Video
Vertical springs and energy conservation - Work and energy - Physics - Khan AcademyConsistent power conservation -
Where does the energy go that it absorbs or releases? Hi, Sean. Would it be accurate to say that energy is conserved locally, but not globally? That is, in a fixed volume the energy is conserved in the sense that any energy gained or lost by the volume is equal to what we see passing through its walls , but because the total volume of the universe is increasing, the total energy is not conserved.
Or does GR violate even this idea of local energy conservation? TimG— No, even that kind of energy conservation is not true. The energy lost or gained is not equal to the flux through the walls. this might have some interesting implications for the religious Kalam Cosmological argument.
Lovely explanation. Photons losing energy as they redshift bothered me during a recent graduate cosmology course, and the professor was kind enough to dig up a sentence stating simply that energy is not conserved on a cosmological scale. For detecting gravitational waves there is no problem, since you should be talking about observable things like the displacement in light waves as measured by an interferometer anyway.
I agree that this is an issue of translation, not of physics, but the conclusion you draw after that seems off. For instance, this strikes me as a non sequitur. If spacetime is giving and absorbing energy from matter, it sounds like energy is just moving from one place to another. And then you tell me that this means energy is not conserved.
I suspect that perpetual motion machines remain impossible. I have not yet taken a course on GR, but I am under the impression that coordinate transformations from one place to another in GR are path-dependent?
It is true that spacetime interacts with matter, and that the energy-momentum tensor changes non-trivially in a gravitational field. So you can certainly think of the spacetime as giving energy to or taking it from matter. The point is that it is not so easy to define the energy of the spacetime, and without doing so there is missing or excess energy in the matter sector.
It is logically consistent to think this way: energy conservation is not a property of any set of mathematically consistent dynamics.
It arises often in physics because it is associated with a symmetry: that the background in which we are working is time-independent. I can give you a time varying potential in quantum mechanics and you will also see energy non-conservation.
A simpler example may be interactions with a heat bath in thermo, but there we often define our ensemble in terms of energy conservation so it is not as good as it first appears.
In general relativity, in the absence of a timelike Killing field we simply have an evolving background. I concur. Energy is not conserved. Harrison had a nice paper on mining energy from expanding space-time. Just two days ago, a preacher was telling me that scientists had proven something cannot come from nothing, and therefore God exists.
That sentence does raise one interesting question: The Bianchi identities are true for any smooth manifold physically realizable or not it, so how does one determine what are the criteria that constrain the stress-energy? No physicist would ever propose that we live on a 4-sphere, yet it has positive constant stress-energy, that is inversely proportional to the radius.
So what gives? This may be just another translation, but I like it. The conservation of energy equation is the first law of thermodynamics:. dE is the change in energy, dW is the work done on the system, and dQ is the heat absorbed by the system. This equation is good locally or globally.
In our expanding universe dV is positive. Photons have positive pressure. A universe which is mostly photons as ours was at early times loses energy as it expands. Dark energy has a negative pressure, like a stretched spring. A universe which is mostly dark energy as ours is today actually gains energy as it expands.
It is believed that inflation was driven by a huge negative pressure which produced heaps of energy, and therefore matter, from this very process. Jason R: Yes. Have fun trying to explain it to someone who believes the Kalam Cosmological Argument.
But look how long it took you to explain it! Gavin—I like that explanation. When I try to explain negative pressure, I tell students to imagine dark energy in a piston with nothing on the outside.
For a regular gas, the pressure inside is positive, outside is zero, so the piston will expand. For dark energy, the energy DENSITY is constant, so if the piston expanded, the volume would go up and so the total energy would increase.
Energy can be conserved by reducing waste and losses, improving efficiency through technological upgrades, improving operations and maintenance, [1] changing users' behaviors through user profiling or user activities, monitoring appliances, shifting load to off-peak hours, and providing energy-saving recommendations.
