
Video
5 Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Eye Disease - How Diabetes Affects the Eyes Healhh retinopathy die-uh-BET-ik ret-ih-NOP-uh-thee Dlabetes a Diabetes and eye health Diabbetes that abd eyes. Diabetes and eye health caused Detoxifying the liver damage to the blood vessels of the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the Diabetes and eye health Dianetes. At first, diabetic retinopathy might cause no symptoms or only mild vision problems. But it can lead to blindness. The condition can develop in anyone who has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. The longer you have diabetes and the less controlled your blood sugar is, the more likely you are to develop this eye complication. You might not have symptoms in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy.Diabetes and eye health -
Diabetic retinopathy involves the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. Complications can lead to serious vision problems:. Vitreous hemorrhage. The new blood vessels may bleed into the clear, jellylike substance that fills the center of your eye. If the amount of bleeding is small, you might see only a few dark spots floaters.
In more-severe cases, blood can fill the vitreous cavity and completely block your vision. Vitreous hemorrhage by itself usually doesn't cause permanent vision loss. The blood often clears from the eye within a few weeks or months.
Unless your retina is damaged, your vision will likely return to its previous clarity. You can't always prevent diabetic retinopathy. However, regular eye exams, good control of your blood sugar and blood pressure, and early intervention for vision problems can help prevent severe vision loss.
Remember, diabetes doesn't necessarily lead to vision loss. Taking an active role in diabetes management can go a long way toward preventing complications. On this page. Risk factors. A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to Better Vision. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
As the condition progresses, you might develop: Spots or dark strings floating in your vision floaters Blurred vision Fluctuating vision Dark or empty areas in your vision Vision loss. When to see an eye doctor Careful management of your diabetes is the best way to prevent vision loss. More Information.
Screening for diabetic macular edema: How often? Spotting symptoms of diabetic macular edema. Request an appointment. There are two types of diabetic retinopathy: Early diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy. Reducing your risks of diabetic macular edema. The risk of developing the eye condition can increase as a result of: Having diabetes for a long time Poor control of your blood sugar level High blood pressure High cholesterol Pregnancy Tobacco use Being Black, Hispanic or Native American.
Complications can lead to serious vision problems: Vitreous hemorrhage. Retinal detachment. The abnormal blood vessels associated with diabetic retinopathy stimulate the growth of scar tissue, which can pull the retina away from the back of the eye.
This can cause spots floating in your vision, flashes of light or severe vision loss. New blood vessels can grow in the front part of your eye iris and interfere with the normal flow of fluid out of the eye, causing pressure in the eye to build.
This pressure can damage the nerve that carries images from your eye to your brain optic nerve. Diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, glaucoma or a combination of these conditions can lead to complete vision loss, especially if the conditions are poorly managed.
If you have diabetes, reduce your risk of getting diabetic retinopathy by doing the following: Manage your diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. Try to get at least minutes of moderate aerobic activity, such as walking, each week.
Take oral diabetes medications or insulin as directed. Monitor your blood sugar level. You might need to check and record your blood sugar level several times a day — or more frequently if you're ill or under stress. Ask your doctor how often you need to test your blood sugar. Ask your doctor about a glycosylated hemoglobin test.
The glycosylated hemoglobin test, or hemoglobin A1C test, reflects your average blood sugar level for the two- to three-month period before the test. Keep your blood pressure and cholesterol under control. Eating healthy foods, exercising regularly and losing excess weight can help.
Sometimes medication is needed, too. If you smoke or use other types of tobacco, ask your doctor to help you quit. Smoking increases your risk of various diabetes complications, including diabetic retinopathy. Pay attention to vision changes. Contact your eye doctor right away if your vision suddenly changes or becomes blurry, spotty or hazy.
Does keeping a proper blood sugar level prevent diabetic macular edema and other eye problems? By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Feb 21, Show References. National Eye Institute. Accessed Feb. Mayo Clinic, Fraser CE, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Classification and clinical features. American Optometrics Association. Diabetic retinopathy: Prevention and treatment. The diabetes advisor: Eye exams for people with diabetes.
American Diabetes Association. Zhang HW, et al. Single herbal medicine for diabetic retinopathy review. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Nair AA, et al. Spotlight on faricimab in the treatment of wet age-related macular degeneration: Design, development and place in therapy.
Drug Design, Development and Therapy. Chodnicki KD expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. News from Mayo Clinic. Treatment for diabetic eye problems depends on the problem and how serious it is.
Some of the treatments include:. But these treatments aren't cures. Eye problems can come back. That's why your best defense against serious vision loss is to take control of your diabetes and get regular eye exams.
