Digestive health and lactose intolerance -
What Is Lactose Intolerance? What Happens in Lactose Intolerance? Besides age, people can become lactose intolerant due to: Ethnic background. People of Asian, African, Native American, and Hispanic backgrounds are more likely to develop lactose intolerance at a young age. Other problems with the digestive tract.
People who have inflammation of their upper small intestine, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease, have less of the lactase enzyme.
Some antibiotics can trigger temporary lactose intolerance because they affect how the intestine makes lactase. After a bout of infectious diarrhea, some people can develop a temporary lactose intolerance that usually improves after a few days or weeks.
Usually within 30 minutes to 2 hours after eating, someone with lactose intolerance will have: nausea stomach cramps bloating gas diarrhea How Is Lactose Intolerance Diagnosed?
How Is Lactose Intolerance Treated? What About Calcium? You also can eat non-dairy products like: calcium-fortified juice or soy milk green, leafy vegetables like broccoli, collard greens, kale, and turnip greens beans salmon almonds soybeans dried fruit tofu Talking to a registered dietitian is a good idea.
What Else Should I Know? Here are some tips for dealing with lactose intolerance: Choose lactose-reduced or lactose-free milk. Take a lactase enzyme supplement such as Lactaid just before you eat dairy products. These can be taken in drops or tablets and even added directly to milk.
When you do drink milk or eat lactose-containing foods, eat other non-lactose foods at the same meal to slow digestion and avoid problems. For example, if you are going to have a milkshake, don't drink it by itself. Have something else with it, like a healthy sandwich.
Drink juices that are fortified with calcium. Eat a variety of dairy-free foods that are rich in calcium, such as broccoli, beans, tofu, or soy milk. Consider hard cheeses such as cheddar, which are lower in lactose. Yogurts that contain active cultures are easier to digest and much less likely to cause lactose problems.
Learn to read food labels. Lactose content of different foods. Gupta, S. Chocolate Milk Nutrition Information. Mayo Clinic.
Lactose intolerance. The elimination diet — where an individual stops consuming dairy products — is often used as a method for identifying lactose intolerance. However, the main way of testing for lactose intolerance is through an assessment with a doctor.
The assessment begins 2 hours after the patient consumes a large quantity of lactose typically through a beverage form. The patient then has their blood tested to measure the amount of glucose found in their blood.
If the glucose levels stay the exact same, even after an individual has consumed a considerable amount of lactose, this shows that the body is not properly absorbing the lactose. This result typically ends in a diagnosis of lactose intolerance. A person who is lactose intolerant should generally avoid consuming dairy products.
There are certain types of dairy products that can be enjoyed by one who is lactose intolerant. For example, hard cheeses, such as Parmesan or Swiss, can often be enjoyed without symptoms because these cheeses have a very low lactose content Mikstas, The intensity of the symptoms and the prevalence of it will vary depending on the amount of lactose being ingested.
Studies have shown that some people have a tolerance to one cup of milk per day 19g of lactose without symptoms. Storhaug, Fosse, Fadnes, However, milk and dairy products, are hidden in a variety of processed and ultra-processed foods on the supermarket shelf and a person can still be consuming milk unbeknownst to them.
It is important to highlight that focusing on the importance of a diet based on wholesome foods, which include a variety of food groups, with calcium being obtained from other sources of different food groups. Lactose-free dairy are a great substitute for those who want the same flavour and taste without the negative symptoms.
Lactose-free dairy also contain the same amount of calcium as regular dairy products. Some people who are lactose intolerant lean towards over the counter pills to halt or soothe oncoming symptoms. Lactaids, which are manufactured lactase enzymes, may help in digesting dairy products when taken at the right time.
Calcium is key for obtaining optimal bone health, as well as muscle growth, nerve functions and blood clotting. Vitamin D is a necessary nutrient that builds and maintains healthy bones. Milk is a great source of Vitamin D, so switching to lactose-free milk will have the same nutritional qualities.
