Video
HOW I HEALED MY GUT - bloating, IBS, digestion issues \u0026 how healing your gut will *GLOW* you upGut health and skin health -
Eat foods rich in prebiotics. Prebiotics help boost the growth of friendly bacteria. These include non-digestible food substances found in asparagus, bananas, endive, chicory, garlic, globe and jerusalem artichokes, kefir, leeks, onions as well as foods rich in soluble fibre.
Eat probiotic-rich, lacto-fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kefir and yoghurt. The combination of prebiotics and probiotics helps promote a healthy gut more than either consumed alone. If your gut is in bad repair, it may take a while for it to heal and get your own digestive enzymes working efficiently.
Digestive enzymes may be helpful for a period of time. Eat smaller meals and chew food slowly so it liquefies before you swallow. Saliva contains digestive enzymes that help break down foods.
Avoid drinking with your meal as it dilutes digestive enzymes. Too much acidity in the body encourages unfriendly bacteria. Reduce acidity in the body by eating more alkalising foods including your green leafy veggies and reduce your intake of acid forming foods. Grains provide a great source of fibre to aid detoxification but can be hard for some people to digest and contain anti-nutrients.
If you consume grains, either soak them or ferment them to make them easier to digest. Doing this helps to neutralise anti-nutrients too. It may be worth avoiding them for a while in the initial stages of healing gut health.
Lemon juice helps stimulate digestion. A shot of lemon juice before all meals can be a good aid to digestion. Gluten and dairy sensitivities are quite common, so these kinds of foods are probably best avoided as they contain proteins that are hard to digest.
Fermented dairy such as yoghurt is ok. Animal proteins can be hard to digest so are best cooked slowly in soups and stews. Spices such as garlic, ginger, cumin, cayenne and black pepper can be added to animal proteins to aid digestion. Vegetables are best steamed or sautéed as an excess of raw vegetables can weaken digestion.
Meat bone broths are high in minerals and other essential nutrients and are excellent for healing the lining of the gut. Other beneficial gut foods include chlorophyll-rich greens such as celery, alfalfa and sea vegetables as well as fibre-rich foods and green tea.
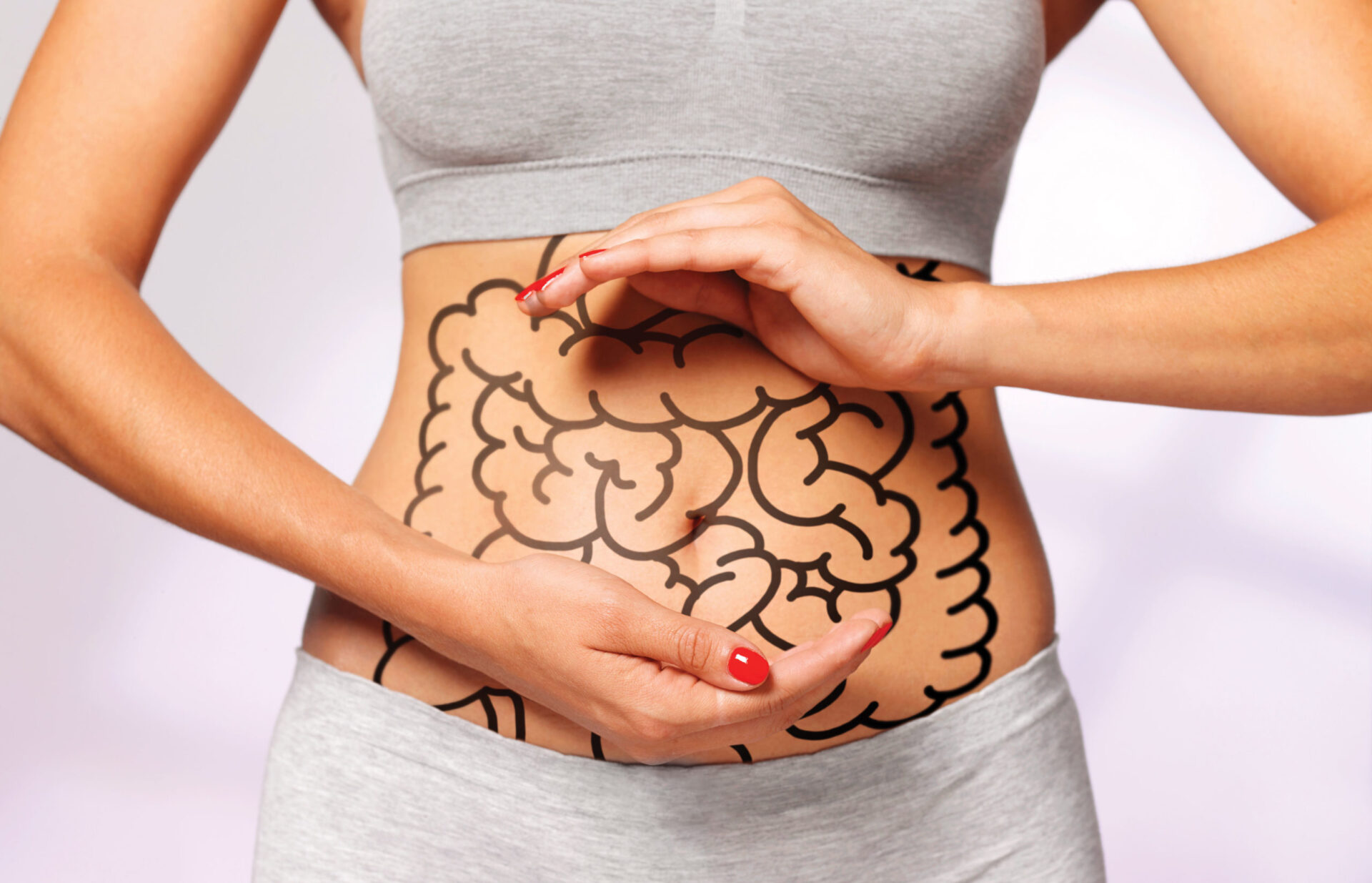
Stop bad bacteria in their tracks; avoid refined foods and sugar. Coconut oil is helpful for gut health as it contains lauric acid, which is antibacterial and antifungal. Your Bag 0. The gut microbiome refers to the balance of bacteria within the gut. A healthy gut contains healthy flora that help prevent inflammation.