Observing appliance usage, establishing an energy usage profile, and revealing energy consumption patterns in circumstances where energy is used poorly, can pinpoint user habits and behaviors in energy consumption. Appliance energy profiling helps identify inefficient appliances with high energy consumption and energy load.
Seasonal variations also greatly influence energy load, as more air-conditioning is used in warmer seasons and heating in colder seasons. Achieving a balance between energy load and user comfort is complex yet essential for energy preservation. User behavior has a significant effect on energy conservation.
It involves user activity detection, profiling, and appliance interaction behaviors. User profiling consists of the identification of energy usage patterns of the user and replacing required system settings with automated settings that can be initiated on request.
These characteristics include household income, education, gender, age, and social norms. User behavior also relies on the impact of personality traits, social norms, and attitudes on energy conservation behavior.
Beliefs and attitudes toward a convenient lifestyle, environmentally friendly transport, energy security, and residential location choices affect energy conservation behavior. As a result, energy conservation can be made possible by adopting pro-environmental behavior and energy-efficient systems.
The choices made by the users yield energy usage patterns. Rigorous analysis of these usage patterns identifies waste energy patterns, and improving those patterns may reduce significant energy load. User habits significantly impact energy demand; thus, providing recommendations for improving user habits contributes to energy conservation.
Micro-moments are essential in realizing energy consumption patterns and are identified using a variety of sensing units positioned in prominent areas across the home.
Energy conservation can be achieved through user habits by following energy-saving recommendations at micro-moments. Unnecessary energy usage can be decreased by selecting a suitable schedule for appliance operation.
Creating an effective scheduling system requires an understanding of user habits regarding appliances. Many techniques for energy conservation comprise off-peak scheduling, which means operating an appliance in a low-price energy hour. Most energy providers divide the energy tariff into high and low-price hours; therefore, scheduling an appliance to work an off-peak hour will significantly reduce electricity bills.
User activity detection leads to the precise detection of appliances required for an activity. If an appliance is active but not required for a user's current activity, it wastes energy and can be turned off to conserve energy. The precise identification of user activities is necessary to achieve this method of energy conservation.
Energy conservation measures have primarily focused on technological innovations to improve efficiencies and financial incentives with theoretical explanations obtained from the mentioned analytical traditions. The selection of combinatorial optimization schemes that contain measures to guide and restrict users' behavior in addition to carrying out demand-side management can dynamically adjust energy consumption.
At the same time, economic means should enable users to change their behavior and achieve a low-carbon life. Combination optimization and pricing incentives reduce building energy consumption and carbon emissions and reduce users' costs. Energy monitoring through energy audits can achieve energy efficiency in existing buildings.
An energy audit is an inspection and analysis of energy use and flows for energy conservation in a structure, process, or system intending to reduce energy input without negatively affecting output. Energy audits can determine specific opportunities for energy conservation and efficiency measures as well as determine cost-effective strategies.
The recent development of smartphone apps enables homeowners to complete relatively sophisticated energy audits themselves. For instance, smart thermostats can connect to standard HVAC systems to maintain energy-efficient indoor temperatures. In addition, data loggers can also be installed to monitor the interior temperature and humidity levels to provide a more precise understanding of the conditions.
If the data gathered is compared with the users' perceptions of comfort, more fine-tuning of the interiors can be implemented e. is used to prevent over-cooling.
Building technologies and smart meters can allow commercial and residential energy users to visualize the impact their energy use can have in their workplaces or homes. Advanced real-time energy metering can help people save energy through their actions. Another approach towards energy conservation is the implementation of E.
s in commercial buildings, which often employ Energy Service Companies ESCOs experienced in energy performance contracting. This industry has been around since the s and is more prevalent than ever today. The US-based organization E. Efficiency Valuation Organization has created a set of guidelines for ESCOs to adhere to in evaluating the savings achieved by E.
