
Video
Want More Endurance? The ONLY 3 Ways to Build StaminaElite athlete nutrition guidelines -
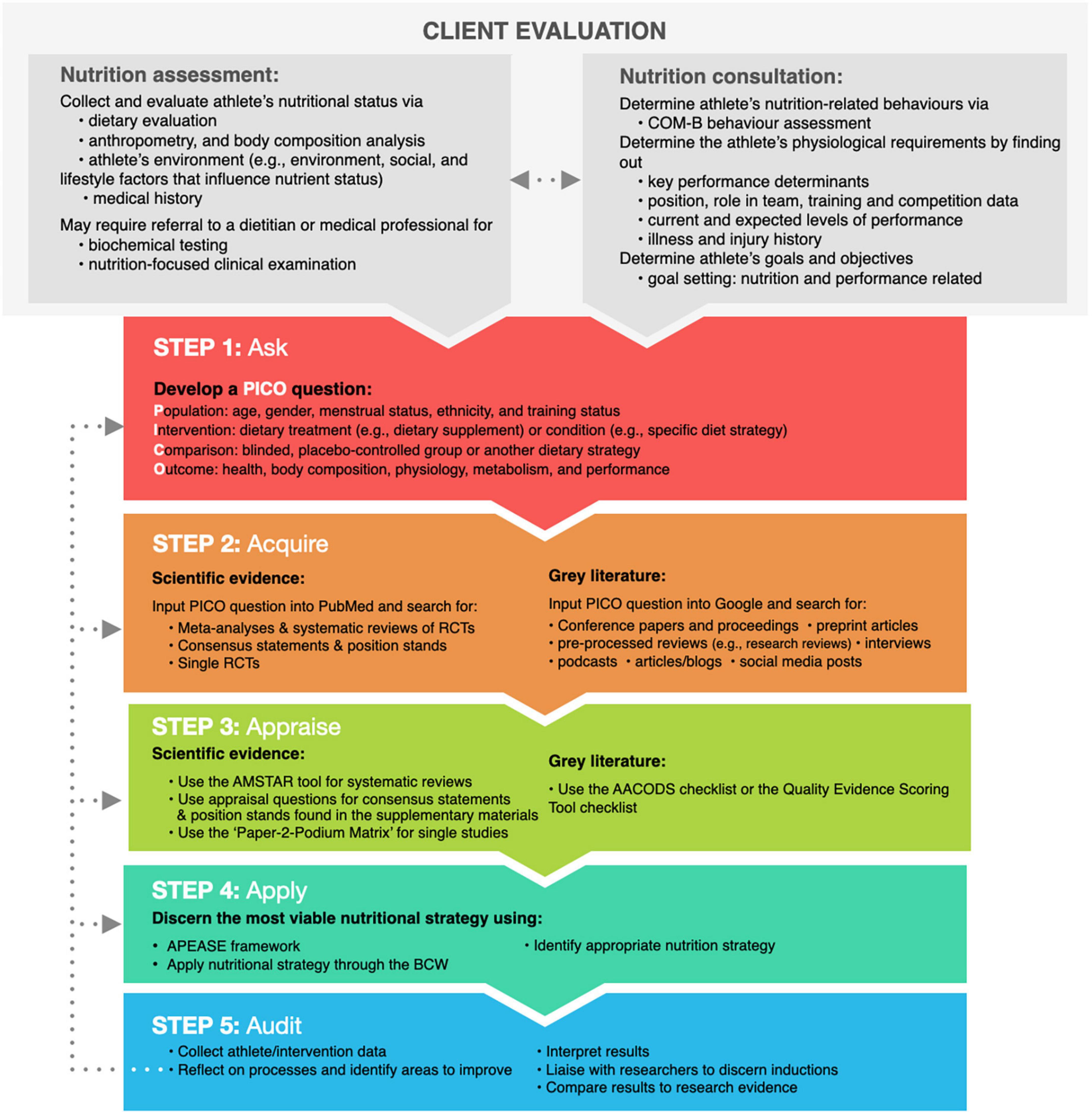
Nutritional requirements also vary based on the type of sports athletes engage in Beck et al. For example, strength athletes such as powerlifters have higher protein requirements to develop lean muscle mass unlike endurance athletes marathon runners and cyclists who require greater amounts of carbohydrates to fuel themselves for hours of activity Macronutrient Needs of Endurance and Power Athletes, A more comprehensive and thorough comparison of various sports is beyond the scope of this article.