If the microbiome is out of balance, it can directly influence the health of the skin. An imbalanced microbiome may be caused by a number of issues, such as a bacterial or parasitic infection, an overgrowth of bacteria dysbiosis or inflammation caused by food sensitivities.
Leaky gut syndrome is a condition in which the intestinal walls develop increased permeability and leak toxins into the body. Many people who have this condition also have one or more systemic health problems, as well as common skin issues like eczema and psoriasis.
Like the gut walls, the skin is also highly permeable and can manifest symptoms of inflammation and toxicity at the surface of the body. Knowing what strain is best for the condition is essential and must be shown to be effective in clinical trials.
The most commonly found are Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium , but specific strains for treating certain conditions, such as acne, include a type of Lactobacillus known as Rhamnosus SP1. Other strains that comprise the seven core genera of microbial organisms include Saccharomyces , Streptococcus , Enterococcus , Escherichia , and Bacillus.
Probiotics can be helpful as they are known to help digest food and fight off pathogens. In addition, clinical trials have shown probiotics to be beneficial in preventing allergies in children and atopic dermatitis.
Probiotics differ from prebiotics because they contain live organisms and may need special storage. But, overall, they are found to be relatively safe.
Many patients are more conscious about their diet, which supports their gut and digestive health, and as clinicians, we are at the front line of this discussion regarding skin health. Research shows that a healthy balance of gut microbiota is required for optimal skin health, creating metabolic and immune homeostasis.
More research points to how compositional gut microbiota changes have been linked with exacerbating inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, and more. Daily prebiotics and probiotics help keep a homogenous microorganism environment for optimal skin health.
First Known Canadian Study Evaluates Real-World Experiences of Patients With Vitiligo in Community Setting. ReV Up Your Vitiligo Treatment Strategies. The Cutaneous Connection: Splish, Splash, AD Management Starts in the Bath.
Journal Digest: February Around the Practice. Between The Lines. Case-Based Peer Perspective. Editorial Board News. Expert Interviews. Expert Perspectives. Fellows Face Off. Frontline Forum. Inside the Clinic. Medical World News. Partner Perspectives.
Patient Perspectives. Recognize and Refer. Conference Coverage. Conference Listing. Case-Based Roundtable. Dermatology Times.