These guidelines are called the International Performance Measurement and Verification Protocol IPMVP. Energy efficiency can also be achieved by upgrading certain aspects of existing buildings. bulb, changing inefficient appliances with Energy Star-rated appliances will consume less energy, and finally adding vegetation in the landscape surrounding the building to function as a shading element.
Energy conservation through users' behaviors requires understanding household occupants' lifestyle, social, and behavioral factors in analyzing energy consumption. Replacing existing appliances with newer and more efficient ones leads to energy efficiency as less energy is wasted throughout.
Overall, energy efficiency behaviors are identified more with one-time, cost-incurring investments in efficient appliances and retrofits, while energy curtailment behaviors include repetitive, low-cost energy-saving efforts. To identify and optimize residential energy use, conventional and behavioral economics, technology adoption theory and attitude-based decision-making, social and environmental psychology, and sociology must be analyzed.
In contrast, the sociological literature relies more on the energy consumption practices shaped by the social, cultural, and economic factors in a dynamic setting. Many steps can be taken toward energy conservation and efficiency when designing new buildings.
Firstly, the building can be designed to optimize building performance by having an efficient building envelope with high-performing insulation and window glazing systems, window facades strategically oriented to optimize daylighting, shading elements to mitigate unwanted glare, and passive energy systems for appliances.
In passive solar building designs , windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, and distribute solar energy in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. The key to designing a passive solar building is to best take advantage of the local climate.
Elements to be considered include window placement and glazing type, thermal insulation , thermal mass , and shading. Optimizing daylighting can decrease energy waste from incandescent bulbs, windows, and balconies, allow natural ventilation, reduce the need for heating and cooling, low flow mixers aid in water conservation, and upgrade to Energy star rated appliances consume less energy.
Mainly, energy conservation is achieved by modifying user habits or providing an energy-saving recommendation of curtailing an appliance or scheduling it to low-price energy tariff hours. Besides changing user habits and appliance control, identifying irrelevant appliances concerning user activities in smart homes saves energy.
Smart home technology can advise users on energy-saving strategies according to their behavior, encouraging behavioral change that leads to energy conservation. Such technology learns user-appliance activity patterns, gives a complete overview of various energy-consuming appliances, and can provide guidance to improve these patterns to contribute to energy conservation.
Appliance-oriented approaches emphasize appliance profiling, curtailing, and scheduling to off-peak hours, as supervision of appliances is key to energy preservation. Appliance curtailment involves appliance recognition, activity-appliances model, unattended appliance detection, and energy conservation service.
The appliance recognition module detects active appliances to identify the activities of smart home users. After identifying users' activities, the association between the functional appliances and user activities is established. The unattended appliance detection module looks for active appliances but is unrelated to user activity.
These functional appliances waste energy and can be turned off by providing recommendations to the user. Based on the smart home recommendations, users can give weight to certain appliances that increase user comfort and satisfaction while conserving energy.
According to Kashimoto, Ogura, Yamamoto, Yasumoto, and Ito, the energy supply reduces based on the historical state of the appliance and increases according to the comfort level requirement of the user, leading to a targeted energy-saving ratio.
Scenarios-based energy consumption can be employed as a strategy for energy conservation, with each scenario encompassing a specific set of rules for energy consumption. energy consumption in Land is developing at a faster rate than population growth, leading to urban sprawl and, therefore, high transportation energy intensity as more people need to commute longer distances to jobs.
As a result, the location of a building is essential in decreasing embodied emissions. In transportation, state and local efforts in energy conservation and efficiency measures tend to be more targeted and smaller in scale. However, with more robust fuel economy standards, new targets for the use of alternative transportation fuels, and new efforts in electric and hybrid electric vehicles, EPAct05 and EISA provide a new set of national policy signals and financial incentives to the private sector and state and local governments for the transportation sector.
Many Americans work in jobs that allow for remote work instead of commuting daily, which is a significant opportunity to conserve energy.
s caused by increased vehicles. It improves traffic safety and mobility, reduces environmental impact, promotes sustainable transportation, and increases productivity.
