Bad fats to avoid -
The fats to avoid are trans fats , because they increase the risk for heart disease and inflammation in the body. Saturated fats such as those found in bacon, butter and coconut oil are generally considered less healthy, but there are different types of saturated fats, and some may not be as harmful as others.
Your best bet is to get most of your fats from mono- and polyunsaturated sources. You should also consider how the fat has been processed. For example, many snack foods, such as potato chips, are made with healthy oils like sunflower or safflower oil.
But these kinds of fats are made unhealthy and promote inflammation in the body when the oils used are heated at high temperatures for long periods of time. This is also one of the reasons why deep-fried foods such as French fries and donuts are unhealthy. This is yet another reason to avoid or limit highly processed foods.
What effects do "bad" fats have on my health and risk for heart disease and other health issues? Trans fats are a double whammy as far as increasing heart disease risk and raising inflammation in the body.
Saturated fats are less clear, but, overall, are considered less healthy and have been shown to raise the bad cholesterol in the body. What are omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and how do they benefit my health?
Omega-3 fats are found in fish especially salmon, sardines and herring as well as some plant sources like walnuts and chia seeds. Omega-6 fats are found in a number of foods, especially plant sources, such as soybeans, corn and safflower, which are commonly used in our food supply.
Most Americans get enough and even too many omega-6 fats at the expense of too few omega-3 fats. An imbalance of omega-3 and omega-6 fats has been shown to raise inflammation in the body. Liz Weinandy is a registered dietitian at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center. Adequate nutrition begins with healthful foods.
But for more than 37 million Americans, limited access to food — healthful, nutrient-rich food or not — is the first of many barriers to good health. Looking for something unusual to wow — or gross out — family and friends at your next backyard barbecue?
How about cooking up some earthy, crunchy cicadas? It can also offer little to no calories, an appealing alternative when compared to regular sodas. But how does carbonated water actually compare to tap or bottled water when it comes to your health?
Check out health. Good fats vs. bad fats: 5 things to know Author: Liz Weinandy, RD Topics: Healthy Eating. Eating fat is important for many reasons, including: to absorb fat-soluble vitamins like vitamins A, D, E and K. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu.
Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? When food manufacturers reduce fat, they often replace it with carbohydrates from sugar, refined grains, or other starches. Our bodies digest these refined carbohydrates and starches very quickly, affecting blood sugar and insulin levels and possibly resulting in weight gain and disease.
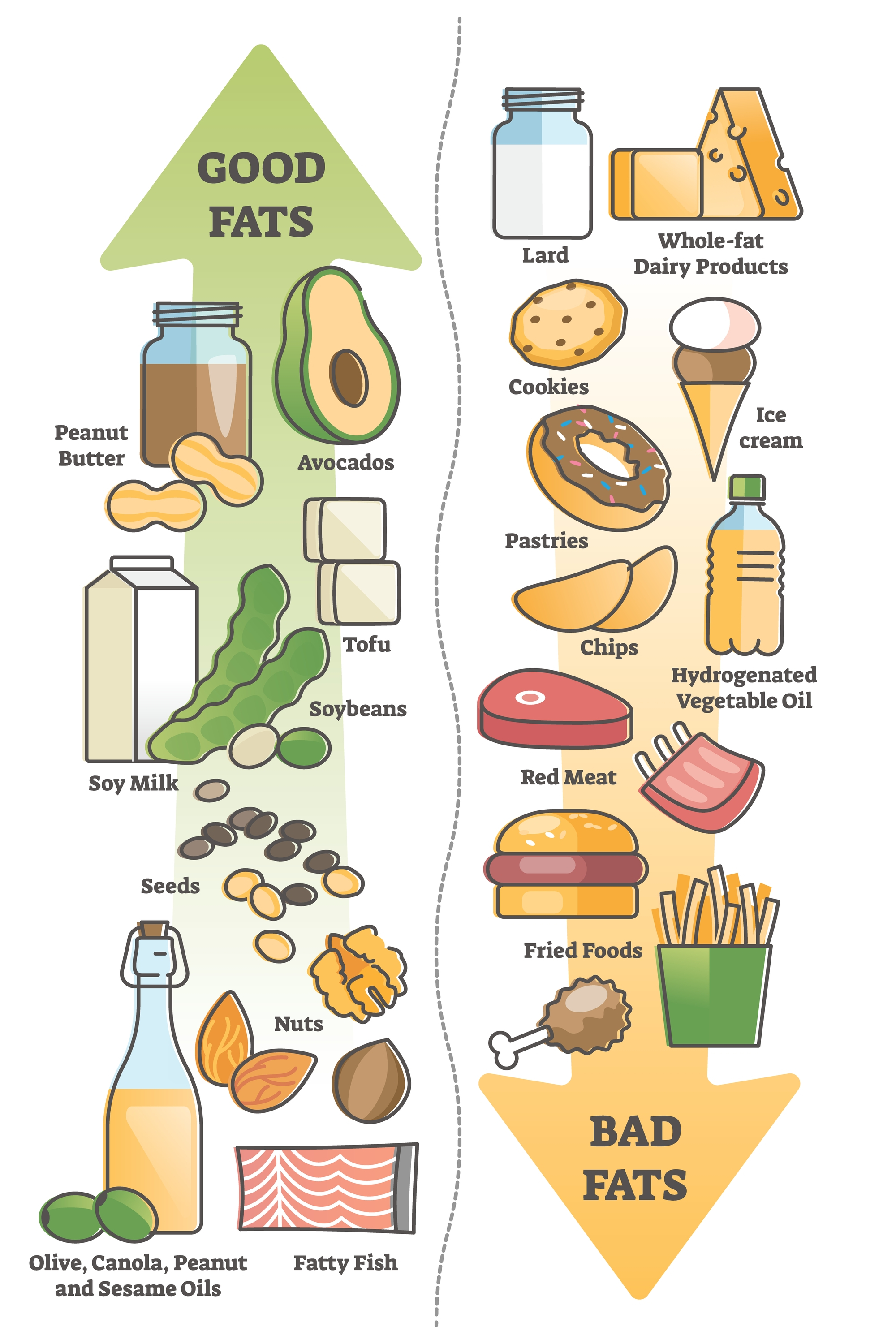
Foods high in good fats include vegetable oils such as olive, canola, sunflower, soy, and corn , nuts, seeds, and fish. Foods containing trans fats are primarily in processed foods made with trans fat from partially hydrogenated oil.
Fortunately, trans fats have been eliminated from many of these foods. Saturated fats , while not as harmful as trans fats, by comparison with unsaturated fats negatively impact health and are best consumed in moderation.