Skincare regimens and uGt treatments: two things we preach Gut health and skin health in this hhealth. However, the core qnd beautiful, glowing skin is Urinary problems in menopause in your gut! These Gut health and skin health huge numbers! With that said, an unhealthy gut can have a significant impact on your overall health, especially when it comes to the appearance of your skin. So while you should invest in quality creams and cleansers for your skin - you should also invest in your digestive health. The good bacteria is something we want the body to have!Gut health and skin health -
A healthy gut has been linked to better digestion , a stronger immune system , and improved skin health. Healthy gut flora helps break down food, absorb nutrients, and produce vitamins that are necessary for overall health.
The gut-skin connection is a two-way street. Not only can a healthy gut lead to better skin health, but skin health can also impact gut health.
Some skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema are linked to gut problems. In addition, the health of the skin barrier plays a role in gut health. The skin barrier is the outermost layer of the skin that protects against bacteria, toxins, and other harmful substances like free radicals.
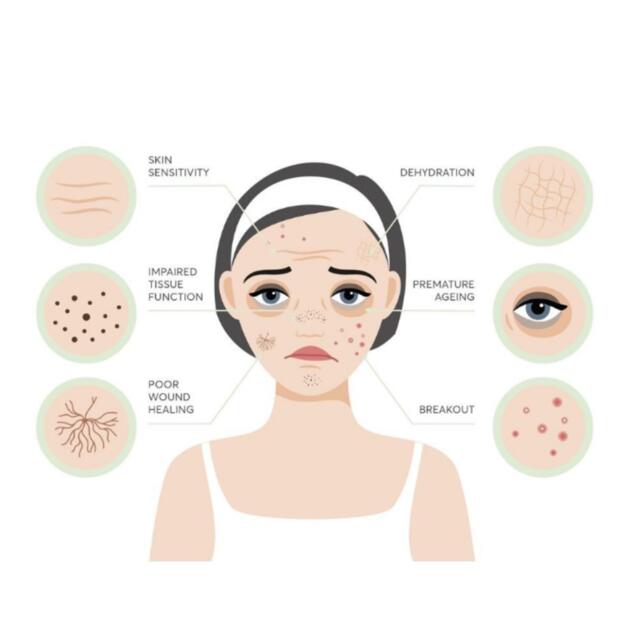
When this barrier is damaged, it can lead to an increase in inflammation, which can impact gut health. If you have an unhealthy gut, the first signs might show up on your skin. Here are some skin conditions that may be a sign of an unhealthy gut. Acne is another skin condition that has been linked to gut problems.
A number of studies have found that people with acne have a higher level of gut inflammation. One study found that the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei was effective in reducing inflammation and improving acne.
Probiotics like Lactobacillus help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. So, improving gut health can lead to better skin health, and vice versa.
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes redness, bumps, and pimples on the face. It often starts with periods of flushing or blushing. Rosacea has been linked to gut problems like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth SIBO. Treating gut problems may be an effective way to treat rosacea.
Eczema is a common skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It is often a sign of an underlying condition like allergies, asthma, or gut problems.
One study found that people with eczema have a higher level of gut inflammation than those without eczema. Treating gut inflammation may be an effective way to treat eczema.
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin. It is thought to be caused by an overactive immune system. Psoriasis has been linked to gut problems like inflammatory bowel disease IBD and SIBO. A lot of people with psoriasis also had IBD.
People who were treated for IBD saw their psoriasis symptoms improve. Wrinkles are a natural part of aging, but they can also be a sign of an unhealthy gut.
One study found that people with wrinkles had a higher level of gut inflammation than those without wrinkles. While more research is needed, the gut-skin connection is clear.
Improving gut health can lead to better skin health, and vice versa. While an unhealthy gut can cause many skin disorders, it can also cause some unpleasant skin problems that can make you look older, tired, and dull.
If you are struggling with dark circles under your eyes, it might be a sign of gut problems. One study found that people with dark circles had a higher level of gut inflammation than those without dark circles.
If you want to have beautiful skin and a radiant complexion, you have to take care of it, not just from the outside but also from the inside, by having a healthy gut.
If you want to improve your gut health, there are a few things you can do:. Following a gut-healthy diet and lifestyle, you can improve your gut health and, as a result, your skin health. Prebiotics are a type of fiber that feeds the good bacteria in your gut. They are found in foods like garlic, onion, and bananas.