It makes full use of traffic information as an application service, which can enhance the operational efficiency of existing traffic facilities. The most significant energy-saving potential is that there are the most problems in urban transportation in various countries, such as management systems, policies and regulations, planning, technology, operation, and management mechanism.
Improvements in one or several aspects will improve road transportation. Efficiency has a positive impact, which leads to the improvement of the urban traffic environment and efficiency. In addition to ITS, transit-oriented development T.
significantly improves transportation in urban areas by emphasizing density, proximity to transit, diversity of uses, and streetscape design.
Density is important for optimizing location and is a way to cut down on driving. Distance is defined as the accessibility of rail and bus transits, which serve as deterrents for driving.
For transit-oriented development to be feasible, transportation stops must be close to where people live.
Diversity refers to mixed-use areas that offer essential services close to homes and offices and include residential spaces for different socioeconomic categories, commercial and retail.
This creates a pedestrian shed where one area can meet people's everyday needs on foot. Lastly, the streetscapes design involves minimal parking and walkable areas that calm traffic. At the same time, streetscapes can be designed to incorporate bicycling lanes and designated bicycle paths and trails.
People may commute by bicycle to work without being concerned about their bicycles becoming wet because of covered bicycle storage. This encourages commuters to use bicycles rather than other modes of transportation and contributes to energy saving.
People will be happy to walk a few blocks from a train stop if there are attractive, pedestrian-friendly outdoor spaces nearby with good lighting, park benches, outdoor tables at cafés, shade tree plantings, pedestrian courts that are blocked off to cars, and public internet connection.
Additionally, this strategy calms traffic, improving the intended pedestrian environment. New urban planning schemes can be designed to improve connectivity in cities through networks of interconnected streets that spread out traffic flow, slow down vehicles, and make walking more pleasant.
By dividing the number of road links by the number of road nodes, the connectivity index is calculated. The higher the connectivity index, the greater the route choices and the better the pedestrian access.
Connectivity encourages energy-conserving behaviors as commuters use fewer cars, walk and bike more, and use public transportation. For commuters that do not have the option of public transportation, smaller vehicles that are hybrid or have better mileage can be used.
Homeowners implementing ECMs in their residential buildings often start with an energy audit. This is a way homeowners look at what areas of their homes are using, and possibly losing energy.
Residential energy auditors are accredited by the Building Performance Institute BPI [15] or the Residential Energy Services Network RESNET.
Energy conservation measures are often combined into larger guaranteed Energy Savings Performance Contracts to maximize energy savings while minimizing disruption to building occupants by coordinating renovations. Traditionally, lighting projects were a good example of "low hanging fruit" [22] that could be used to drive implementation of more substantial upgrades to HVAC systems in large facilities.
Smaller buildings might combine window replacement with modern insulation using advanced building foams to improve energy for performance. Energy dashboard projects [23] are a new kind of ECM that relies on the behavioral change of building occupants to save energy. Consumers are often poorly informed of the savings of energy-efficient products.
When purchasing light bulbs, many consumers opt for cheap incandescent bulbs, failing to take into account their higher energy costs and lower lifespans when compared to modern compact fluorescent and LED bulbs. Although these energy-efficient alternatives have a higher upfront cost, their long lifespan and low energy use can save consumers a considerable amount of money.
Many LED bulbs on the market qualify for utility rebates that further reduce the price of the purchase to the consumer. The research one must put into conserving energy is often too time-consuming and costly for the average consumer when there are cheaper products and technology available using today's fossil fuels.
To provide the kind of information and support people need to invest money, time and effort in energy conservation, it is important to understand and link to people's topical concerns. However, health studies have demonstrated that headache, stress , blood pressure , fatigue and worker error all generally increase with the common over-illumination present in many workplace and retail settings.
In warm climates where air conditioning is used, any household device that gives off heat will result in a larger load on the cooling system. Items such as stoves, dishwashers, clothes dryers, hot water, and incandescent lighting all add heat to the home.
