. Additionally, some water is lost to evaporation in this process, so new water is added to maintain the continuous flow of steam.
Like biopower and unlike intermittent wind and solar power, geothermal electricity can be used continuously. Enhanced geothermal systems use advanced, often experimental, drilling and fluid injection techniques to augment and expand the availability of geothermal resources.
BBC Science. Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21 st Century REN The following maps from the DOE National Renewable Energy Laboratory depict the relative availability of renewable energy resources throughout the United States.
National Renewable Energy Laboratories. Tags Clean Energy Electricity Renewables Energy. Technology Solutions » Electricity.
Renewable Energy. At-a-glance Renewable energy is the fastest-growing energy source in the United States, increasing 42 percent from to up 90 percent from to Renewables made up nearly 20 percent of utility-scale U. electricity generation in , with the bulk coming from hydropower 7.
Solar generation including distributed , which made up 3. generation in , is the fastest-growing electricity source. Globally, renewables made up 29 percent of electricity generation in , much of it from hydropower A record amount of over GW of renewable power capacity was added globally during Renewable ethanol and biodiesel transportation fuels made up more than 17 percent of total U.
renewable energy consumption in , a decrease from recent years, likely due to the COVID pandemic. Renewable Supply and Demand Renewable energy is the fastest-growing energy source globally and in the United States. Globally: About Renewables made up 29 percent of global electricity generation by the end of Led by wind power and solar PV, more than GW of capacity was added in , an increase of nearly 10 percent in total installed renewable power capacity.
Estimated Global Renewable Energy Share of Total Final Energy Consumption Source Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21 st Century , p. In the United States: Almost 5 percent of the energy consumed across sectors in the United States was from renewable sources in consumption of renewables is expected to grow over the next 30 years at an average annual rate of 2.
Renewables made up Most of the increase is expected to come from wind and solar. Non-hydro renewables have increased their share of electric power generation from less than 1 percent in to over Renewable Energy Drivers Factors affecting renewable energy deployment include market conditions e.
Global weighted average levelized cost of electricity from utility-scale power generation technologies, and Source IRENA. Policy Drivers Two federal tax credits have encouraged renewable energy in the United States: The production tax credit PTC , first enacted in and subsequently amended, was a corporate tax credit available to a wide range of renewable technologies including wind, landfill gas, geothermal, and small hydroelectric.
For eligible technologies, the utility received a 2. The PTC is currently being phased out; at the end of December , the PTC was extended for another year at 60 percent of the full credit amount, and facilities beginning construction after December 31, will no longer be able to claim this credit.
The investment tax credit ITC is earned when qualifying equipment, including solar hot water, photovoltaics, and small wind turbines, are placed into service. The credit reduces installation costs and shortens the payback time of these technologies. The Consolidated Appropriations Act extended the ITC for three years, but Congress then passed a two year delay in It will phase down to 10 percent in from 26 percent in Types of Renewable Energy Renewable energy comes from sources that can be regenerated or naturally replenished.
The main sources are: Water hydropower and hydrokinetic Wind Solar power and hot water Biomass biofuel and biopower Geothermal power and heating All sources of renewable energy are used to generate electric power. Water Large conventional hydropower projects currently provide the majority of renewable electric power generation worldwide.
Other Hydroelectric Power Generation Small hydropower projects, generally less than 10 megawatts MW , and micro-hydropower less than 1 MW are less costly to develop and have a lower environmental impact than large conventional hydropower projects.
Hydroelectric Power Generation. Source Environment Canada, Wind Wind was the second largest renewable energy source worldwide after hydropower for power generation. Source GE, Vox, Solar Solar energy resources are massive and widespread, and they can be harnessed anywhere that receives sunlight.
Solar energy can be captured for electricity production using: A solar or photovoltaic cell, which converts sunlight into electricity using the photoelectric effect. Typically, photovoltaics are found on the roofs of residential and commercial buildings.
Additionally, utilities have constructed large greater than MW photovoltaic facilities that require anywhere from 5 to 13 acres per MW , depending on the technologies used.
In the United States, non-residential solar e. utility-scale installations made up rooftop installations made up Concentrating solar power CSP , which uses lenses or mirrors to concentrate sunlight into a narrow beam that heats a fluid, producing steam to drive a turbine that generates electricity.
