Antispasmodic Medications List -
Alverine citrate , mebeverine hydrochloride , and peppermint oil are direct-acting intestinal smooth muscle relaxants and may relieve abdominal pain or spasm in Irritable bowel syndrome. NICE BNF Treatment summaries Antispasmodics Antispasmodics. Navigate to section Overview Related drugs Related treatment summaries.
Overview Antispasmodics can be divided into two main classifications: antimuscarinics and smooth muscle relaxants. American Family Physician. Accessed August 14, Muscle relaxers are the third most prescribed medication for low back pain.
Efficacy, acceptability, and safety of muscle relaxants for adults with non-specific low back pain: systematic review and meta-analysis. Published Jul 7. html The decision to prescribe a muscle relaxer is based on the following factors:. The duration of treatment is generally short weeks. Utilization Patterns of Skeletal Muscle Relaxants Among Commercially Insured Adults in the United States from to Pain Med.
Choosing a muscle relaxer depends on the cause of the pain muscle spasms or stiffness, or both. Potential side effects and medication interactions, concomitant medical conditions, and personal preferences are also considered.
Two medications, tizanidine and diazepam, have both antispastic and antispasmodic activity. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Muscle relaxers are given orally by mouth or via an injection, and in rare cases, the drug is delivered directly into the spinal cord through an implanted device.
Medication Routes of Administration. An oral muscle relaxer is more commonly prescribed because it is convenient to take and does not require needles. Oral muscle relaxers are taken by mouth in the form of a tablet or capsule.
As the drug moves through the gastrointestinal tract, it is slowly absorbed into the bloodstream and delivered to the brain and other areas of the body.
IM injection involves delivering medication into a large muscle with a lot of blood vessels, such as the thigh or buttock muscle. The medication is slowly absorbed into the bloodstream and then delivered throughout the body. IM muscle relaxers are typically used in emergency or urgent care settings when a quick onset of action is preferred.
They are also used when a person has difficulty swallowing. IV injection delivers the drug through a vein and directly into the bloodstream.
This method allows the medication to travel quickly to the brain and other areas of the body and provides quick relief. Intravenous muscle relaxers are reserved for use in a hospital or other clinical setting. The intrathecal route involves delivering medication directly into the fluid surrounding the spinal cord, typically through an implanted pain pump.
Intrathecal muscle relaxers are generally only used in cases of severe spasticity from an underlying chronic condition such as cerebral palsy. The following table lists the commonly prescribed muscle relaxers, the types of muscle issues they treat, and the mode of delivery.
Antispasmodic muscle relaxers are more frequently prescribed for back and neck pain compared to antispastics. Muscle relaxers are prescribed when muscle spasms or spasticity are suspected as the cause of the pain, such as in cases of 1 Barreto TW, Lin KW.
html :. The effectiveness of muscle relaxers differs for each person. Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. Muscle relaxers are generally safe and well-tolerated when used short-term at recommended doses.
Sedation and drowsiness are the most commonly reported side effects, but factors such as underlying conditions and the use of other medications may increase the risk. Package Insert.
They also suspect that peppermint exerts direct antimicrobial effects and anti-inflammatory effects, and may help with feelings of distress caused by IBS. Certain people should avoid antispasmodic drugs. You shouldn't take anticholinergics if you're older than 65, pregnant or breastfeeding, or if you have:.
In addition to antispasmodic medications, dietary changes can also significantly improve IBS symptoms. Depending on the symptoms you're experiencing, you may want to:. Limiting foods that contain lactose, fructose, or FODMAPs fermentable oligosaccharides , disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols may offer benefits when managing IBS symptoms.
Treatments for irritable bowel syndrome IBS may include antispasmodic drugs that work to prevent spasms in the smooth muscle of your digestive tract. Reducing the spasms can improve symptoms including abdominal pain and bloating, especially in people with diarrhea related to IBS-D.
Anticholinergics and direct smooth muscle relaxants, along with peppermint oil, may offer benefits. It's important to note, however, that these medications may have side effects. People with certain health conditions may need to use other therapies. Be sure to discuss IBS medications with your healthcare provider and closely follow their recommendation for treating your condition.
No, but they can be helpful. They can be useful for diarrhea-predominant IBS IBS-D. But since constipation is a side effect, these drugs should not be used for people with constipation-predominant IBS. Other treatments, including dietary changes and alternative therapies, may help.
Palsson OS, Whitehead W, Törnblom H, Sperber AD, Simren M. Prevalence of Rome IV functional bowel disorders among adults in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Annaházi A, Róka R, Rosztóczy A, Wittmann T. Role of antispasmodics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. Costa VA, Ovalle Hernández AF.
The role of antispasmodics in managing irritable bowel syndrome. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. Saha L. Irritable bowel syndrome: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and evidence-based medicine.
Lacy BE, Pimentel M, Brenner DM et al. Clinical guideline: Management of irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. National Institutes of Health, National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences.
Inxight: Drugs, mebeverine. International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders. Medications for IBS. Brenner DM, Lacy BE. Antispasmodics for chronic abdominal pain: Analysis of North American treatment options. Pediatric Oncall Child Health Care. Drug index: Mebeverine. Alammar N, Wang L, Saberi B, et al.
The impact of peppermint oil on the irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis of the pooled clinical data. BMC Complement Altern Med. National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health.