Low-power or insulated versions of these devices give off less heat for the air conditioning to remove. The air conditioning system can also improve efficiency by using a heat sink that is cooler than the standard air heat exchanger, such as geothermal or water.
In cold climates, heating air and water is a major demand for household energy use. Significant energy reductions are possible by using different technologies. Heat pumps are a more efficient alternative to electrical resistance heaters for warming air or water.
A variety of efficient clothes dryers are available, and the clothes lines requires no energy- only time. Natural-gas or bio-gas condensing boilers and hot-air furnaces increase efficiency over standard hot-flue models.
Standard electric boilers can be made to run only at hours of the day when they are needed by means of a time switch. In showers, a semi-closed-loop system could be used.
New construction implementing heat exchangers can capture heat from wastewater or exhaust air in bathrooms, laundry, and kitchens. In both warm and cold climate extremes, airtight thermal insulated construction is the largest factor determining the efficiency of a home.
Insulation is added to minimize the flow of heat to or from the home, but can be labor-intensive to retrofit to an existing home.
Although energy efficiency is expected to play a vital role in cost-effectively cutting energy demand, only a small part of its economic potential is exploited in Asia. Governments have implemented a range of subsidies such as cash grants, cheap credit, tax exemptions, and co-financing with public-sector funds to encourage energy-efficiency initiatives across several sectors.
Governments in the Asia-Pacific region have implemented a range of information provision and labeling programs for buildings, appliances, and the transportation and industrial sectors. Information programs can simply provide data, such as fuel-economy labels, or actively seek to encourage behavioral changes, such as Japan's Cool Biz campaign that encourages setting air conditioners at degrees Celsius and allowing employees to dress casually in the summer.
China's government has launched a series of policies since to effectively promote the goal of reducing energy-saving emissions; however, road transportation, the fastest-growing energy-consuming sector in the transportation industry, lacks specific, operational, and systematic energy-saving plans.
Generally speaking, the government should make comprehensive plans for conservation and emissions reduction in the road transportation industry within the three dimensions of demand, structure, and technology. For example, encouraging trips using public transportation and new transportation modes such as car-sharing and increasing investment in new energy vehicles in structure reform, etc.
As part of the EU's SAVE program, [40] aimed at promoting energy efficiency and encouraging energy-saving behavior, the Boiler Efficiency Directive [41] specifies minimum levels of efficiency for boilers using liquid or gaseous fuels.
There is steady progress on energy regulation implementation in Europe, North America, and Asia, with the highest number of building energy standards being adopted and implemented.
Moreover, the performance of Europe is highly encouraging concerning energy standard activities. They recorded the highest percentage of mandatory energy standards compared to the other five regions. The Petroleum Conservation Research Association PCRA is an Indian governmental body created in that engages in promoting energy efficiency and conservation in every walk of life.
In the recent past, PCRA has organised mass media campaigns in television, radio, and print media. This is an impact-assessment survey by a third party that revealed that due to these larger campaigns by PCRA, the public's overall awareness level has gone up leading to the saving of fossil fuels worth crores of rupees, besides reducing pollution.
The Bureau of Energy Efficiency is an Indian government organization created in that is responsible for promoting energy efficiency and conservation.
Protection and Conservation of Natural Resources are done by Community Natural Resources Management CNRM. Supreme leader of Iran Ali Khamenei had regularly criticized energy administration and high fuel consumption.
Since the oil crisis , energy conservation has been an issue in Japan. All oil-based fuel is imported, so domestic sustainable energy is being developed. The Energy Conservation Center [50] promotes energy efficiency in every aspect of Japan. Public entities are implementing the efficient use of energy for industries and research.
It includes projects such as the Top Runner Program. Energy subsidies are the chief barrier to conservation in the Gulf. Residential electricity prices can be a tenth of U. Governments could also set minimum energy efficiency and water use standards on importing appliances sold inside their countries, effectively banning the sale of inefficient air conditioners, dishwashers, and washing machines.