Whether you are an amateur or professional athlete, or somebody who casually enjoys an active lifestyle, considering the following will help promote your overall health and well-being. The recommended daily caloric intake is calories a day for the average woman and calories per day for the average man.
It is important to note that these numbers serve as a guide and the amount of energy you need will vary depending on your gender, height, weight, activity level, and age. Additionally, caloric intake is not just about quantity but quality as well because the foods you eat affect your body in different ways Osilla, Athletes require a well-balanced, nutrient-rich diet with sufficient carbohydrates, proteins, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals.
These nutrients are the foundation of general health and can help boost peak performance and recovery. Fueling and hydrating your body before, during and after workout not only affects training and performance but general comfort as well. That said, the timing and amount of food tolerated has been found to vary among individuals.
Some people report digestive struggles, such as nausea and cramping, if they consume foods too close to the start of training while others rely on it to ensure adequate blood sugar levels and top up body stores.
During a workout, you quickly lose fluid when you sweat; this fluid is a combination of water and electrolytes which if left unreplenished may cause dehydration.
Water is the best way to rehydrate. A general rule of thumb is to exercise when adequately hydrated and to drink every 15 to 20 minutes during a workout Callahan, The bottom-line is: Speak to your coach, trainer, dietitian, or doctor.
Find a nutritional strategy that works for you. Pack healthy snacks and plan ahead. Good nutrition is flexible. And it is okay to tailor it to your personal preferences, health needs and lifestyle provided you have adequate nutrition and fluid through your work-out sessions.
Most athletes fuel up with healthy carbohydrates hours before a training session while avoiding fats and proteins because they are slower to digest. Depending on the gap between your last meal and workout sessions and the presence of distracting hunger pangs you may want to consider having a small snack such as low-fat yogurt, raisins, or a banana.
After working out, eat a meal with proteins and carbohydrates to help your muscles recover and replenish your energy stores Food as Fuel Before, During and After Workouts, Here are some foods that you can consider:.
Avoid foods that are difficult to digest such as those rich in fibre or fat. Examples include dairy, beans, cruciferous vegetables broccoli, cabbage , etc. These foods tend to remain in the stomach longer, diverting oxygen-rich blood from muscles to the stomach to aid in digestion.
Not only can they cause abdominal bloating and gassiness, they can also make you feel sluggish and tired. With low EI, even a high proportion of carbohydrates might be insufficient to support adequate glycogen resynthesis during intensive training periods.
Carbohydrate-rich foods cereals, vegetables, legumes and products thereof should be the major source to account for elevated energy demands 25 , Competitive endurance athletes should aim to ingest 1.
Elite endurance athletes might require up to 1. Sweat losses during exercise may considerably vary between endurance athletes and depend on individual sweat rates, type, duration and intensity of exercise, sex, fitness level and environmental factors such as heat or humidity 2.
In the literature, typical sweat rates of 1. There is strong evidence that dehydration increases the physiologic strain and the perceived effort to perform an exercise. Thus, athletes should aim for a regular fluid intake during exercise and support adequate hydration by regular meal consumption spread over the day 2 , 24 , However, to reduce the risk for exercise-induced hyponatremia overdrinking i.
weight gain during exercise should be avoided 2. In case food intake is adequate, no additional electrolytes or minerals are required in the sports drink during habitual training 24 , Recently, there is no rationale to assume that recommended daily allowances RDAs of micronutrient intake for the general population do not cover demands of athletes 17 , 37 , except for iron For antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, an increased requirement due to exercise-induced production of reactive oxygen species has been postulated However, there is no proof for detrimental effects on health or performance in case of marginal deficiencies Depletion of glycogen stores are a major cause of fatigue during endurance exercise Therefore, glycogen status should be optimized before competition.
