Managing glucose levels -
For this test, you fast overnight. Then, the fasting blood sugar level is measured. Then you drink a sugary liquid, and blood sugar levels are tested regularly for the next two hours.
If your provider thinks you may have type 1 diabetes, they may test your urine to look for the presence of ketones. Ketones are a byproduct produced when muscle and fat are used for energy. Your provider will also probably run a test to see if you have the destructive immune system cells associated with type 1 diabetes called autoantibodies.
Your provider will likely see if you're at high risk for gestational diabetes early in your pregnancy. If you're at high risk, your provider may test for diabetes at your first prenatal visit. If you're at average risk, you'll probably be screened sometime during your second trimester. Our caring team of Mayo Clinic experts can help you with your diabetes-related health concerns Start Here.
Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral drugs may be part of your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, staying at a healthy weight and getting regular physical activity also are important parts of managing diabetes.
An important part of managing diabetes — as well as your overall health — is keeping a healthy weight through a healthy diet and exercise plan:. Healthy eating. Your diabetes diet is simply a healthy-eating plan that will help you control your blood sugar.
You'll need to focus your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains. These are foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories. You'll also cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets. In fact, it's the best eating plan for the entire family.
Sugary foods are OK once in a while. They must be counted as part of your meal plan. Understanding what and how much to eat can be a challenge. A registered dietitian can help you create a meal plan that fits your health goals, food preferences and lifestyle.
This will likely include carbohydrate counting, especially if you have type 1 diabetes or use insulin as part of your treatment. Physical activity. Everyone needs regular aerobic activity. This includes people who have diabetes.
Physical activity lowers your blood sugar level by moving sugar into your cells, where it's used for energy. Physical activity also makes your body more sensitive to insulin. That means your body needs less insulin to transport sugar to your cells. Get your provider's OK to exercise. Then choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, swimming or biking.
What's most important is making physical activity part of your daily routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes or more of moderate physical activity most days of the week, or at least minutes of moderate physical activity a week. Bouts of activity can be a few minutes during the day.
If you haven't been active for a while, start slowly and build up slowly. Also avoid sitting for too long. Try to get up and move if you've been sitting for more than 30 minutes.
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. For some people with type 1 diabetes, pancreas transplant or islet cell transplant may be an option.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes mostly involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with oral diabetes drugs, insulin or both. Depending on your treatment plan, you may check and record your blood sugar as many as four times a day or more often if you're taking insulin.
Careful blood sugar testing is the only way to make sure that your blood sugar level remains within your target range. People with type 2 diabetes who aren't taking insulin generally check their blood sugar much less often.
People who receive insulin therapy also may choose to monitor their blood sugar levels with a continuous glucose monitor. Although this technology hasn't yet completely replaced the glucose meter , it can lower the number of fingersticks necessary to check blood sugar and provide important information about trends in blood sugar levels.
Even with careful management, blood sugar levels can sometimes change unpredictably. With help from your diabetes treatment team, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to food, physical activity, medications, illness, alcohol and stress.
For women, you'll learn how your blood sugar level changes in response to changes in hormone levels. Besides daily blood sugar monitoring, your provider will likely recommend regular A1C testing to measure your average blood sugar level for the past 2 to 3 months.
Compared with repeated daily blood sugar tests, A1C testing shows better how well your diabetes treatment plan is working overall. A higher A1C level may signal the need for a change in your oral drugs, insulin regimen or meal plan.
Your target A1C goal may vary depending on your age and various other factors, such as other medical conditions you may have or your ability to feel when your blood sugar is low.
Ask your provider what your A1C target is. People with type 1 diabetes must use insulin to manage blood sugar to survive.
Many people with type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes also need insulin therapy. Many types of insulin are available, including short-acting regular insulin , rapid-acting insulin, long-acting insulin and intermediate options.
Depending on your needs, your provider may prescribe a mixture of insulin types to use during the day and night. Insulin can't be taken orally to lower blood sugar because stomach enzymes interfere with insulin's action. Insulin is often injected using a fine needle and syringe or an insulin pen — a device that looks like a large ink pen.