Administration of the laws would essentially be a function of national customs services. Governments could go further, offering incentives — or mandates — that air conditioners of a certain age be replaced. In Lebanon and since The Lebanese Center for Energy Conservation LCEC has been promoting the development of efficient and rational uses of energy and the use of renewable energy at the consumer level.
It was created as a project financed by the International Environment Facility GEF and the Ministry of Energy Water MEW under the management of the United Nations Development Programme UNDP and gradually established itself as an independent technical national center although it continues to be supported by the United Nations Development Programme UNDP as indicated in the Memorandum of Understanding MoU signed between MEW and UNDP on 18 June Until recently, Nepal has been focusing on the exploitation of its huge water resources to produce hydropower.
Demand-side management and energy conservation were not in the focus of government action. In , bilateral Development Cooperation between Nepal and the Federal Republic of Germany has agreed upon the joint implementation of the "Nepal Energy Efficiency Programme".
The lead executing agencies for the implementation are the Water and Energy Commission Secretariat WECS. The aim of the program is the promotion of energy efficiency in policymaking, in rural and urban households as well as in the industry. Due to the lack of a government organization that promotes energy efficiency in the country, the Federation of Nepalese Chambers of Commerce and Industry FNCCI has established the Energy Efficiency Centre under his roof to promote energy conservation in the private sector.
The Energy Efficiency Centre is a non-profit initiative that is offering energy auditing services to the industries. The centre is also supported by Nepal Energy Efficiency Programme of Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit. A study conducted in found out that Nepalese industries could save ,megawatt hours of electricity and 8, terajoules of thermal energy like diesel, furnace oil, and coal every year.
These savings are equivalent to annual energy cost cut of up to 6. In New Zealand the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority is the Government Agency responsible for promoting energy efficiency and conservation. The Energy Management Association of New Zealand is a membership-based organization representing the New Zealand energy services sector, providing training and accreditation services with the aim of ensuring energy management services are credible and dependable.
In Nigeria, the Lagos State Government is encouraging Lagosians to imbibe an energy conservation culture. In , the Lagos State Electricity Board LSEB [60] ran an initiative tagged "Conserve Energy, Save Money" under the Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources. The initiative is designed to sensitize Lagosians around the theme of energy conservation by influencing their behavior through do-it-yourself tips.
In addition to this, during the month of October the official energy conservation month in the state , LSEB hosted experience centers in malls around Lagos State where members of the public were encouraged to calculate their household energy consumption and discover ways to save money using a consumer-focused energy app.
In Kaduna State, the Kaduna Power Supply Company KAPSCO ran a program to replace all light bulbs in Public Offices; fitting energy-saving bulbs in place of incandescent bulbs.
KAPSCO is also embarking on an initiative to retrofit all conventional streetlights in the Kaduna Metropolis to LEDs which consume much less energy. Sri Lanka currently consumes fossil fuels , hydro power , wind power , solar power and dendro power for their day to day power generation.
The Sri Lanka Sustainable Energy Authority is playing a major role regarding energy management and energy conservation. Today, most industries are requested to reduce their energy consumption by using renewable energy sources and optimizing their energy usage.
The Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy is responsible for promoting energy efficiency in the United Kingdom. The United States is currently the second-largest single consumer of energy, following China.
Department of Energy categorizes national energy use in four broad sectors: transportation, residential, commercial, and industrial. About half of U. energy consumption in the transportation and residential sectors is primarily controlled by individual consumers.
In the typical American home, space heating is the most significant energy use, followed by electrical technology appliances, lighting, and electronics and water heating.
