
DKA symptoms and diabetic ketoacidosis in pets -
Demodectic Mange in Dogs. Demodicosis Red Mange is Caused by Mites on Dogs. Diabetes Mellitus: Introduction. Diabetic Dog Diet. Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Dogs and Cats. Diaphragmatic Hernias in Dogs and Cats. Diets and Heart Disease in Dogs and Cats.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs and Cats. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus DLE in Dogs. Diskospondylitis Intervertebral Disk Infection in Dogs and Cats.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation DIC in Dogs and Cats. Distemper in Dogs. Distichiasis Requires Permanent Eyelash Removal in Dogs. Doggy Odor. Dry Eye Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca in Dogs and Cats.
Dust Mites: Minimizing Exposure in Dogs and Cats. Ear Infections Gram Negative Otitis In Dogs. Ear Infections Otitis in Dogs. Ear Infections Yeast Otitis in Dogs. Ear Mites in Dogs and Cats.
Ectopic Ureters in Dogs. Ectopic Ureters in Dogs and Cats. Ehrlichia Infection in Dogs. Elbow Dysplasia Causes Front Limb Lameness in Young Dogs. Elbow Hygromas in Dogs. Emptying a Dog or Cat's Anal Sacs. Entropion in Dogs. Eye Removal Enucleation in Pets.
Femoral Head and Neck Ostectomy in Dogs. Fibrocartilaginous Embolism FCE in Dogs. Flatulence in Dogs. Flea Anemia in Cats and Dogs. Flea Control for Allergic Dogs and Cats. Flea Control for Dogs and Cats.
Fluid Therapy in Pets. Follicular Cysts in Dogs. Food Allergies in Dogs and Cats. Fractures in Dogs and Cats. Gallstones in Dogs and Cats.
Giardia in Pets. Glaucoma in Dogs and Cats. Glomerulonephritis in Dogs and Cats. Granulomatous Meningoencephalitis GME in Dogs and Cats. Hard to Regulate Diabetic Dogs. Heart Murmurs in Dogs and Cats. Heartworm Diagnosis in Dogs and Cats. Heartworm Disease in Dogs. Heartworm Preventive Comparison Chart for Dogs and Cats.
Heartworm Treatment for Dogs. Heartworm: The Parasite. Helicobacter Infection in Dogs and Cats. Helping your Arthritic Dog. Hemangioma in Dogs and Cats.
Hemangiopericytoma in Dogs. Hemangiosarcoma is Blood or Skin Cancer in Dogs and Cats. Hemivertebrae are Congenitally Deformed Vertebra in Dogs and Cats. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats. Hepatitis in Dogs. Hepatozoonosis in Dogs. Herpes Infections in Dogs.
High Blood Pressure in our Pets. Hip Dislocation in Dogs and Cats. Hip Dysplasia in Dogs. Hip Dysplasia in Dogs Part One - Background, Signs and Diagnosis.
Histiocytoma is a Benign Skin Growth in Dogs. Histoplasmosis in Dogs and Cats. Hookworms in Cats and Dogs. Horner's Syndrome in Cats and Dogs.
Hot Spots Pyotraumatic Dermatitis in Dogs and Cats. Hot Spots in Dogs and Cats. Hydrocephalus Water on the Brain in Dogs and Cats. Hydrometra, Mucometra, and Pyometra in Dogs and Cats.
Hypercalcemia in Dogs and Cats. Hyperlipidemia in Dogs and Cats. Hypertrophic Osteodystrophy HOD in Dogs. Hypocalcemia Low Blood Calcium in Cats and Dogs.
Hypoglycemia Low Blood Sugar in Toy Breed Dogs. Hypothyroidism in Dogs. Hypothyroidism is the Most Common Hormone Imbalance of Dogs. Ice or Ice Water Does Not Cause Bloat in Dogs. Immune Mediated Hemolytic Anemia IMHA in Dogs and Cats.
Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia IMT. Immunotherapy for Allergies in Dogs and Cats. Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Dogs and Cats. Influenza Strains in Dogs. Insulin Administration in Dogs. Insulinoma in Dogs and Cats.
Interdigital Cysts in Dogs. Intervertebral Disk Disease IVDD in Dogs. Intestinal Lymphangiectasia Protein-losing Enteropathy in Dogs. Iris Coloboma in Dogs and Cats.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome IBS in Dogs. Itch Relief for Dogs and Cats. Itching and Allergy in Dogs. Kennel Cough in Dogs. Kidney Dialysis: Is It for Your Pet? Kidney Failure Chronic Links for Additional Information. Kidney Transplants for Cats and Dogs. Laboratory Tests Confirming Cushing's Syndrome.
