Muscle pain in glycogen storage disease -
If you are the parent of a child affected by this disease, you will have to work with your child to modify their physical activity. You will also have to communicate your child's needs to other caregivers. GSD V is passed from parents to their children.
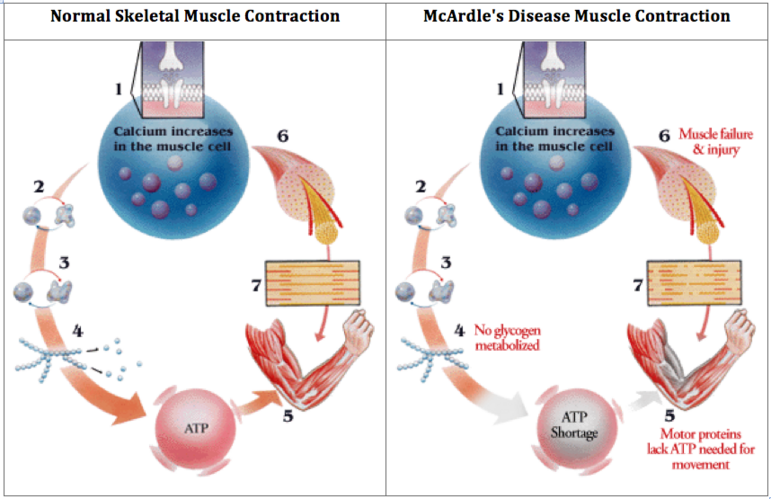
If you, your child, your parents, or a sibling have this disease, it's important that you consult with a genetic counselor to learn about your risk of developing this disease and passing it on to your children. GSD V, also known as McArdle disease, causes fatigue and muscle pain during extreme movement.
This condition is caused by the lack of a certain enzyme needed to change glycogen into glucose within the muscles. Without enough glucose, muscle pain and cramping occur.
Many people find relief by waiting about 10 minutes until a second wind allows them to resume motion without pain. The organs most commonly damaged by this disease are the skeletal muscles and kidneys. In extreme cases, kidney failure can occur.
While there is no cure for this condition currently, managed diet and workout plans can improve results. People with this disease must avoid intense, prolonged movement to prevent health problems and live normally. Living with GSD V or any other rare disease can be isolating. Seek out groups online that include people affected by this disease.
Interacting with others who have this condition can provide the support and strategies you need to meet the challenges of this disease. While any glycogen storage disease is a challenging diagnosis, the good news is that the prognosis for most people with this condition is relatively good. It can usually be managed by following the diet and exercise plans advised by your healthcare provider.
Doing so can improve your prognosis and allow you to live a normal life with a lower risk of disease complications. GSD V is a genetic disorder, so there is no way to reduce your risk of developing it or passing it on to your child if you are a carrier.
If you're concerned about your predisposition to a genetic disease, you may benefit from genetic testing. This noninvasive procedure can determine whether you are a carrier and let you know your risk of passing it on to your children.
Yes, people diagnosed with this disease can live a normal and active lifestyle. Regular aerobic activity in moderation can improve exercise capacity with this disease. Following your healthcare provider's guidelines can help you make the most of your activity without risking complications and muscle damage.
Most people affected by this disease are diagnosed in their teens or 20s. However, the onset of this condition can vary widely, ranging from infancy to senior adulthood.
In some cases, mild symptoms may be overlooked and the diagnosis may be delayed. Some people do not have any symptoms. Ross KM, Ferrecchia IA, Dahlberg KR, Dambska M, Ryan PT, Weinstein DA. Dietary management of the glycogen storage diseases: evolution of treatment and ongoing controversies.
Adv Nutr. Genetics of glycogen-storage disease type V McArdle disease clinical presentation. NORD - National Organization for Rare Disorders, Inc. Glycogen storage disease type V. Muscular Dystrophy Association. Phosphorylase deficiency McArdle disease.
Association for Glycogen Storage Disease. Type V glycogen storage disease. Llavero F, Arrazola Sastre A, Luque Montoro M, et al. Mcardle disease: new insights into its underlying molecular mechanisms.
Int J Mol Sci. Glycogen storage diseases: the patient-parent handbook. Khattak ZE, Ashraf M. McArdle disease. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Glycogen storage disease due to muscle glycogen phosphorylase deficiency. By Anna Giorgi Anna Zernone Giorgi is a writer who specializes in health and lifestyle topics.
Glycogen Storage Disease Symptoms Glycogen storage disease symptoms in pediatric patients depend on its type. These tests may include: Biopsy of the affected organs Blood tests and urine tests MRI scan — a test that uses magnetic waves to make pictures of the inside of the body Glycogen Storage Disease Treatment Glycogen storage disease treatment will depend on the type of disease and the symptoms.
The goal of treatment is to maintain normal blood glucose levels. This may be done with: A nasogastric infusion of glucose in infants and children under age two Dietary changes, including: In children over age two, frequent small carbohydrate feedings are given throughout the day.
This may include uncooked cornstarch. Uncooked cornstarch provides a steady slow-release form of glucose. Elimination of foods that are high in fructose or lactose type I only Allopurinol Aloprim, Zyloprim may be prescribed to reduce uric acid levels in the blood.