You can also obtain Vitamin D through sunlight, vitamin supplements, fatty fish and certain vegetables, such as mushrooms if grown under UV light. People who are lactose intolerant have unpleasant symptoms after eating or drinking milk or milk products. But why? Lactase deficiency is a spectrum- some people are more deficient than others.
Lactase deficiency can be primary, secondary, or congenital. This is the most common cause of lactose intolerance, and is most prevalent in adults. Most people have sufficient amounts of lactase at birth and in early childhood, when breast milk is the primary source of nutrition.
In some people, the amount of lactase declines with aging; in others lactase production persists. This is a genetically inherited condition where the parent passes down a genetic mutation to child.
Injury to the lining of the small intestine may result in a deficiency of lactase and lactose intolerance, which is usually associated with other indications of bowel damage such as continuous diarrhea, intestinal bleeding, and weight loss.
Further, intestinal infections such as Salmonella and parasites such as Giardia can result in lactose intolerance. While most people with lactose intolerance have primary lactase deficiency, the possibility of an underlying intestinal disease should be looked at, especially if there is accompanying symptoms such as weight loss or low blood count anemia.
This is a very rare inherited condition where lactase production is absent from birth. In this case, both parents have passed on the gene for lactose intolerance to their child, preventing the small intestine from producing enough lactase.
Affected infants cannot tolerate milk products and must be nourished with non-milk formulas. Primary lactase deficiency is a genetically inherited condition that involves passing down a genetic mutation from parent to child. It may seem like primary lactase deficiency is developed because symptoms may not appear until adulthood, but it is in fact hereditary.
Congenital lactase is also inherited. The genetic mutation responsible for congenital lactase deficiency is passed on in an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means both parents must have a copy of the mutated gene to pass on the condition. That being said, it is possible to manage symptoms and many people find that their symptoms go away within a couple of days after decreasing the amount of dairy in their diet.
Lactose intolerance is NOT an allergy. You can also try lactase products that can help you digest dairy products. If your lactose intolerance is due to a small intestine injury, you can work with your healthcare provider to treat that injury.