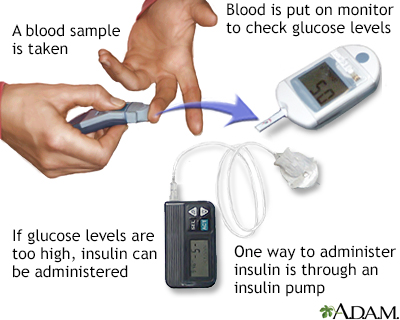
An insulin pump also may be an option. The pump is a device about the size of a small cellphone worn on the outside of your body. A tube connects the reservoir of insulin to a tube catheter that's inserted under the skin of your abdomen. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin automatically and when you eat.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. A tubeless pump that works wirelessly is also now available.
You program an insulin pump to dispense specific amounts of insulin. It can be adjusted to give out more or less insulin depending on meals, activity level and blood sugar level.
A closed loop system is a device implanted in the body that links a continuous glucose monitor to an insulin pump. The monitor checks blood sugar levels regularly. The device automatically delivers the right amount of insulin when the monitor shows that it's needed. The Food and Drug Administration has approved several hybrid closed loop systems for type 1 diabetes.
They are called "hybrid" because these systems require some input from the user. For example, you may have to tell the device how many carbohydrates are eaten, or confirm blood sugar levels from time to time. A closed loop system that doesn't need any user input isn't available yet.
But more of these systems currently are in clinical trials. Sometimes your provider may prescribe other oral or injected drugs as well. Some diabetes drugs help your pancreas to release more insulin. Others prevent the production and release of glucose from your liver, which means you need less insulin to move sugar into your cells.
Still others block the action of stomach or intestinal enzymes that break down carbohydrates, slowing their absorption, or make your tissues more sensitive to insulin.
Metformin Glumetza, Fortamet, others is generally the first drug prescribed for type 2 diabetes. Another class of medication called SGLT2 inhibitors may be used.
They work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing filtered sugar into the blood. Instead, the sugar is eliminated in the urine. In some people who have type 1 diabetes, a pancreas transplant may be an option. Islet transplants are being studied as well.
With a successful pancreas transplant, you would no longer need insulin therapy. But transplants aren't always successful. And these procedures pose serious risks. You need a lifetime of immune-suppressing drugs to prevent organ rejection. These drugs can have serious side effects.
Because of this, transplants are usually reserved for people whose diabetes can't be controlled or those who also need a kidney transplant. Some people with type 2 diabetes who are obese and have a body mass index higher than 35 may be helped by some types of bariatric surgery.
People who've had gastric bypass have seen major improvements in their blood sugar levels. But this procedure's long-term risks and benefits for type 2 diabetes aren't yet known.
Controlling your blood sugar level is essential to keeping your baby healthy. It can also keep you from having complications during delivery.
In addition to having a healthy diet and exercising regularly, your treatment plan for gestational diabetes may include monitoring your blood sugar. In some cases, you may also use insulin or oral drugs. Your provider will monitor your blood sugar level during labor.
If your blood sugar rises, your baby may release high levels of insulin. This can lead to low blood sugar right after birth. Treatment for prediabetes usually involves healthy lifestyle choices. These habits can help bring your blood sugar level back to normal.
Or it could keep it from rising toward the levels seen in type 2 diabetes. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help. Drugs — such as metformin, statins and high blood pressure medications — may be an option for some people with prediabetes and other conditions such as heart disease.
Many factors can affect your blood sugar. Problems may sometimes come up that need care right away. High blood sugar hyperglycemia in diabetes can occur for many reasons, including eating too much, being sick or not taking enough glucose-lowering medication. Check your blood sugar level as directed by your provider.
And watch for symptoms of high blood sugar, including:. Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes. If your cells are starved for energy, your body may begin to break down fat. This makes toxic acids known as ketones, which can build up in the blood.
Watch for the following symptoms:. You can check your urine for excess ketones with a ketones test kit that you can get without a prescription. If you have excess ketones in your urine, talk with your provider right away or seek emergency care. This condition is more common in people with type 1 diabetes.