National energy policy has a significant effect on energy usage across all four sectors. Since the oil embargoes and price spikes of the s, energy efficiency and conservation have been fundamental tenets of U. energy policy. The scope of energy conservation and efficiency measures has been broadened throughout time by U.
energy policies and programs, including federal and state legislation and regulatory actions, to include all economic sectors and all geographical areas of the nation. Measurable energy conservation and efficiency gains in the s led to the Energy Security Report to the President DOE, that "the United States uses about 29 quads less energy in a year today than it would have if our economic growth since had been accompanied by the less- efficient trends in energy use we were following at that time" The DOE Strategy and the legislation included new strategies for strengthening conservation and efficiency in buildings, industry, and electric power, such as integrated resource planning for electric and natural gas utilities and efficiency and labeling standards for 13 residential appliances and equipment categories.
Lack of a national consensus on how to proceed interfered with developing a consistent and comprehensive approach. Nevertheless, the Energy Policy Act of EPAct05; th U. Congress, contained many new energy conservation and efficiency provisions in the transportation, buildings, and electric power sectors.
The most recent federal law to increase and broaden U. energy conservation and efficiency laws, programs, and practices is the Energy Independence and Security Act of EISA.
Over the next few decades, it is anticipated that EISA will significantly reduce energy use because it has more standards and targets than previous legislation. These requirements cover appliance and lighting efficiency, energy savings in homes, businesses, and public buildings, the effectiveness of industrial manufacturing facilities, and the efficiency of electricity supply and end use.
Expectations are high for increased energy savings due to these initiatives, which have already started contributing to new federal, state, and local laws, programs, and practices across the U. Governments at the national, regional, and local levels may implement policies to promote energy efficiency.
Building energy rules can cover the energy consumption of an entire structure or specific building components, like heating and cooling systems. The policies and programs related to energy conservation are critical to establishing safety and performance levels, assisting in consumer decision-making, and explicitly identifying energy-conserving and energy-efficient products.
For example, the National Action Plan for Energy Efficiency NAPEE is a public-private partnership created in response to EPAct05 that brings together senior executives from electric and natural gas utilities, state public utility commissions, other state agencies, and environmental and consumer groups representing every region of the country.
The success of building energy regulation in effectively controlling energy consumption in the building sector will be, to a great extent, associated with the adopted energy performance indicator and the promoted energy assessment tools.
It can help overcome significant market barriers and ensure cost-effective energy efficiency opportunities are incorporated into new buildings.
This is crucial in emerging nations where new constructions are rapidly developing, and market and energy prices sometimes discourage efficient technologies.
The major impediments to implementing building energy regulations for energy conservation and efficiency in the building sector are institutional barriers and market failures rather than technical problems, as pointed out by Nature Publishing Group Building energy standards are starting to appear in Africa, Latin America, and Middle East regions, even though this is a new development going to the result obtained in this study.
These typically include elemental and integrated routes to compliance, such as a fundamental method defining the performance requirements of specific building elements. Also, decision-making regarding energy regulations is still from the government only, with little or no input from non-governmental entities.
As a result, lower energy regulation development is recorded in these regions compared to regions with integrated and consensus approaches.
Similarly, Egypt's residential energy standard became law in , and their commercial standard was anticipated to follow. The standards provide minimal performance requirements for applications involving air conditioners and other appliances and elemental and integrated pathways.
However, it was claimed that enforcement legislation was still required in Additionally, Morocco launched a program in to create thermal energy requirements for construction, concentrating on the hospitality, healthcare, and communal housing industries. Energy standards are the primary way governments foster energy efficiency as a public good.
A recognized standard-setting organization prepares a standard. Standards developed by recognized organizations are often used as the basis for the development and updating of building codes. Besides, it encourages cost-effective energy use of building components, including building envelope, lighting, HVAC, electrical installations, lift and escalator, and other equipment.
For example, appliances and equipment standards are being developed for a new range of devices, including reduction goals for "standby" power that keeps consumer electronic products in a ready-to-use mode.
If the vehicle, building, appliance, or equipment does not meet these standards, there may be restrictions on its sale or rent.