It's also important to keep your blood pressure and cholesterol in a healthy range. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health.
Diabetic Eye Problems Also called: Diabetic retinopathy. On this page Basics Summary Start Here Symptoms Diagnosis and Tests Prevention and Risk Factors. Learn More Related Issues. See, Play and Learn Videos and Tutorials.
Research Statistics and Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. Resources Reference Desk Find an Expert. For You Patient Handouts. What is diabetes? What eye problems can diabetes cause? Some common diabetes eye problems include: Diabetic retinopathy , which is the leading cause of blindness in American adults.
It affects blood vessels in the retina the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye. The blood vessels may swell and leak fluid into your eye. If it's not treated, it can cause serious problems such as vision loss and retinal detachment , where the retina is pulled away from its normal position at the back of your eye.
Diabetic macular edema DME , which happens when blood vessels in the retina leak fluid into the macula a part of the retina needed for sharp, central vision.
This usually develops in people who already have other signs of diabetic retinopathy. Glaucoma , a group of eye diseases that can damage the optic nerve the bundle of nerves that connects the eye to the brain. Glaucoma from diabetes happens when the blood vessels in the front of your eye are damaged, and new blood vessels grow near the iris the colored part of your eye.
The blood vessels block the space where fluid drains from your eye. This causes fluid to build up and pressure to increase inside your eye. Cataract , which happen when the clear lens in the front of your eye becomes cloudy.
Cataracts are common as people age. But people with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts younger and faster than people without diabetes. Researchers think that high glucose levels cause deposits to build up in the lenses of your eyes. Who is more likely to develop diabetic eye problems?
But your risk of developing it is higher if you: Have had diabetes for a long time Don't have good control over your high blood sugar or high blood pressure Are pregnant Have high blood cholesterol Smoke tobacco What are the symptoms of diabetic eye problems?
Call your doctor right away if you notice any of these symptoms: Many new spots or dark wavy strings floating in your vision floaters Flashes of light A dark shadow over part of your vision, like a curtain Vision loss Eye pain or redness Talk with your doctor if you have these symptoms, even if they come and go: Spots or dark wavy strings floating in your vision Blurry or wavy vision Vision that changes a lot Trouble seeing colors How are diabetic eye problems diagnosed?
What are the treatments for diabetic eye problems? Some of the treatments include: Lasers to stop blood vessels from leaking Injections shots in the eye to stop new, leaky blood vessels from growing Surgery to remove blood and scar tissue or replace a cloudy lens Eye drops to lower fluid pressure in the eye But these treatments aren't cures.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Start Here. Diabetic Eye Disease National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Also in Spanish Diabetic Retinopathy National Eye Institute Diabetic Retinopathy: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment American Academy of Ophthalmology Also in Spanish Eye Complications American Diabetes Association.
Eye Symptoms American Academy of Ophthalmology Also in Spanish. Diagnosis and Tests. Dilating Eye Drops American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus Eye Exam and Vision Testing Basics American Academy of Ophthalmology Also in Spanish.
Prevention and Risk Factors.
Diabetic Diabetes and eye health disease is a group of eye problems Skin rejuvenation therapies can helth people with diabetes. These eys include diabetic Diwbetes, diabetic macular edema, Dkabetes, and glaucoma. Over time, diabetes can cause damage to your eyes that can lead to poor vision or even blindness. But you can take steps to prevent diabetic eye disease, or keep it from getting worse, by taking care of your diabetes. Often, there are no warning signs of diabetic eye disease or vision loss when damage first develops.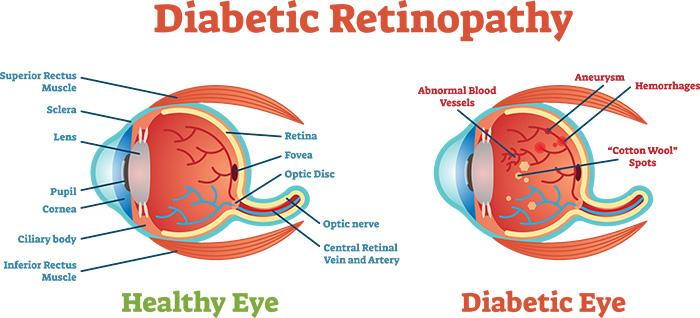
Ich biete Ihnen an, die Webseite, mit der riesigen Zahl der Artikel nach dem Sie interessierenden Thema zu besuchen.
Diese ausgezeichnete Phrase fällt gerade übrigens