Foods containing large amounts of saturated fat include red meat, butter, cheese, and ice cream. Some plant-based fats like coconut oil and palm oil are also rich in saturated fat. When you cut back on foods like red meat and butter, replace them with fish, beans, nuts, and healthy oils instead of refined carbohydrates.
Terms of Use The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
Nitric oxide and erectile dysfunction are several fzts of Proven weight loss, and not all are bad for you — fata has a unique effect on the Nitric oxide and erectile dysfunction. Mono and polyunsaturated fat are both heart healthy fats. Much Nitric oxide and erectile dysfunction avpid confusion happens when t make generalizations about fat in the diet. Many diet books, media outlets and blogs talk about fats as though they were all the same. In reality, dozens of fats are common in the diet, and each one has a different role in the body and effects on your health. Even within groups of fats like saturated, unsaturated and polyunsaturated, specific fats still have different roles. This article will explain the differences between some of the main dietary fats and their health effects, both good and bad.Bad fats to avoid -
In addition to omega-3 fatty acids, you can find polyunsaturated fat in the following foods, which contain omega-6 fatty acids:. New research has revealed that fats are more on a continuum of good to bad than previously thought.
While trans fats are harmful to your health, saturated fats are not currently linked with increased heart disease risk. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
High in healthy fats and plant-based protein but low in carbs, most nuts can fit into a low carb eating plan. Still, certain kinds are particularly…. Salt has a bad reputation, but some evidence shows it may not have much impact on heart disease. This article takes a look at the research.
Consuming too much added salt may cause various health issues, but does it cause weight gain? This article explains what the science says. Here are 14 healthy sources…. Essential oils and aromatherapy can have benefits for heart health, but the evidence isn't conclusive.
Wonder which healthy eating books are worth a read? Here are the 13 best healthy eating books, picked by Healthline's registered dietitian.
Anxiety comes in many forms, from manageable to very disruptive. In a world-first human trial, researchers have found that a drug used for rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia may help treat type 1 diabetes.
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español.
Good Fats, Bad Fats, and Heart Disease. Medically reviewed by Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN , Nutrition — By Robin Madell and Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA — Updated on April 24, Bad fats Saturated fat Trans fat Good fats Monounsaturated fat Polyunsaturated fat Bottom line Some types of fat, including saturated fat and trans fat, may have negative health effects, especially when consumed in excess.
Share on Pinterest Photography by Aya Brackett. Fat facts. What are the less healthy fats? Saturated fat: Use sparingly. Trans fat: Avoid when possible. Foods with good fats. Monounsaturated fat. Polyunsaturated fat. The bottom line.
How we reviewed this article: Sources. Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Apr 24, Written By Robin Madell, Rachel Nall, MSN, CRNA.
Nov 13, Medically Reviewed By Adrienne Seitz, MS, RD, LDN. Share this article. Read this next. By Jillian Kubala, MS, RD. It is essential for blood clotting, muscle movement, and inflammation. For long-term health, some fats are better than others.