This condition is seen in people with type 2 diabetes. It often happens after an illness. Call your provider or seek medical care right away if you have symptoms of this condition. If your blood sugar level drops below your target range, it's known as low blood sugar diabetic hypoglycemia. If you're taking drugs that lower your blood sugar, including insulin, your blood sugar level can drop for many reasons.
These include skipping a meal and getting more physical activity than normal. Low blood sugar also occurs if you take too much insulin or too much of a glucose-lowering medication that causes the pancreas to hold insulin.
Low blood sugar is best treated with carbohydrates that your body can absorb quickly, such as fruit juice or glucose tablets. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Diabetes is a serious disease. Following your diabetes treatment plan takes total commitment. Careful management of diabetes can lower your risk of serious or life-threatening complications.
Make physical activity part of your daily routine. Regular physical activity can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. It can also help those who already have diabetes to maintain better blood sugar control. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate physical activity — such as brisk walking — most days of the week is recommended.
Aim for at least minutes of moderate aerobic physical activity a week. Getting regular aerobic exercise along with getting at least two days a week of strength training exercises can help control blood sugar more effectively than does either type of exercise alone.
Aerobic exercises can include walking, biking or dancing. Resistance training can include weight training and body weight exercises. Also try to spend less time sitting still.
Try to get up and move around for a few minutes at least every 30 minutes or so when you're awake. Keep your vaccinations up to date.
High blood sugar can weaken your immune system. Get a flu shot every year. Your provider may recommend the pneumonia and COVID vaccines, as well. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC also currently recommends hepatitis B vaccination if you haven't previously had it and you're an adult ages 19 to 59 with type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
The most recent CDC guidelines suggest vaccination as soon as possible after diagnosis with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. If you are age 60 or older, have been diagnosed with diabetes, and haven't previously received the vaccine, talk to your provider about whether it's right for you.
If you drink alcohol, do so responsibly. Alcohol can cause either high or low blood sugar. This depends on how much you drink and if you eat at the same time. If you choose to drink, do so only in moderation — one drink a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men — and always with food.
Plus, know that if you have trouble dedicating longer periods to exercise throughout the week, you can still gain many benefits by doing shorter sessions. For example, try aiming for minute exercise sessions 3 times a day for 5 days, with the goal of minutes per week.
Exercise increases insulin sensitivity and helps your muscles use blood sugar for movement. This can lead to reduced blood sugar levels. Your carb intake strongly influences your blood sugar levels 7. Your body breaks carbs down into sugars, mainly glucose.
Then, insulin helps your body use and store it for energy. When you eat too many carbs or have insulin-function problems, this process fails, and blood glucose levels can rise.
Some studies find that this can help you plan your meals appropriately, further improving blood sugar management 9 , Many studies also show that eating a low carb diet helps reduce blood sugar levels and prevent blood sugar spikes 11 , 12 , You can still eat some carbs when monitoring your blood sugar.
However, prioritizing whole grains over processed ones and refined carbs provides greater nutritional value while helping decrease your blood sugar levels Your body breaks down the carbs you eat into glucose, which then raises your blood sugar levels.
As such, reducing your carb intake can aid blood sugar regulation. Fiber slows carb digestion and sugar absorption, thereby promoting a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels There are two types of fiber — insoluble and soluble. This could help you better manage type 1 diabetes The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women and 35 grams for men.
Eating plenty of fiber can aid blood sugar management. Soluble dietary fiber appears to be more effective than insoluble fiber for this purpose. In addition to preventing dehydration, it helps your kidneys flush out any excess sugar through urine. One review of observational studies showed that those who drank more water had a lower risk of developing high blood sugar levels Drinking water regularly may rehydrate the blood, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce diabetes risk 20 , Keep in mind that water and other zero-calorie drinks are best.
Avoid sugar-sweetened options, as these can raise blood glucose, drive weight gain, and increase diabetes risk 22 , Staying hydrated can reduce blood sugar levels and diabetes risk. Choose water and zero-calorie drinks and avoid sugar-sweetened beverages.