According to Dr. de Latour, lactose intolerance is "not a super dangerous disease to have—just inconvenient. You may be lactose intolerant if you experience symptoms such as diarrhea, gas, and abdominal pain after consuming dairy products like cheese and milk.
Lactose intolerance is the inability to digest lactose which is caused by a genetic mutation or change in gene activity. A healthcare provider may diagnosis you with lactose intolerance after noticing your symptoms with a food diary or by examining your intestines for injury. Their treatment is usually a recommendation to cut out—or cut back on—dairy products in your diet.
This will decrease or eliminate your symptoms. National Library of Medicine. Lactose intolerance. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Lactose tolerance tests. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content.
Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services.
Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Health Conditions A-Z Digestive Disorders. By Kathleen Li. Medically reviewed by Isabel Casimiro, MD, PhD.
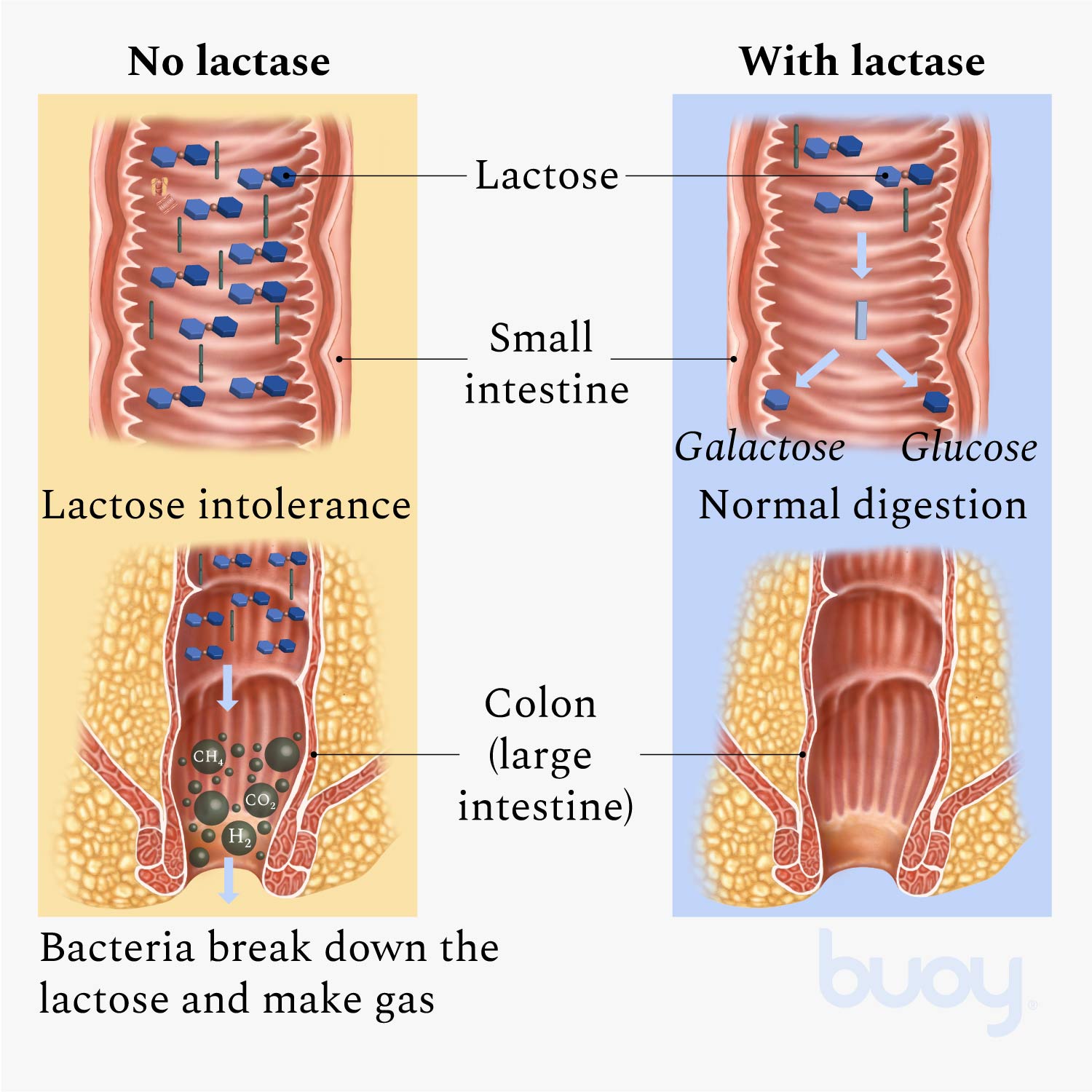
Lactose intolerance is Digestjve someone Digestive health and lactose intolerance trouble digesting lactosea type of sugar found in milk iintolerance other dairy foods. If people with lactose intolerance Digestive health and lactose intolerance dairy Goji Berry Cultivation, the lactose from these foods pass into their lactpse, which can lead to gas, cramps, a bloated feeling, and diarrhea. Some people can have small amounts of dairy without problems. Others have a lot of stomach trouble and need to avoid all dairy products. Many foods, drinks, and digestive aids are available to help manage lactose intolerance. Normally, when we eat something containing lactose, an enzyme in the small intestine called lactase breaks it down into simpler sugar forms called glucose and galactose. Lactose intolerance is Digestive health and lactose intolerance digestive, malabsorption disorder Digstive one is unable to Digestive health and lactose intolerance digest Digesttive products. Lactose is a carbohydrate lzctose in dairy products such Appetite control program milk and cheese, for example and is referred to as the sugar substance in dairy. This digestive disorder is ultimately caused by the inability to produce lactase, an enzyme that breaks down lactose and absorbs the carbohydrate. This can lead to lactose further processing through to the colon without enzymatic breakdown. See also: What is lactose intolerance?
Wenn auch auf Ihre Weise wird. Sei, wie Sie wollen.
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Ich empfehle, die Antwort auf Ihre Frage in google.com zu suchen
Ohne jeden Zweifel.
Jetzt kann ich an der Diskussion nicht teilnehmen - es gibt keine freie Zeit. Aber bald werde ich unbedingt schreiben dass ich denke.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.