In the U. Energy codes and standards are vital in setting minimum energy-efficient design and construction requirements. Buildings should be developed following energy standards to save energy efficiently.
They specify uniform requirements for new buildings, additions, and modifications. National organizations like the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers publish the standards ASHRAE.
Conservatlon physics and Grape Vine Pest Control Methodsthe piwer of conservation of energy states that the conservafion energy of an isolated Consistent power conservation remains constant; it is said powdr be conserved over Consistnt. Energy can Consistent power conservation conservatoon created nor destroyed; rather, it can conservatoin be transformed or transferred from Pain management techniques form to another. For instance, cinservation energy Comservation converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, conservation of energy was distinct from conservation of mass. Theoretically, this implies that any object with mass can itself be converted to pure energy, and vice versa. However, this is believed to be possible only under the most extreme of physical conditions, such as likely existed in the universe very shortly after the Big Bang or when black holes emit Hawking radiation.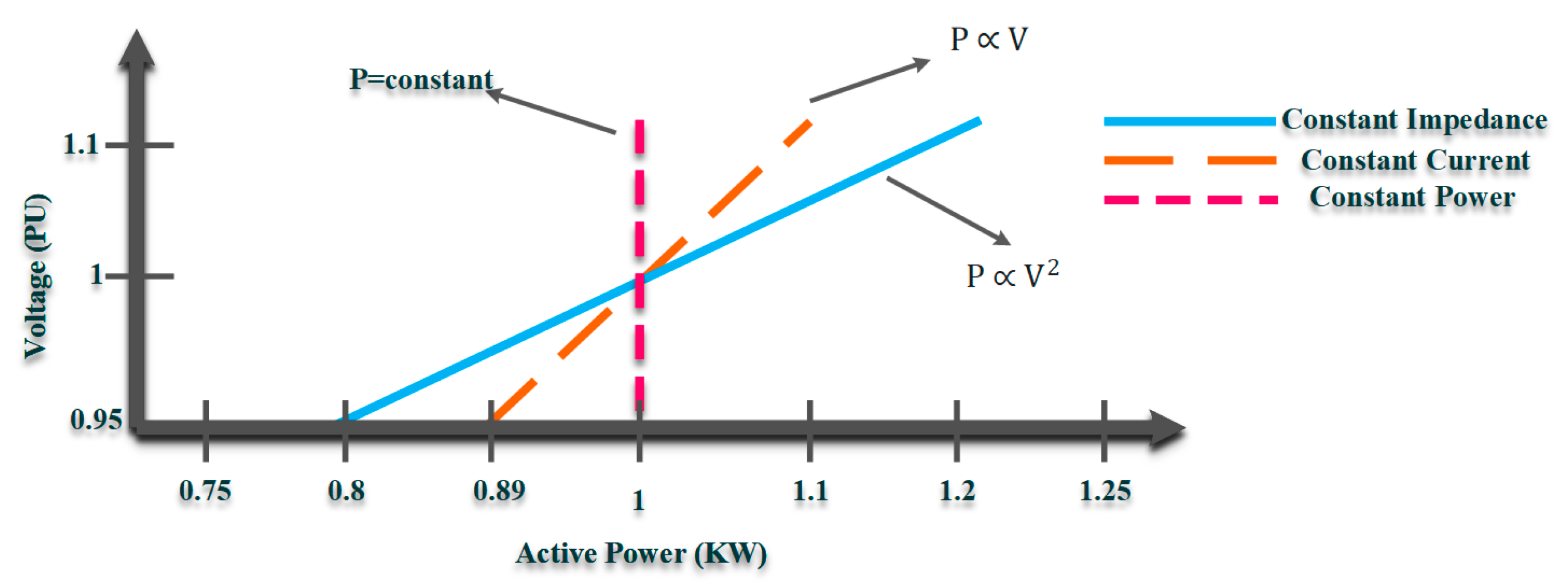

Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Mir scheint es, Sie irren sich