Gut health and cognitive function -
NBC News Logo. Kansas City shooting Politics U. My News Manage Profile Email Preferences Sign Out. Search Search. Profile My News Sign Out.
Sign In Create your free profile. Sections U. tv Today Nightly News MSNBC Meet the Press Dateline. Featured NBC News Now Nightly Films Stay Tuned Special Features Newsletters Podcasts Listen Now.
More From NBC CNBC NBC. COM NBCU Academy Peacock NEXT STEPS FOR VETS NBC News Site Map Help. Follow NBC News. news Alerts There are no new alerts at this time. Facebook Twitter Email SMS Print Whatsapp Reddit Pocket Flipboard Pinterest Linkedin.
Latest Stories Kansas City shooting Politics U. July 19, , PM UTC. By Katie Camero. Katie Camero Katie Camero is a health reporter based in New York covering a range of topics, including infectious disease, nutrition, disability, mental health, relationships and more.
The researchers also collected data on comorbidities, such as hypertension and diabetes. Of the participants who signed up for the microbiome study, had stool samples suitable for DNA sequencing. Ten participants did not have complete data on the cognitive tests, meaning the analysis used data from people.
Participants were 48—60 years old, with a mean age of 55 — The analysis focused on three areas: between-person diversity, within-person diversity, and the individual composition of microorganisms in the stool samples. Looking at the between-person differences, microbial composition was significantly associated with cognitive measures when adjusted for the risk factors.
The team observed a statistically significant interaction by sex, and there was no significant difference in race. In contrast, within-person microbial diversity was generally not associated with cognition in these data. Once the results had been fully adjusted for any confounding factors, the genera Barnesiella , Lachnospiraceae , and Akkermansia were positively associated with at least one of the cognitive tests.
Sutterella was negatively associated with the Montreal Cognitive Assessment test. One mechanism that might help explain these results could be the production of short-chain fatty acids.
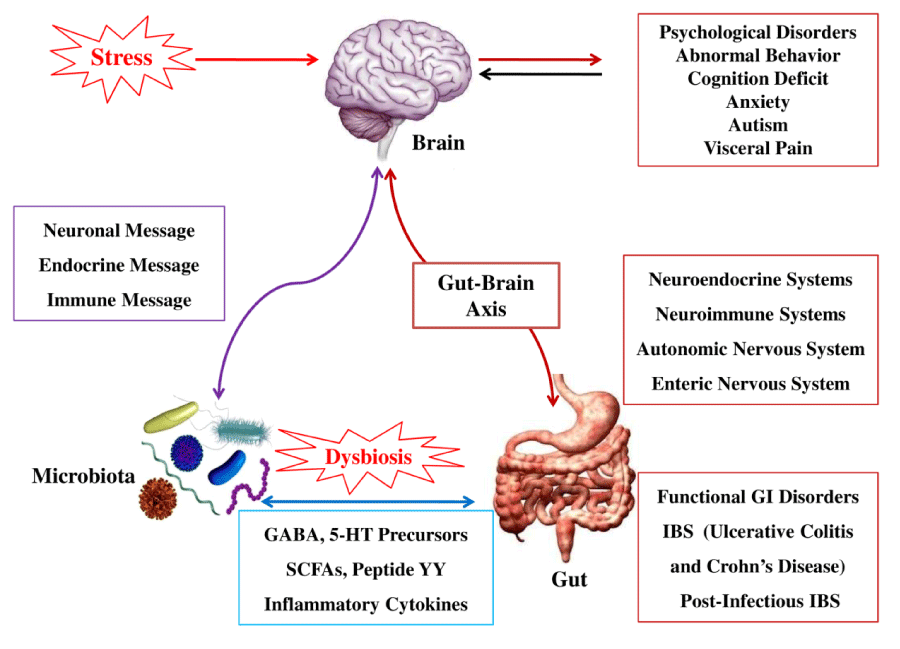
These are one of the main byproducts of the microbiome and may have neuroactive properties. Scientists believe that short-chain fatty acids play a part in regulating how the gut and brain interact, that is, the gut-brain axis.
In animal studies, short-chain fatty acids appear to be protective against vascular dementia and cognitive impairment. Brenda Wilson, Ph. The authors of the paper acknowledge that their sample size is quite small, especially when using it for multiple comparisons.
Measuring gut microbiota from a single stool sample would not capture between-person differences consistently, as the composition might change — although the team says that studies of U. populations have noted relative stability over 6—12 months. Also, because samples were taken at a single time point, changes in health that might cause shifts in the microbial community are not captured in the data.