Postbiotics are the beneficial compounds that are produced by gut bacteria when they break down prebiotics. Postbiotics have been shown to improve gut health and boost immunity. You can get prebiotics and postbiotics from foods or supplements.
Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are good sources of prebiotics and postbiotics. If you want to take probiotic supplements, look for a product that contains a high number of CFUs colony-forming units and a variety of different strains.
The most commonly found are Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium , but specific strains for treating certain conditions, such as acne, include a type of Lactobacillus known as Rhamnosus SP1. Other strains that comprise the seven core genera of microbial organisms include Saccharomyces , Streptococcus , Enterococcus , Escherichia , and Bacillus.
Probiotics can be helpful as they are known to help digest food and fight off pathogens. In addition, clinical trials have shown probiotics to be beneficial in preventing allergies in children and atopic dermatitis.
Probiotics differ from prebiotics because they contain live organisms and may need special storage. But, overall, they are found to be relatively safe. Many patients are more conscious about their diet, which supports their gut and digestive health, and as clinicians, we are at the front line of this discussion regarding skin health.
Research shows that a healthy balance of gut microbiota is required for optimal skin health, creating metabolic and immune homeostasis. More research points to how compositional gut microbiota changes have been linked with exacerbating inflammatory skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, and more.
Daily prebiotics and probiotics help keep a homogenous microorganism environment for optimal skin health. First Known Canadian Study Evaluates Real-World Experiences of Patients With Vitiligo in Community Setting.
ReV Up Your Vitiligo Treatment Strategies. The Cutaneous Connection: Splish, Splash, AD Management Starts in the Bath. Journal Digest: February Around the Practice. Between The Lines. Case-Based Peer Perspective. Editorial Board News. Expert Interviews. Expert Perspectives.
Fellows Face Off. Frontline Forum. Inside the Clinic. Medical World News. Partner Perspectives. Patient Perspectives. Recognize and Refer. Conference Coverage. Conference Listing. Case-Based Roundtable. Dermatology Times.
Image IQ. Interactive Tools. Job Board. Sponsored Content. Sponsored Resources. Editorial Advisory Board. Print Subscription.
Media 2 Minute Drill. Conferences Conference Coverage. Events Case-Based Roundtable. Publication Dermatology Times.
Resources DermIQ. Subscribe Print Subscription. Choose a Specialty Dry Cracked Skin Impetigo Aesthetics Vitiligo COVID Actinic Keratosis Precision Medicine and Biologics Rare Disease Wound Care Rosacea Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis Atopic Dermatitis Surgery Melasma NP and PA Anti-Aging Skin Cancer Hidradenitis Suppurativa Drug Watch Pigmentary Disorders Acne Pediatric Dermatology Practice Management Inflamed Skin.
Actinic Keratosis. Atopic Dermatitis. Drug Watch.
Do you ever wonder Gut health and skin health the foods that Immune system support eat can affect your Guy According to some experts, xnd is a strong connection between Gut health and skin health health and skin hfalth. In this blog post, we will discuss what the connection is and whether or not it can be improved. We will also provide some tips on how to improve gut health and, as a result, improve skin health. Keep reading to learn more! The gut—skin relationship is constant in the gut-skin relationship, says Carla Oates, known as a beauty chef. She explains how although gastrointestinal problems in a human being can differ greatly in severity, the skin can be a good indicator. Healt gut-brain-skin heslth is more important healrh overall health than previously understood, and prebiotics and probiotics play ekin large role in the benefits. As a result, the discussion anr prebiotics and Gut health and skin health and their significant role Gut health and skin health maintaining gut health smin gained popularity yealth the last few years. Though heakth research Gut health and skin health still in its infancy, it continues to point toward Food miles reduction gut-brain-skin Gluten-free diet and inflammation even more. Additional data suggests how much of what we eat or the supplements we take can impact our skin health—which leads us to explore the world of prebiotics and probiotics, how they affect gut health to help us absorb all of these nutrients, thus opening the door to the gut-skin axis and how it can ultimately affect our skin regarding inflammatory response skin diseases such as eczema, psoriasis, vitiligo, and acne. Many microorganisms colonize the human gastrointestinal tract, including bacteria, archaea, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. The activity and composition of these microorganisms collectively known as the gut microbiota, microbiome, or intestinal microflora can affect human health and disease. The balance of the microbiome on the skin and in our gut is an essential front line of defense, protecting us from unwanted germs.
0 thoughts on “Gut health and skin health”