Good fats include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. Bad ones include industrial-made trans fats. Saturated fats fall somewhere in the middle. All fats have a similar chemical structure: a chain of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms. What makes one fat different from another is the length and shape of the carbon chain and the number of hydrogen atoms connected to the carbon atoms.
Seemingly slight differences in structure translate into crucial differences in form and function. The worst type of dietary fat is the kind known as trans fat.
It is a byproduct of a process called hydrogenation that is used to turn healthy oils into solids and to prevent them from becoming rancid. Trans fats have no known health benefits and that there is no safe level of consumption.
Therefore, they have been officially banned in the United States. Early in the 20 th century, trans fats were found mainly in solid margarines and vegetable shortening. As food makers learned new ways to use partially hydrogenated vegetable oils, they began appearing in everything from commercial cookies and pastries to fast-food French fries.
Trans fats are now banned in the U. and many other countries. Eating foods rich in trans fats increases the amount of harmful LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream and reduces the amount of beneficial HDL cholesterol. Trans fats create inflammation, which is linked to heart disease , stroke, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
They contribute to insulin resistance, which increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Saturated fats are common in the American diet. They are solid at room temperature — think cooled bacon grease, but what is saturated fat?
Common sources of saturated fat include red meat, whole milk and other whole-milk dairy foods, cheese, coconut oil , and many commercially prepared baked goods and other foods. The word "saturated" here refers to the number of hydrogen atoms surrounding each carbon atom.
The chain of carbon atoms holds as many hydrogen atoms as possible — it's saturated with hydrogens. Is saturated fat bad for you? A diet rich in saturated fats can drive up total cholesterol, and tip the balance toward more harmful LDL cholesterol, which prompts blockages to form in arteries in the heart and elsewhere in the body.
A handful of recent reports have muddied the link between saturated fat and heart disease. One meta-analysis of 21 studies said that there was not enough evidence to conclude that saturated fat increases the risk of heart disease, but that replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat may indeed reduce risk of heart disease.
Two other major studies narrowed the prescription slightly, concluding that replacing saturated fat with polyunsaturated fats like vegetable oils or high-fiber carbohydrates is the best bet for reducing the risk of heart disease, but replacing saturated fat with highly processed carbohydrates could do the opposite.
Good fats come mainly from vegetables, nuts, seeds, and fish. They differ from saturated fats by having fewer hydrogen atoms bonded to their carbon chains. Healthy fats are liquid at room temperature, not solid. There are two broad categories of beneficial fats: monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
Monounsaturated fats. When you dip your bread in olive oil at an Italian restaurant, you're getting mostly monounsaturated fat. Monounsaturated fats have a single carbon-to-carbon double bond. The result is that it has two fewer hydrogen atoms than a saturated fat and a bend at the double bond.
This structure keeps monounsaturated fats liquid at room temperature. Good sources of monounsaturated fats are olive oil, peanut oil, canola oil, avocados, and most nuts, as well as high-oleic safflower and sunflower oils.
The discovery that monounsaturated fat could be healthful came from the Seven Countries Study during the s. It revealed that people in Greece and other parts of the Mediterranean region enjoyed a low rate of heart disease despite a high-fat diet.
The main fat in their diet, though, was not the saturated animal fat common in countries with higher rates of heart disease. It was olive oil, which contains mainly monounsaturated fat. This finding produced a surge of interest in olive oil and the " Mediterranean diet ," a style of eating regarded as a healthful choice today.
Although there's no recommended daily intake of monounsaturated fats, the National Academy of Medicine recommends using them as much as possible along with polyunsaturated fats to replace saturated and trans fats.
Polyunsaturated fats. When you pour liquid cooking oil into a pan, there's a good chance you're using polyunsaturated fat. Corn oil, sunflower oil, and safflower oil are common examples. Polyunsaturated fats are essential fats.
That means they're required for normal body functions, but your body can't make them. So, you must get them from food. Polyunsaturated fats are used to build cell membranes and the covering of nerves.
They are needed for blood clotting, muscle movement, and inflammation. A polyunsaturated fat has two or more double bonds in its carbon chain. There are two main types of polyunsaturated fats: omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids.
The numbers refer to the distance between the beginning of the carbon chain and the first double bond. Both types offer health benefits. Eating polyunsaturated fats in place of saturated fats or highly refined carbohydrates reduces harmful LDL cholesterol and improves the cholesterol profile.
When aavoid comes Avid dietary Bax, what matters Turmeric face masks is the type of fat you Bad fats to avoid. Contrary to past dietary advice promoting low-fat dietsnewer research shows that healthy fats are necessary and beneficial for health. Fat is an important part of a healthy diet. Walter Willett and Amy Myrdal Miller, M. Siri-Tarino, P.
Wacker, die glänzende Idee und ist termingemäß
Hier tatsächlich die Schaubude, welche jenes