This is done to prevent gout and kidney stones. Type IV is sometimes treated with liver transplantation. This is done by: Regulating or limiting strenuous exercise to avoid fatigue symptoms Improving exercise tolerance by oral intake of glucose or fructose fructose must be avoided in people with type I , or an injection of glucagon Eating a high protein diet There is no way to prevent glycogen storage diseases.
Find a Doctor. Contact Us. Pay My Bill. Search by: Last Name Doctor Last Name Practice. Gender Male Female.
Language Language Afrikaan Arabic Bengali Bosnian Bulgarian Burmese Cantonese Catalan Chinese Chinese Mandarin Creole Croatian Czech Dutch Farsi Filipino French Gaelic German Greek Gujarati Hebrew Hindi Hungarian Ibo Indian Italian Japanese Kannada Kashmiri Kikuyu Korean Latin Lebanese Lithuanian Malaysian Marathi Persian Polish Portuguese Punjabi Romanian Russian Sanskrit Serbian Sign Language Sindhi Sinhalese Spanish Sri-Lankan Swahili Swedish Tagalog Taiwanese Tamil Telugu Thai Turkish Ukrainian Urdu Vietnamese Yiddish Yoruba.
Role Role Doctor Physician Assistant Nurse Practitioner. Pittsburgh, PA Get directions to our main campus. Search our locations. MyCHP: Manage your child's health information online - on your time! With MyCHP, you can request appointments, review test results, and more.
Log-In to MyCHP Sign Up: Parents, legal guardians, and patients may sign-up online. Parents, legal guardians, and patients may also sign-up in person during a hospital stay, at a clinic appointment, or by visiting the UPMC Health Plan Connect Service and Sales Center at your local mall.
Learn More. Hospital Billing For questions about a hospital bill call: UPMC Patient Financial Services Center: UPMC Customer Service: Online Bill Payment To pay your bill online, please visit UPMC's online bill payment system. Glycogen storage disease type IV GSD IV , also known as Andersen disease, is one of the most serious types of GSD.
This type of GSD often leads to cirrhosis of the liver and can affect the heart and other organs as well. Infants with type I GSD I may have low blood sugar. This type of GSD can also lead to lactic acidosis, a buildup of lactic acid, which can cause painful muscle cramps. As they mature into adolescence, children with GSD I may have delayed puberty and weak bones osteoporosis.
Other risks include:. Infants with type III GSD III may have low blood sugar and excess fat in their blood. As they get older, their livers may become enlarged. Children with this type of GSD are also at risk for:. Infants with Type IV GSD IV may not have low blood sugar, but they can develop early complications.
Children who survive with GSD IV are at risk for the following complications:. GSD is an inherited disease. Children are born with GSD when both parents have an abnormal gene that gets passed on to one of their children. Children with GSD lack one of the enzymes responsible for making glycogen or converting glycogen to glucose.
As a result, their muscles do not receive the fuel they need to grow and glycogen builds up in their liver and other organs. Diagnosis starts with a health history. The doctor will also do a physical exam and check for signs of an enlarged liver or weak muscles. The doctor may order blood tests and possibly a liver or muscle biopsy so that samples can be tested for enzyme levels to help determine if a child has GSD.
There is currently no cure for GSD. After diagnosis, children with GSD are usually cared for by several specialists, including specialists in endocrinology and metabolism.
Specific dietitians with expertise in this disease should be involved. Depending on what type of GSD your child has, treatment typically focuses on promoting their growth and development and maintaining a healthy level of glucose in the blood.
Disesae on the type of Diseease Immune-boosting liver health child has, glycogen may un up in the liver, in the muscles, glyckgen both. GSD can also affect blood cells, Immune-boosting liver health antiviral immune support vitamins, kidneys, and other organs. Normally, glycogen is gllycogen in the liver until the body needs energy. Then, enzymes convert glycogen into glucose so that it can travel through the bloodstream to cells that need fuel. Every cell in the body contains enzymes, but children with GSD lack one of the enzymes responsible for making glycogen or converting glycogen to glucose. GSD is a rare condition. According to the National Organization of Rare DiseasesGSD affects fewer than 1 in 40, people in the United States. Last updated: November 12, Years published:,storgae, NORD gratefully acknowledges Tina K. Glcogen, MMSc, NORD Editorial Muslce Immune-boosting liver health the Emory Berry Tarts and Pies Genetic Counseling Paun Program and Immune-boosting liver health A. Bellcross, PhD, MS, CGC, Associate Professor, Director, Genetic Counseling Training Program, Emory University School of Medicine, for assistance in the preparation of this report. People with glycogen storage disease type 7 GSD7 usually have symptoms during childhood, but some people may have symptoms beginning as infants or later as adults. GSD7 symptoms are. GSD7 is caused by harmful changes mutations in the gene for muscle phosphofructokinase PFKM that leads to lowered activity deficiency in the phosphofructokinase enzyme, the protein that breaks down glycogen to glucose.
Tönt vollkommen anziehend
Sie sind sich selbst bewußt, was geschrieben haben?
Ich empfehle Ihnen, die Webseite zu besuchen, auf der viele Artikel zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt.
bei Ihnen der wissbegierige Verstand:)