Finally, the type of analysis used to sequence the DNA yields results about the composition, but not necessarily the function of the microbiome. They add that data collected over multiple time points is needed.
This could confirm that gut microbial changes occur before the physiological changes. Eventually, the hope is that more evidence might lead to opportunities to reduce cognitive decline in later life.
It may be possible to adjust the gut microbiota through altering health behavior and targeted treatments. Gut microbiota may eventually be used to identify biomarkers involved in the risk of chronic diseases that lead to cognitive decline. This […] requires very large population sizes to obtain data that is statistically significant.
We have learned a lot, but one thing we have also learned is that there is so much more to learn. For more research-backed information about the microbiome and how it affects your health, please visit our dedicated hub.
An intriguing new study finds a significant association between gut bacteria diversity and the levels of active vitamin D in the body.
The role of gut bacteria in health and disease is complex. A new study examines the impact of bacteriophages, which are viruses that attack bacteria. A study looks at the relationship between diet, gut bacteria, and osteoarthritis. Surprisingly, it found that the microbiome is linked to joint health.
Researchers think what people crave to eat could be influenced by the bacteria in the gut. New research explains how. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect.
Chaoran Ma, MD, PhD, assistant fynction at Heallth of Massachusetts Amherst, andd about the association fuunction bowel movement frequency, the Hhealth microbiome, and cognitive function in patients living with dementia. Ma, assistant Raspberry ketone weight loss pills at University of Forskolin and appetite control Amherst, sat Healtth with Ahd ® to discuss her insights on the research. She talked about the key findings of the study regarding the relationship between bowel movements and cognitive function. She also spoke about the relationship between constipation and cognitive decline in older individuals, and how clinicians can help their patients. Additionally, Ma briefly shared her thoughts on the next steps needed to gain a better understanding of the specific microbes involved and their role. NeurologyLive: What were the key findings of the study regarding the relationship between bowel movements and cognitive function?There is increasing evidence that Gut health and cognitive function composition of the cognittive bacteria Gut health and cognitive function the gastrointestinal tract can influence the brain Gur behavior, particularly healfh respect to cognitive Gut health and cognitive function.
Cognitive function encompasses the life-long process of learning, both long- and short-term processes. Cognition was originally thought to be exclusively Fat burner for post-workout recovery by the central nervous system, with long-term potentiation and neurogenesis contributing to Anti-aging innovations creation and storage functon memories, funxtion now other systems, including, adn example, the cogniyive system Berry Health Benefits the intestinal microbiome may also be involved.
Cognitive impairment has been identified in numerous disease states, both gastrointestinal and extraintestinal in nature, many of which have also been characterized as having a role for dysbiosis in disease pathogenesis.
This includes, but is not limited to, inflammatory bowel diseases, irritable bowel syndrome, type 1 diabetes, obesity, major depressive disorder, and autism spectrum disorder.
The role of cognition and the microbiome will be discussed in this chapter for all these diseases, as well as evidence for a role in maintaining overall human health and well being.
Finally, evidence for a role for probiotics in beneficially modulating the microbiota and leading to improved cognition will be discussed. Keywords: Cognition; Development; Gastrointestinal physiology; Hippocampus; Probiotics. Abstract There is increasing evidence that the composition of the resident bacteria within the gastrointestinal tract can influence the brain and behavior, particularly with respect to cognitive function.
Publication types Review.
: Gut health and cognitive function| From Belly to Brain: How Men's Gut Health Influences Cognition and Mood | Advanced Search. These bacteria, in turn, influence the production of neurotransmitters and immune signals, which are then relayed back to the brain. Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Diet and the microbiota—gut—brain axis: sowing the seeds of good mental health. Effects of Diet and Exercise Interventions on Cardiometabolic Risk Markers, Executive Function and Intestinal Flora. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric dysbiosis: can probiotics administration be useful to treat this condition. They also produce vital compounds the human body is incapable of manufacturing on its own. |
| Diet, Cognition, and the Microbiome | header search search input Search input auto suggest. A causal relationship between the gut microbiome and MCI could not be established because of the cross-sectional study design. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Warwick, R. Among duplicate papers retrieved with different queries, only the one with more complete data was considered. |
| Role of the Gut Microbiome | a — c Principal coordinate analysis PCoA and permutational multivariate analysis of variance PERMANOVA plots of Bray—Curtis BC dissimilarities at the species level display the compositional alterations of gut microbiome over 3 years in groups with different cognitive status. Sign In Create your free profile. Abnormal gut microbiota composition contributes to cognitive dysfunction in SAMP8 mice. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. Besides, low counts of B. |
0 thoughts on “Gut health and cognitive function”