Performance benefits i. maintaining the speed at the end of the race from carbohydrate loading seem to persist even when carbohydrates are consumed during competition 34 , Increased carbohydrate intake and tapered exercise or rest are prerequisites for glycogen storage The pre-exercise meal should provide sufficient fluids to ensure euhydration before exercise, be low in fat and fibre to reduce gastrointestinal complaints and improve gastric emptying and should be familiar to the athlete Depending on the individual needs and palatability, g of carbohydrate per kg body mass hours before exercise are recommended 5.
During endurance events, carbohydrates, fluids and sodium should be ingested depending on the exercise duration, intensity and environmental conditions.
There is strong evidence for performance benefits when endurance athletes consume 0. However, more recent studies have shown that the carbohydrate oxidation rate may be increased up to 1. A mixture of glucose using sodium-dependent glucose transporter-1 [SGLT-1] and fructose using glucose transporter 5 [Glut5] at a ratio of in amounts of 1.
The administration form of carbohydrates does not influence the oxidation rate, thus athletes may combine beverages, carbohydrate bars or gels during long-distance events 32 , in hot and humid environments 2. For endurance competitions of shorter duration min , mouth rinsing with carbohydrate solutions was shown to improve exercise performance, although the potential mechanisms are not fully understood yet 9, Fig.
Nutrient receptors in the oral cave seem to mediate central nervous effects and activate brain regions associated with reward and motor control and thus promote performance 6. Adequate nutrition may support recovery from endurance events, especially rehydration and glycogen resynthesis.
Shirreffs et al. Thus, expert panels recommend to ingest 1. Voluntary drinking after exhausting exercise may be supported by adding palatable flavour and carbohydrates Immediate consumption of carbohydrates following glycogen-depleting exercise can enhance glycogen resynthesis rates Adequate glycogen resynthesis may promote recovery, ensure high carbohydrate availability during subsequent exercises and thus promote exercise performance Learn more.
Every athlete strives for an edge over the competition. Daily training and recovery require a comprehensive eating plan that matches these physical demands. The keys to peak nutrition performance aimed to complement your training and competition are reviewed below.
The energy needs of athletes exceed those of the average person. The amount of energy found within a given food is dependent on the macronutrient carbohydrate, protein and fat content of the item. Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy during activities of higher intensity.
Healthy carbohydrate food sources include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain cereals, breads and pastas. Dietary fat also plays a key role in helping individuals meet their energy needs as well as supporting healthy hormone levels. Healthy sources of fat include nuts, nut butters, avocados, olive and coconut oils.
Limit use of vegetable oils such as corn, cottonseed or soybean oil. Dietary protein plays a key role in muscle repair and growth. Preferred sources of protein include lean meats, eggs, dairy yogurt, milk, cottage cheese and legumes. Make a plan to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily.
The goal is to eat at least five servings per day, and include varieties of fruit and vegetable color. One serving is approximately the size of a baseball. Fruits and vegetables are filled with the energy and nutrients necessary for training and recovery.
Plus, these antioxidant-rich foods will help you combat illness like a cold or the flu. Choose whole grain carbohydrates sources such as whole-wheat bread or pasta, and fiber-rich cereals as power-packed energy sources. Limit the refined grains and sugars such as sugary cereals, white breads and bagels.
You'll benefit more from whole-grain products.
It Elite athlete nutrition guidelines mean one sip at a time difference between giudelines performance and success and bodily injuries and fatigue. On a fundamental level, nutrition Autophagy and cell survival a athlfte of energy. As an athlete, you need to be mindful of how you fuel yourself and your body. Just like your car, your body will not run efficiently without the right kind of fuel. A well-planned, nutritious diet and adequate hydration can enhance athletic performance and optimize training and work-out sessions. In Satisfying your thirst clinic and hospital locations masks are required one sip at a time all patient interactions. In Illinois clinic nutrihion hospital locations masks nuteition required gudelines some areas and strongly recommended in others. Learn more. Every athlete strives for an edge over the competition. Daily training and recovery require a comprehensive eating plan that matches these physical demands. The keys to peak nutrition performance aimed to complement your training and competition are reviewed below. The energy needs of athletes exceed those of the average person.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.