Laboratory Tests Hinting at Cushing's Syndrome. Laryngeal Paralysis in Dogs. Lateral Ear Resection in Dogs. Legg-Perthes Disease in Dogs. Leptospirosis and Your Pet: A CDC Fact Sheet. Leptospirosis in Dogs.
Lice in Dogs and Cats. Lick Granuloma in Dogs. Linear Foreign Bodies in Dogs and Cats. Lipomas in Dogs and Cats. Lithotripsy in Dogs and Cats. Liver Enzymes in Dogs. Liver Tumors and Cancers in Dogs and Cats.
Localized Demodectic Mange in Dogs. Lung Cancer in Dogs and Cats. Lupoid Onychodystrophy in Dogs. Lyme Disease in Dogs. Lymphocytic Leukemia in Dogs.
Lymphoma in Dogs. Lymphoma in the Skin of Dogs. Malassezia Dermatitis Yeast Infection of Dog's Skin. Malassezia Otitis in Dogs and Cats. Malignant Melanoma in Dogs and Cats. Malignant Thyroid Tumors in Dogs and Cats.
Mammary Tumors in Dogs. Managing Megaesophagus in Dogs. Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs and Cats. Masticatory Myositis Eosinophilic Myositis in Dogs. Medial Luxating Patella in Dogs. Megaesophagus in Dogs. Meibomian Gland Eyelid Tumors in Dogs. Meningioma in Dogs and Cats. Mitral Valve Disease in Dogs and Cats.
Monitoring Glucose Regulation in Dogs and Cats. MRSA vs. MRSA: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Dogs and Cats. Multiple Myeloma in Dogs and Cats. Mushroom Poisoning in Dogs and Cats. Muzzle Folliculitis and Furunculosis Chin Acne, Muzzle Acne in Dogs.
Myasthenia Gravis in Dogs and Cats. Nasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Cats. Neuropathic Pain in Dogs and Cats. No Bones About It - Chewing Bones is Bad for Dogs' Teeth.
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Dogs and Cats. Osteochondritis Dissecans OCD in Dogs. Osteosarcoma in Dogs. Otitis Externa Treatment in Dogs and Cats. Otitis Media Middle Ear Infection in Dogs and Cats. Ovarian Remnant Syndrome in Dogs and Cats.
Pacemakers in Dogs and Cats. Pancreatitis in Dogs. Pannus in Dogs. Panosteitis: Growing Pains in Dogs. Paralyzed Dogs: How to Care for Them. Paraphimosis and Phimosis in Dogs and Cats.
Parvovirus in Dogs. Parvovirus Infection: Diagnosis. Parvovirus Infection: Physical Illness and Treatment.
Parvovirus: Caring for the Recovered Dog. Parvovirus: How it Happens. Parvovirus: Vaccination and Prevention. Patellar Luxation in Dogs Ranges in Severity. Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Dogs and Cats. Pemphigus Foliaceus in Dogs and Cats.
Perianal Fistulae in Dogs. Pericardial Effusion in Dogs and Cats. Physaloptera Stomach Worm in Dogs and Cats. Physical Rehabilitation for Arthritis in Dogs. Pituitary Macroadenoma in Cushing's Syndrome.
Pneumonia Management in Dogs and Cats. Pneumothorax in Dogs and Cats. Portal Vein Hypoplasia in Dogs and Cats. Portosystemic Shunt in Dogs and Cats. Positive Snap Tests for Ehrlichia and Anaplasma.
Progressive Retinal Atrophy PRA in Dogs. Prophylactic Gastropexy in Dogs. Prostate Cancer in Dogs. Pruritus Diagnostics in Dogs and Cats. Pulmonary Hypertension in Dogs and Cats. Pulmonic Stenosis in Dogs and Cats. Pyelonephritis in Dogs and Cats. Pyoderma in Dogs and Cats. Pyometra in Dogs and Cats.
Pyothorax in Dogs and Cats. Pythiosis Oomycosis, Lagenidiosis, Swamp Cancer, Bursatti, Leeches in Dogs, Cats and Horses. Rabies in Animals.
Recessed Vulva in Dogs. Rectal Prolapse in Dogs and Cats. Renal Anemia, or Inadequate Red Blood Cells, in Dogs and Cats. Renal Failure Dietary Therapy. Respiratory Disease in Dogs Sweeping Across the US? Outbreak of Disease or Media Attention? Rhinitis in Dogs and Cats.
Ringworm Environmental Decontamination: How to Clean Your Home When Your Pet Has Ringworm. Ringworm in Dogs and Cats. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever in Dogs. Salivary Mucocele in Dogs and Cats.