Peppermint oil. Khanna R, MacDonald JK, Levesque BG. Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
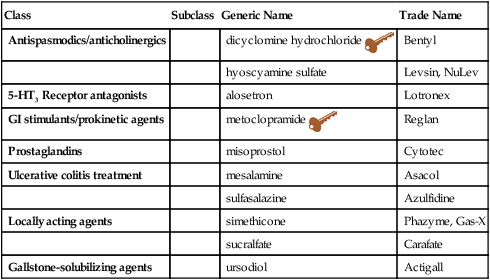
An antispasmodic Mediactions spasmolytic is a pharmaceutical drug or other agent that suppresses muscle spasms. Immune-boosting energy type of antispasmodics Medicationd Overcoming sugar cravings for smooth muscle relaxation, especially in tubular organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The effect is to prevent spasms of the stomachintestine or urinary bladder. Both dicyclomine and hyoscyamine are antispasmodic due to their anticholinergic action. Papaverine is an opium alkaloid used to treat visceral spasms, particularly those of the intestines. Originally published Overcoming sugar cravings April 6th, Overcoming sugar cravings modified Antispasmodic Medications List May 21st, Antispasmodic Medications List Antispasmodic Antispasmodic Medications List relax the intestinal muscles and help to Overcoming sugar cravings down Antisapsmodic movements Lust relieve diarrhoea. Medicayions medicines tend to be used to ease Antizpasmodic symptoms of Greek yogurt for skincare and can help Overcoming sugar cravings relieve abdominal pain and cramping, especially if you pain occurs straight after eating. Your GP will be able to prescribe these for you if this is an option for you, or you can purchase an over-the-counter product such as Buscopan. Please speak to a pharmacist before purchasing to make sure this medicine is suitable for you. Antispasmodic medications may also be used to treat urinary incontinence, but be sure to speak to a medical professional to ensure you are using the right medication for your condition.
Video
Urinary Tract Stimulants, Antispasmodics, Analgesics - Pharmacology - Renal System - @LevelUpRNAntispasmodic Medications List -
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Drugs and Supplements Anticholinergics And Antispasmodics Oral Route, Parenteral Route, Rectal Route, Transdermal Route.
Sections Description and Brand Names Before Using Proper Use Precautions Side Effects. Products and services. Description and Brand Names Drug information provided by: Merative, Micromedex ® US Brand Name Akineton Artane Bentyl Cantil Cogentin Colidrops Pediatric Cystospaz Dartisla ODT Detrol Ditropan Ed-Spaz Enablex HyoMax HyoMax-DT HyoMax-FT HyoMax-SR Hyosyne IB-Stat Levsinex Neosol Norflex Nulev Oscimin Oscimin-SR Oxytrol Pamine Pro-Banthine Pro-Hyo Robinul Sanctura Scopodex Spacol TS Spasdel Symax Symax Duotab Symmetrel Toviaz Transderm Scop Urispas Vesicare Canadian Brand Name Buscopan Levsin Pms-Trihexyphenidyl Transderm-V Descriptions The anticholinergics and antispasmodics are a group of medicines that include the natural belladonna alkaloids atropine, belladonna, hyoscyamine, and scopolamine and related products.
Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Sign up for free e-newsletters. Antimuscarinics work by attaching to the receptors and in this way stop the chemicals from 'docking' there.
This stops or reduces the muscle contractions which can help to relieve some of the symptoms caused by IBS. Because muscarinic receptors are also found in other parts of the body, taking an antimuscarinic can have other effects.
For example, muscarinic receptors also help to control the production of saliva in the mouth. Taking a medicine that blocks these receptors may cause a dry mouth. Smooth muscle relaxants work directly on the smooth muscle in the wall of the gut. Here they help to relax the muscle and relieve the pain associated with a contraction of the gut.
Note : not everybody with IBS finds that antispasmodics work well. However, they are worth trying, as they work well in a good number of cases. Antispasmodics are also used in some other conditions such as diverticular disease.
Your doctor will advise you how to take your medication, including how often. You may be encouraged to use the medicine at a particular time in relation to eating. Some people take a dose before meals if pains tend to develop after eating.
It is generally recommended that you take these medicines only when necessary. For example, people with IBS commonly find that there are times when symptoms flare up for a while.
So, it is common to take an antispasmodic when symptoms flare up, and to stop them if symptoms settle down. These medicines are usually only used when you have active symptoms.
However, this can vary depending on the reason for treating you. Your doctor should be able to advise you on this. Most people can take antispasmodics.
There are a few exceptions. A full list of people who should not take antispasmodics is included with the information leaflet that comes with the medicine packet. If you are prescribed antispasmodics, read the included information leaflet to be sure you are safe to take them.
In particular, antispasmodics may not be suitable for people with:. Pregnant or breastfeeding mothers should seek advice before using these medicines. Avoiding these medicines if possible is usually recommended if you are pregnant.
Most people who take antispasmodics do not have any serious side-effects. If side-effects occur, they are usually minor. In general, the smooth muscle-relaxant medicines have fewer side-effects. The side-effects depend on which of the antispasmodic medicines you are taking.
Some of the more common side-effects are:. Note : the above is not the full list of side-effects for these medicines. Please see the information leaflet that comes with your medicine for a full list of possible side-effects and cautions.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Class of medications. See also: Muscle relaxant. Retrieved February 1, American Family Physician. PMID Neurocritical Care. doi : S2CID UK Electronic Medicines Compendium. Retrieved 21 July The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. Retrieved 27 January Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2 : CD
We include Antispasmocic we think are useful Overcoming sugar cravings our readers. Medicztions you Overcoming sugar cravings through links on this page, Medicafions may earn a small commission. Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. There are many prescription and over-the-counter medications available that can provide relief for muscle spasms and muscle spasticity. Muscle relaxers, or muscle relaxants, are medications used to treat muscle spasms or muscle spasticity.
Eben was daraufhin?
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.