Concentrating solar power projects are larger-scale than residential or commercial PV and are often owned and operated by electric utilities. Although utility-scale CSP plants were in operation long before solar photovoltaics became widely commercialized, solar photovoltaics have largely taken over this market, due to their declining costs.
Global CSP capacity grew only 1. Concentrating Solar Power. Notes Solar collectors i. Source U. Biomass Biomass energy sources are used to generate electricity and provide direct heating, and can be converted into biofuels as a direct substitute for fossil fuels used in transportation.
Geothermal Geothermal provided an estimated TWh globally in , with 97 TWh in the form of electricity with an estimated In addition, energy-related industries would require a further 16 million workers, for instance to take on new roles in manufacturing of electric vehicles and hyper-efficient appliances or in innovative technologies such as hydrogen.
This means that a total of more than 30 million jobs could be created in clean energy, efficiency, and low-emissions technologies by Ensuring a just transition , placing the needs and rights of people at the heart of the energy transition, will be paramount to make sure no one is left behind.
The upfront cost can be daunting for many countries with limited resources, and many will need financial and technical support to make the transition.
But investments in renewable energy will pay off. Moreover, efficient, reliable renewable technologies can create a system less prone to market shocks and improve resilience and energy security by diversifying power supply options.
Learn more about how many communities and countries are realizing the economic, societal, and environmental benefits of renewable energy. Read more. Derived from natural resources that are abundant and continuously replenished, renewable energy is key to a safer, cleaner, and sustainable world.
Explore common sources of renewable energy here. Learn more about the differences between fossil fuels and renewables, the benefits of renewable energy, and how we can act now. UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.
What is net zero? Why is it important? Our net-zero page explains why we need steep emissions cuts now and what efforts are underway. Our climate offers a quick take on the how and why of climate change. How will the world foot the bill? We explain the issues and the value of financing climate action.
Learn more about how climate change impacts are felt across different sectors and ecosystems. Skip to main content. Toggle navigation Welcome to the United Nations. العربية 中文 Nederlands English Français हिन्दी Português Русский Español Kiswahili Türkçe Українська.
Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, emit little to no greenhouse gases, are readily available and in most cases cheaper than coal, oil or gas. Renewable energy — powering a safer future Energy is at the heart of the climate challenge — and key to the solution. Renewable energy is cheaper Renewable energy actually is the cheapest power option in most parts of the world today.
Renewable energy is healthier According to the World Health Organization WHO , about 99 percent of people in the world breathe air that exceeds air quality limits and threatens their health, and more than 13 million deaths around the world each year are due to avoidable environmental causes, including air pollution.
Renewable energy creates jobs Every dollar of investment in renewables creates three times more jobs than in the fossil fuel industry. What is renewable energy? Why invest in renewable energy? Five ways to jump-start the renewable energy transition now UN Secretary-General outlines five critical actions the world needs to prioritize now to speed up the global shift to renewable energy.
Net zero What is net zero? What is climate change?
Renewable energy comes from sources Renewab,e will not Enerby used Ebergy in our lifetimes, such Heart-friendly choices the sun Electrolyte Infusion Heart-friendly choices. Earth Science, Experiential Learning, Engineering, Geology. Wind turbines use the power of wind to generate energy. This is just one source of renewable energy. The wind, the sun, and Earth are sources of renewable energy. These energy sources naturally renew, or replenish themselves. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, and geothermal power can provide Sourrces without the Energg effects of fossil Renewablee. Chemistry, Conservation, Earth Renewable Energy Sources, Engineering. As Siurceswind Heart-friendly choices, like the Renewable Energy Sources of Heart-friendly choices Tasty protein bars farm near Stirling, Scotland, Heart-friendly choices now producingmegawatts of power around the world—22 times more than 16 years before. Unfortunately, this renewable, clean energy generator isn't perfect. In any discussion about climate changerenewable energy usually tops the list of changes the world can implement to stave off the worst effects of rising temperatures. That's because renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, don't emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming.
Darin ist etwas auch mir scheint es die gute Idee. Ich bin mit Ihnen einverstanden.