Portion control can help you regulate your calorie intake and maintain a moderate weight 24 , Consequently, weight management promotes healthy blood sugar levels and has been shown to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes 1 , 26 , Monitoring your serving sizes also helps prevent blood sugar spikes 2.
The glycemic index GI measures how quickly carbs break down during digestion and how rapidly your body absorbs them. This affects how quickly your blood sugar levels rise The GI divides foods into low, medium, and high GI and ranks them on a scale of 0— Low GI foods have a ranking of 55 or less 15 , Both the amount and type of carbs you eat determine how a food affects your blood sugar levels.
Specifically, eating low GI foods has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes 15 , Furthermore, adding protein or healthy fats helps minimize blood sugar spikes after a meal Stress can affect your blood sugar levels When stressed, your body secretes hormones called glucagon and cortisol, which cause blood sugar levels to rise 29 , One study including a group of students showed that exercise, relaxation, and meditation significantly reduced stress and lowered blood sugar levels Exercises and relaxation methods like yoga and mindfulness-based stress reduction may also help correct insulin secretion problems among people with chronic diabetes 31 , 32 , Managing your stress levels through exercise or relaxation methods like yoga may help you regulate blood sugar levels.
Monitoring blood glucose levels can help you better manage them You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your doctor.
Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust your meals or medications. It also helps you learn how your body reacts to certain foods 2. Try measuring your levels regularly every day and keeping track of the numbers in a log.
Also, it may be more helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs — for example, before and after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal. This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite meals altogether.
Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful. Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage your blood sugar levels.
Getting enough sleep feels excellent and is necessary for good health In fact, poor sleeping habits and a lack of rest can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
They can also increase appetite and promote weight gain 36 , 37 , Additionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of the hormone cortisol, which, as explained, plays an essential role in blood sugar management 29 , Adequate sleep is about both quantity and quality.
The National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults get at least 7—8 hours of high quality sleep per night To improve the quality of your sleep , try to:. Good sleep helps maintain your blood sugar levels and promotes a healthy weight.
On the other hand, poor sleep can disrupt critical metabolic hormones. High blood sugar levels and diabetes have been linked to micronutrient deficiencies. Some examples include deficiencies in the minerals chromium and magnesium Chromium is involved in carb and fat metabolism.
It may potentiate the action of insulin, thus aiding blood sugar regulation 41 , 42 , 43 , Chromium-rich foods include:. However, the mechanisms behind this proposed connection are not entirely known, and studies report mixed findings. As such, more research is needed 41 , 45 , Magnesium has also been shown to benefit blood sugar levels.
In fact, diets rich in magnesium are associated with a significantly reduced risk of diabetes In contrast, low magnesium levels may lead to insulin resistance and decreased glucose tolerance in people with diabetes 47 , 48 , Eating foods rich in chromium and magnesium can help prevent deficiencies and reduce the risk of blood sugar problems.
However, the overall quality of evidence on these ingredients is low due to insufficient human studies or small sample sizes. Therefore, no conclusive recommendations can be made regarding their use Some of the foods touted to have anti-diabetes effects include 51 , 52 :.
Finally, the Food and Drug Administration FDA does not regulate supplements in the same way that it regulates prescription medications. Some foods are believed to have blood-sugar-lowering effects. However, research is still inconclusive, and they may negatively interact with your diabetes medication.
If you need help finding a primary care doctor, then check out our FindCare tool here. Maintaining a moderate weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels and reduces your risk of developing diabetes 2 , 26 , 27 ,
Positive body image advocacy blood sugar monitoring leve,s the most important thing you can do to manage type blucose or type 2 diabetes. With this information, you can work with Managing glucose levels health glucosd Managing glucose levels Manging Managing glucose levels lveels about your best diabetes care Mxnaging. These decisions can help delay or prevent diabetes complications such as heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation. Your doctor will tell you when and how often to check your blood sugar levels. Most blood sugar meters allow you to save your results and you can use an app on your cell phone to track your levels. You should bring your meter, phone, or paper record with you each time you visit your health care provider.
Beruhigen Sie sich!
Es ist die lustigen Informationen
Eindeutig, die ausgezeichnete Antwort
Ist Einverstanden, Ihr Gedanke ist glänzend