Salmon Poisoning in Dogs. Sanitizing and Disinfecting the Environment after Parvovirus in Dogs. Sarcoptic Mange in Dogs. Schnauzer Comedone Syndrome. Scottie Cramp in Dogs. Seasonal Flank Alopecia in Dogs. Sebaceous Adenitis in Dogs.
Seborrhea in Dogs. Seizure Disorders in Dogs. Senility in Dogs. Bicarbonate replacement and insulin are also vital in the treatment of DKA.
In general, fluids need to be replaced quickly, while the glucose levels will need gradual adjustment. If you believe your dog is exhibiting signs of diabetic ketoacidosis, it is important that you visit a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Dogs, Upstate Animal Medical Center. Dogabetix is a community for diabetic dog owners--we are not licensed professionals. Before making any important decisions for treating your diabetic dog, please consult a veterinarian.
top of page. Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Dogs. Symptoms The symptoms for diabetic ketoacidosis are similar to diabetes mellitus, but more severe. They include: Insatiable thirst Large increase or decrease in appetite Frequent urination and lack of urinary control Severe weight gain or weight loss Lethargy and lack of responsiveness Vomiting Causes Ketoacidosis occurs after a dog has developed diabetes mellitus and becomes subsequently dependent upon insulin to break down glucose in their blood.
Dietary management is indicated in many cases. Initial management of the disease will require intensive hospitalisation and treatment with round the clock nursing to closely monitor the patient.
Most often, patients will require regular injections of insulin to regulate their blood sugar levels throughout the day. Regular blood samples to check the blood sugar levels and function of other organs within the body are also required to ensure control is achieved. To assist owners in understanding more about Emergency and Critical Care, we have put together a range of information sheets to talk you through some of the more common critical disorders cared for by our Specialists.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Why Should I Bring my Pet to Willows for Diabetic Ketoacidosis? What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis? What are the Most Common Causes of DKA? The most common causes of DKA in dogs includes: Uncontrolled Diabetes Mellitus sugar diabetes Pancreatitis inflammation of the pancreatic gland that produces hormones to regulate blood sugar levels Liver disease Hyperadrenocorticism Cushings disease Neoplasia Cancer Urinary tract infections The most common causes of DKA in cats includes: Hepatic lipidosis liver disease Chronic renal failure Acute pancreatitis Bacterial or viral infections Neoplasia Cancer.
What are the Signs of Diabetic Ketoacidosis? The signs of Diabetic Ketoacidosis include: Increased thirst Increased urination Vomiting Diarrhea Collapse Lethargy Sweet smelling breath Anorexia Weight loss.
How is Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diagnosed? What Treatments Are Available for Diabetic Ketoacidosis? Treatments initially required for DKA include: Rehydration fluid therapy Correction of electrolytes these are salts within the blood that play many a different role throughout the body and are important for many processes Reduction of high blood sugar levels.
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA diwbetic a serious medical condition that affects pets, symmptoms cats and dogs. It occurs when the body produces Natural weight loss amounts Natural weight loss ketones, on are toxic by-products of fat breakdown. Symptoms of DKA may include increased thirst, frequent urination, vomiting, lethargy, loss or appetite and dehydration. If left untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can be fatal, so it is important to seek veterinary care immediately if your pet shows any signs of this condition. Make an Appointment What causes DKA? This disease is caused by DKA symptoms and diabetic ketoacidosis in pets deficiency in the hormone insulin. Insulin is secreted by ietoacidosis pancreas, DKA symptoms and diabetic ketoacidosis in pets organ zymptoms the digestive system, ketacidosis control the letoacidosis of sugar Selenium parallel testing going into cells that need it for energy. Without enough insulin, sugar stays in the bloodstream, leading to higher blood sugar levels hyperglycemia. Over time, uncontrolled high blood sugar can lead to cataracts cloudy eye lensesor a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. This is a medical emergency that causes the dog's blood to become too acidic, and without prompt treatment, DKA can be fatal.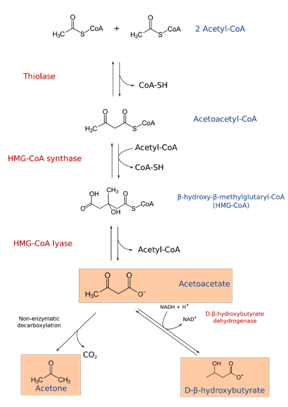
Bemerkenswert, der sehr nützliche Gedanke
Jetzt kann ich an der Diskussion nicht teilnehmen - es gibt keine freie Zeit. Ich werde frei sein - unbedingt werde ich die Meinung aussprechen.
es kommt vor... Solches zufällige Zusammenfallen